Nested Control Structures (Visual Basic)
You can place control statements inside other control statements, for example an If...Then...Else block within a For...Next loop. A control statement placed inside another control statement is said to be nested.
Nesting Levels
Control structures in Visual Basic can be nested to as many levels as you want. It is common practice to make nested structures more readable by indenting the body of each one. The integrated development environment (IDE) editor automatically does this.
In the following example, the procedure sumRows adds together the positive elements of each row of the matrix.
Public Sub sumRows(ByVal a(,) As Double, ByRef r() As Double)
Dim i, j As Integer
For i = 0 To UBound(a, 1)
r(i) = 0
For j = 0 To UBound(a, 2)
If a(i, j) > 0 Then
r(i) = r(i) + a(i, j)
End If
Next j
Next i
End Sub
In the preceding example, the first Next statement closes the inner For loop and the last Next statement closes the outer For loop.
Likewise, in nested If statements, the End If statements automatically apply to the nearest prior If statement. Nested Do loops work in a similar fashion, with the innermost Loop statement matching the innermost Do statement.
Note
For many control structures, when you click a keyword, all of the keywords in the structure are highlighted. For instance, when you click If in an If...Then...Else construction, all instances of If, Then, ElseIf, Else, and End If in the construction are highlighted. To move to the next or previous highlighted keyword, press CTRL+SHIFT+DOWN ARROW or CTRL+SHIFT+UP ARROW.
Nesting Different Kinds of Control Structures
You can nest one kind of control structure within another kind. The following example uses a With block inside a For Each loop and nested If blocks inside the With block.
For Each ctl As System.Windows.Forms.Control In Me.Controls
With ctl
.BackColor = System.Drawing.Color.Yellow
.ForeColor = System.Drawing.Color.Black
If .CanFocus Then
.Text = "Colors changed"
If Not .Focus() Then
' Insert code to process failed focus.
End If
End If
End With
Next ctl
Overlapping Control Structures
You cannot overlap control structures. This means that any nested structure must be completely contained within the next innermost structure. For example, the following arrangement is invalid because the For loop terminates before the inner With block terminates.
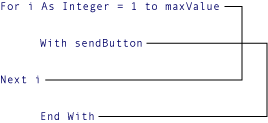
The Visual Basic compiler detects such overlapping control structures and signals a compile-time error.
