Automatically scale Azure HDInsight clusters
Azure HDInsight's free Autoscale feature can automatically increase or decrease the number of worker nodes in your cluster based on the cluster metrics and scaling policy adopted by the customers. The Autoscale feature works by scaling the number of nodes within preset limits based on either performance metrics or a defined schedule of scale-up and scale-down operations.
How it works
The Autoscale feature uses two types of conditions to trigger scaling events: thresholds for various cluster performance metrics (called load-based scaling) and time-based triggers (called schedule-based scaling). Load-based scaling changes the number of nodes in your cluster, within a range that you set, to ensure optimal CPU usage and minimize running cost. Schedule-based scaling changes the number of nodes in your cluster based on a schedule of scale-up and scale-down operations.
The following video provides an overview of the challenges, which Autoscale solves and how it can help you to control costs with HDInsight.
Choosing load-based or schedule-based scaling
Schedule-based scaling can be used:
- When your jobs are expected to run on fixed schedules and for a predictable duration or When you anticipate low usage during specific times of the day. For example, test and dev environments in post-work hours, end-of day jobs.
Load based scaling can be used:
- When the load patterns fluctuate substantially and unpredictably during the day. For example, order data processing with random fluctuations in load patterns based on various factors.
Cluster metrics
Autoscale continuously monitors the cluster and collects the following metrics:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Total Pending CPU | The total number of cores required to start execution of all pending containers. |
| Total Pending Memory | The total memory (in MB) required to start execution of all pending containers. |
| Total Free CPU | The sum of all unused cores on the active worker nodes. |
| Total Free Memory | The sum of unused memory (in MB) on the active worker nodes. |
| Used Memory per Node | The load on a worker node. A worker node on which 10 GB of memory is used, is considered under more load than a worker with 2 GB of used memory. |
| Number of Application Masters per Node | The number of Application Master (AM) containers running on a worker node. A worker node that is hosting two AM containers, is considered more important than a worker node that is hosting zero AM containers. |
The above metrics are checked every 60 seconds. Autoscale makes scale-up and scale-down decisions based on these metrics.
For a complete list of cluster metrics, see Supported metrics for Microsoft.HDInsight/clusters.
Load-based scale conditions
When the following conditions are detected, Autoscale issues a scale request:
| Scale-up | Scale-down |
|---|---|
| Total pending CPU is greater than total free CPU for more than 3-5 minutes. | Total pending CPU is less than total free CPU for more than 3-5 minutes. |
| Total pending memory is greater than total free memory for more than 3-5 minutes. | Total pending memory is less than total free memory for more than 3-5 minutes. |
For scale-up, Autoscale issues a scale-up request to add the required number of nodes. The scale-up is based on how many new worker nodes are needed to meet the current CPU and memory requirements.
For scale-down, Autoscale issues a request to remove some nodes. The scale-down is based on the number of Application Master (AM) containers per node. And the current CPU and memory requirements. The service also detects which nodes are candidates for removal based on current job execution. The scale down operation first decommissions the nodes, and then removes them from the cluster.
Ambari DB sizing considerations for autoscaling
It's recommended that Ambari DB is sized correctly to reap the benefits of autoscale. Customers should use the correct DB tier and use the custom Ambari DB for large size clusters. Please read the Database and Headnode sizing recommendations.
Cluster compatibility
Important
The Azure HDInsight Autoscale feature was released for general availability on November 7th, 2019 for Spark and Hadoop clusters and included improvements not available in the preview version of the feature. If you created a Spark cluster prior to November 7th, 2019 and want to use the Autoscale feature on your cluster, the recommended path is to create a new cluster, and enable Autoscale on the new cluster.
Autoscale for Interactive Query (LLAP) was released for general availability for HDI 4.0 on August 27th, 2020. Autoscale is only available on Spark, Hadoop, and Interactive Query, clusters
The following table describes the cluster types and versions that are compatible with the Autoscale feature.
| Version | Spark | Hive | Interactive Query | HBase | Kafka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDInsight 4.0 without ESP | Yes | Yes | Yes* | No | No |
| HDInsight 4.0 with ESP | Yes | Yes | Yes* | No | No |
| HDInsight 5.0 without ESP | Yes | Yes | Yes* | No | No |
| HDInsight 5.0 with ESP | Yes | Yes | Yes* | No | No |
* Interactive Query clusters can only be configured for schedule-based scaling, not load-based.
Get started
Create a cluster with load-based Autoscaling
To enable the Autoscale feature with load-based scaling, complete the following steps as part of the normal cluster creation process:
On the Configuration + pricing tab, select the
Enable autoscalecheckbox.Select Load-based under Autoscale type.
Enter the intended values for the following properties:
- Initial Number of nodes for Worker node.
- Min number of worker nodes.
- Max number of worker nodes.
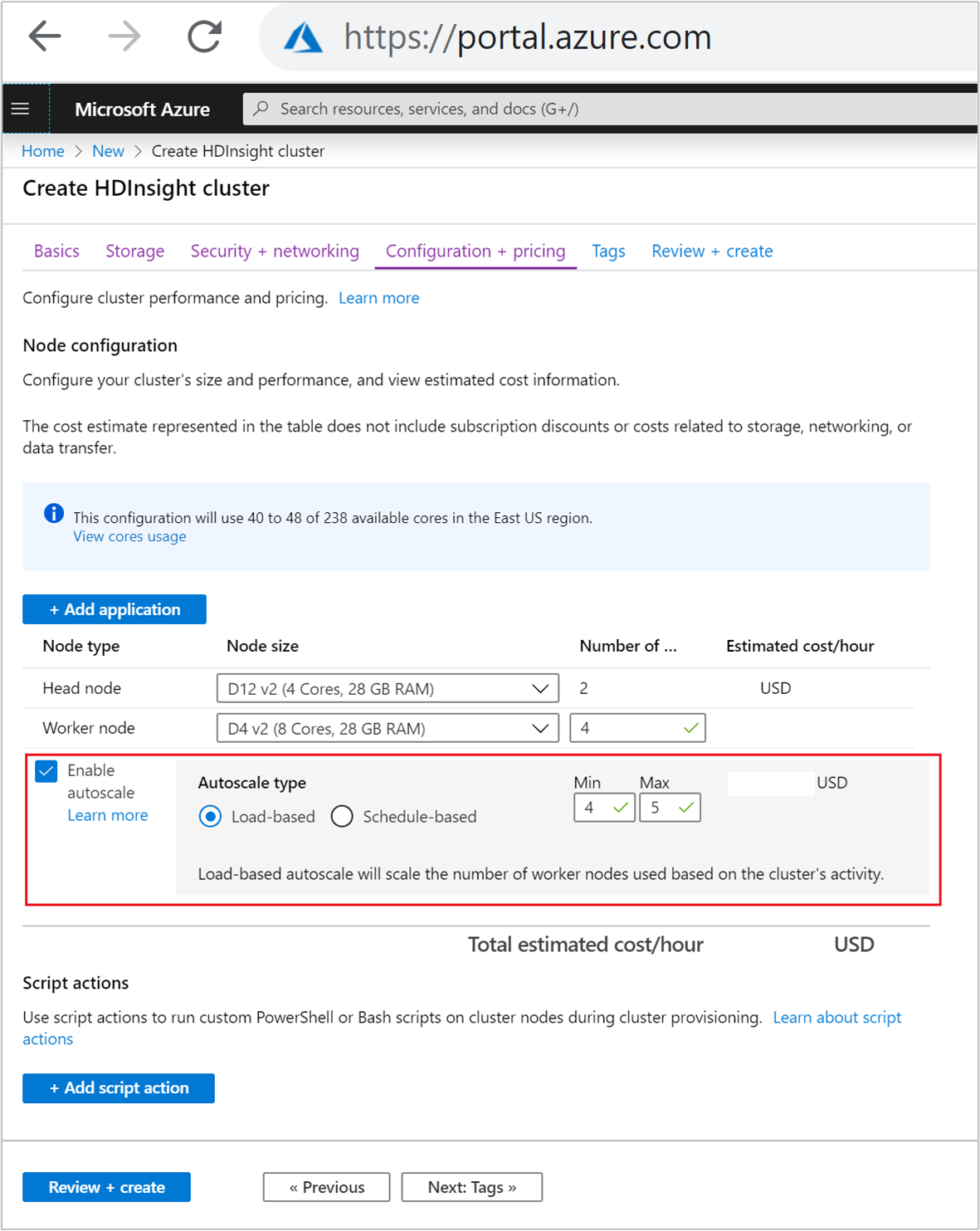
The initial number of worker nodes must fall between the minimum and maximum, inclusive. This value defines the initial size of the cluster when it's created. The minimum number of worker nodes should be set to three or more. Scaling your cluster to fewer than three nodes can result in it getting stuck in safe mode because of insufficient file replication. For more information, see Getting stuck in safe mode.
Create a cluster with schedule-based Autoscaling
To enable the Autoscale feature with schedule-based scaling, complete the following steps as part of the normal cluster creation process:
On the Configuration + pricing tab, check the
Enable autoscalecheckbox.Enter the Number of nodes for Worker node, which controls the limit for scaling up the cluster.
Select the option Schedule-based under Autoscale type.
Select Configure to open the Autoscale configuration window.
Select your timezone and then click + Add condition
Select the days of the week that the new condition should apply to.
Edit the time the condition should take effect and the number of nodes that the cluster should be scaled to.
Add more conditions if needed.
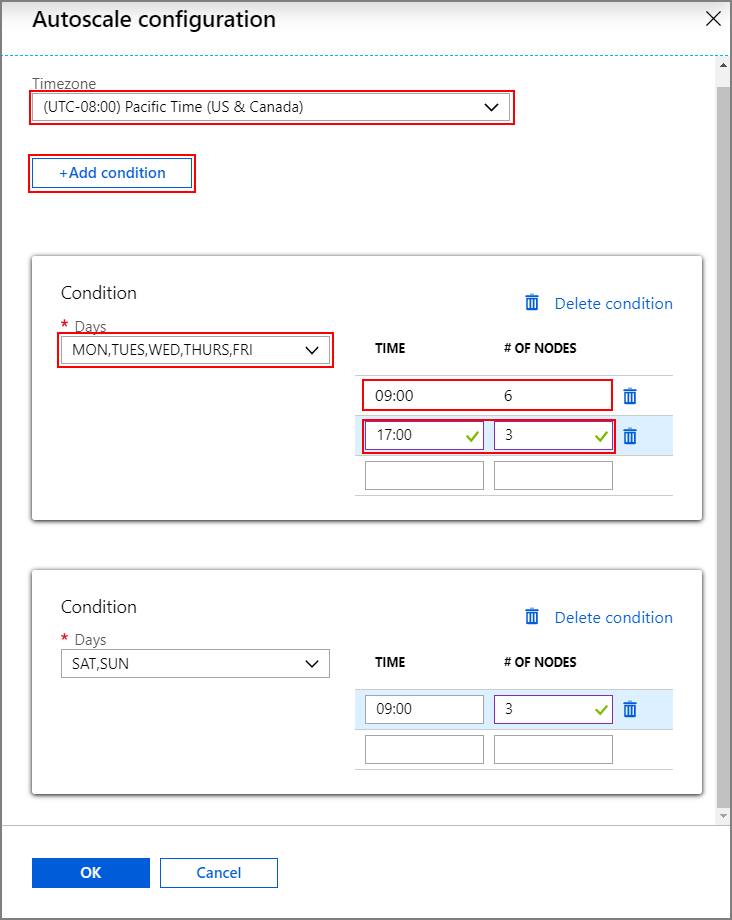
The number of nodes must be between 3 and the maximum number of worker nodes that you entered before adding conditions.
Final creation steps
Select the VM type for worker nodes by selecting a VM from the drop-down list under Node size. After you choose the VM type for each node type, you can see the estimated cost range for the whole cluster. Adjust the VM types to fit your budget.
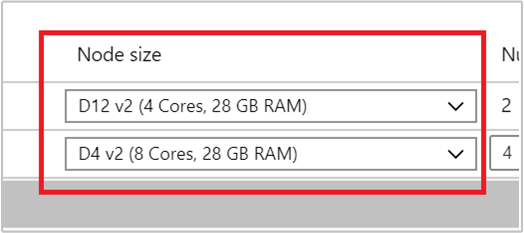
Your subscription has a capacity quota for each region. The total number of cores of your head nodes and the maximum worker nodes can't exceed the capacity quota. However, this quota is a soft limit; you can always create a support ticket to get it increased easily.
Note
If you exceed the total core quota limit, You will receive an error message saying 'the maximum node exceeded the available cores in this region, please choose another region or contact the support to increase the quota.'
For more information on HDInsight cluster creation using the Azure portal, see Create Linux-based clusters in HDInsight using the Azure portal.
Create a cluster with a Resource Manager template
Load-based autoscaling
You can create an HDInsight cluster with load-based Autoscaling an Azure Resource Manager template, by adding an autoscale node to the computeProfile > workernode section with the properties minInstanceCount and maxInstanceCount as shown in the json snippet. For a complete Resource Manager template, see Quickstart template: Deploy Spark Cluster with load-based autoscale enabled.
{
"name": "workernode",
"targetInstanceCount": 4,
"autoscale": {
"capacity": {
"minInstanceCount": 3,
"maxInstanceCount": 10
}
},
"hardwareProfile": {
"vmSize": "Standard_D13_V2"
},
"osProfile": {
"linuxOperatingSystemProfile": {
"username": "[parameters('sshUserName')]",
"password": "[parameters('sshPassword')]"
}
},
"virtualNetworkProfile": null,
"scriptActions": []
}
Schedule-based autoscaling
You can create an HDInsight cluster with schedule-based Autoscaling an Azure Resource Manager template, by adding an autoscale node to the computeProfile > workernode section. The autoscale node contains a recurrence that has a timezone and schedule that describes when the change takes place. For a complete Resource Manager template, see Deploy Spark Cluster with schedule-based Autoscale Enabled.
{
"autoscale": {
"recurrence": {
"timeZone": "Pacific Standard Time",
"schedule": [
{
"days": [
"Monday",
"Tuesday",
"Wednesday",
"Thursday",
"Friday"
],
"timeAndCapacity": {
"time": "11:00",
"minInstanceCount": 10,
"maxInstanceCount": 10
}
}
]
}
},
"name": "workernode",
"targetInstanceCount": 4
}
Enable and disable Autoscale for a running cluster
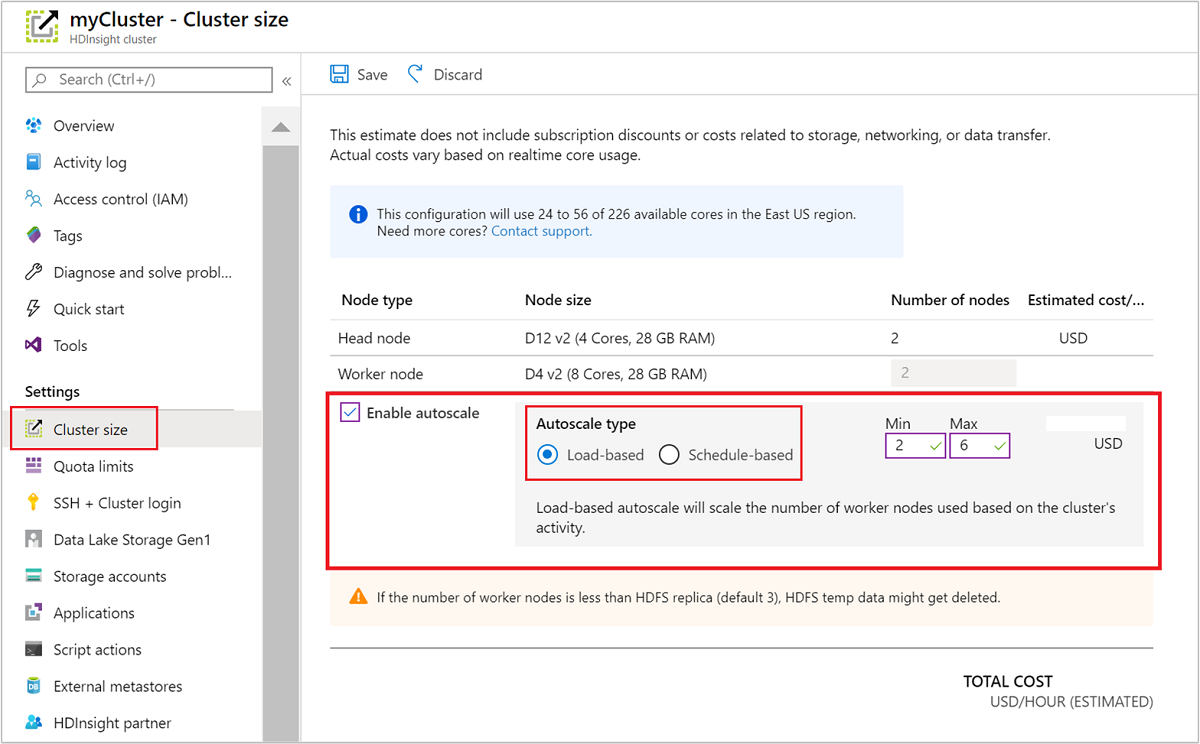
Using the Azure portal
To enable Autoscale on a running cluster, select Cluster size under Settings. Then select Enable autoscale. Select the type of Autoscale that you want and enter the options for load-based or schedule-based scaling. Finally, select Save.
Using the REST API
To enable or disable Autoscale on a running cluster using the REST API, make a POST request to the Autoscale endpoint:
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{subscription Id}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroup Name}/providers/Microsoft.HDInsight/clusters/{CLUSTERNAME}/roles/workernode/autoscale?api-version=2018-06-01-preview
Use the appropriate parameters in the request payload. The following json payload could be used to enable Autoscale. Use the payload {autoscale: null} to disable Autoscale.
{ "autoscale": { "capacity": { "minInstanceCount": 3, "maxInstanceCount": 5 } } }
See the previous section on enabling load-based autoscale for a full description of all payload parameters. It's not recommended to disable autoscale service forcefully on a running cluster.
Monitoring Autoscale activities
Cluster status
The cluster status listed in the Azure portal can help you monitor Autoscale activities.
All of the cluster status messages that you might see are explained in the following list.
| Cluster status | Description |
|---|---|
| Running | The cluster is operating normally. All of the previous Autoscale activities have completed successfully. |
| Updating | The cluster Autoscale configuration is being updated. |
| HDInsight configuration | A cluster scale up or scale down operation is in progress. |
| Updating Error | HDInsight met issues during the Autoscale configuration update. Customers can choose to either retry the update or disable autoscale. |
| Error | Something is wrong with the cluster, and it isn't usable. Delete this cluster and create a new one. |
To view the current number of nodes in your cluster, go to the Cluster size chart on the Overview page for your cluster. Or select Cluster size under Settings.
Operation history
You can view the cluster scale-up and scale-down history as part of the cluster metrics. You can also list all scaling actions over the past day, week, or other period of time.
Select Metrics under Monitoring. Then select Add metric and Number of Active Workers from the Metric dropdown box. Select the button in the upper right to change the time range.

Best practices
Consider the latency of scale up and scale down operations
It can take 10 to 20 minutes for the overall scaling operation to complete. When setting up a customized schedule, plan for this delay. For example, if you need the cluster size to be 20 at 9:00 AM, set the schedule trigger to an earlier time such as 8:30 AM or earlier so that the scaling operation has completed by 9:00 AM.
Prepare for scaling down
During the cluster scaling down process, Autoscale decommissions the nodes to meet the target size. In load based autoscaling, If tasks are running on those nodes, Autoscale waits until the tasks are completed for Spark and Hadoop clusters. Since each worker node also serves a role in HDFS, the temporary data is shifted to the remaining worker nodes. Make sure there's enough space on the remaining nodes to host all temporary data.
Note
In case of schedule-based Autoscale scale-down, graceful decommission is not supported. This can cause job failures during a scale down operation, and it's recommended to plan schedules based on the anticipated job schedule patterns to include sufficient time for the ongoing jobs to conclude. You can set the schedules looking at historical spread of completion times so as to avoid job failures.
Configure schedule-based Autoscale based on usage pattern
You need to understand your cluster usage pattern when you configure schedule based Autoscale. Grafana dashboard can help you understand your query load and execution slots. You can get the available executor slots and total executor slots from the dashboard.
Here's a way you can estimate how many worker nodes needed. We recommend giving another 10% buffer to handle the variation of the workload.
Number of executor slots used = Total executor slots – Total available executor slots.
Number of worker nodes required = Number of executor slots actually used / (hive.llap.daemon.num.executors + hive.llap.daemon.task.scheduler.wait.queue.size).
*hive.llap.daemon.num.executors is configurable and default is 4.
*hive.llap.daemon.task.scheduler.wait.queue.size is configurable and default is 10.
Custom Script Actions
Custom Script Actions are mostly used for customizing the nodes (HeadNode / WorkerNodes) which enable our customers to configure certain libraries and tools, which are being used by them. One common use case is the job(s) that run on the cluster might have some dependencies on the third party library, which is owned by the Customer, and it should be available on nodes for the job to succeed. For Autoscale, we currently support custom script actions, which are persisted, hence every time the new nodes get added to the cluster as part of scale up operation, these persisted script actions would get executed and post that the containers or jobs would be allocated on them. Although have custom script actions helps bootstrapping the new nodes, it's advisable to keep it minimal as it would add up to the overall scale up latency and can cause impact to the scheduled jobs.
Be aware of the minimum cluster size
Don't scale your cluster down to fewer than three nodes. Scaling your cluster to fewer than three nodes can result in it getting stuck in safe mode because of insufficient file replication. For more information, see getting stuck in safe mode.
Microsoft Entra Domain Services & Scaling Operations
If you use an HDInsight cluster with Enterprise Security Package (ESP) that is joined to a Microsoft Entra Domain Services managed domain, we recommend throttling load on the Microsoft Entra Domain Services. In complex directory structures scoped sync we recommend avoiding impact to scaling operations.
Set the Hive configuration Maximum Total Concurrent Queries for the peak usage scenario
Autoscale events don't change the Hive configuration Maximum Total Concurrent Queries in Ambari. This means that the Hive Server 2 Interactive Service can handle only the given number of concurrent queries at any point of time even if the Interactive Query daemons count is scaled up and down based on load and schedule. The general recommendation is to set this configuration for the peak usage scenario to avoid manual intervention.
However, you may experience a Hive Server 2 restart failure if there are only a few worker nodes and the value for maximum total concurrent queries is configured too high. At a minimum, you need the minimum number of worker nodes that can accommodate the given number of Tez Ams (equal to the Maximum Total Concurrent Queries configuration).
Limitations
Interactive Query Daemons count
If autoscale-enabled Interactive Query clusters, an autoscale up/down event also scales up/down the number of Interactive Query daemons to the number of active worker nodes. The change in the number of daemons isn't persisted in the num_llap_nodes configuration in Ambari. If Hive services are restarted manually, the number of Interactive Query daemons is reset as per the configuration in Ambari.
If the Interactive Query service is manually restarted, you need to manually change the num_llap_node configuration (the number of node(s) needed to run the Hive Interactive Query daemon) under Advanced hive-interactive-env to match the current active worker node count. Interactive Query Cluster supports only Schedule-Based Autoscale.
Next steps
Read about guidelines for scaling clusters manually in Scaling guidelines.