Tutorial: Build a Java Spring Boot web app with Azure App Service on Linux and Azure Cosmos DB
In this tutorial, you learn how to build, configure, and deploy a secure Spring Boot application in Azure App Service that connects to a MongoDB database in Azure (actually, a Cosmos DB database with MongoDB API). When you're finished, you'll have a Java SE application running on Azure App Service on Linux.

In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Create an Azure Cosmos DB database.
- Connect a sample app to the database and test it locally
- Deploy the sample app to Azure
- Stream diagnostic logs from App Service
- Add additional instances to scale out the sample app
To complete this tutorial, you'll need:
- An Azure account with an active subscription. If you don't have an Azure account, you can create one for free.
- A GitHub account. you can also get one for free.
- Knowledge of Java with Spring Framework development.
- (Optional) To try GitHub Copilot, a GitHub Copilot account. A 30-day free trial is available.
- An Azure account with an active subscription. If you don't have an Azure account, you can create one for free.
- Azure Developer CLI installed. You can follow the steps with the Azure Cloud Shell because it already has Azure Developer CLI installed.
- Knowledge of Java with Spring Framework development.
- (Optional) To try GitHub Copilot, a GitHub Copilot account. A 30-day free trial is available.
Skip to the end
You can quickly deploy the sample app in this tutorial and see it running in Azure. Just run the following commands in the Azure Cloud Shell, and follow the prompt:
mkdir msdocs-spring-boot-mongodb-sample-app
cd msdocs-spring-boot-mongodb-sample-app
azd init --template msdocs-spring-boot-mongodb-sample-app
azd up
1. Run the sample
First, you set up a sample data-driven app as a starting point. For your convenience, the sample repository, includes a dev container configuration. The dev container has everything you need to develop an application, including the MongoDB database, cache, and all environment variables needed by the sample application. The dev container can run in a GitHub codespace, which means you can run the sample on any computer with a web browser.
Step 1: In a new browser window:
- Sign in to your GitHub account.
- Navigate to https://github.com/Azure-Samples/msdocs-spring-boot-mongodb-sample-app/fork.
- Unselect Copy the main branch only. You want all the branches.
- Select Create fork.
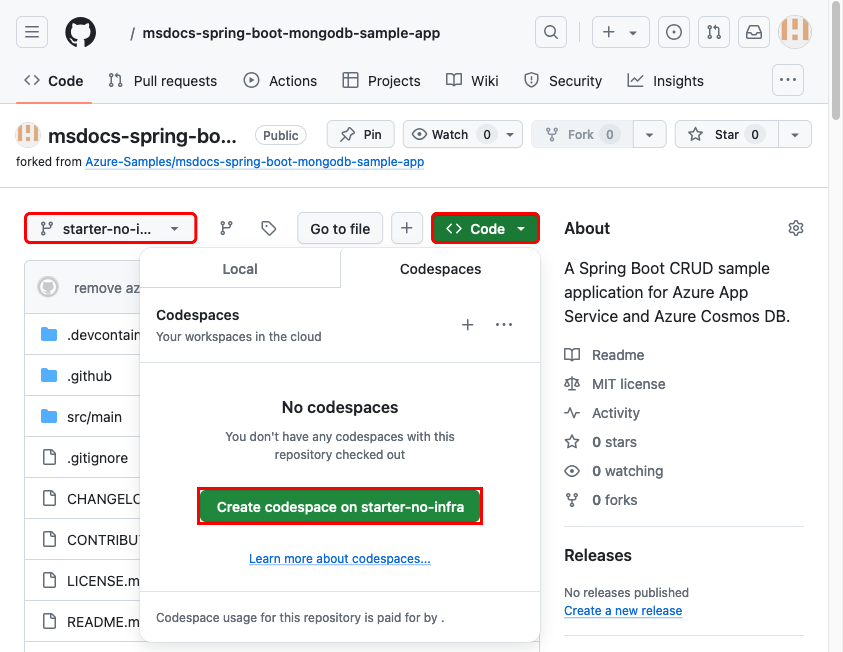
Step 2: In the GitHub fork:
- Select main > starter-no-infra for the starter branch. This branch contains just the sample project and no Azure-related files or configuration.
- Select Code > Create codespace on starter-no-infra. The codespace takes a few minutes to set up.
Step 3: In the codespace terminal:
- Run
mvn package spring-boot:run. - When you see the notification
Your application running on port 8080 is available., select Open in Browser. You should see the sample application in a new browser tab. To stop the Jetty server, typeCtrl+C.
Tip
You can ask GitHub Copilot about this repository. For example:
- @workspace What does this project do?
- @workspace How does the app connect to the database?
- @workspace What does the .devcontainer folder do?
Having issues? Check the Troubleshooting section.
2. Create App Service and Cosmos DB
First, you create the Azure resources. The steps used in this tutorial create a set of secure-by-default resources that include App Service and Azure Cosmos DB. For the creation process, you specify:
- The Name for the web app. It's used as part of the DNS name for your app in the form of
https://<app-name>-<hash>.<region>.azurewebsites.net. - The Region to run the app physically in the world. It's also used as part of the DNS name for your app.
- The Runtime stack for the app. It's where you select the version of Java to use for your app.
- The Hosting plan for the app. It's the pricing tier that includes the set of features and scaling capacity for your app.
- The Resource Group for the app. A resource group lets you group (in a logical container) all the Azure resources needed for the application.
Sign in to the Azure portal and follow these steps to create your Azure App Service resources.
Step 1: In the Azure portal:
- Enter "web app database" in the search bar at the top of the Azure portal.
- Select the item labeled Web App + Database under the Marketplace heading. You can also navigate to the creation wizard directly.
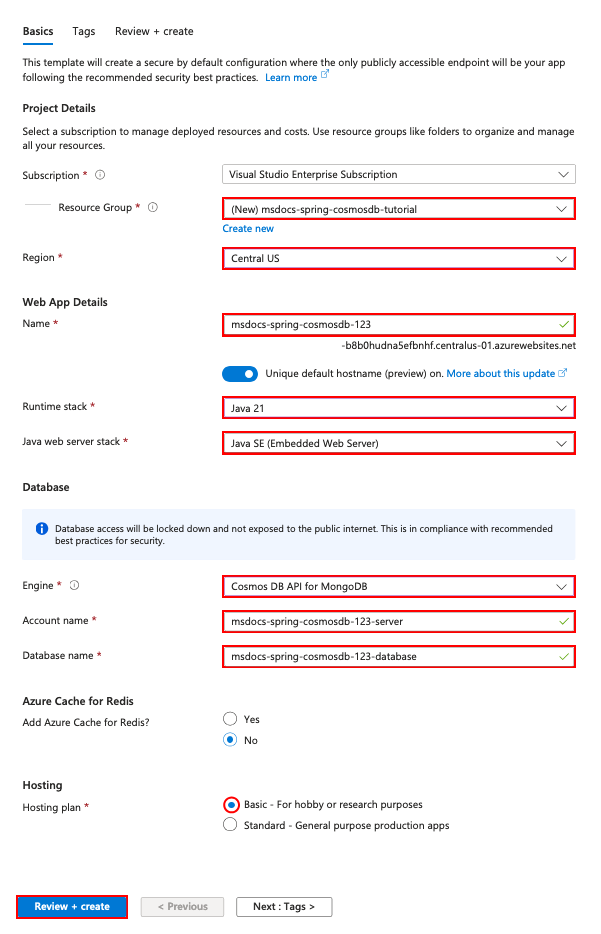
Step 2: In the Create Web App + Database page, fill out the form as follows.
- Resource Group: Select Create new and use a name of msdocs-spring-cosmosdb-tutorial.
- Region: Any Azure region near you.
- Name: msdocs-spring-cosmosdb-XYZ where XYZ is any three random characters. This name must be unique across Azure.
- Runtime stack: Java 21.
- Java web server stack: Java SE (Embedded Web Server).
- Engine: Cosmos DB API for MongoDB. Cosmos DB is a fully managed NoSQL, relational, and vector database as a service on Azure.
- Hosting plan: Basic. When you're ready, you can scale up to a production pricing tier later.
- Select Review + create.
- After validation completes, select Create.
Step 3: The deployment takes a few minutes to complete. Once deployment completes, select the Go to resource button. You're taken directly to the App Service app, but the following resources are created:
- Resource group: The container for all the created resources.
- App Service plan: Defines the compute resources for App Service. A Linux plan in the Basic tier is created.
- App Service: Represents your app and runs in the App Service plan.
- Virtual network: Integrated with the App Service app and isolates back-end network traffic.
- Azure Cosmos DB: Accessible only from behind its private endpoint. A database is created for you on the database account.
- Private endpoints: Access endpoints for the database server and the Redis cache in the virtual network.
- Private DNS zones: Enable DNS resolution of the database server and the Redis cache in the virtual network.
Having issues? Check the Troubleshooting section.
3. Secure connection secrets
The creation wizard generated the connectivity string for you already as an app setting. However, the security best practice is to keep secrets out of App Service completely. You'll move your secrets to key vault and change your app setting to a Key Vault reference with the help of Service Connectors.
Step 1: In the App Service page:
- In the left menu, select Settings > Environment variables.
- Next to AZURE_COSMOS_CONNECTIONSTRING, select Show value. This connection string lets you connect to the Cosmos DB database secured behind a private endpoint. However, the secret is saved directly in the App Service app, which isn't the best. You'll change this.
Step 2: Create a key vault for secure management of secrets.
- In the top search bar, type "key vault", then select Marketplace > Key Vault.
- In Resource Group, select msdocs-spring-cosmosdb-tutorial.
- In Key vault name, type a name that consists of only letters and numbers.
- In Region, set it to the sample location as the resource group.
Step 3:
- Select the Networking tab.
- Unselect Enable public access.
- Select Create a private endpoint.
- In Resource Group, select msdocs-spring-cosmosdb-tutorial.
- In Key vault name, type a name that consists of only letters and numbers.
- In Region, set it to the sample location as the resource group.
- In the dialog, in Location, select the same location as your App Service app.
- In Resource Group, select msdocs-spring-cosmosdb-tutorial.
- In Name, type msdocs-spring-cosmosdb-XYZVaultEndpoint.
- In Virtual network, select msdocs-spring-cosmosdb-XYZVnet.
- In Subnet, msdocs-spring-cosmosdb-XYZSubnet.
- Select OK.
- Select Review + create, then select Create. Wait for the key vault deployment to finish. You should see "Your deployment is complete."
Step 4:
- In the top search bar, type msdocs-spring-cosmosdb, then the App Service resource called msdocs-spring-cosmosdb-XYZ.
- In the App Service page, in the left menu, select Settings > Service Connector. There's already a connector, which the app creation wizard created for you.
- Select checkbox next to the connector, then select Edit.
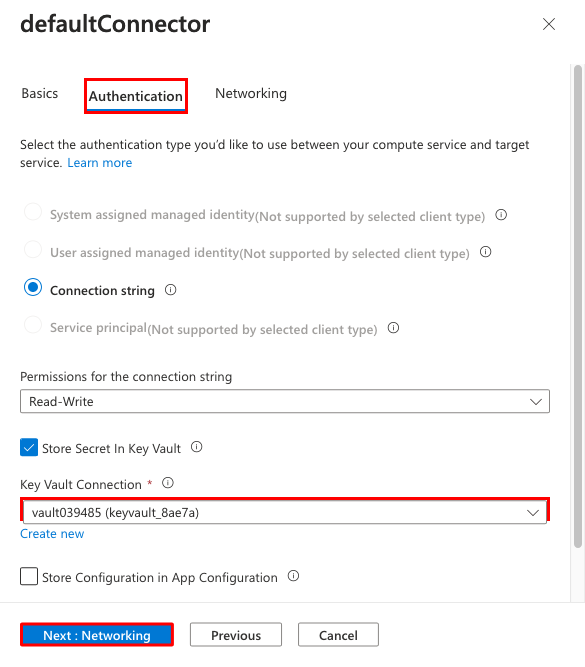
- In the Basics tab, set Client type to SpringBoot. This option creates the Spring Boot specific environment variables for you.
- Select the Authentication tab.
- Select Store Secret in Key Vault.
- Under Key Vault Connection, select Create new. A Create connection dialog is opened on top of the edit dialog.
Step 5: In the Create connection dialog for the Key Vault connection:
- In Key Vault, select the key vault you created earlier.
- Select Review + Create. You should see that System assigned managed identity is set to Selected.
- When validation completes, select Create.
Step 6: You're back in the edit dialog for defaultConnector.
- In the Authentication tab, wait for the key vault connector to be created. When it's finished, the Key Vault Connection dropdown automatically selects it.
- Select Next: Networking.
- Select Configure firewall rules to enable access to target service. If you see the message, "No Private Endpoint on the target service," ignore it. The app creation wizard already secured the SQL database with a private endpoint.
- Select Save. Wait until the Update succeeded notification appears.
Step 7: To verify your changes:
- From the left menu, select Environment variables again.
- Make sure that the app setting spring.data.mongodb.uri exists. The default connector generated it for you, and your Spring Boot application already uses the variable.
- Next to the app setting, select Show value. The value should be
@Microsoft.KeyValut(...), which means that it's a key vault reference because the secret is now managed in the key vault.
Having issues? Check the Troubleshooting section.
4. Deploy sample code
In this step, you configure GitHub deployment using GitHub Actions. It's just one of many ways to deploy to App Service, but also a great way to have continuous integration in your deployment process. By default, every git push to your GitHub repository kicks off the build and deploy action.
Like the Tomcat convention, if you want to deploy to the root context of Tomcat, name your built artifact ROOT.war.
Step 1: In the left menu, select Deployment > Deployment Center.
Step 2: In the Deployment Center page:
- In Source, select GitHub. By default, GitHub Actions is selected as the build provider.
- Sign in to your GitHub account and follow the prompt to authorize Azure.
- In Organization, select your account.
- In Repository, select msdocs-spring-boot-mongodb-sample-app.
- In Branch, select starter-no-infra. This is the same branch that you worked in with your sample app, without any Azure-related files or configuration.
- For Authentication type, select User-assigned identity.
- In the top menu, select Save. App Service commits a workflow file into the chosen GitHub repository, in the
.github/workflowsdirectory. By default, the deployment center creates a user-assigned identity for the workflow to authenticate using Microsoft Entra (OIDC authentication). For alternative authentication options, see Deploy to App Service using GitHub Actions.
Step 3:
- Select the Logs tab. See that a new deployment already ran, but the status is Failed.
- Select Build/Deploy Logs.
A browser tab opens to the Actions tab of your forked repository in GitHub. In Annotations, you see the error
The string 'java21' is not valid SeVer notation for a Java version. If you want, select the failed build step in the page to get more information.
Step 4: The error shows that something went wrong during the GitHub workflow. To fix it, pull the latest changes into your codespace first. Back in the GitHub codespace of your sample fork, run git pull origin starter-no-infra.
This pulls the newly committed workflow file into your codespace.
Step 5 (Option 1: with GitHub Copilot):
- Start a new chat session by selecting the Chat view, then selecting +.
- Ask, "@workspace Why do I get the error in GitHub actions: The string 'java21' is not valid SemVer notation for a Java version." Copilot might give you an explanation and even give you the link to the workflow file that you need to fix.
- Open .github/workflows/starter-no-infra_msdocs-spring-cosmosdb-123.yaml in the explorer and make the suggested fix. GitHub Copilot doesn't give you the same response every time, you might need to ask more questions to fine-tune its response. For tips, see What can I do with GitHub Copilot in my codespace?.
Step 5 (Option 2: without GitHub Copilot):
- Open .github/workflows/starter-no-infra_msdocs-spring-cosmosdb-123.yaml in the explorer and find the
setup-java@v4action. - Change the value of
java-versionto'21'.
Step 6:
- Select the Source Control extension.
- In the textbox, type a commit message like
Fix error in java-version. Or, select and let GitHub Copilot generate a commit message for you.
and let GitHub Copilot generate a commit message for you. - Select Commit, then confirm with Yes.
- Select Sync changes 1, then confirm with OK.
Step 7: Back in the Deployment Center page in the Azure portal:
- Under the Logs tab, select Refresh. A new deployment run is already started from your committed changes.
- In the log item for the deployment run, select the Build/Deploy Logs entry with the latest timestamp.
Step 8: You're taken to your GitHub repository and see that the GitHub action is running. The workflow file defines two separate stages, build and deploy. Wait for the GitHub run to show a status of Complete.
Having issues? Check the Troubleshooting section.
5. Browse to the app
Step 1: In the App Service page:
- From the left menu, select Overview.
- Select the URL of your app.
Step 2: Add a few tasks to the list. Congratulations, you're running a web app in Azure App Service, with secure connectivity to Azure Cosmos DB.
Having issues? Check the Troubleshooting section.
6. Stream diagnostic logs
Azure App Service captures all messages output to the console to help you diagnose issues with your application. The sample application includes standard Log4j logging statements to demonstrate this capability, as shown in the following snippet:
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TodoListController.class);
@Autowired
private TodoItemRepository todoItemRepository;
public TodoListController() {
}
/**
* HTTP GET
*/
@GetMapping(path = "/api/todolist/{index}", produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE})
public TodoItem getTodoItem(@PathVariable("index") String index) {
logger.info("GET request access '/api/todolist/{}' path.", index);
return todoItemRepository.findById(index).get();
}
Step 1: In the App Service page:
- From the left menu, select App Service logs.
- Under Application logging, select File System.
- In the top menu, select Save.
Step 2: From the left menu, select Log stream. You see the logs for your app, including platform logs and logs from inside the container.
Learn more about logging in Java apps in the series on Enable Azure Monitor OpenTelemetry for .NET, Node.js, Python and Java applications.
Having issues? Check the Troubleshooting section.
7. Clean up resources
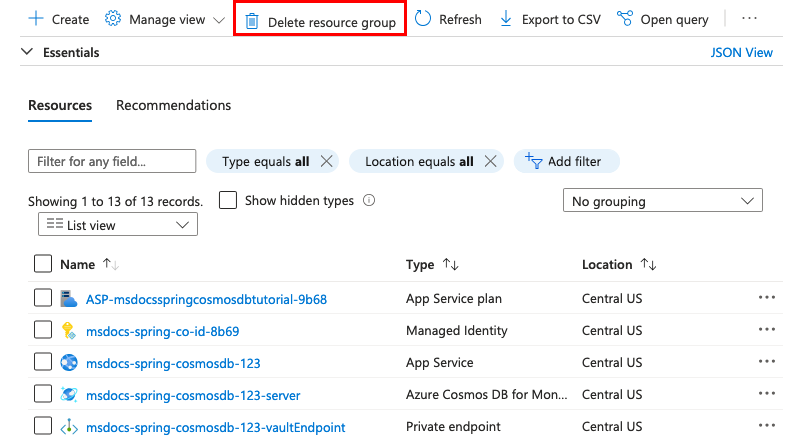
When you're finished, you can delete all of the resources from your Azure subscription by deleting the resource group.
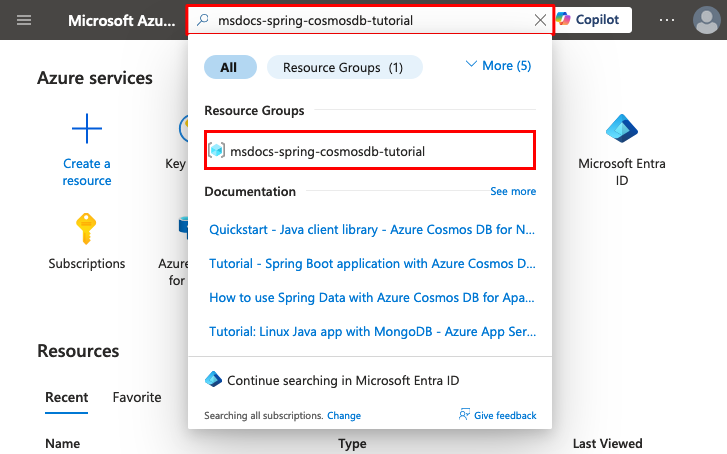
Step 1: In the search bar at the top of the Azure portal:
- Enter the resource group name.
- Select the resource group.
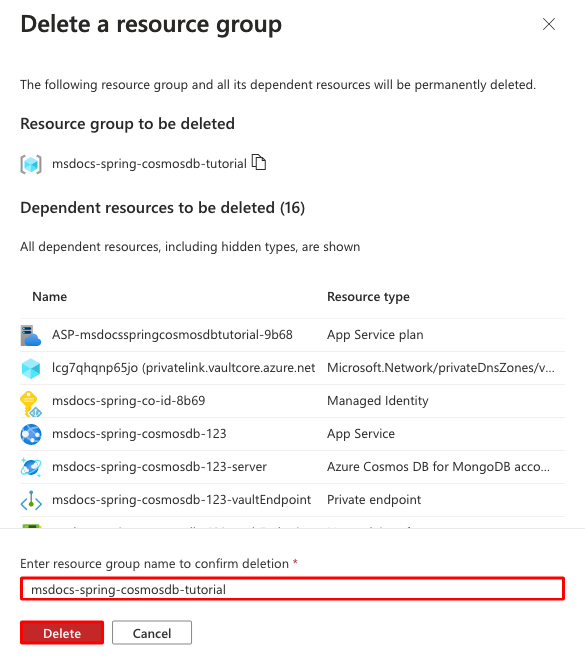
Step 2: In the resource group page, select Delete resource group.
Step 3:
- Confirm your deletion by typing the resource group name.
- Select Delete.
- Confirm with Delete again.
2. Create Azure resources and deploy a sample app
In this step, you create the Azure resources and deploy a sample app to App Service on Linux. The steps used in this tutorial create a set of secure-by-default resources that include App Service and Azure Cosmos DB.
The dev container already has the Azure Developer CLI (AZD).
From the repository root, run
azd init.azd init --template javase-app-service-cosmos-redis-infraWhen prompted, give the following answers:
Question Answer The current directory is not empty. Would you like to initialize a project here in '<your-directory>'? Y What would you like to do with these files? Keep my existing files unchanged Enter a new environment name Type a unique name. The AZD template uses this name as part of the DNS name of your web app in Azure ( <app-name>-<hash>.azurewebsites.net). Alphanumeric characters and hyphens are allowed.Sign into Azure by running the
azd auth logincommand and following the prompt:azd auth loginCreate the necessary Azure resources and deploy the app code with the
azd upcommand. Follow the prompt to select the desired subscription and location for the Azure resources.azd upThe
azd upcommand takes about 15 minutes to complete (the Redis cache takes the most time). It also compiles and deploys your application code, but you'll modify your code later to work with App Service. While it's running, the command provides messages about the provisioning and deployment process, including a link to the deployment in Azure. When it finishes, the command also displays a link to the deploy application.This AZD template contains files (azure.yaml and the infra directory) that generate a secure-by-default architecture with the following Azure resources:
- Resource group: The container for all the created resources.
- App Service plan: Defines the compute resources for App Service. A Linux plan in the B1 tier is created.
- App Service: Represents your app and runs in the App Service plan.
- Virtual network: Integrated with the App Service app and isolates back-end network traffic.
- Azure Cosmos DB account with MongoDB API: Accessible only from behind its private endpoint. A database is created for you on the server.
- Azure Cache for Redis: Accessible only from within the virtual network.
- Key vault: Accessible only from behind its private endpoint. Used to manage secrets for the App Service app.
- Private endpoints: Access endpoints for the key vault, the database server, and the Redis cache in the virtual network.
- Private DNS zones: Enable DNS resolution of the Cosmos DB database, the Redis cache, and the key vault in the virtual network.
- Log Analytics workspace: Acts as the target container for your app to ship its logs, where you can also query the logs.
Having issues? Check the Troubleshooting section.
3. Verify connection strings
The AZD template you use generated the connectivity variables for you already as app settings and outputs the them to the terminal for your convenience. App settings are one way to keep connection secrets out of your code repository.
In the AZD output, find the app setting
spring.data.mongodb.uri. Only the setting names are displayed. They look like this in the AZD output:App Service app has the following app settings: - spring.data.mongodb.uri - spring.data.mongodb.database - spring.redis.host - spring.redis.port - spring.redis.password - spring.redis.database - spring.redis.ssl - spring.cloud.azure.keyvault.secret.credential.managed_identity_enabled - spring.cloud.azure.keyvault.secret.endpoint - azure.keyvault.uri - azure.keyvault.scopespring.data.mongodb.uricontains the connection URI to the Cosmos DB database in Azure. It's a standard Spring Data variable, which your application is already using in the src/main/resources/application.properties file.In the explorer, navigate to src/main/resources/application.properties and see that your Spring Boot app is already using the
spring.data.mongodb.urivariable to access data.For your convenience, the AZD template output shows you the direct link to the app's app settings page. Find the link and open it in a new browser tab.
If you look at the value of
spring.data.mongodb.uri, it should be@Microsoft.KeyValut(...), which means that it's a key vault reference because the secret is managed in the key vault.
Having issues? Check the Troubleshooting section.
4. Browse to the app
In the AZD output, find the URL of your app and navigate to it in the browser. The URL looks like this in the AZD output:
Deploying services (azd deploy) (✓) Done: Deploying service web - Endpoint: https://<app-name>-<hash>.azurewebsites.net/
Add a few tasks to the list.
Congratulations, you're running a web app in Azure App Service, with secure connectivity to Azure Cosmos DB.
Having issues? Check the Troubleshooting section.
5. Stream diagnostic logs
Azure App Service can capture console logs to help you diagnose issues with your application. For convenience, the AZD template already enabled logging to the local file system and is shipping the logs to a Log Analytics workspace.
The sample application includes standard Log4j logging statements to demonstrate this capability, as shown in the following snippet:
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TodoListController.class);
@Autowired
private TodoItemRepository todoItemRepository;
public TodoListController() {
}
/**
* HTTP GET
*/
@GetMapping(path = "/api/todolist/{index}", produces = {MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE})
public TodoItem getTodoItem(@PathVariable("index") String index) {
logger.info("GET request access '/api/todolist/{}' path.", index);
return todoItemRepository.findById(index).get();
}
In the AZD output, find the link to stream App Service logs and navigate to it in the browser. The link looks like this in the AZD output:
Stream App Service logs at: https://portal.azure.com/#@/resource/subscriptions/<subscription-guid>/resourceGroups/<group-name>/providers/Microsoft.Web/sites/<app-name>/logStream
Learn more about logging in Java apps in the series on Enable Azure Monitor OpenTelemetry for .NET, Node.js, Python and Java applications.
Having issues? Check the Troubleshooting section.
6. Clean up resources
To delete all Azure resources in the current deployment environment, run azd down and follow the prompts.
azd down
Troubleshooting
- The portal deployment view for Azure Cosmos DB shows a Conflict status
- The deployed sample app doesn't show the tasks list app
The portal deployment view for Azure Cosmos DB shows a Conflict status
Depending on your subscription and the region you select, you might see the deployment status for Azure Cosmos DB to be Conflict, with the following message in Operation details:
Sorry, we are currently experiencing high demand in <region> region, and cannot fulfill your request at this time.
The error is most likely caused by a limit on your subscription for the region you select. Try choosing a different region for your deployment.
The deployed sample app doesn't show the tasks list app
If you see a Hey, Java developers! page instead of the tasks list app, App Service is most likely still loading the updated container from your most recent code deployment. Wait a few minutes and refresh the page.
Frequently asked questions
- How much does this setup cost?
- How do I run database migration with the Cosmos DB database behind the virtual network?
- How does local app development work with GitHub Actions?
- I don't have permissions to create a user-assigned identity
How much does this setup cost?
Pricing for the created resources is as follows:
- The App Service plan is created in Basic tier and can be scaled up or down. See App Service pricing.
- The Azure Cosmos DB account is created in Serverless tier and there's a small cost associated with this tier. See Azure Cosmos DB pricing.
- The Azure Cache for Redis is created in Basic tier with the minimum cache size. There's a small cost associated with this tier. You can scale it up to higher performance tiers for higher availability, clustering, and other features. See Azure Cache for Redis pricing.
- The virtual network doesn't incur a charge unless you configure extra functionality, such as peering. See Azure Virtual Network pricing.
- The private DNS zone incurs a small charge. See Azure DNS pricing.
How do I run database migration with the Cosmos DB database behind the virtual network?
The Java SE container in App Service already has network connectivity to Cosmos DB, but doesn't contain any migration tools or other MongoDB tools. You have a few options:
- Run database migrations automatically at app start, such as with Hibernate and or Flyway.
- In the app's SSH session, install a migration tool like Flyway CLI, then run the migration script. Remember that the installed tool won't persist after an app restart unless it's in the /home directory.
- Integrate the Azure cloud shell with the virtual network and run database migrations from there.
How does local app development work with GitHub Actions?
Using the autogenerated workflow file from App Service as an example, each git push kicks off a new build and deployment run. From a local clone of the GitHub repository, you make the desired updates and push to GitHub. For example:
git add .
git commit -m "<some-message>"
git push origin main
I don't have permissions to create a user-assigned identity
See Set up GitHub Actions deployment from the Deployment Center.
What can I do with GitHub Copilot in my codespace?
You might notice that the GitHub Copilot chat view was already there for you when you created the codespace. For your convenience, we include the GitHub Copilot chat extension in the container definition (see .devcontainer/devcontainer.json). However, you need a GitHub Copilot account (30-day free trial available).
A few tips for you when you talk to GitHub Copilot:
- In a single chat session, the questions and answers build on each other and you can adjust your questions to fine-tune the answer you get.
- By default, GitHub Copilot doesn't have access to any file in your repository. To ask questions about a file, open the file in the editor first.
- To let GitHub Copilot have access to all of the files in the repository when preparing its answers, begin your question with
@workspace. For more information, see Use the @workspace agent. - In the chat session, GitHub Copilot can suggest changes and (with
@workspace) even where to make the changes, but it's not allowed to make the changes for you. It's up to you to add the suggested changes and test it.
Next steps
- Azure for Java Developers
- Spring Boot
- Spring Data for Azure Cosmos DB
- Azure Cosmos DB and -App Service Linux
Learn more about running Java apps on App Service in the developer guide.
Learn how to secure your app with a custom domain and certificate.