Assessment Overview (migrate to Azure SQL)
This article provides an overview of assessments for migrating on-premises SQL Server instances from a VMware, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Physical environment to SQL Server on Azure VM or Azure SQL Database or Azure SQL Managed Instance using the Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment tool.
What's an assessment?
An assessment with the Discovery and assessment tool is a point in time snapshot of data and measures the readiness and estimates the effect of migrating on-premises servers to Azure.
Types of assessments
There are three types of assessments that you can create using the Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment tool.
| Assessment Type | Details |
|---|---|
| Azure VM | Assessments to migrate your on-premises servers to Azure virtual machines. You can assess your on-premises servers in VMware and Hyper-V environment, and physical servers for migration to Azure VMs using this assessment type. |
| Azure SQL | Assessments to migrate your on-premises SQL servers from your VMware, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Physical environments to SQL Server on Azure VM, or Azure SQL Database, or Azure SQL Managed Instance. |
| Azure App Service | Assessments to migrate your on-premises ASP.NET web apps, running on IIS web servers, from your VMware environment to Azure App Service. |
| Azure VMware Solution (AVS) | Assessments to migrate your on-premises servers to Azure VMware Solution (AVS). You can assess your on-premises VMware VMs for migration to Azure VMware Solution (AVS) using this assessment type. Learn more. |
Note
If the number of Azure VM or AVS assessments are incorrect on the Discovery and assessment tool, click on the total number of assessments to navigate to all the assessments and recalculate the Azure VM or AVS assessments. The Discovery and assessment tool then shows the correct count for that assessment type.
An Azure SQL assessment provides two sizing criteria:
| Sizing criteria | Details | Data |
|---|---|---|
| As on-premises | Assessments that make recommendations based on the on-premises SQL Server configuration alone | The Azure SQL configuration is based on the on-premises SQL Server configuration, which includes cores allocated, total memory allocated and database sizes. |
| Performance-based | Assessments that make recommendations based on collected performance data | The Azure SQL configuration is based on performance data of SQL instances and databases, which includes CPU utilization, Memory utilization, IOPS (Data and Log files), throughput, and latency of IO operations. |
How do I assess my on-premises SQL servers?
You can assess your on-premises SQL Server instances by using the configuration and utilization data collected by a lightweight Azure Migrate appliance. The appliance discovers on-premises SQL server instances and databases and sends the configuration and performance data to Azure Migrate. Learn More.
How do I assess with the appliance?
If you're deploying an Azure Migrate appliance to discover on-premises servers, do the following steps:
- Set up Azure and your on-premises environment to work with Azure Migrate.
- For your first assessment, create an Azure Migrate project and add the Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment tool to it.
- Deploy a lightweight Azure Migrate appliance. The appliance continuously discovers on-premises servers and sends configuration and performance data to Azure Migrate. Deploy the appliance as a VM or a physical server. You don't need to install anything on servers that you want to assess.
After the appliance begins discovery, you can gather servers you want to assess into a group and run an assessment for the group with assessment type Azure SQL.
Follow our tutorial for assessing SQL Server instances to try out these steps.
How does the appliance calculate performance data for SQL instances and databases?
The appliance collects performance data for compute settings with these steps:
- The appliance collects a real-time sample point. For SQL servers, it collects a sample point every 30 seconds.
- The appliance aggregates the sample data points collected every 30 seconds over 10 minutes. To create the data point, the appliance selects the peak values from all samples. It sends the max, mean and variance for each counter to Azure.
- Azure Migrate stores all the 10-minute data points for the last month.
- When you create an assessment, Azure Migrate identifies the appropriate data point to use for right-sizing. Identification is based on the percentile values for performance history and percentile utilization.
- For example, if the performance history is one week and the percentile utilization is the 95th percentile, the assessment sorts the 10-minute sample points for the last week. It sorts them in ascending order and picks the 95th percentile value for right-sizing.
- The 95th percentile value makes sure you ignore any outliers, which might be included if you picked the 99th percentile.
- If you want to pick the peak usage for the period and don't want to miss any outliers, select the 99th percentile for percentile utilization.
- This value is multiplied by the comfort factor to get the effective performance utilization data for these metrics that the appliance collects:
- CPU utilization (%)
- Memory utilization (%)
- Read IO/s and Write IO/s (Data and Log files)
- Read MB/s and Write MB/s (Throughput)
- Latency of IO operations
What properties are used to create and customize an Azure SQL assessment?
The Azure SQL assessment properties include:
| Section | Setting | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Target and pricing settings | Target location | The Azure region to which you want to migrate. Azure SQL configuration and cost recommendations are based on the location that you specify. |
| Target and pricing settings | Environment type | The environment for the SQL deployments to apply pricing applicable to Production or Dev/Test. |
| Target and pricing settings | Offer/Licensing program | The Azure offer if you're enrolled. Currently, the field is Pay-as-you-go by default, which gives you retail Azure prices. You can avail additional discount by applying reserved capacity and Azure Hybrid Benefit on top of Pay-as-you-go offer. You can apply Azure Hybrid Benefit on top of Pay-as-you-go offer and Dev/Test environment. The assessment doesn't support applying Reserved Capacity on top of Pay-as-you-go offer and Dev/Test environment. If the offer is set to Pay-as-you-go and Reserved capacity is set to No reserved instances, the monthly cost estimates are calculated by multiplying the number of hours chosen in the VM uptime field with the hourly price of the recommended SKU. |
| Target and pricing settings | Savings options - Azure SQL MI and DB (PaaS) | Specify the reserved capacity savings option that you want the assessment to consider to help optimize your Azure compute cost. Azure reservations (1 year or 3 year reserved) are a good option for the most consistently running resources. When you select 'None', the Azure compute cost is based on the Pay as you go rate or based on actual usage. You need to select pay-as-you-go in offer/licensing program to be able to use Reserved Instances. When you select any savings option other than 'None', the 'Discount (%)' and "VM uptime" settings aren't applicable. The monthly cost estimates are calculated by multiplying 744 hours with the hourly price of the recommended SKU. |
| Target and pricing settings | Savings options - SQL Server on Azure VM (IaaS) | Specify the savings option that you want the assessment to consider to help optimize your Azure compute cost. Azure reservations (1 year or 3 year reserved) are a good option for the most consistently running resources. Azure Savings Plan (1 year or 3 year savings plan) provide additional flexibility and automated cost optimization. Ideally post migration, you could use Azure reservation and savings plan at the same time (reservation is consumed first), but in the Azure Migrate assessments, you can only see cost estimates of 1 savings option at a time. When you select 'None', the Azure compute cost is based on the Pay as you go rate or based on actual usage. You need to select pay-as-you-go in offer/licensing program to be able to use Reserved Instances or Azure Savings Plan. When you select any savings option other than 'None', the 'Discount (%)' and "VM uptime" settings aren't applicable. The monthly cost estimates are calculated by multiplying 744 hours in the VM uptime field with the hourly price of the recommended SKU. |
| Target and pricing settings | Currency | The billing currency for your account. |
| Target and pricing settings | Discount (%) | Any subscription-specific discounts you receive on top of the Azure offer. The default setting is 0%. |
| Target and pricing settings | VM uptime | Specify the duration (days per month/hour per day) that servers/VMs run. This is useful for computing cost estimates for SQL Server on Azure VM where you're aware that Azure VMs might not run continuously. Cost estimates for servers where recommended target is SQL Server on Azure VM are based on the duration specified. Default is 31 days per month/24 hours per day. |
| Target and pricing settings | Azure Hybrid Benefit | Specify whether you already have a Windows Server and/or SQL Server license or Enterprise Linux subscription (RHEL and SLES). Azure Hybrid Benefit is a licensing benefit that helps you to significantly reduce the costs of running your workloads in the cloud. It works by letting you use your on-premises Software Assurance-enabled Windows Server and SQL Server licenses on Azure. For example, if you have a SQL Server license and they're covered with active Software Assurance of SQL Server Subscriptions, you can apply for the Azure Hybrid Benefit when you bring licenses to Azure. |
| Assessment criteria | Sizing criteria | Set to Performance-based by default, which means Azure Migrate collects performance metrics pertaining to SQL instances and the databases managed by it to recommend an optimal-sized SQL Server on Azure VM and/or Azure SQL Database and/or Azure SQL Managed Instance configuration. You can change this to As on-premises to get recommendations based on just the on-premises SQL Server configuration without the performance metric based optimizations. |
| Assessment criteria | Performance history | Indicate the data duration on which you want to base the assessment. (Default is one day) |
| Assessment criteria | Percentile utilization | Indicate the percentile value you want to use for the performance sample. (Default is 95th percentile) |
| Assessment criteria | Comfort factor | Indicate the buffer you want to use during assessment. This accounts for issues like seasonal usage, short performance history, and likely increases in future usage. |
| Assessment criteria | Optimization preference | Specify the preference for the recommended assessment report. Selecting Minimize cost would result in the Recommended assessment report recommending those deployment types that have least migration issues and are most cost effective, whereas selecting Modernize to PaaS would result in Recommended assessment report recommending PaaS(Azure SQL MI or DB) deployment types over IaaS Azure(VMs), wherever the SQL Server instance is ready for migration to PaaS irrespective of cost. |
| Azure SQL Managed Instance sizing | Service Tier | Choose the most appropriate service tier option to accommodate your business needs for migration to Azure SQL Managed Instance: Select Recommended if you want Azure Migrate to recommend the best suited service tier for your servers. This can be General purpose or Business critical. Select General Purpose if you want an Azure SQL configuration designed for budget-oriented workloads. Select Business Critical if you want an Azure SQL configuration designed for low-latency workloads with high resiliency to failures and fast failovers. |
| Azure SQL Managed Instance sizing | Instance type | Defaulted to Single instance. |
| Azure SQL Managed Instance sizing | Pricing Tier | Defaulted to Standard. |
| SQL Server on Azure VM sizing | VM series | Specify the Azure VM series you want to consider for SQL Server on Azure VM sizing. Based on the configuration and performance requirements of your SQL Server or SQL Server instance, the assessment recommends a VM size from the selected list of VM series. You can edit settings as needed. For example, if you don't want to include D-series VM, you can exclude D-series from this list. As Azure SQL assessments intend to give the best performance for your SQL workloads, the VM series list only has VMs that are optimized for running your SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines (VMs). Learn more. |
| SQL Server on Azure VM sizing | Storage Type | Defaulted to Recommended, which means the assessment recommends the best suited Azure Managed Disk based on the chosen environment type, on-premises disk size, IOPS and throughput. |
| Azure SQL Database sizing | Service Tier | Choose the most appropriate service tier option to accommodate your business needs for migration to Azure SQL Database: Select Recommended if you want Azure Migrate to recommend the best suited service tier for your servers. This can be General purpose or Business critical. Select General Purpose if you want an Azure SQL configuration designed for budget-oriented workloads. Select Business Critical if you want an Azure SQL configuration designed for low-latency workloads with high resiliency to failures and fast failovers. |
| Azure SQL Database sizing | Instance type | Defaulted to Single database. |
| Azure SQL Database sizing | Purchase model | Defaulted to vCore. |
| Azure SQL Database sizing | Compute tier | Defaulted to Provisioned. |
| High availability and disaster recovery properties | Disaster recovery region | Defaulted to the cross-region replication pair of the Target location. In an unlikely event when the chosen Target location doesn't yet have such a pair, the specified Target location itself is chosen as the default disaster recovery region. |
| High availability and disaster recovery properties | Multi-subnet intent | Defaulted to Disaster recovery. Select Disaster recovery if you want asynchronous data replication where some replication delays are tolerable. This allows higher durability using geo-redundancy. In the event of failover, data that hasn't yet been replicated might be lost. Select High availability if you desire the data replication to be synchronous and no data loss due to replication delay is allowable. This setting allows assessment to leverage built-in high availability options in Azure SQL Databases and Azure SQL Managed Instances, and availability zones and zone-redundancy in Azure Virtual Machines to provide higher availability. In the event of failover, no data is lost. |
| High availability and disaster recovery properties | Internet Access | Defaulted to Available. Select Available if you allow outbound Internet access from Azure VMs. This allows the use of Cloud Witness which is the recommended approach for Windows Server Failover Clusters in Azure Virtual Machines. Select Not available if the Azure VMs have no outbound Internet access. This requires the use of a Shared Disk as a witness for Windows Server Failover Clusters in Azure Virtual Machines. |
| High availability and disaster recovery properties | Async commit mode intent | Defaulted to Disaster recovery. Select Disaster recovery if you're using asynchronous commit availability mode to enable higher durability for the data without affecting performance. In the event of failover, data that hasn't yet been replicated might be lost. Select High availability if you're using asynchronous commit data availability mode to improve availability and scale out read traffic. This setting allows assessment to leverage built-in high availability features in Azure SQL Databases, Azure SQL Managed Instances, and Azure Virtual Machines to provide higher availability and scale out. |
| Security | Security | Defaulted to Yes, with Microsoft Defender for Cloud. Specifies whether you want to assess readiness and cost for security tooling on Azure. If the setting has the default value Yes, with Microsoft Defender for Cloud, it will assess security readiness and costs for your Azure SQL MI/DB with Microsoft Defender for Cloud. |
Review the best practices for creating an assessment with Azure Migrate.
Calculate readiness
Note
The assessment only includes databases that are in online status. In case the database is in any other status, the assessment ignores the readiness, sizing and cost calculation for such databases. In case you wish to assess such databases, change the status of the database and recalculate the assessment in some time.
Azure SQL readiness
Readiness checks for different migration strategies:
Recommended deployment, Instances to SQL Server on Azure VM, Instances to Azure SQL MI, Database to Azure SQL DB:
Azure SQL readiness for SQL instances and databases is based on a feature compatibility check with SQL Server on Azure VM, Azure SQL Database, and Azure SQL Managed Instance:
- The Azure SQL assessment considers the SQL Server instance features that are currently used by the source SQL Server workloads (SQL Agent jobs, linked servers, etc.) and the user databases schemas (tables, views, triggers, stored procedures etc.) to identify compatibility issues.
- If there are no compatibility issues found, the instance is marked as Ready for the target deployment type (SQL Server on Azure VM or Azure SQL Database or Azure SQL Managed Instance)
- If there are non-critical compatibility issues, such as deprecated or unsupported features that don't block the migration to a specific target deployment type, the instance is marked as Ready (hyperlinked) with warning details and recommended remediation guidance. This includes the situation where the source data has an Always On Availability Group configuration and the required replicas exceed those available with the specific target deployment type.
- If there are any compatibility issues that might block the migration to a specific target deployment type, the instance is marked as Ready with conditions with issue details and recommended remediation guidance.
- In the Recommended deployment, Instances to Azure SQL MI, and Instances to SQL Server on Azure VM readiness reports, if there's even one database in a SQL instance, which isn't ready for a particular target deployment type, the instance is marked as Ready with conditions for that deployment type.
- Not ready: The assessment couldn't find a SQL Server on Azure VM/Azure SQL MI/Azure SQL DB configuration meeting the desired configuration and performance characteristics. Review the recommendation to make the instance/server ready for the desired target deployment type.
- If the discovery is still in progress or there are any discovery issues for a SQL instance or database, the instance is marked as Unknown as the assessment couldn't compute the readiness for that SQL instance.
Note
In the recommended deployment strategy, migrating instances to SQL Server on Azure VM is the recommended strategy for migrating SQL Server instances. Though, when SQL Server credentials are not available, the Azure SQL assessment provides right-sized lift-and-shift ie "Server to SQL Server on Azure VM" recommendations.
All servers to SQL Server on Azure VM:
Refer to readiness here.
Recommended deployment type
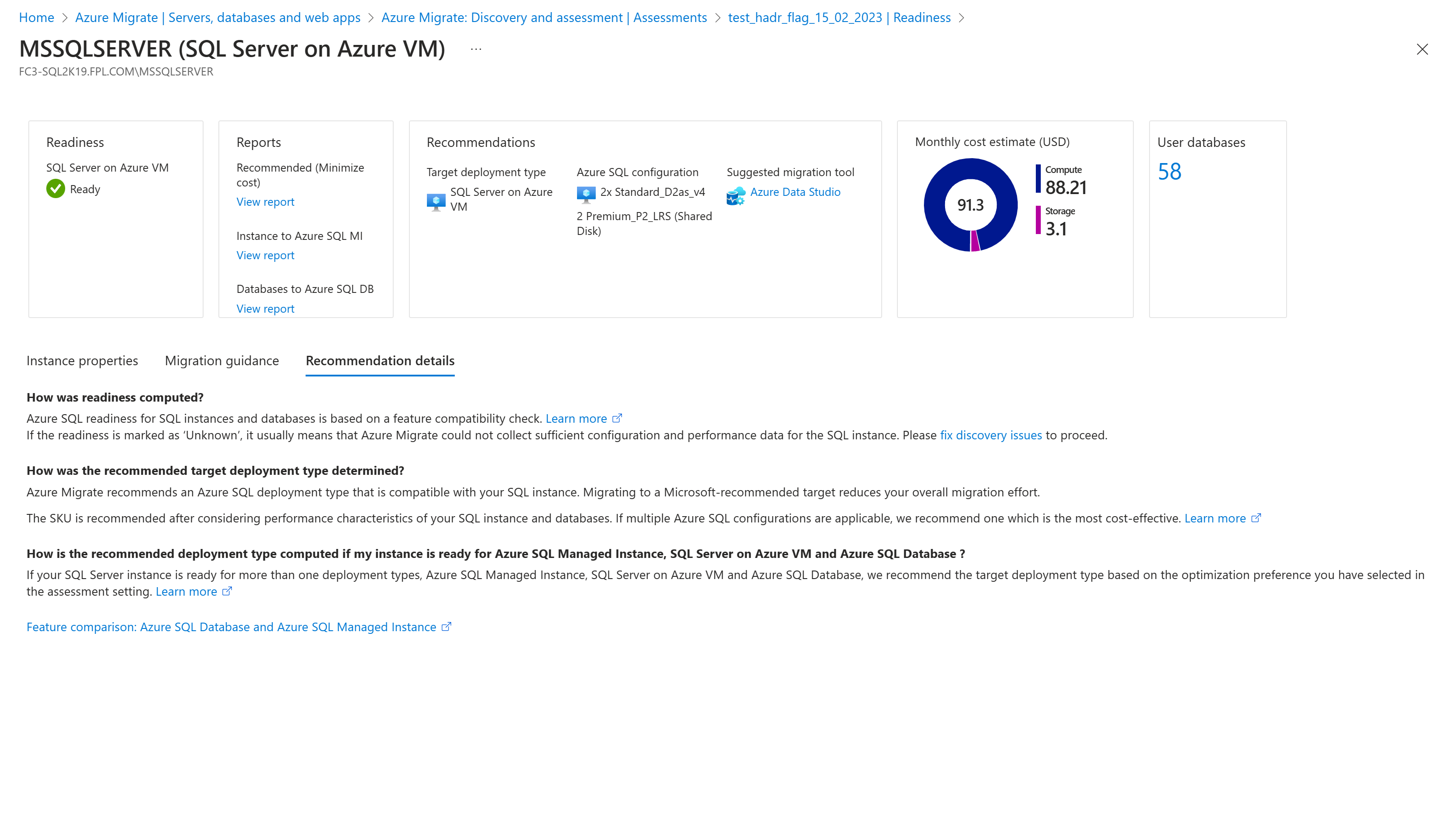
For the recommended deployment migration strategy, the assessment recommends an Azure SQL deployment type that is the most compatible with your SQL instance and is the most cost-effective. Migrating to a Microsoft-recommended target reduces your overall migration effort. If your instance is ready for SQL Server on Azure VM, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and Azure SQL Database, the target deployment type, which has the least migration readiness issues and is the most cost-effective is recommended. If you select the target deployment type as Recommended in the Azure SQL assessment properties, Azure Migrate recommends an Azure SQL deployment type that is compatible with your SQL instance. Migrating to a Microsoft-recommended target reduces your overall migration effort.
Note
In the recommended deployment strategy, if the source SQL Server is good fit for all three deployment targets- SQL Server on Azure VM, Azure SQL Managed Instance and Azure SQL Database, the assessment recommends a specific option that optimizes your cost and fits within the size and performance boundaries.
Security readiness
If the database/instance is marked as Ready for the target deployment type Azure SQL DB/MI, it's automatically considered Ready for Microsoft Defender for SQL. If the database/instance is marked as Ready for the target deployment type SQL Server on Azure VM, it's considered Ready for Microsoft Defender for SQL if it's running any of these versions:
- SQL Server versions 2012, 2014, 2016, 2017, 2019, 2022
- For all other versions, it's marked as Ready with Conditions.
Calculate sizing
After the assessment determines the readiness and the recommended Azure SQL deployment type, it computes a specific service tier and Azure SQL configuration (SKU size) that can meet or exceed the on-premises SQL Server performance. This calculation depends on whether you're using As on-premises or Performance-based sizing criteria.
As on-premises sizing calculation
If you use As on-premises sizing criteria, the assessment uses only SQL instance configuration data and doesn't consider performance data.
Instances to Azure SQL MI and Databases to Azure SQL DB configuration
The assessment computes a specific service tier and Azure SQL configuration (SKU size) that can meet or exceed the on-premises SQL instance configuration:
- During the discovery process, Azure Migrate collects SQL instance configuration that includes:
- vCores (allocated)
- Memory (allocated)
- Total DB size and database file organizations
- Database size is calculated by adding all the data and log files.
- The assessment aggregates all the configuration data and tries to find the best match across various Azure SQL service tiers and configurations and picks a configuration that can match or exceed the SQL instance requirements, optimizing the cost.
Instances to SQL Server on Azure VM configuration
Instance to SQL Server on Azure VM assessment report covers the ideal approach for migrating SQL Server instances and databases to SQL Server on Azure VM, adhering to the best practices. Learn more.
Storage sizing
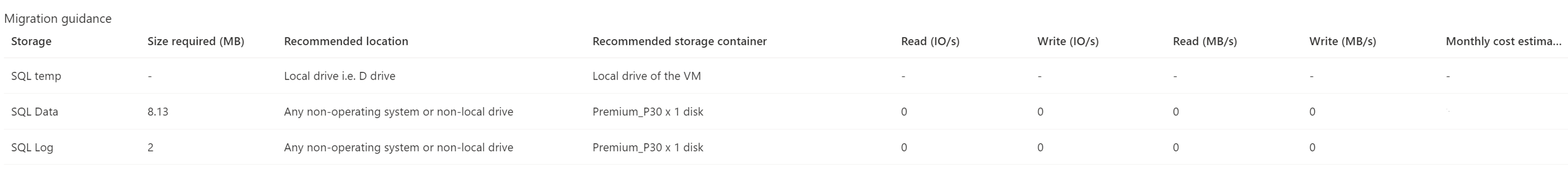
For storage sizing, the assessment maps each of the instance disk to an Azure disk. Sizing works as follows:
The disk size needed for each of the disks is the size of SQL Data and SQL Log drives.
The assessment recommends creating a storage disk pool for all SQL Log and SQL Data drives. For temp drives, the assessment recommends storing the files in the local drive.
If the assessment can't find a disk for the required size, it marks the instance as unsuitable for migrating to SQL Server on Azure VM
If the assessment finds a set of suitable disks, it selects the disks that support the location specified in the assessment settings.
If the environment type is Production, the assessment tries to find Premium disks to map each of the disks, else it tries to find a suitable disk, which could either be Premium or Standard SSD disk.
- If there are multiple eligible disks, assessment selects the disk with the lowest cost.
Compute sizing
After it calculates storage requirements, the assessment considers CPU and RAM requirements of the instance to find a suitable VM size in Azure.
- The assessment looks at the allocated cores and RAM to find a suitable Azure VM size.
- If no suitable size is found, the server is marked as unsuitable for Azure.
- If a suitable size is found, Azure Migrate applies the storage calculations. It then applies location and pricing-tier settings for the final VM size recommendation.
- If there are multiple eligible Azure VM sizes, the one with the lowest cost is recommended.
Note
As Azure SQL assessments are intended to give the best performance for your SQL workloads, the VM series list only has VMs that are optimized for running your SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines (VMs). Learn more.
Servers to SQL Server on Azure VM configuration
For All servers to SQL Server on Azure VM migration strategy, refer compute and storage sizing here.
Note
Confidence ratings are not applicable to Azure SQL assessments using As on-premises sizing criteria.
Performance-based sizing calculation
If you use Performance-based sizing, the assessment uses both SQL instance configuration and performance data to generate recommendations that meet or exceed the performance requirements.
Instances to Azure SQL MI and Databases to Azure SQL DB configuration
The assessment computes a specific service tier and Azure SQL configuration (SKU size) that can meet or exceed the on-premises SQL instance performance requirements:
- During the discovery process, Azure Migrate collects SQL instance configuration and performance that includes:
- vCores (allocated) and CPU utilization (%)
- CPU utilization for a SQL instance is the percentage of allocated CPU utilized by the instance on the SQL server
- CPU utilization for a database is the percentage of allocated CPU utilized by the database on the SQL instance
- Memory (allocated) and memory utilization (%)
- Read IO/s and Write IO/s (Data and Log files)
- Read IO/s and Write IO/s at a SQL instance level is calculated by adding the Read IO/s and Write IO/s of all databases discovered in that instance.
- Read MB/s and Write MB/s (Throughput)
- Latency of IO operations
- Total DB size and database file organizations
- Database size is calculated by adding all the data and log files.
- Always On Failover Cluster Instance network subnet configuration (Single Subnet or Multi-Subnet)
- Always On Availability Group configurations
- Network configuration of participating instances (Single Subnet or Multi-Subnet)
- Number and type of secondary replicas
- Availability Mode: Synchronous Commit vs Asynchronous Commit
- Connection Mode: Read-only vs None
- vCores (allocated) and CPU utilization (%)
- The assessment aggregates all the configuration and performance data and tries to find the best match across various Azure SQL service tiers and configurations and picks a configuration that can match or exceed the SQL instance performance requirements, optimizing the cost.
Instances to SQL Server on Azure VM configuration
Instance to SQL Server on Azure VM assessment report covers the ideal approach for migrating SQL Server instances and databases to SQL Server on Azure VM, adhering to the best practices. Learn more.
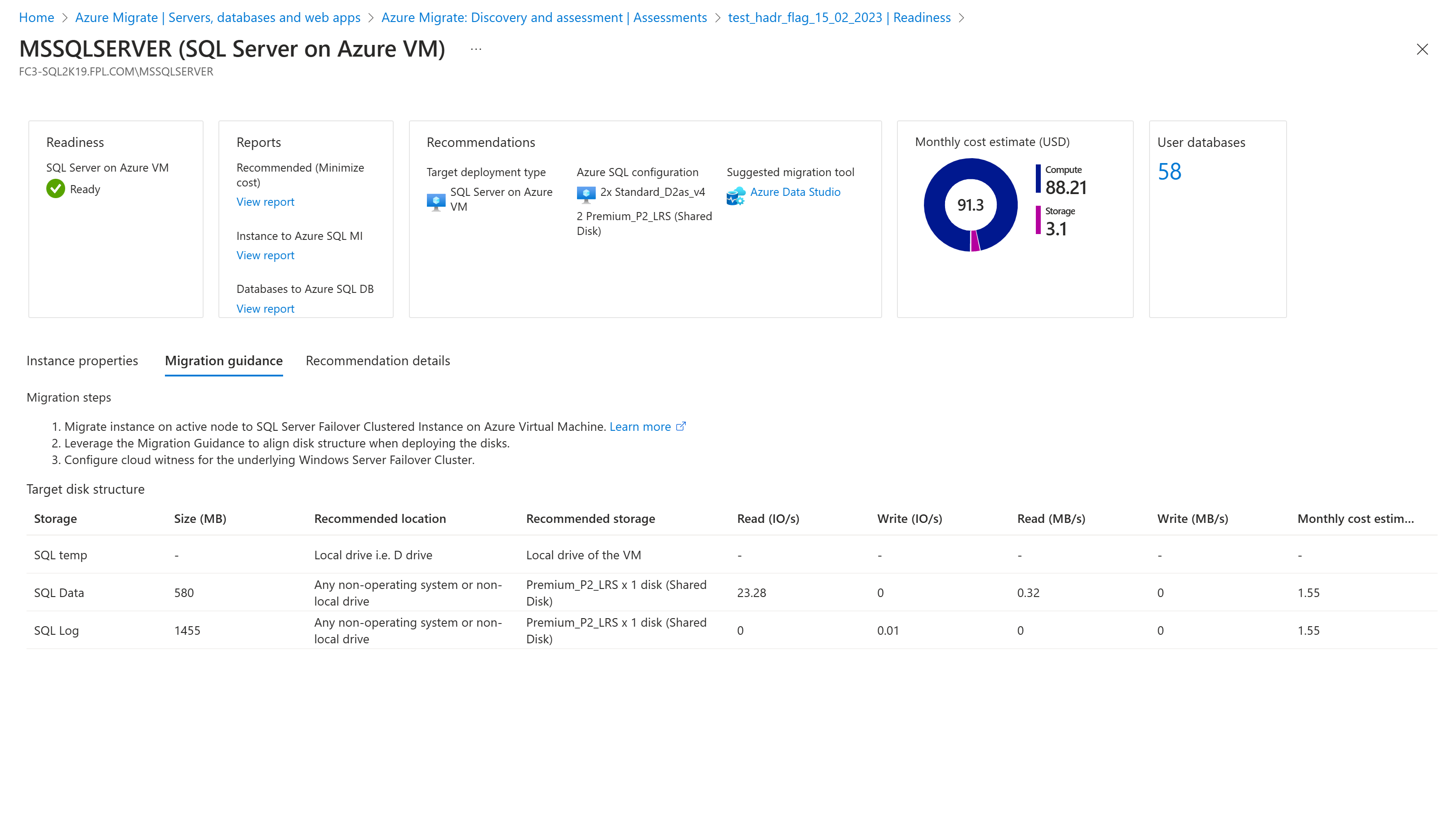
If the source is a SQL Server Always On Failover Cluster Instance (FCI), the assessment report covers the approach for migrating to a two-node SQL Server Failover Cluster Instance. This preserves the high availability and disaster recovery intents while adhering to the best practices. Learn more.
Storage sizing
For storage sizing, the assessment maps each of the instance disk to an Azure disk. Sizing works as follows:
Assessment adds the read and write IOPS of a disk to get the total IOPS required. Similarly, it adds the read and write throughput values to get the total throughput of each disk. The disk size needed for each of the disks is the size of SQL Data and SQL Log drives.
The assessment recommends creating a storage disk pool for all SQL Log and SQL Data drives. For temp drives, the assessment recommends storing the files in the local drive.
- If the assessment can't find a disk for the required size, IOPS and throughput, it marks the instance as unsuitable for migrating to SQL Server on Azure VM
- If the assessment finds a set of suitable disks, it selects the disks that support the location specified in the assessment settings.
- If the source is a SQL Server Always On Failover Cluster Instance, shared disk configuration is selected.
- If the environment type is Production, the assessment tries to find Premium disks to map each of the disks, else it tries to find a suitable disk, which could either be Premium or Standard SSD disk.
- If there are multiple eligible disks, assessment selects the disk with the lowest cost.
Compute sizing
After it calculates storage requirements, the assessment considers CPU and RAM requirements of the instance to find a suitable VM size in Azure.
- The assessment looks at the effective utilized cores and RAM to find a suitable Azure VM size. Effective utilized RAM or memory for an instance is calculated by aggregating the buffer cache (buffer pool size in MB) for all the databases running in an instance.
- If no suitable size is found, the server is marked as unsuitable for Azure.
- If a suitable size is found, Azure Migrate applies the storage calculations. It then applies location and pricing-tier settings for the final VM size recommendation.
- If there are multiple eligible Azure VM sizes, the one with the lowest cost is recommended.
- If the source is a SQL Server Always On Failover Cluster Instance, the compute size is used again for a second Azure VM to meet the need for two nodes.
Note
As Azure SQL assessments are intended to give the best performance for your SQL workloads, the VM series list only has VMs that are optimized for running your SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines (VMs). Learn more.
Servers to SQL Server on Azure VM configuration
For All servers to SQL Server on Azure VM migration strategy, refer compute and storage sizing here.
Confidence ratings
Each Azure SQL assessment is associated with a confidence rating. The rating ranges from one (lowest) to five (highest) stars. The confidence rating helps you estimate the reliability of the size recommendations Azure Migrate provides.
- The confidence rating is assigned to an assessment. The rating is based on the availability of data points that are needed to compute the assessment.
- For performance-based sizing, the assessment collects performance data of all the SQL instances and databases, which include:
- CPU utilization (%)
- Memory utilization (%)
- Read IO/s and Write IO/s (Data and Log files)
- Read MB/s and Write MB/s (Throughput)
- Latency of IO operations
If any of these utilization numbers isn't available, the size recommendations might be unreliable. This table shows the assessment confidence ratings, which depend on the percentage of available data points:
| Data point availability | Confidence rating |
|---|---|
| 0%-20% | 1 star |
| 21%-40% | 2 stars |
| 41%-60% | 3 stars |
| 61%-80% | 4 stars |
| 81%-100% | 5 stars |
Low confidence ratings
Here are a few reasons why an assessment could get a low confidence rating:
You didn't profile your environment for the duration for which you're creating the assessment. For example, if you create the assessment with performance duration set to one day, you must wait at least a day after you start discovery for all the data points to get collected.
The Assessment isn't able to collect the performance data for some or all the servers in the assessment period. For a high confidence rating, ensure that:
- Servers are powered on for the duration of the assessment.
- Outbound connections on ports 443 are allowed.
- If Azure Migrate connection status of the SQL agent in Azure Migrate is Connected, check the last heartbeat.
- Azure Migrate connection status for all SQL instances is Connected in the discovered SQL instance section.
Recalculate the assessment to reflect the latest changes in confidence rating.
Some databases or instances were created during the time for which the assessment was calculated. For example, you created an assessment for the performance history of the last month, but some databases or instances were created only a week ago. In this case, the performance data for the new servers won't be available for the entire duration and the confidence rating would be low.
Note
As Azure SQL assessments are performance-based assessments, if the confidence rating of any assessment is less than five stars, we recommend that you wait at least a day for the appliance to profile the environment and then recalculate the assessment. Otherwise, performance-based sizing might be unreliable.
Recommendation details
Once the readiness and sizing calculation is complete, the optimization preference is applied to arrive at a recommended target and configuration. The Recommendation Details provide a detailed explanation of the readiness and sizing calculations behind the recommendation.
Migration guidance
This section provides guidance to configure the target resource and steps to migrate. The steps are specific to the source and the target deployment combinations. This guidance is specifically useful for users who intend to migrate Always On Failover Cluster Instances (FCI) and Availability Groups (AG).
Calculate monthly costs
After sizing recommendations are complete, Azure SQL assessment calculates the compute and storage costs for the recommended Azure SQL configurations using an internal pricing API. It aggregates the compute and storage cost across all instances to calculate the total monthly compute cost.
Compute cost
- To calculate the compute cost for an Azure SQL configuration, the assessment considers the following properties:
- Azure Hybrid Benefit for SQL and Windows licenses or Enterprise Linux subscription (RHEL and SLES)
- Environment type
- Reserved capacity
- Azure target location
- Currency
- Offer/Licensing program
- Discount (%)
Storage cost
- The storage cost estimates only include data files and not log files.
- For calculating storage cost for an Azure SQL configuration, the assessment considers following properties:
- Azure target location
- Currency
- Offer/Licensing program
- Discount (%)
- Backup storage cost isn't included in the assessment.
- Azure SQL Database
- A minimum of 5 GB storage cost is added in the cost estimate and additional storage cost is added for storage in 1 GB increments. Learn More.
- Azure SQL Managed Instance
- There's no storage cost added for the first 32 GB/instance/month storage and additional storage cost is added for storage in 32 GB increments. Learn More.
Security cost
For SQL Server instances and DBs recommended for SQL Server on Azure VM, Azure SQL MI or Azure SQL DB, if they're ready to run Defender for SQL, the Defender for SQL per SQL Server instance for that region is added. For DBs recommended to Azure SQL DB, cost is rolled up at instance level.
Next steps
- Review best practices for creating assessments.
- Learn how to run an Azure SQL assessment.