Kubernetes Services in AKS
You can use Kubernetes Services to logically group pods and provide network connectivity by allowing direct access to them through a specific IP address or DNS name on a designated port. This allows you to expose your application workloads to other services within the cluster or to external clients without having to manually manage the network configuration for each pod hosting a workload.
You can specify what kind of service you want using Kubernetes Service type values. For more information, see the Kubernetes Service documentation.
The following Service types are available in AKS: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, and ExternalName.
ClusterIP
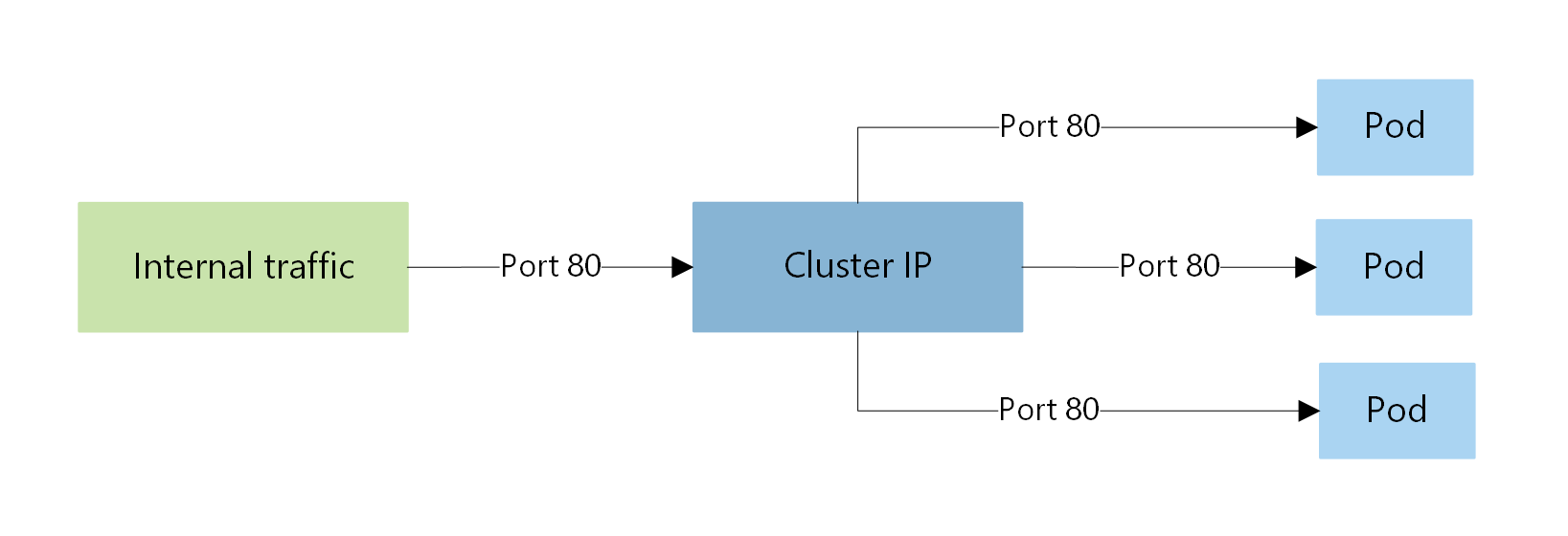
ClusterIP creates an internal IP address for use within the AKS cluster. The ClusterIP Service is good for internal-only applications that support other workloads within the cluster. ClusterIP is used by default if you don't explicitly specify a type for a Service.
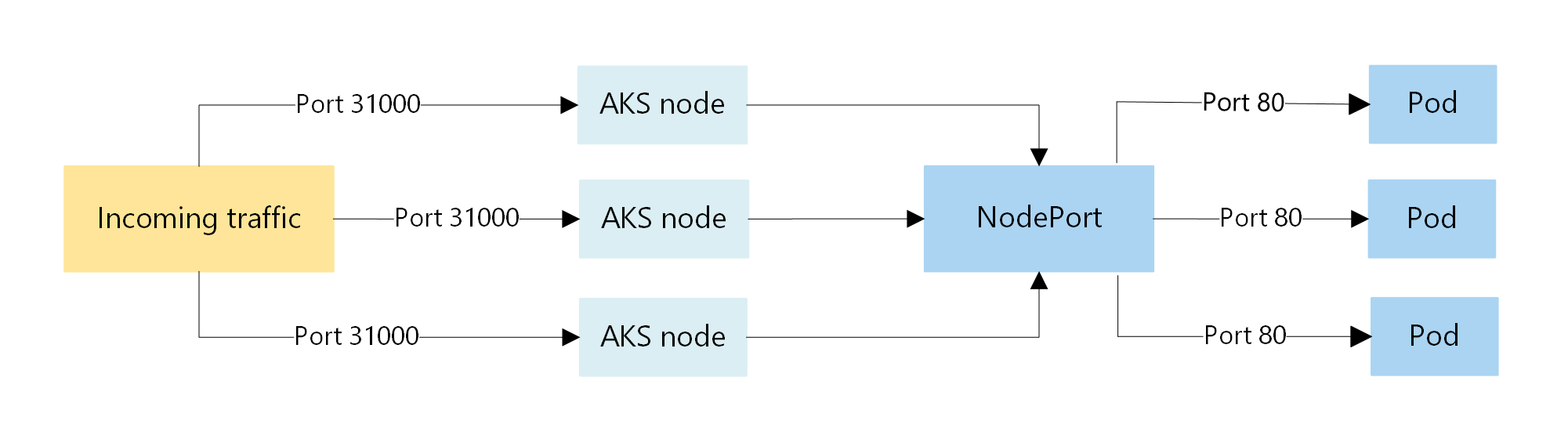
NodePort
NodePort creates a port mapping on the underlying node that allows the application to be accessed directly with the node IP address and port.
LoadBalancer
LoadBalancer creates an Azure load balancer resource, configures an external IP address, and connects the requested pods to the load balancer backend pool. To allow customer traffic to reach the application, load balancing rules are created on the desired ports.
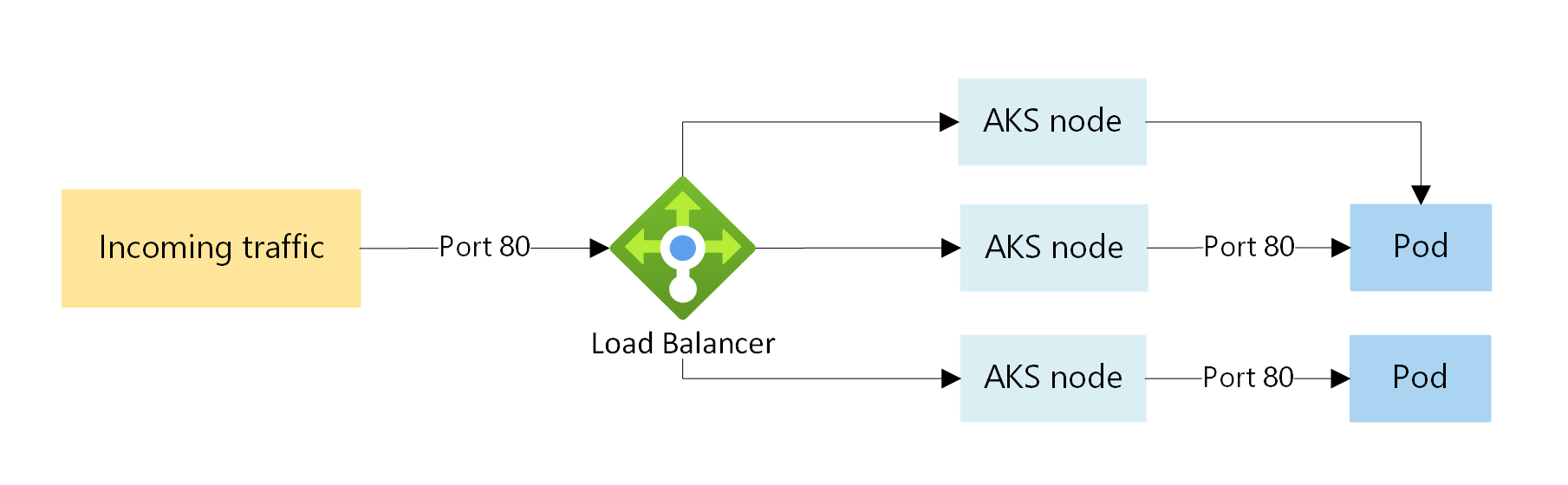
For HTTP load balancing of inbound traffic, you can also use an Ingress controller.
ExternalName
ExternalName creates a specific DNS entry for easier application access. You can dynamically assign the load balancers and service IP address, or you can specify an existing static IP address. You can assign both internal and external static IP addresses. Existing static IP addresses are often tied to a DNS entry.
You can create both internal and external load balancers. Internal load balancers are only assigned a private IP address, so they can't be accessed from the Internet.
Azure Kubernetes Service
