About Multi-user authorization using Resource Guard
Multi-user authorization (MUA) for Azure Backup allows you to add an additional layer of protection to critical operations on your Recovery Services vaults and Backup vaults. For MUA, Azure Backup uses another Azure resource called the Resource Guard to ensure critical operations are performed only with applicable authorization.
Note
Multi-user authorization using Resource Guard for Backup vault is now generally available.
How does MUA for Backup work?
Azure Backup uses the Resource Guard as an additional authorization mechanism for a Recovery Services vault or a Backup vault. Therefore, to perform a critical operation (described below) successfully, you must have sufficient permissions on the associated Resource Guard as well.
Important
To function as intended, the Resource Guard must be owned by a different user, and the vault admin mustn't have Contributor, Backup MUA Admin, or Backup MUA Operator permissions on the Resource Guard. You can place Resource Guard in a subscription or tenant different from the one containing the vaults to provide better protection.
Critical operations
The following table lists the operations defined as critical operations and can be protected by a Resource Guard. You can choose to exclude certain operations from being protected using the Resource Guard when associating vaults with it.
Note
You can't excluded the operations denoted as Mandatory from being protected using the Resource Guard for vaults associated with it. Also, the excluded critical operations would apply to all vaults associated with a Resource Guard.
Choose a vault
| Operation | Mandatory/ Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Disable soft delete or security features | Mandatory | Disable soft delete setting on a vault. |
| Remove MUA protection | Mandatory | Disable MUA protection on a vault. |
| Delete protection | Optional | Delete protection by stopping backups and performing delete data. |
| Modify protection | Optional | Add a new backup policy with reduced retention or change policy frequency to increase RPO. |
| Modify policy | Optional | Modify backup policy to reduce retention or change policy frequency to increase RPO. |
| Get backup security PIN | Optional | Change MARS security PIN. |
| Stop backup and retain data | Optional | Delete protection by stopping backups and performing retain data forever or retain as per policy. |
| Disable immutability | Optional | Disable immutability setting on a vault. |
Concepts and process
The concepts and the processes involved when using MUA for Azure Backup are explained below.
Let’s consider the following two personas for a clear understanding of the process and responsibilities. These two personas are referenced throughout this article.
Backup admin: Owner of the Recovery Services vault or the Backup vault who performs management operations on the vault. To begin with, the Backup admin must not have any permissions on the Resource Guard. This can be Backup Operator or Backup Contributor RBAC role on the Recovery Services vault.
Security admin: Owner of the Resource Guard and serves as the gatekeeper of critical operations on the vault. Hence, the Security admin controls permissions that the Backup admin needs to perform critical operations on the vault. This can be Backup MUA Admin RBAC role on the Resource Guard.
Following is a diagrammatic representation for performing a critical operation on a vault that has MUA configured using a Resource Guard.
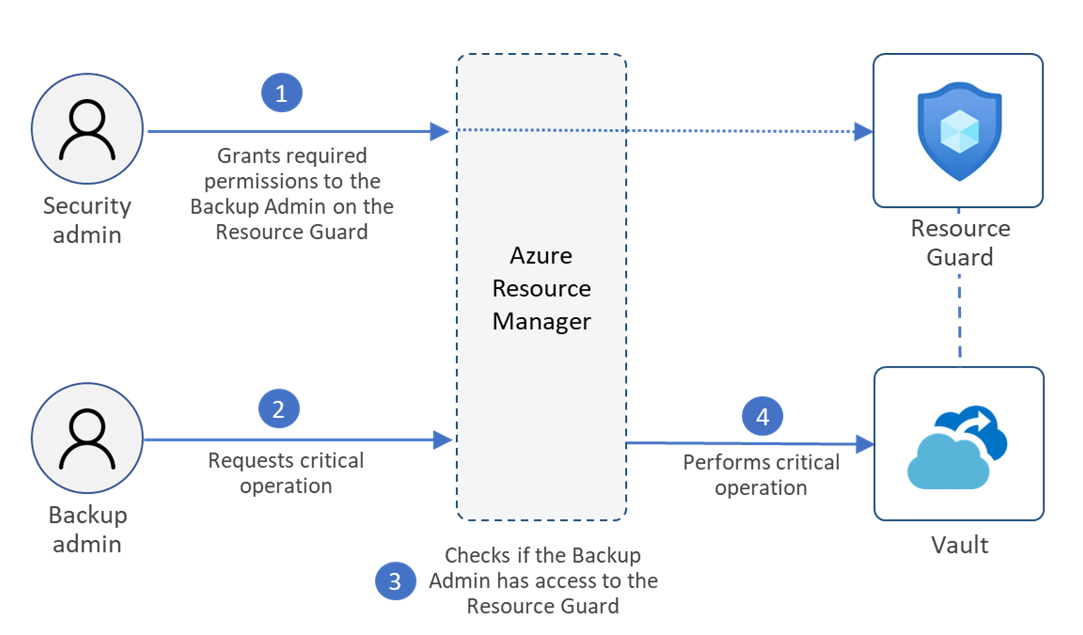
Here's the flow of events in a typical scenario:
The Backup admin creates the Recovery Services vault or the Backup vault.
The Security admin creates the Resource Guard.
The Resource Guard can be in a different subscription or a different tenant with respect to the vault. Ensure that the Backup admin doesn't have Contributor, Backup MUA Admin, or Backup MUA Operator permissions on the Resource Guard.
The Security admin grants the Reader role to the Backup Admin for the Resource Guard (or a relevant scope). The Backup admin requires the reader role to enable MUA on the vault.
The Backup admin now configures the vault to be protected by MUA via the Resource Guard.
Now, if the Backup admin or any user who has write access to the vault wants to perform a critical operation that is protected with Resource Guard on the vault, they need to request access to the Resource Guard. The Backup Admin can contact the Security admin for details on gaining access to perform such operations. They can do this using Privileged Identity Management (PIM) or other processes as mandated by the organization. They can request for “Backup MUA Operator” RBAC role which allows users to perform only critical operations protected by the Resource Guard and does not allow to delete the resource Guard.
The Security admin temporarily grants the “Backup MUA Operator” role on the Resource Guard to the Backup admin to perform critical operations.
Then the Backup admin initiates the critical operation.
The Azure Resource Manager checks if the Backup admin has sufficient permissions or not. Since the Backup admin now has “Backup MUA Operator” role on the Resource Guard, the request is completed. If the Backup admin doesn't have the required permissions/roles, the request will fail.
The Security admin must ensure to revoke the privileges to perform critical operations after authorized actions are performed or after a defined duration. You can use JIT tools Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management to ensure the same.
Note
- If you grant the Contributor or Backup MUA Admin role on the Resource Guard access temporarily to the Backup Admin, it also provides the delete permissions on the Resource Guard. We recommend you to provide Backup MUA Operator permissions only.
- MUA provides protection on the above listed operations performed on the vaulted backups only. Any operations performed directly on the data source (that is, the Azure resource/workload that is protected) are beyond the scope of the Resource Guard.
Usage scenarios
The following table lists the scenarios for creating your Resource Guard and vaults (Recovery Services vault and Backup vault), along with the relative protection offered by each.
Important
The Backup admin must not have Contributor, Backup MUA Admin, or Backup MUA Operator permissions to the Resource Guard in any scenario as this overrides adding MUA protection on the vault.
| Usage scenario | Protection due to MUA | Ease of implementation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vault and Resource Guard are in the same subscription. The Backup admin doesn't have access to the Resource Guard. |
Least isolation between the Backup admin and the Security admin. | Relatively easy to implement since only one subscription is required. | Resource level permissions/ roles need to be ensured are correctly assigned. |
| Vault and Resource Guard are in different subscriptions but the same tenant. The Backup admin doesn't have access to the Resource Guard or the corresponding subscription. |
Medium isolation between the Backup admin and the Security admin. | Relatively medium ease of implementation since two subscriptions (but a single tenant) are required. | Ensure that permissions/ roles are correctly assigned for the resource or the subscription. |
| Vault and Resource Guard are in different tenants. The Backup admin doesn't have access to the Resource Guard, the corresponding subscription, or the corresponding tenant. |
Maximum isolation between the Backup admin and the Security admin, hence, maximum security. | Relatively difficult to test since requires two tenants or directories to test. | Ensure that permissions/ roles are correctly assigned for the resource, the subscription or the directory. |