Tutorial: Ingest events from Azure Event Hubs into Azure Monitor Logs (Public Preview)
Azure Event Hubs is a big data streaming platform that collects events from multiple sources to be ingested by Azure and external services. This article explains how to ingest data directly from an event hub into a Log Analytics workspace.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Create a destination table for event hub data in your Log Analytics workspace
- Create a data collection endpoint
- Create a data collection rule
- Grant the data collection rule permissions to the event hub
- Associate the data collection rule with the event hub
Prerequisites
To send events from Azure Event Hubs to Azure Monitor Logs, you need these resources:
Log Analytics workspace where you have at least contributor rights.
Your Log Analytics workspace needs to be linked to a dedicated cluster or to have a commitment tier.
Event Hubs namespace that permits public network access. If public network access is disabled, ensure that "Allow trusted Microsoft services to bypass this firewall" is set to "Yes."
Event hub with events. You can send events to your event hub by following the steps in Send and receive events in Azure Event Hubs tutorials or by configuring the diagnostic settings of Azure resources.
Supported regions
Azure Monitor currently supports ingestion from Event Hubs in these regions:
| Americas | Europe | Middle East | Africa | Asia Pacific |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil South | France Central | UAE North | South Africa North | Australia Central |
| Brazil Southeast | North Europe | Australia East | ||
| Canada Central | Norway East | Australia Southeast | ||
| Canada East | Switzerland North | Central India | ||
| East US | Switzerland West | East Asia | ||
| East US 2 | UK South | Japan East | ||
| South Central US | UK West | Jio India West | ||
| West US | West Europe | Korea Central | ||
| West US 3 | Southeast Asia |
You need to create your Data Collection Rule Association (DCRA) in the same region as the Event Hub. The Log Analytics workspace can be in any region, but the Data Collection Rule (DCR) and Data Collection Endpoint (DCE) must be in the same region as the Log Analytics workspace.
For minimum latency, we recommend placing all resources in the same region.
Collect required information
You need your subscription ID, resource group name, workspace name, workspace resource ID, and event hub instance resource ID in subsequent steps:
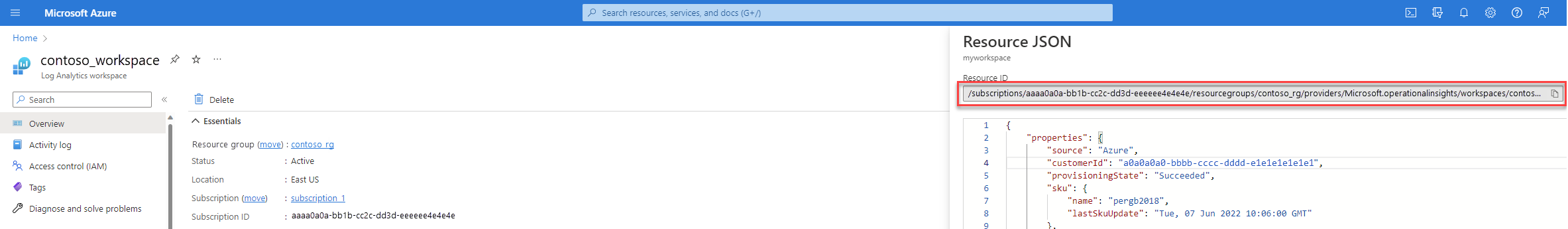
Navigate to your workspace in the Log Analytics workspaces menu and select Properties and copy your Subscription ID, Resource group, and Workspace name. You'll need these details to create resources in this tutorial.
Select JSON to open the Resource JSON screen and copy the workspace's Resource ID. You'll need the workspace resource ID to create a data collection rule.
Navigate to your event hub instance, select JSON to open the Resource JSON screen, and copy the event hub instance's Resource ID. You'll need the event hub instance's resource ID to associate the data collection rule with the event hub.
Create a destination table in your Log Analytics workspace
Before you can ingest data, you need to set up a destination table. You can ingest data into custom tables and supported Azure tables.
To create a custom table into which to ingest events, in the Azure portal:
Select the Cloud Shell button and ensure the environment is set to PowerShell.
Run this PowerShell command to create the table, providing the table name (
<table_name>) in the JSON (that too with suffix _CL in case of custom table), and setting the<subscription_id>,<resource_group_name>,<workspace_name>, and<table_name>values in theInvoke-AzRestMethod -Pathcommand:$tableParams = @' { "properties": { "schema": { "name": "<table_name>", "columns": [ { "name": "TimeGenerated", "type": "datetime", "description": "The time at which the data was ingested." }, { "name": "RawData", "type": "string", "description": "Body of the event." }, { "name": "Properties", "type": "dynamic", "description": "Additional message properties." } ] } } } '@ Invoke-AzRestMethod -Path "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourcegroups/<resource_group_name>/providers/microsoft.operationalinsights/workspaces/<workspace_name>/tables/<table_name>?api-version=2021-12-01-preview" -Method PUT -payload $tableParams
Important
- Column names must start with a letter and can consist of up to 45 alphanumeric characters and underscores (
_). _ResourceId,id,_ResourceId,_SubscriptionId,TenantId,Type,UniqueId, andTitleare reserved column names.- Column names are case-sensitive. Make sure to use the correct case in your data collection rule.
Create a data collection endpoint
To collect data with a data collection rule, you need a data collection endpoint:
Create a data collection endpoint.
Important
Create the data collection endpoint in the same region as your Log Analytics workspace.
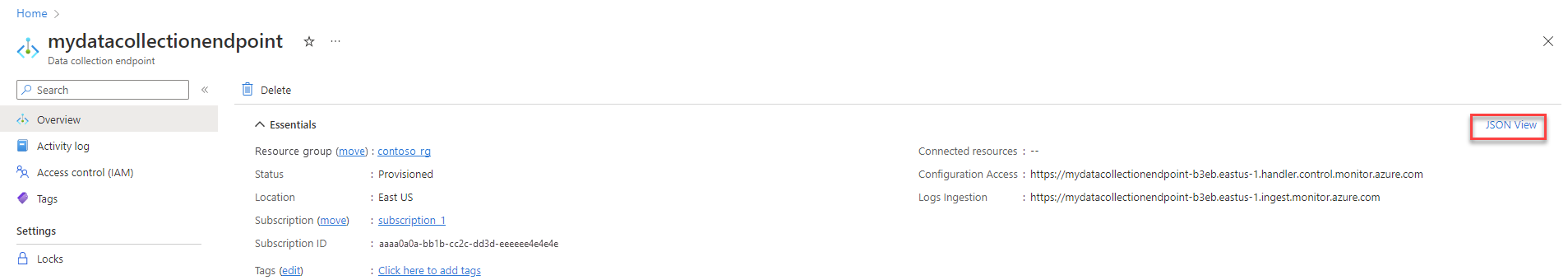
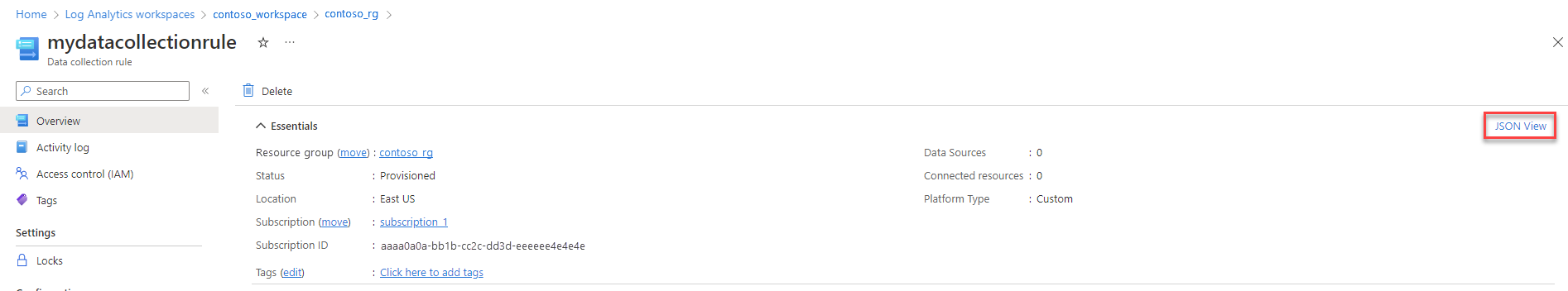
From the data collection endpoint's Overview screen, select JSON View.
Copy the Resource ID for the data collection rule. You'll use this information in the next step.
Create a data collection rule
Azure Monitor uses data collection rules to define which data to collect, how to transform that data, and where to send the data.
To create a data collection rule in the Azure portal:
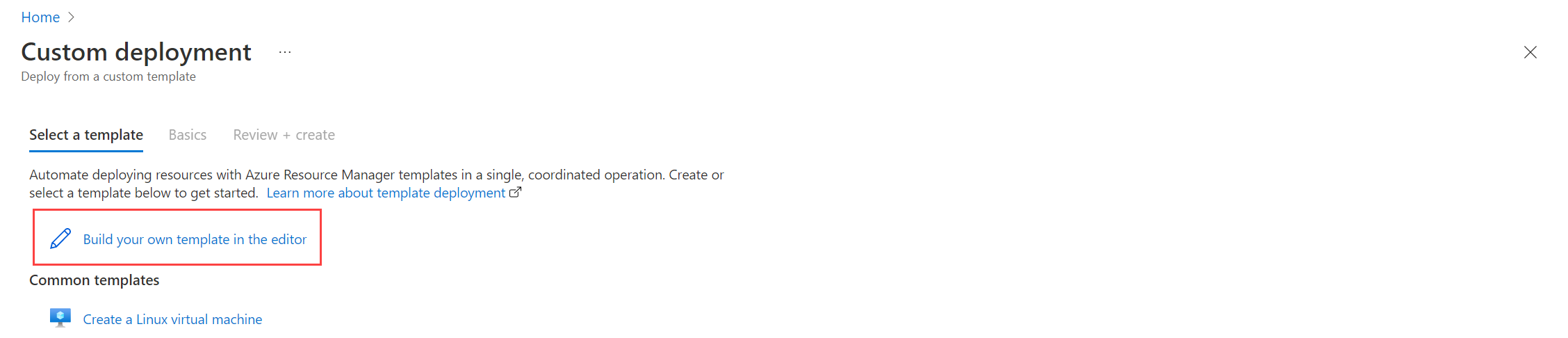
In the portal's search box, type in template and then select Deploy a custom template.
Select Build your own template in the editor.
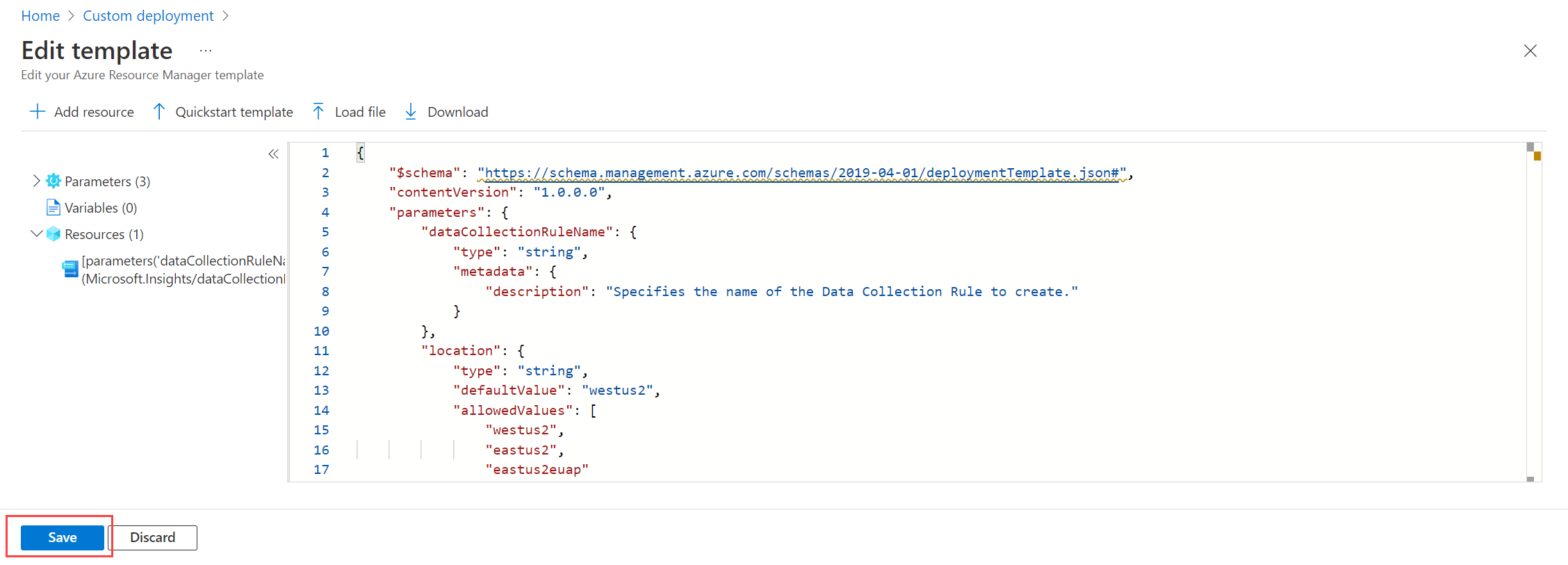
Paste the Resource Manager template below into the editor and then select Save.
Notice the following details in the data collection rule below:
identity- Defines which type of managed identity to use. In our example, we use system-assigned identity. You can also configure user-assigned managed identity.dataCollectionEndpointId- Resource ID of the data collection endpoint.streamDeclarations- Defines which data to ingest from the event hub (incoming data). The stream declaration can't be modified.TimeGenerated- The time at which the data was ingested from event hub to Azure Monitor Logs.RawData- Body of the event. For more information, see Read events.Properties- User properties from the event. For more information, see Read events.
datasources- Specifies the event hub consumer group and the stream to which you ingest the data.destinations- Specifies all of the destinations where the data will be sent. You can ingest data to one or more Log Analytics workspaces.dataFlows- Matches the stream with the destination workspace and specifies the transformation query and the destination table. In our example, we ingest data to the custom table we created previously. You can also ingest into a supported Azure table.transformKql- Specifies a transformation to apply to the incoming data (stream declaration) before it's sent to the workspace. In our example, we settransformKqltosource, which doesn't modify the data from the source in any way, because we're mapping incoming data to a custom table we've created specifically with the corresponding schema. If you're ingesting data to a table with a different schema or to filter data before ingestion, define a data collection transformation.
{ "$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#", "contentVersion": "1.0.0.0", "parameters": { "dataCollectionRuleName": { "type": "string", "metadata": { "description": "Specifies the name of the data collection Rule to create." } }, "workspaceResourceId": { "type": "string", "metadata": { "description": "Specifies the Azure resource ID of the Log Analytics workspace to use." } }, "endpointResourceId": { "type": "string", "metadata": { "description": "Specifies the Azure resource ID of the data collection endpoint to use." } }, "tableName": { "type": "string", "metadata": { "description": "Specifies the name of the table in the workspace." } }, "consumerGroup": { "type": "string", "metadata": { "description": "Specifies the consumer group of event hub." }, "defaultValue": "$Default" } }, "resources": [ { "type": "Microsoft.Insights/dataCollectionRules", "name": "[parameters('dataCollectionRuleName')]", "location": "[resourceGroup().location]", "apiVersion": "2022-06-01", "identity": { "type": "systemAssigned" }, "properties": { "dataCollectionEndpointId": "[parameters('endpointResourceId')]", "streamDeclarations": { "Custom-MyEventHubStream": { "columns": [ { "name": "TimeGenerated", "type": "datetime" }, { "name": "RawData", "type": "string" }, { "name": "Properties", "type": "dynamic" } ] } }, "dataSources": { "dataImports": { "eventHub": { "consumerGroup": "[parameters('consumerGroup')]", "stream": "Custom-MyEventHubStream", "name": "myEventHubDataSource1" } } }, "destinations": { "logAnalytics": [ { "workspaceResourceId": "[parameters('workspaceResourceId')]", "name": "MyDestination" } ] }, "dataFlows": [ { "streams": [ "Custom-MyEventHubStream" ], "destinations": [ "MyDestination" ], "transformKql": "source", "outputStream": "[concat('Custom-', parameters('tableName'))]" } ] } } ] }On the Custom deployment screen, specify a Subscription and Resource group to store the data collection rule and then provide values for the parameters defined in the template, including:
- Region - Region for the data collection rule. Populated automatically based on the resource group you select.
- Data Collection Rule Name - Give the rule a name.
- Workspace Resource ID - See Collect required information.
- Endpoint Resource ID - Generated when you create the data collection endpoint.
- Table Name - The name of the destination table. In our example, and whenever you use a custom table, the table name must end with the suffix _CL. If you're ingesting data to an Azure table, enter the table name - for example,
Syslog- without the suffix. - Consumer Group - By default, the consumer group is set to
$Default. If needed, change the value to a different event hub consumer group.
Select Review + create and then Create when you review the details.
When the deployment is complete, expand the Deployment details box, and select your data collection rule to view its details. Select JSON View.
Copy the Resource ID for the data collection rule. You'll use this information in the next step.
Configure user-assigned managed identity (optional)
To configure your data collection rule to support user-assigned identity, in the example above, replace:
"identity": {
"type": "systemAssigned"
},
with:
"identity": {
"type": "userAssigned",
"userAssignedIdentities": {
"<identity_resource_Id>": {
}
}
},
To find the <identity_resource_Id> value, navigate to your user-assigned managed identity resource in the Azure portal, select JSON to open the Resource JSON screen and copy the managed identity's Resource ID.
Ingest log data into an Azure table (optional)
To ingest data into a supported Azure table:
In the data collection rule, change
outputStream:From:
"outputStream": "[concat('Custom-', parameters('tableName'))]"To:
"outputStream": "outputStream": "[concat(Microsoft-', parameters('tableName'))]"In
transformKql, define a transformation that sends the ingested data into the target columns in the destination Azure table.
Grant the event hub permission to the data collection rule
With managed identity, you can give any event hub, or Event Hubs namespace, permission to send events to the data collection rule and data collection endpoint you created. When you grant the permissions to the Event Hubs namespace, all event hubs within the namespace inherit the permissions.
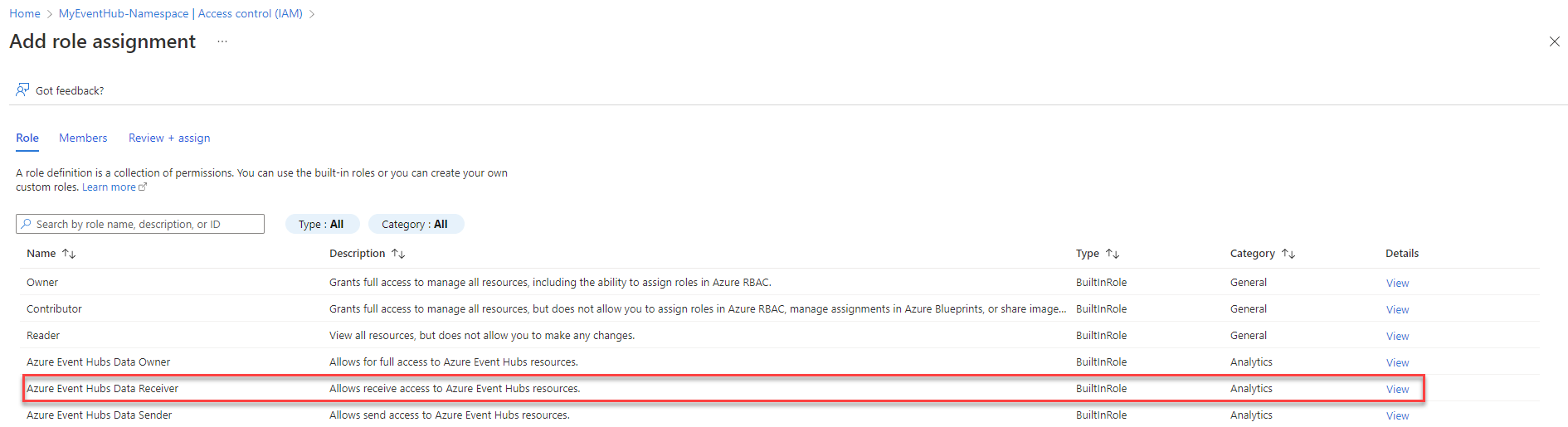
From the event hub or Event Hubs namespace in the Azure portal, select Access Control (IAM) > Add role assignment.
Select Azure Event Hubs Data Receiver and select Next.
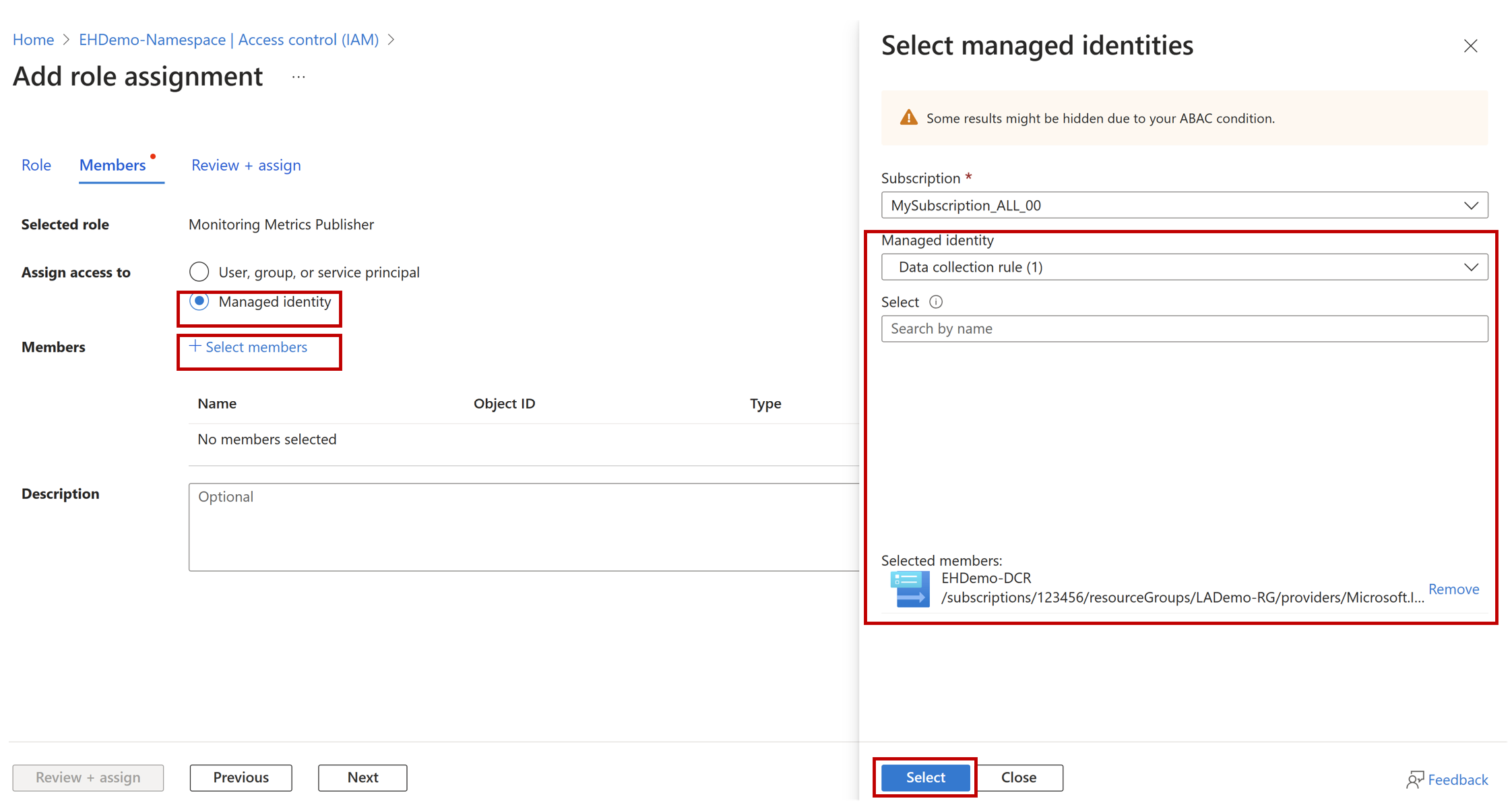
Select Managed identity for Assign access to and click Select members. Select Data collection rule, search for your data collection rule by name, and click Select.
Select Review + assign and verify the details before saving your role assignment.
Associate the data collection rule with the event hub
The final step is to associate the data collection rule to the event hub from which you want to collect events.
You can associate a single data collection rule with multiple event hubs that share the same consumer group and ingest data to the same stream. Alternatively, you can associate a unique data collection rule to each event hub.
Important
You must associate at least one data collection rule to the event hub to ingest data from an event hub. When you delete all data collection rule associations related to the event hub, you'll stop ingesting data from the event hub.
To create a data collection rule association in the Azure portal:
In the Azure portal's search box, type in template and then select Deploy a custom template.
Select Build your own template in the editor.
Paste the Resource Manager template below into the editor and then select Save.
{ "$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#", "contentVersion": "1.0.0.0", "parameters": { "eventHubResourceID": { "type": "string", "metadata": { "description": "Specifies the Azure resource ID of the event hub to use." } }, "associationName": { "type": "string", "metadata": { "description": "The name of the association." } }, "dataCollectionRuleID": { "type": "string", "metadata": { "description": "The resource ID of the data collection rule." } } }, "resources": [ { "type": "Microsoft.Insights/dataCollectionRuleAssociations", "apiVersion": "2021-09-01-preview", "scope": "[parameters('eventHubResourceId')]", "name": "[parameters('associationName')]", "properties": { "description": "Association of data collection rule. Deleting this association will break the data collection for this event hub.", "dataCollectionRuleId": "[parameters('dataCollectionRuleId')]" } } ] }On the Custom deployment screen, specify a Subscription and Resource group to store the data collection rule association and then provide values for the parameters defined in the template, including:
- Region - Populated automatically based on the resource group you select.
- Event Hub Instance Resource ID - See Collect required information.
- Association Name - Give the association a name.
- Data Collection Rule ID - Generated when you create the data collection rule.
Select Review + create and then Create when you review the details.
Check your destination table for ingested events
Azure Monitor Logs ingests all events that exist in the Event Hub at the time of the DCRA creation, provided their retention period hasn't expired, and all new events.
To check your destination table for ingested events:
Navigate to your workspace and select Logs.
Write a simple query in the query editor and select Run:
<table_name>You should see events from your event hub.
Clean up resources
In this tutorial, you created the following resources:
- Custom table
- Data collection endpoint
- Data collection rule
- Data collection rule association
Evaluate whether you still need these resources. Delete the resources you don't need individually, or delete all of these resources at once by deleting the resource group. Resources you leave running can cost you money.
To stop ingesting data from the event hub, delete all data collection rule associations related to the event hub, or delete the data collection rules themselves. These actions also reset event hub checkpointing.
Known issues and limitations
- If you transfer a subscription between Microsoft Entra directories, you need to follow the steps described in Known issues with managed identities for Azure resources to continue ingesting data.
- You can ingest messages of up to 64 KB from Event Hubs to Azure Monitor Logs.
Next steps
Learn more about to: