Monitor the capacity of a volume
This article describes ways to monitor the capacity utilization of an Azure NetApp Files volume.
Using Windows or Linux clients
This section shows how to use a Windows or Linux client to monitor the volume capacity. The scenarios described in this section assume a volume configured at 1 TiB size (quota) on a 4 TiB Ultra service-level capacity pool.
Windows (SMB) clients
You can use Windows clients to check the used and available capacity of a volume through the network mapped drive properties. You can use one of the following two methods:
Go to File Explorer, right-click the mapped drive, and select Properties to display capacity.
Use the
dircommand at the command prompt: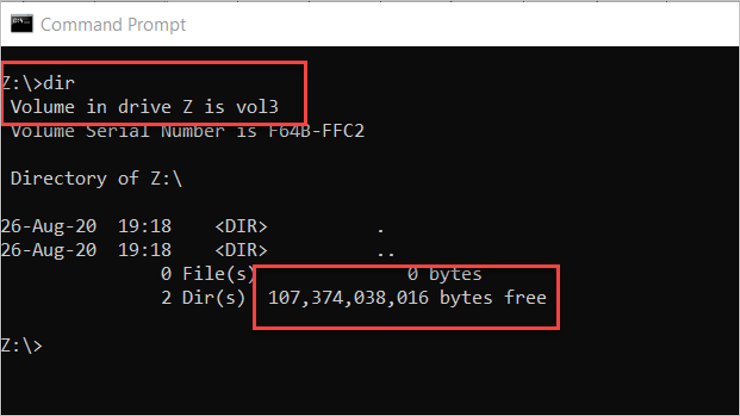
The available space is accurate using File Explorer or the dir command. However, the consumed/used space will be an estimate when snapshots are generated on the volume. The consumed snapshot capacity counts towards the total consumed space on the volume. To get the absolute volume consumption, including the capacity used by snapshots, use the Azure NetApp Metrics in the Azure portal.
Linux (NFS) clients
Linux clients can check the used and available capacity of a volume using the df -h. Using the h option displays the size, including used and available space in human readable format (using M, G and T unit sizes).
The following snapshot shows volume capacity reporting in Linux:
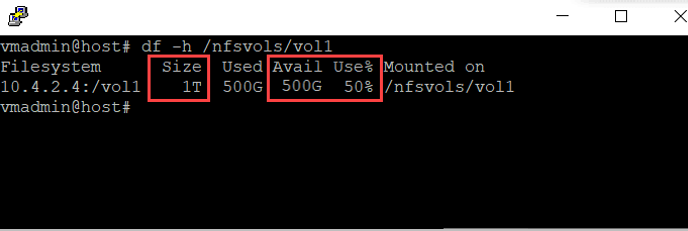
The available space is accurate using the df command. However, the consumed/used space will be an estimate when snapshots are generated on the volume. The consumed snapshot capacity counts towards the total consumed space on the volume. To get the absolute volume consumption, including the capacity used by snapshots, use the Azure NetApp Metrics in the Azure portal.
Note
The du command doesn’t account for the space used by snapshots generated in the volume. As such, it’s not recommended for determining the available capacity in a volume.
Using Azure portal
Azure NetApp Files leverages the standard Azure Monitor functionality. As such, you can use Azure Monitor to monitor Azure NetApp Files volumes.
Using Azure CLI
You can use the az netappfiles volume commands of the Azure command line (CLI) tools to monitor a volume.
Using REST API
See REST API for Azure NetApp Files and REST API using PowerShell for Azure NetApp Files.
The REST API specification and example code for Azure NetApp Files are available through the resource-manager GitHub directory.
