Exchange peering walkthrough
In this article, you learn how to set up and manage an Exchange peering.
Create an Exchange peering
To provision an Exchange peering, complete the following steps:
- Review Microsoft peering policy to understand requirements for Exchange peering.
- Find Microsoft peering location and peering facility ID in PeeringDB
- Request Exchange peering for a peering location using the instructions in Create and modify an Exchange peering.
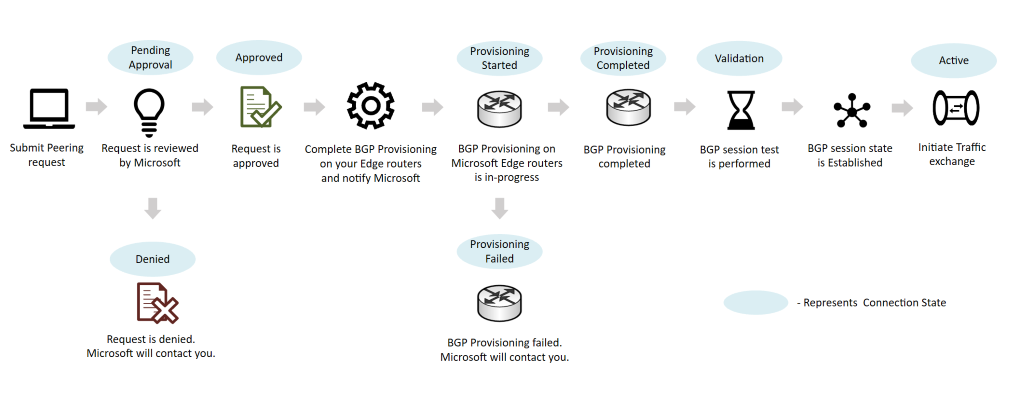
- After you submit a peering request, Microsoft will review the request and contact you if necessary.
- Once peering request is approved, connection state changes to Approved.
- Configure BGP session at your end and notify Microsoft.
- Microsoft provisions BGP session with DENY ALL policy and validate end-to-end.
- If successful, you receive a notification that peering connection state is Active.
- Traffic is then allowed through the new peering.
Note
Connection states are different than standard BGP session states.
Convert a legacy Exchange peering to Azure resource
To convert a legacy Exchange peering to an Azure resource, complete the following steps:
- Follow the instructions in Convert a legacy Exchange peering to Azure resource
- After you submit the conversion request, Microsoft will review the request and contact you if necessary.
- Once approved, you see your Exchange peering with a connection state as Active.
Deprovision an Exchange peering
Contact Microsoft peering to deprovision an Exchange peering.
When an Exchange peering is set for deprovision, the connection state changes to PendingRemove.
Important
If you run PowerShell cmdlet to delete the Exchange peering when the connection state is ProvisioningStarted or ProvisioningCompleted, the operation will fail.
Related content
- Learn about the Prerequisites to set up peering with Microsoft.
- Learn about the Peering policy.