Localize the UI Library in an application
Localization is a key to making products that can be used across the world and by people who speak different languages. The Azure Communication Services UI Library provides out-of-the-box support for some languages and capabilities, such as right to left (RTL). Developers can provide their own localization files for the UI Library.
In this article, you learn how to set up localization correctly by using the UI Library in your application.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
- A deployed Communication Services resource. Create a Communication Services resource.
- A user access token to enable the call client. Get a user access token.
- Optional: Completion of the quickstart for getting started with UI Library composites.
Set up localization
For detailed documentation and quickstarts about the Web UI Library, see the Web UI Library Storybook.
To learn more, see Localization in the Web UI Library.
For more information, see the open-source Android UI Library and the sample application code.
Available languages
The following table lists CallCompositeSupportedLocale IDs for out-of-the-box translations. If you want to localize the composite, pass a Locale object from CallCompositeSupportedLocale into CallCompositeLocalizationOptions as options into CallComposite.
| Language | CallCompositeSupportedLocale |
|---|---|
| Arabic (Saudi Arabia) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.AR_SA |
| German (Germany) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.DE_DE |
| English (US) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.EN_US |
| English (UK) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.EN_UK |
| Spanish (Spain) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.ES_ES |
| Spanish | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.ES |
| Finnish (Finland) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.FI_FI |
| French (France) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.FR_FR |
| French | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.FR |
| Hebrew (Israel) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.IW_IL |
| Italian (Italy) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.IT_IT |
| Italian | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.IT |
| Japanese (Japan) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.JA_JP |
| Japanese | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.JA |
| Korean (Korea) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.KO_KR |
| Korean | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.KO |
| Dutch (Netherlands) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.NL_NL |
| Dutch | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.NL |
| Norwegian (Bokmål) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.NB_NO |
| Polish (Poland) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.PL_PL |
| Polish | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.PL |
| Portuguese (Brazil) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.PT_BR |
| Portuguese | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.PT |
| Russian (Russia) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.RU_RU |
| Russian | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.RU |
| Swedish (Sweden) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.SV_SE |
| Turkish (Turkey) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.TR_TR |
| Turkish | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.TR |
| Chinese (Simplified) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.ZH_CN |
| Chinese (Traditional) | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.ZH_TW |
| Chinese | CallCompositeSupportedLocale.ZH |
Localization provider
CallCompositeLocalizationOptions is an options wrapper that sets all the strings for Android UI Library components by using CallCompositeSupportedLocale. By default, all text labels use English strings. You can use CallCompositeLocalizationOptions to set a different language by passing a Locale object from CallCompositeSupportedLocale. Out of the box, the UI Library includes a set of Locale objects that are usable with the UI components and composites.
You can also get a list of Locale objects by using the static function CallCompositeSupportedLocale.getSupportedLocales().
To use CallCompositeLocalizationOptions, specify CallCompositeSupportedLocale and pass it to CallCompositeBuilder. The following example localizes the composite to French.
import com.azure.android.communication.ui.calling.models.CallCompositeLocalizationOptions
import com.azure.android.communication.ui.calling.models.CallCompositeSupportedLocale
// CallCompositeSupportedLocale provides a list of supported locales
val callComposite: CallComposite =
CallCompositeBuilder().localization(
CallCompositeLocalizationOptions(CallCompositeSupportedLocale.FR)
).build()
Layout direction
Certain cultures (for example, Arabic and Hebrew) might need localization to have a right-to-left layout. You can specify layoutDirection as part of CallCompositeLocalizationOptions. The layout of the composite will be mirrored, but the text will remain in the direction of the string.
import com.azure.android.communication.ui.calling.models.CallCompositeLocalizationOptions
import com.azure.android.communication.ui.calling.models.CallCompositeSupportedLocale
// CallCompositeSupportedLocale provides a list of supported locales
val callComposite: CallComposite =
CallCompositeBuilder().localization(
CallCompositeLocalizationOptions(CallCompositeSupportedLocale.FR, LayoutDirection.LTR)
).build()
LayoutDirection.RTL |
LayoutDirection.LTR |
|---|---|
|
|
Customizing translations
There are two options to customize the language translations that we provide. You can use the list of localization keys to override a particular string for the key/value pair. You can specify the locale as one of the supported languages. When a key isn't provided, it will fall back to a supported translation string. If you specify an unsupported language, you should provide translations for all the keys for that language (by using the string.xml file) and then fall back to English strings when a key isn't provided.
Let's say you want to have the control bar use strings from the English (US) locale, but you want to change the label of the Join Call button to Start Meeting in setup view. Create a string.xml file (or other file name) with the key/value pair for selected keys that you want to override. The following example overrides the key azure_communication_ui_calling_setup_view_button_join_call.
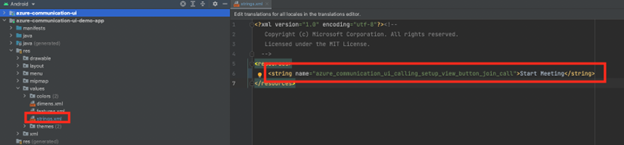
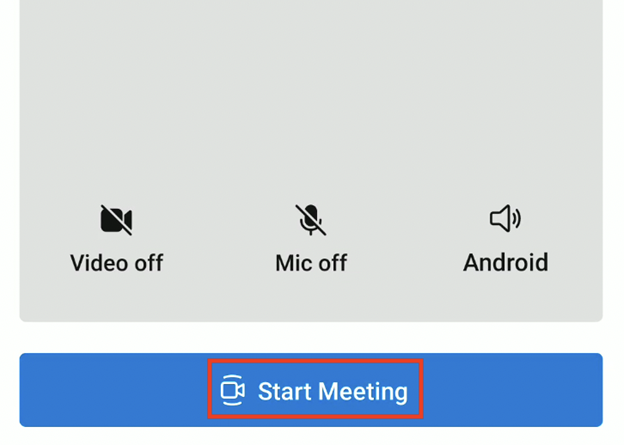
For more information, see the open-source iOS UI Library and the sample application code.
Language detection
If your application supports localization, the UI Library is displayed based on the user's system-preferred language if it's part of the available languages listed in the next section. Otherwise, the language defaults to the predefined English (en) strings.
Available languages
The following table lists out-of-the-box translations for locale. If you want to localize the composite, pass locale into LocalizationOptions as options into CallComposite.
| Language | SupportedLocale | Identifier |
|---|---|---|
| Chinese, Simplified | zh |
zh |
| Chinese, Simplified | zhHans |
zh-Hans |
| Chinese, Simplified (China mainland) | zhHansCN |
zh-Hans-CN |
| Chinese, Traditional | zhHant |
zh-Hant |
| Chinese, Traditional (Taiwan) | zhHantTW |
zh-Hant-TW |
| Dutch | nl |
nl |
| Dutch (Netherlands) | nlNL |
nl-NL |
| English | en |
en |
| English (United Kingdom) | enGB |
en-GB |
| English (United States) | enUS |
en-US |
| French | fr |
fr |
| French (France) | frFR |
fr-FR |
| German | de |
de |
| German (Germany) | deDE |
de-DE |
| Italian | it |
it |
| Italian (Italy) | itIT |
it-IT |
| Japanese | ja |
ja |
| Japanese (Japan) | jaJP |
ja-JP |
| Korean | ko |
ko |
| Korean (South Korea) | koKR |
ko-KR |
| Portuguese | pt |
pt |
| Portuguese (Brazil) | ptBR |
pt-BR |
| Russian | ru |
ru |
| Russian (Russia) | ruRU |
ru-RU |
| Spanish | es |
es |
| Spanish (Spain) | esES |
es-ES |
| Turkish | tr |
tr |
| Turkish (Türkiye) | trTR |
tr-TR |
You can also get a list of locale structures by using the static function SupportedLocale.values.
let locales: [Locale] = SupportedLocale.values.map{ $0.identifier }
print(locales)
// ["de", "de-DE", "en", "en-GB", "en-US", "es", "es-ES", "fr", "fr-FR", "it", "it-IT", "ja", "ja-JP", "ko", "ko-KR", "nl", "nl-NL", "pt", "pt-BR", "ru", "ru-RU", "tr", "tr-TR", "zh", "zh-Hans", "zh-Hans-CN", "zh-Hant", "zh-Hant-TW"]
LocalizationOptions
LocalizationOptions is an options wrapper that sets all the strings for UI Library components by using locale. By default, all text labels use English (en) strings. You can use LocalizationOptions to set a different locale structure. Out of the box, the UI Library includes a set of locale structures that are usable with the UI components and composites.
To use LocalizationOptions, specify a Swift locale structure (with or without a region code) and pass it to CallCompositeOptions. The following example localizes the composite to French for France (fr-FR).
// Creating a Swift locale structure
var localizationOptions = LocalizationOptions(locale: Locale(identifier: "fr-FR"))
// Use IntelliSense SupportedLocale to get supported locale structures
localizationOptions = LocalizationOptions(locale: SupportedLocale.frFR)
let callCompositeOptions = CallCompositeOptions(localization: localizationOptions)
let callComposite = CallComposite(withOptions: callCompositeOptions)
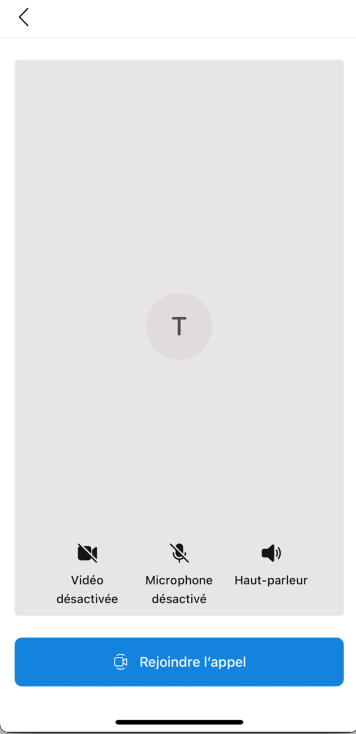
Layout direction
Certain cultures (for example, Arabic and Hebrew) might need localization to have right-to-left layout. You can specify layoutDirection as part of LocalizationOptions. The layout of the composite will be mirrored, but the text will remain in the direction of the string.
var localizationOptions: LocalizationOptions
// Initializer with locale and layoutDirection
localizationOptions = LocalizationOptions(locale: Locale(identifier: "en"),
layoutDirection: .rightToLeft)
// Initializer with locale, localizableFilename, and layoutDirection
localizationOptions = LocalizationOptions(locale: Locale(identifier: "en"),
localizableFilename: "Localizable",
layoutDirection: .rightToLeft)
// Add localizationOptions as an option
let callCompositeOptions = CallCompositeOptions(localization: localizationOptions)
let callComposite = CallComposite(withOptions: callCompositeOptions)
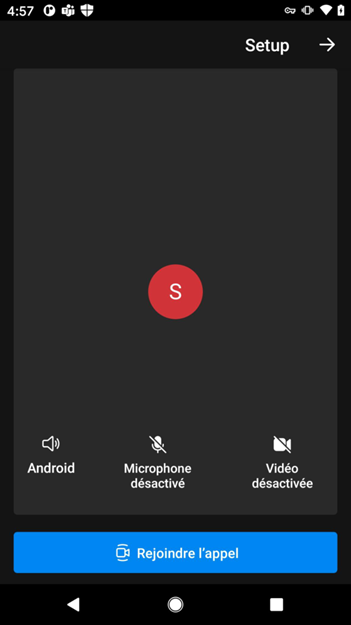
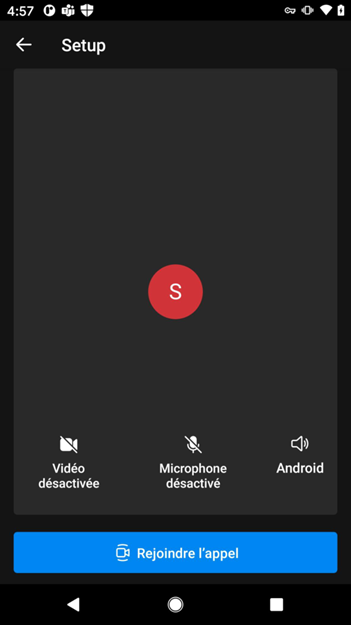
The following example shows right-to-left layout mirroring. If you don't specify layoutDirection, it defaults to false (left-to-right layout).
layoutDirection = .leftToRight (default) |
layoutDirection = .rightToLeft |
|---|---|
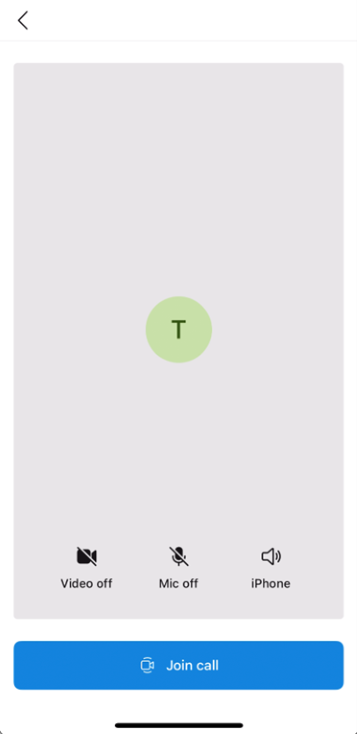
|
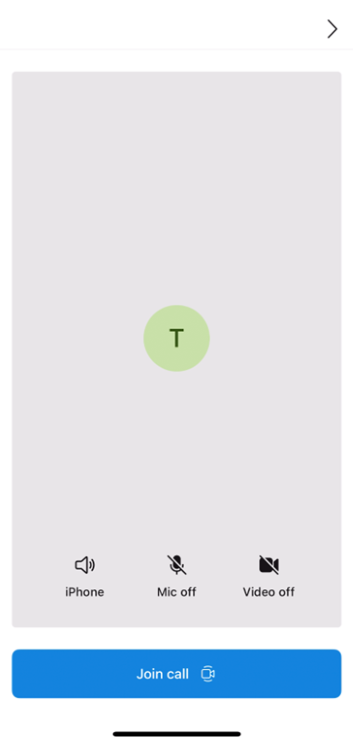
|
Customizing translations
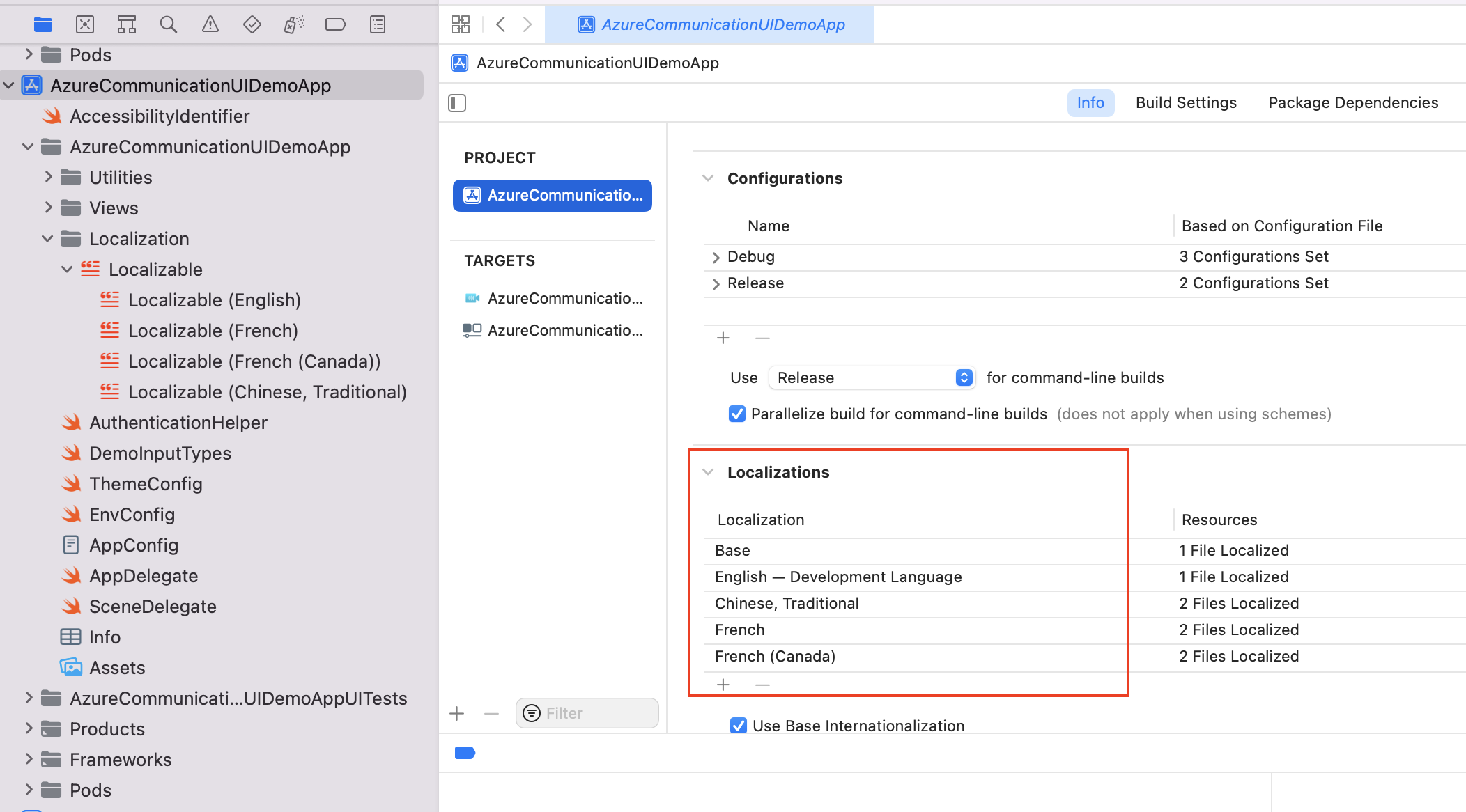
There are two options to customize the language translations that we provide. To override a particular string, you can use the list of localization keys for the key/value pair. You can specify locale as one of the supported languages. When a key isn't provided, it falls back to a supported translation string. If you specify an unsupported language, you should provide translations for all the keys for that language (by using the Localizable.strings file) and then fall back to English strings when a key isn't provided.
Let's say you want to have the control bar use strings from the English (US) locale, but you want to change the label of the Join Call button to Start Meeting in setup view. Enable localization in the project for the locale instance that you want to override. Create a Localizable.strings file (or another file name with the extension .strings) with the key/value pair for selected keys that you want to override. The following example overrides the key AzureCommunicationUI.SetupView.Button.JoinCall.
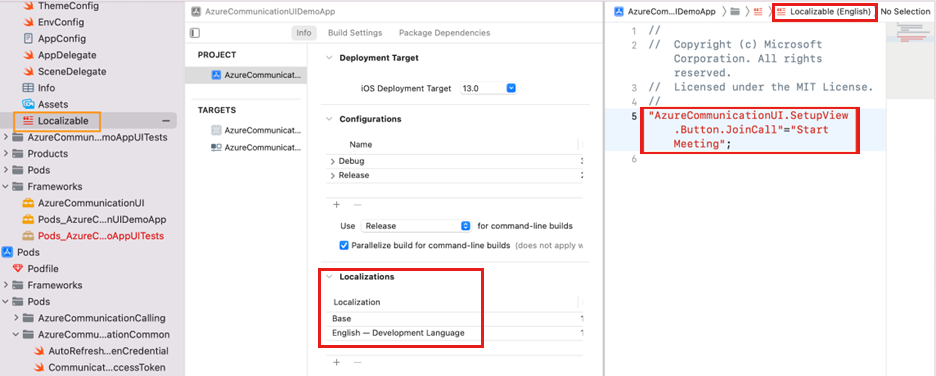
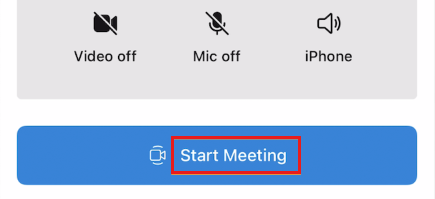
To specify that you're overriding with Localizable.strings, create a LocalizationOptions object to specify locale and localizationFilename. Or when you're using the locale initializer, it looks at keys in Localizable.strings for locale.collatorIdentifier as the language in your project.
let localizationOptions = LocalizationOptions(locale: Locale(identifier: "fr"),
localizableFilename: "Localizable")
let callCompositeOptions = CallCompositeOptions(localization: localizationOptions)
let callComposite = CallComposite(withOptions: callCompositeOptions)
Accessibility voiceover for localization
For voiceover to work properly for a localization, make sure the language is added into your app's localizations. The voiceover then detects that the app supports the language specified in LocalizationOptions for locale. It selects the speech voice for the language by using the voice found in Settings > Accessibility > Speech on the device. You can verify that the language is added to your project, as shown in the following example.