Capture changed data from Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 to Azure SQL Database by using a change data capture resource
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
In this article, you use the Azure Data Factory user interface to create a change data capture (CDC) resource. The resource picks up changed data from an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 source and adds it to Azure SQL Database in real time.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Create a CDC resource.
- Monitor CDC activity.
You can modify and expand the configuration pattern in this article.
Prerequisites
Before you begin the procedures in this article, make sure that you have these resources:
- Azure subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free Azure account.
- SQL database. You use Azure SQL Database as a source data store. If you don't have a SQL database, create one in the Azure portal.
- Storage account. You use Delta Lake stored in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 as a target data store. If you don't have a storage account, see Create a storage account for the steps to create one.
Create a CDC artifact
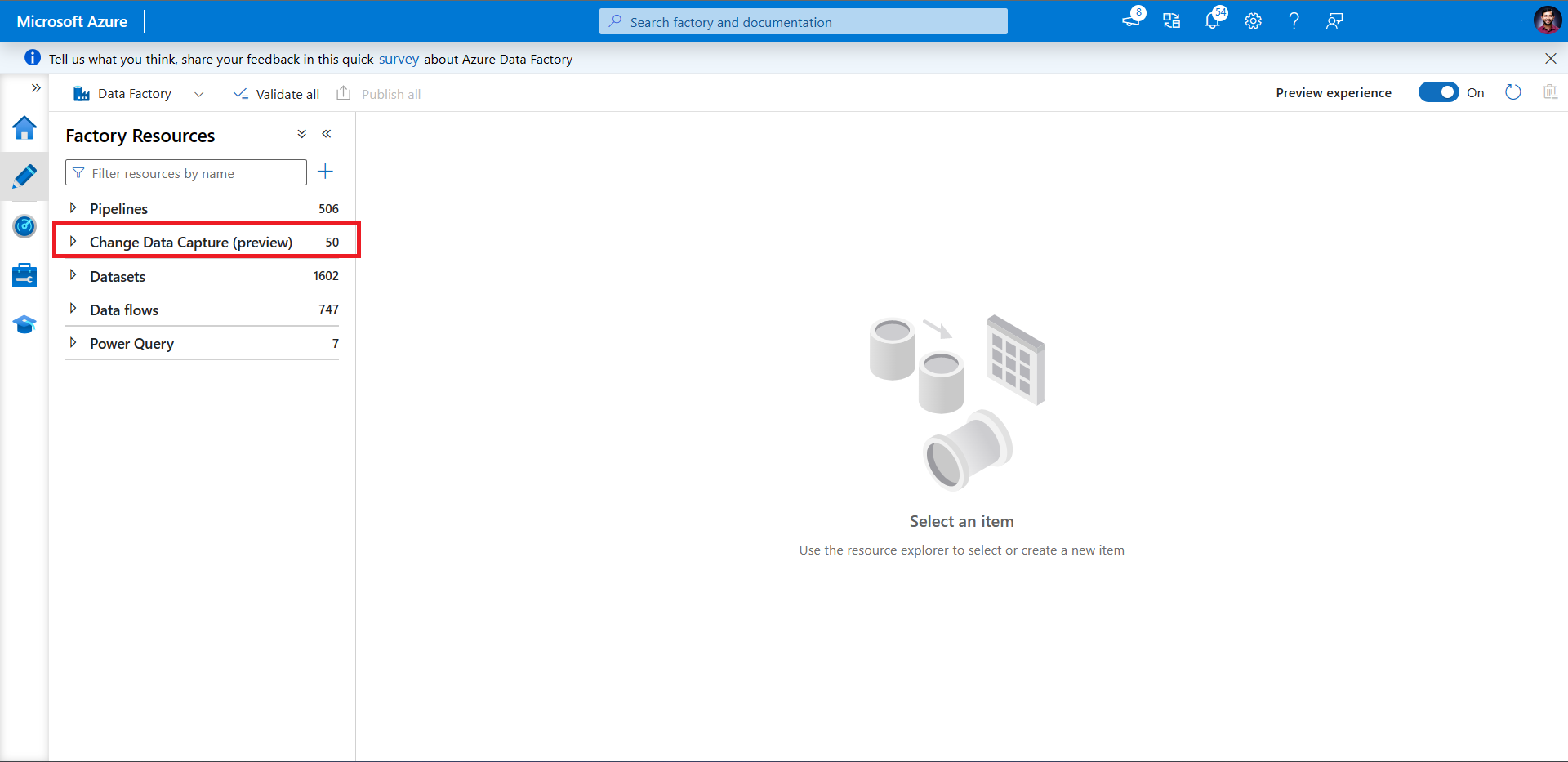
Go to the Author pane in your data factory. Below Pipelines, a new top-level artifact called Change Data Capture (preview) appears.
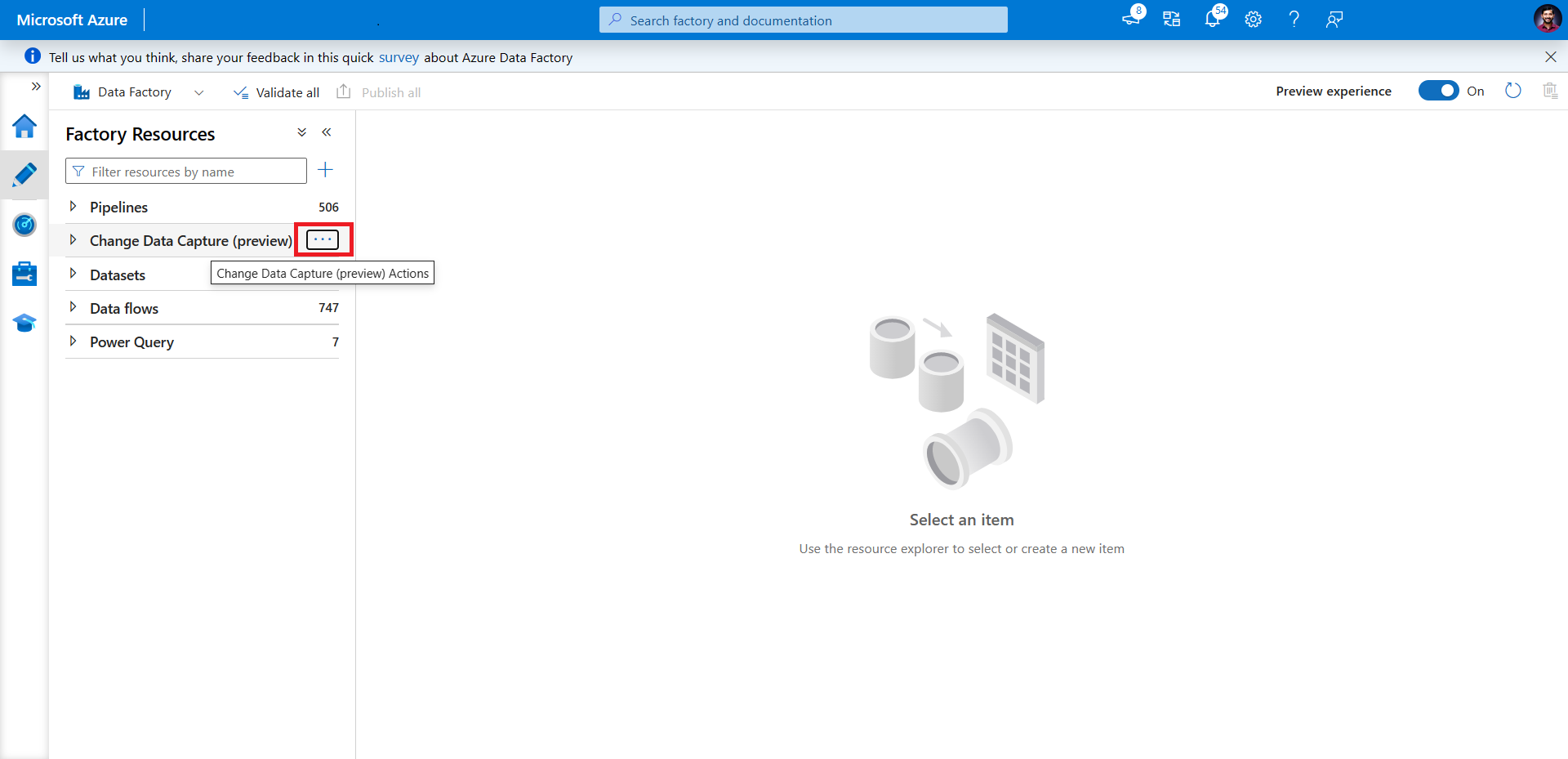
Hover over Change Data Capture (preview) until three dots appear. Then select Change Data Capture (preview) Actions.
Select New CDC (preview). This step opens a flyout to begin the guided process.
You're prompted to name your CDC resource. By default, the name is "adfcdc" with a number that increments by 1. You can replace this default name with a name that you choose.
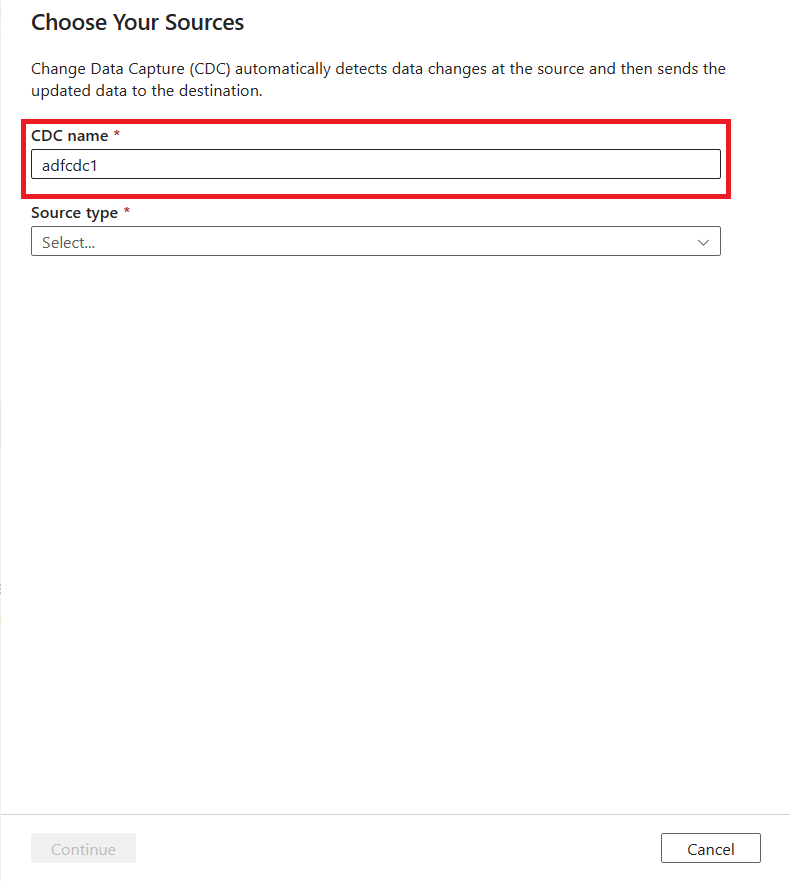
Use the dropdown list to choose your data source. For this article, select DelimitedText.
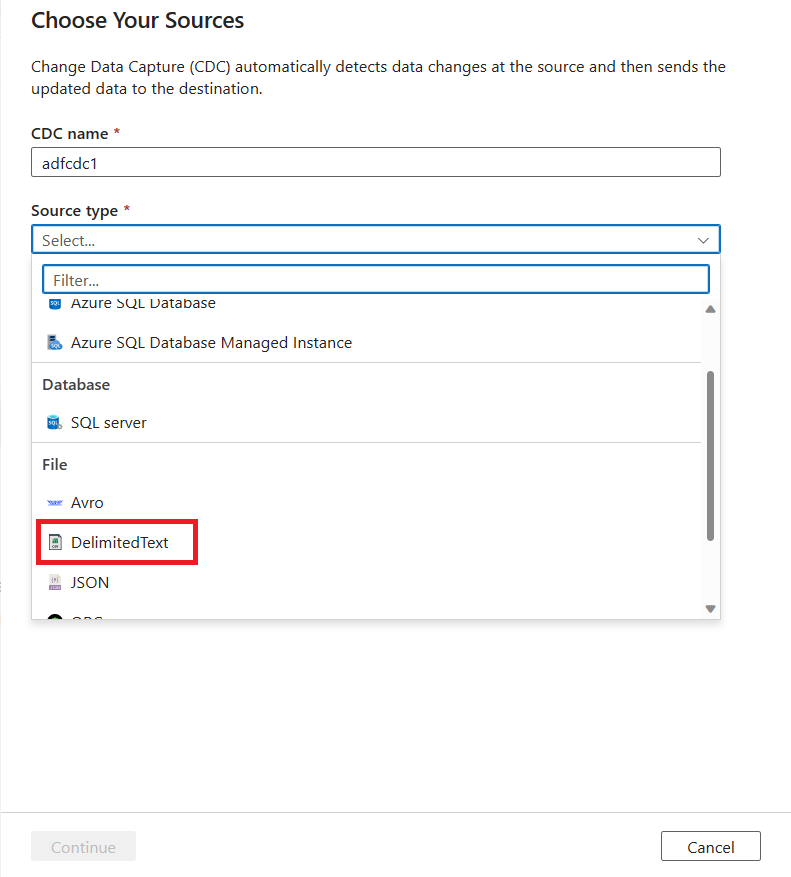
You're prompted to select a linked service. Create a new linked service or select an existing one.
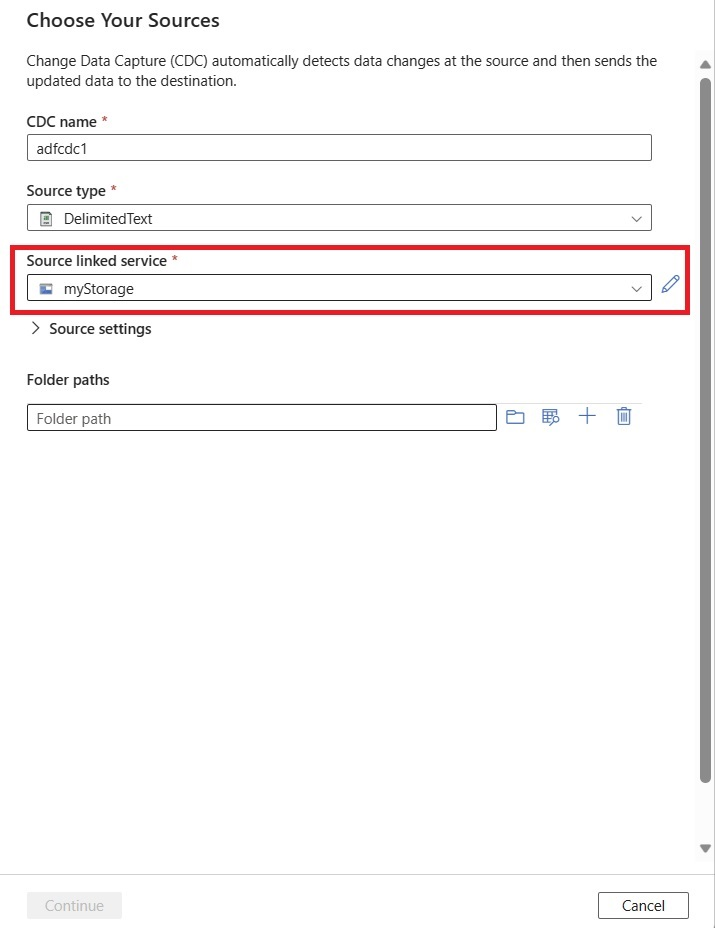
Use the Source settings area to optionally set advanced source configurations, including column and row delimiters.
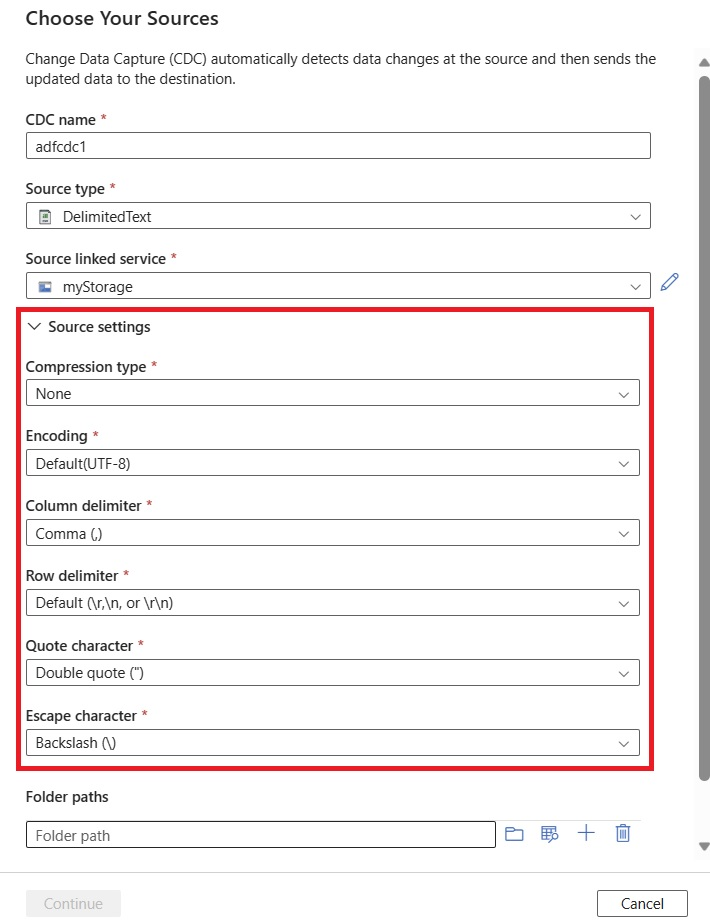
If you don't manually edit these source settings, they're set to the defaults.
Use the Browse button to select your source data folder.
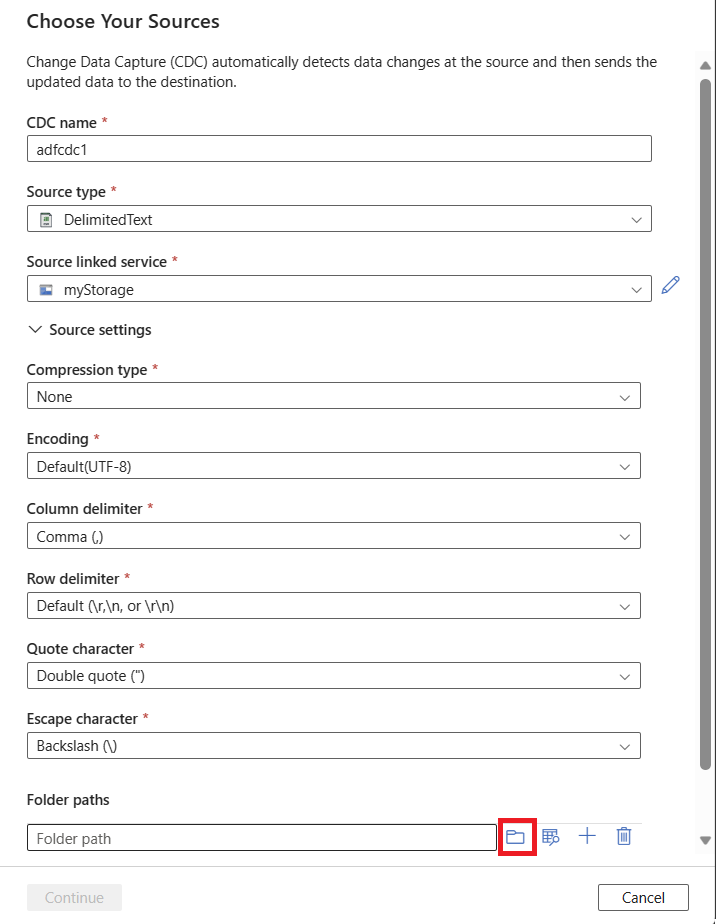
After you select a folder path, select Continue to set your data target.
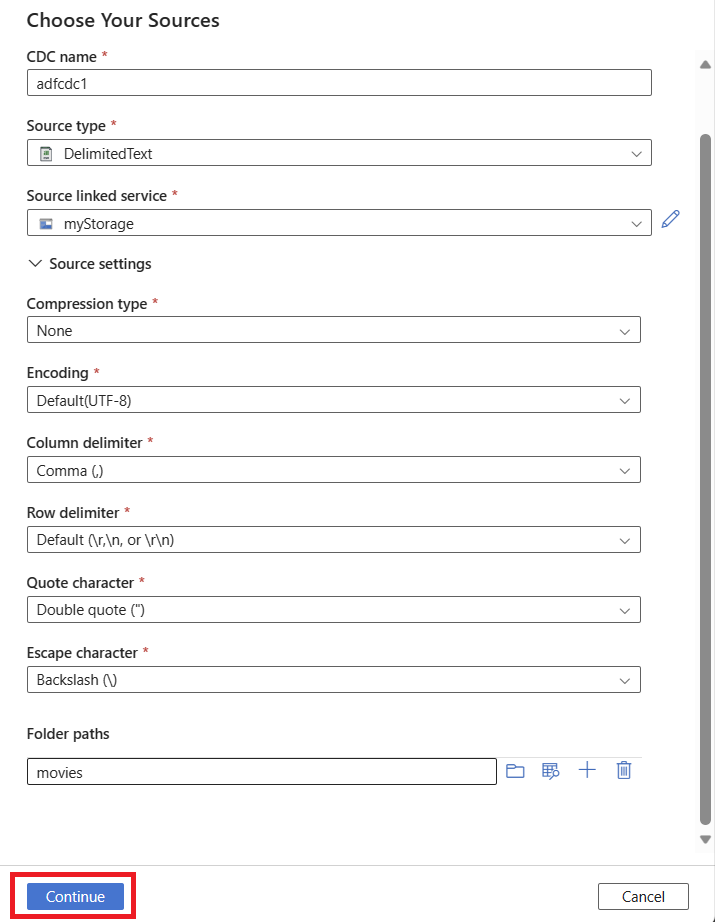
You can choose to add multiple source folders by using the plus (+) button. The other sources must also use the same linked service that you already selected.
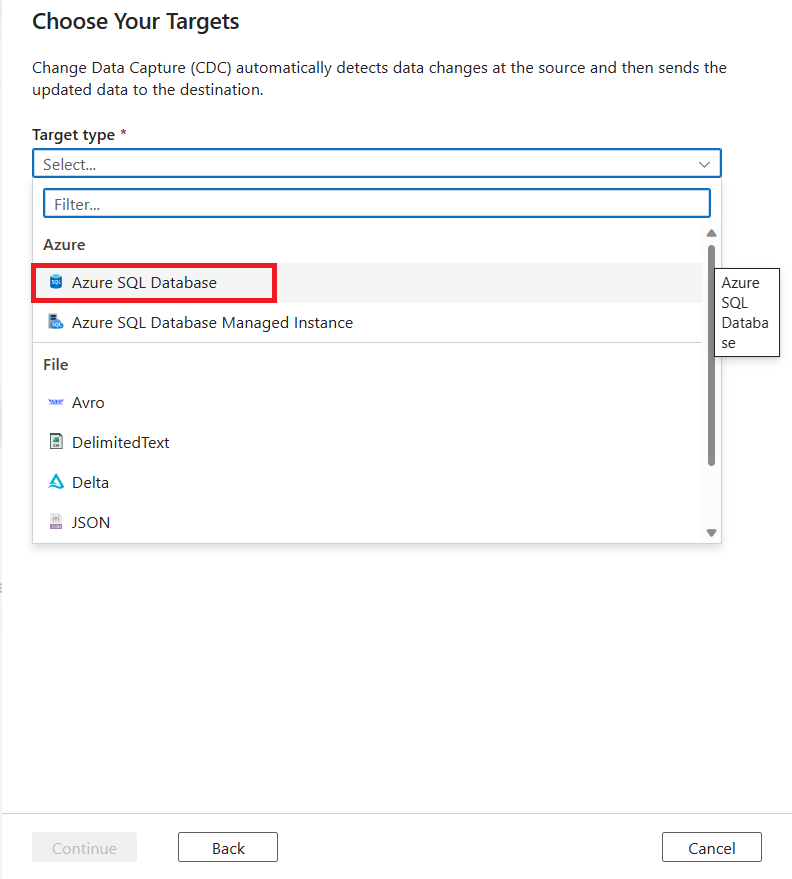
Select a Target type value by using the dropdown list. For this article, select Azure SQL Database.
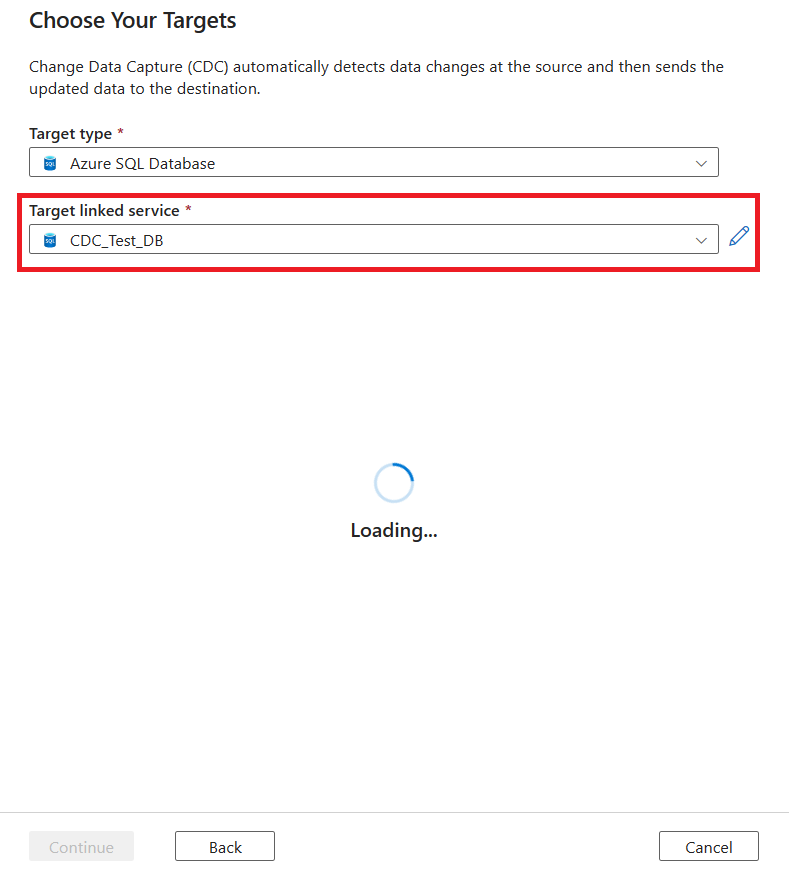
You're prompted to select a linked service. Create a new linked service or select an existing one.
For Target tables, you can create a new target table or select an existing one:
To create a target table, select the New entities tab, and then select Edit new tables.
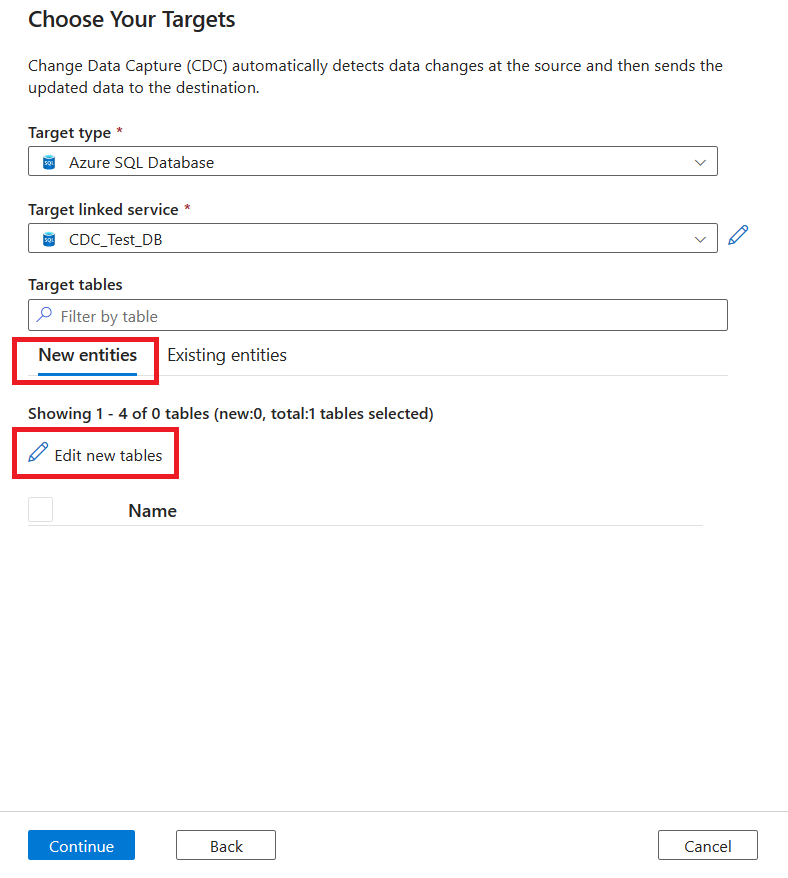
To select an existing table, select the Existing entities tab, and then use the checkbox to choose a table. Use the Preview button to view your table data.
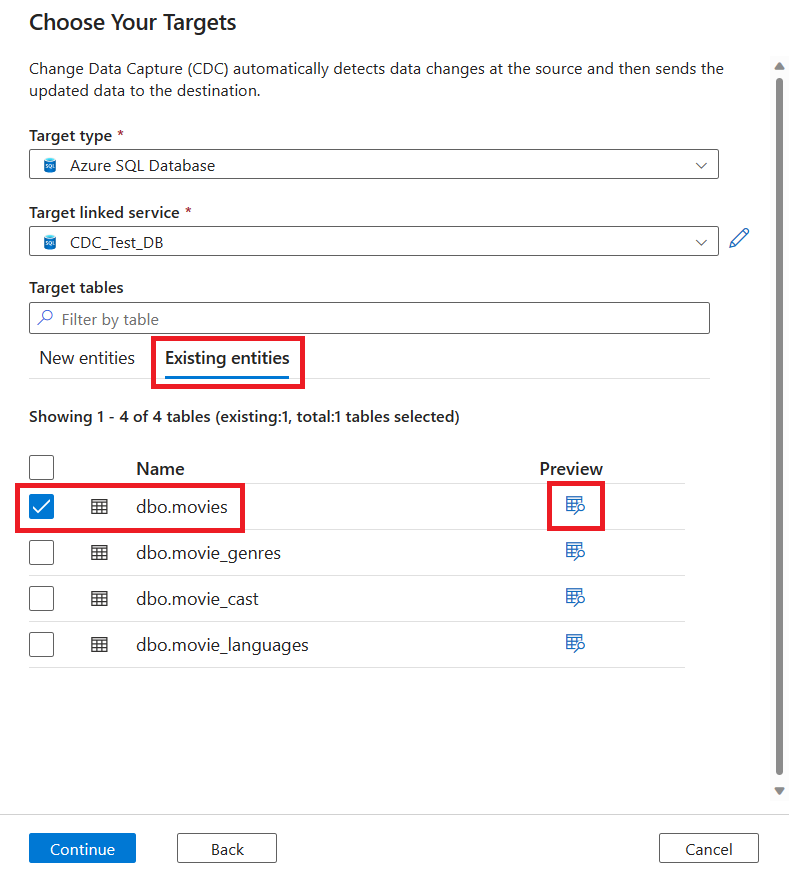
If existing tables at the target have matching names, they're selected by default under Existing entities. If not, new tables with matching names are created under New entities. Additionally, you can edit new tables by using the Edit new tables button.
You can use the checkboxes to choose multiple target tables from your SQL database. After you finish choosing target tables, select Continue.
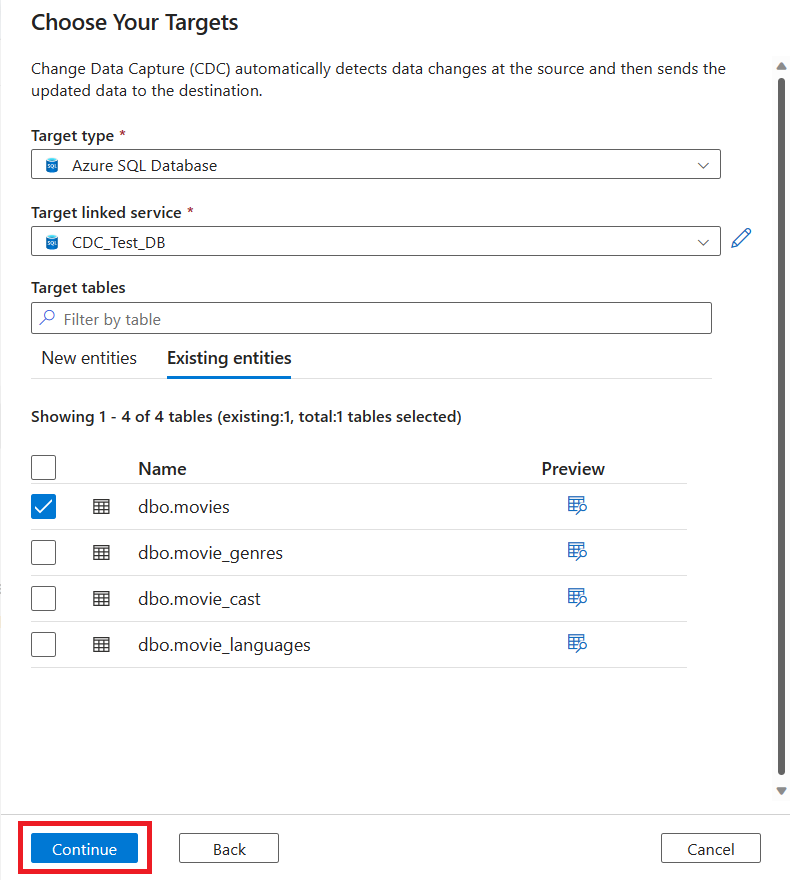
A new tab for capturing change data appears. This tab is the CDC studio, where you can configure your new resource.
A new mapping is automatically created for you. You can update the Source Table and Target Table selections for your mapping by using the dropdown lists.
After you select your tables, their columns are mapped by default with the Auto map toggle turned on. Auto map automatically maps the columns by name in the sink, picks up new column changes when the source schema evolves, and flows this information to the supported sink types.
If you want to use Auto map and not change any column mappings, go directly to step 18.
If you want to enable the column mappings, select the mappings and turn off the Auto map toggle. Then, select the Column mappings button to view the mappings.
You can switch back to automatic mapping anytime by turning on the Auto map toggle.
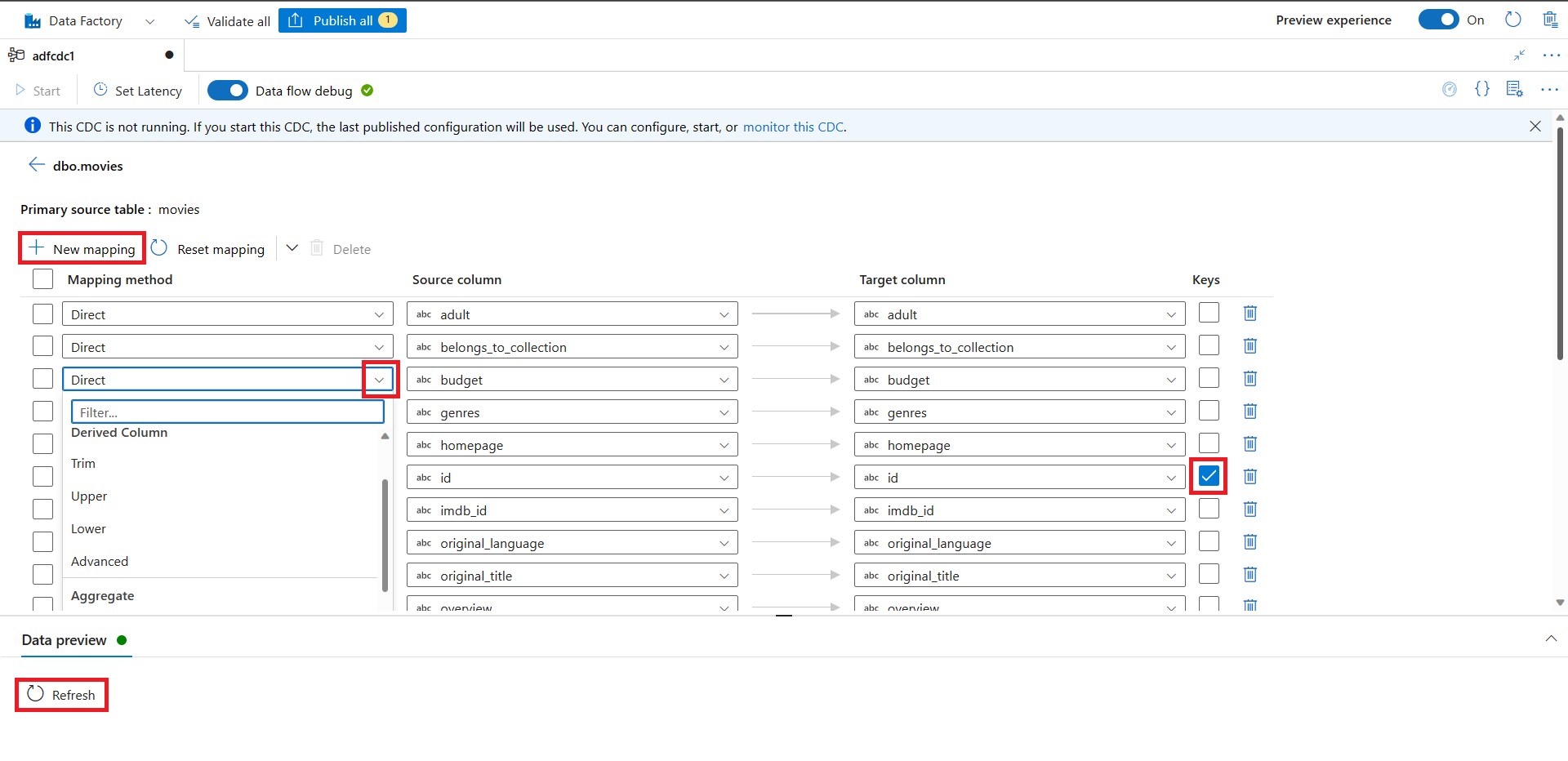
View your column mappings. Use the dropdown lists to edit your column mappings for Mapping method, Source column, and Target column.
From this page, you can:
- Add more column mappings by using the New mapping button. Use the dropdown lists to make selections for Mapping method, Source column, and Target column.
- Select the Keys column if you want to track the delete operation for supported sink types.
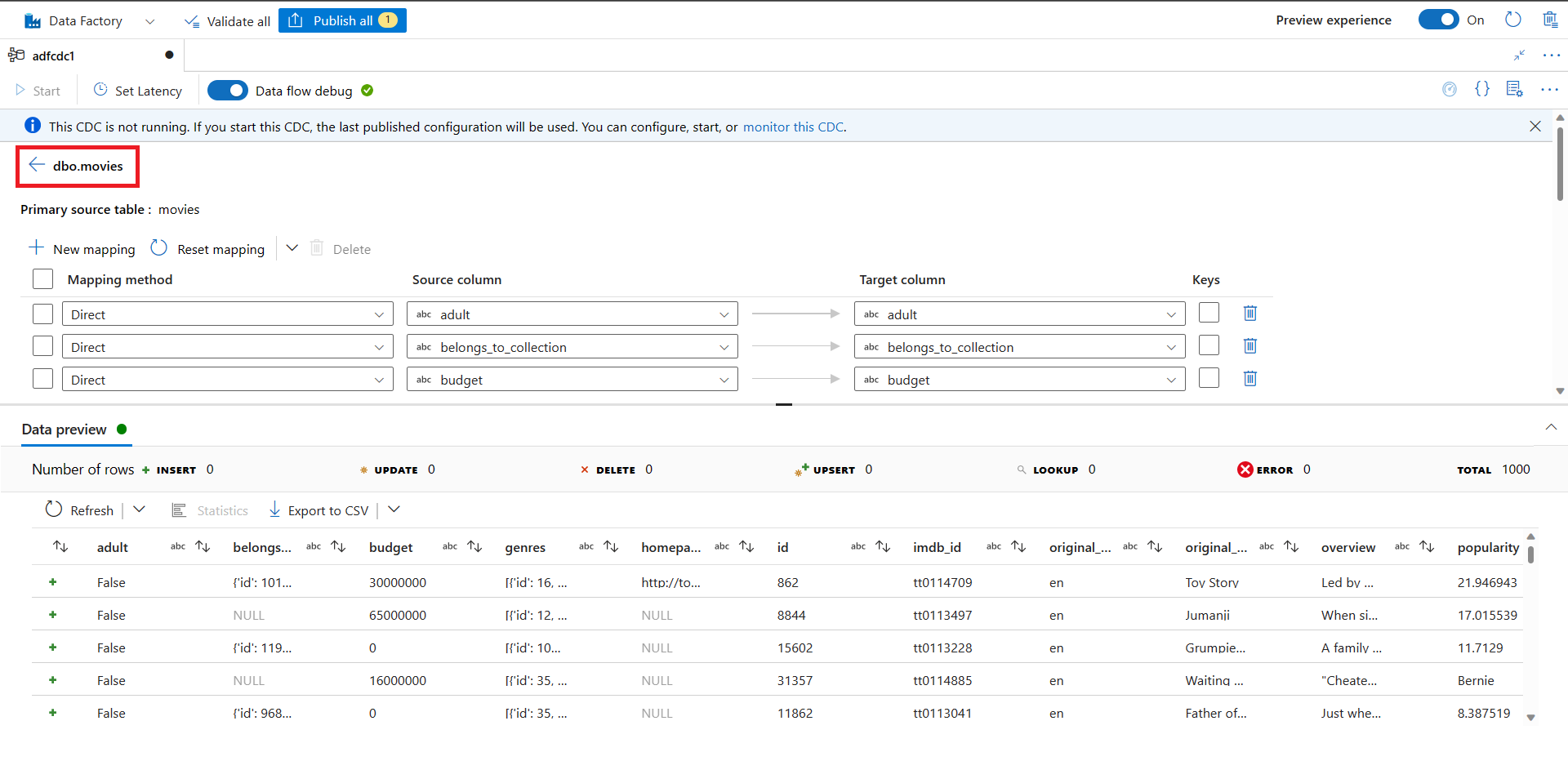
- Select the Refresh button under Data preview to visualize how the data looks at the target.
When your mapping is complete, select the arrow button to return to the main CDC canvas.
You can add more source-to-target mappings in one CDC artifact. Use the Edit button to add more data sources and targets. Then, select New mapping and use the drop-down lists to set a new source and target. You can turn Auto map on or off for each of these mappings independently.
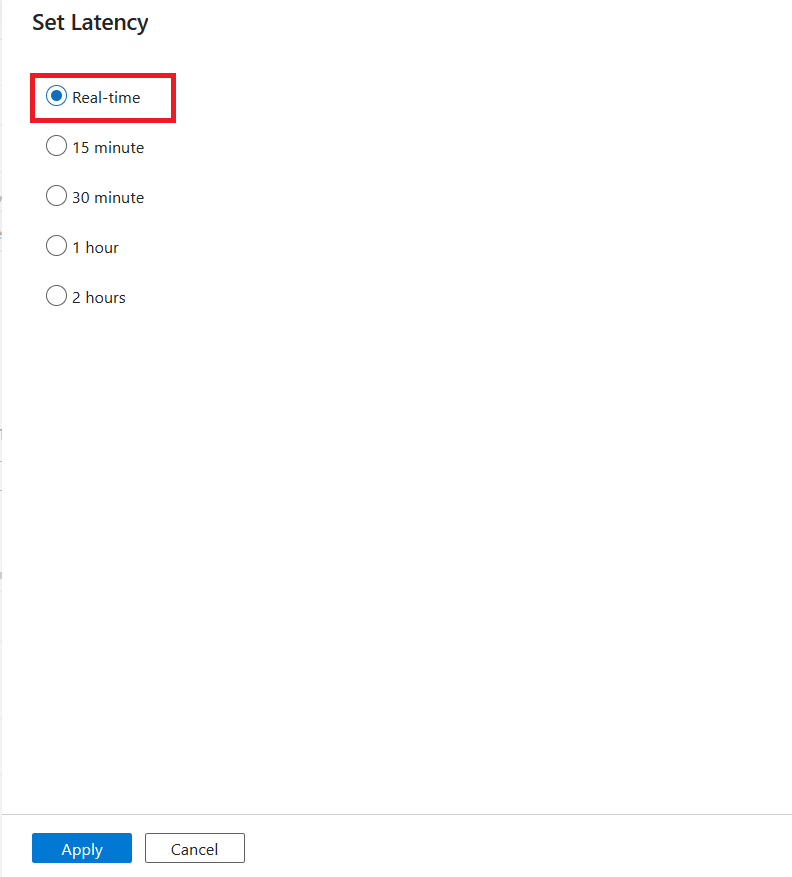
After your mappings are complete, set your CDC latency by using the Set Latency button.
Select the latency of your CDC, and then select Apply to make the changes.
By default, latency is set to 15 minute. The example in this article uses the Real-time option for latency. Real-time latency continuously picks up changes in your source data in intervals of less than 1 minute.
For other latencies (for example, if you select 15 minutes), your change data capture will process your source data and pick up any changed data since the last processed time.
Note
If support is extended to streaming data integration (Azure Event Hubs and Kafka data sources), the latency will be set to Real-time by default.
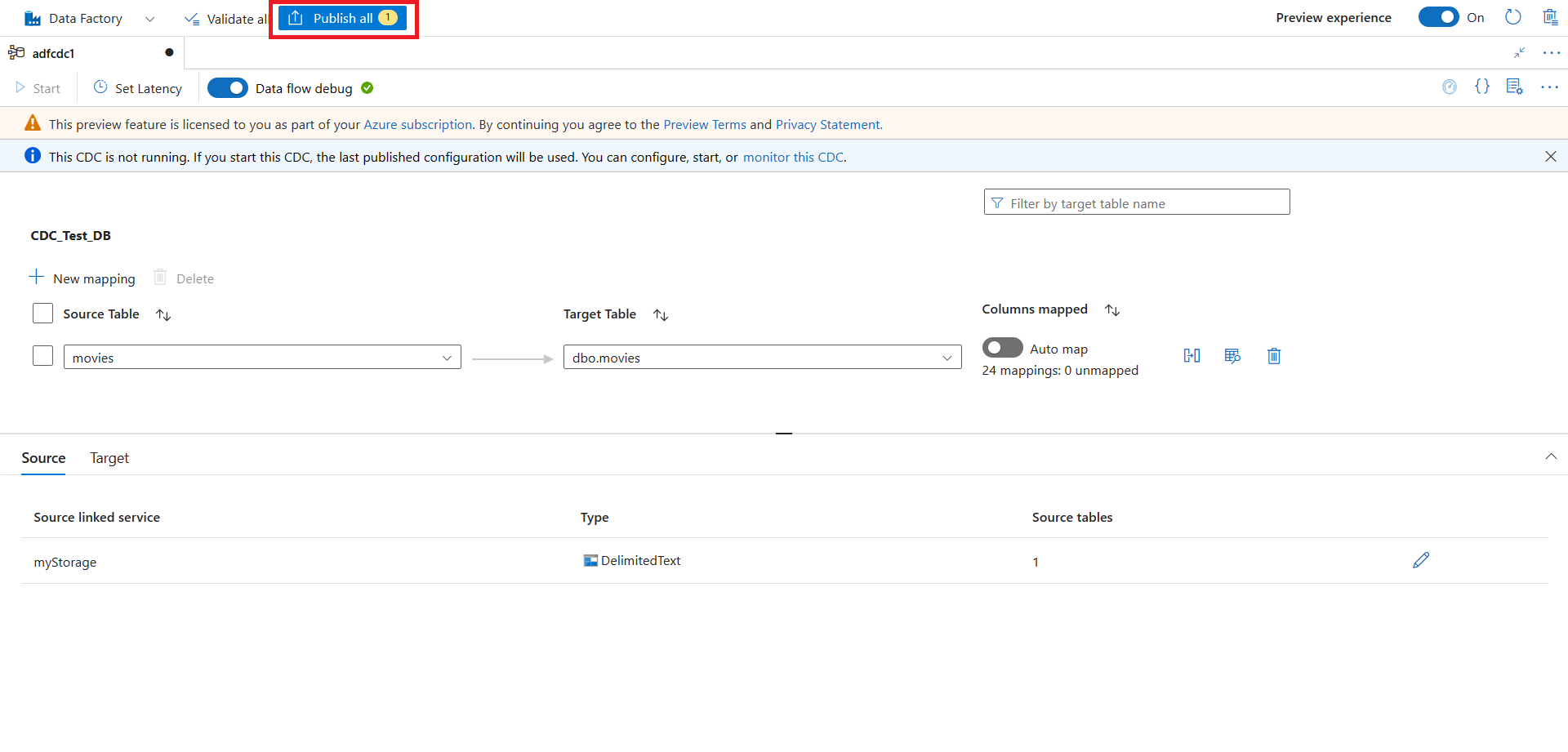
After you finish configuring your CDC, select Publish all to publish your changes.
Note
If you don't publish your changes, you won't be able to start your CDC resource. The Start button in the next step will be unavailable.
Select Start to start running your change data capture.
Monitor your change data capture
Open the Monitor pane by using either of these methods:
Select Change Data Capture (preview) to view your CDC resources.
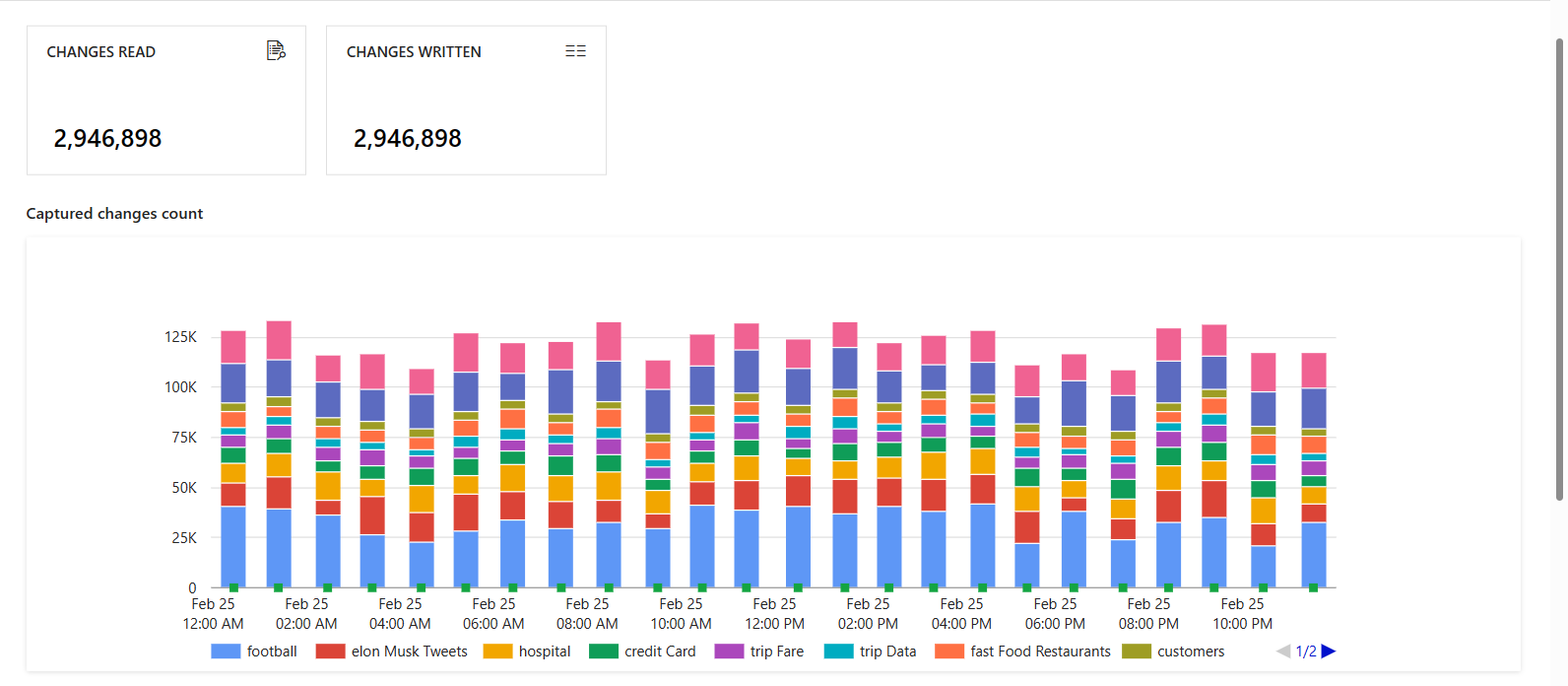
The Change Data Capture pane shows the Source, Target, Status, and Last processed information for your change data capture.
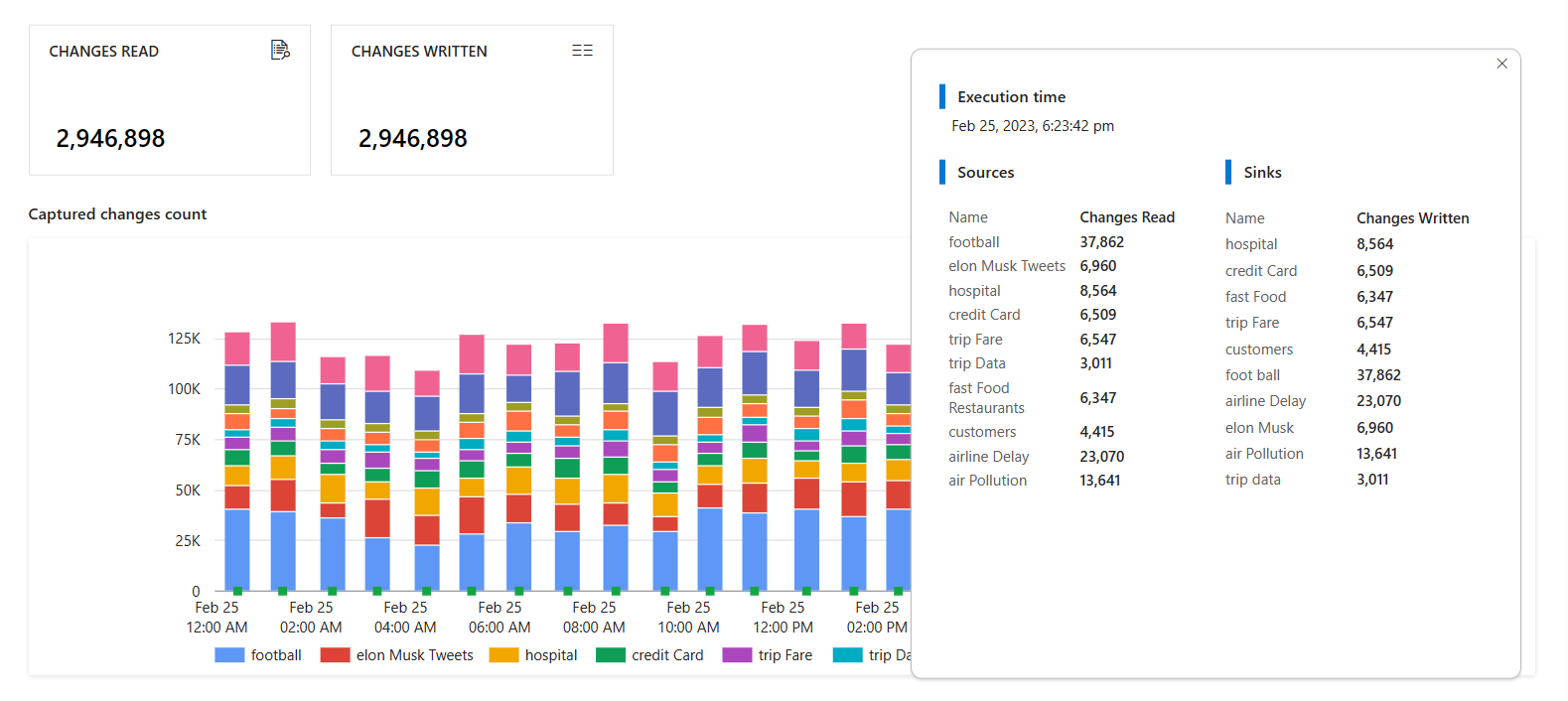
Select the name of your CDC to see more details. You can see how many changes (insert, update, or delete) were read and written, along with other diagnostic information.
If you set up multiple mappings in your change data capture, each mapping appears as a different color. Select the bar to see specific details for each mapping, or use the diagnostics information at the bottom of the pane.