Restore Azure Database for PostgreSQL backups
This article explains how to restore a database to an Azure PostgreSQL server backed up by Azure Backup.
You can restore a database to any Azure PostgreSQL server of a different/same subscription but within the same region of the vault, if the service has the appropriate set of permissions on the target server.
Restore Azure PostgreSQL database
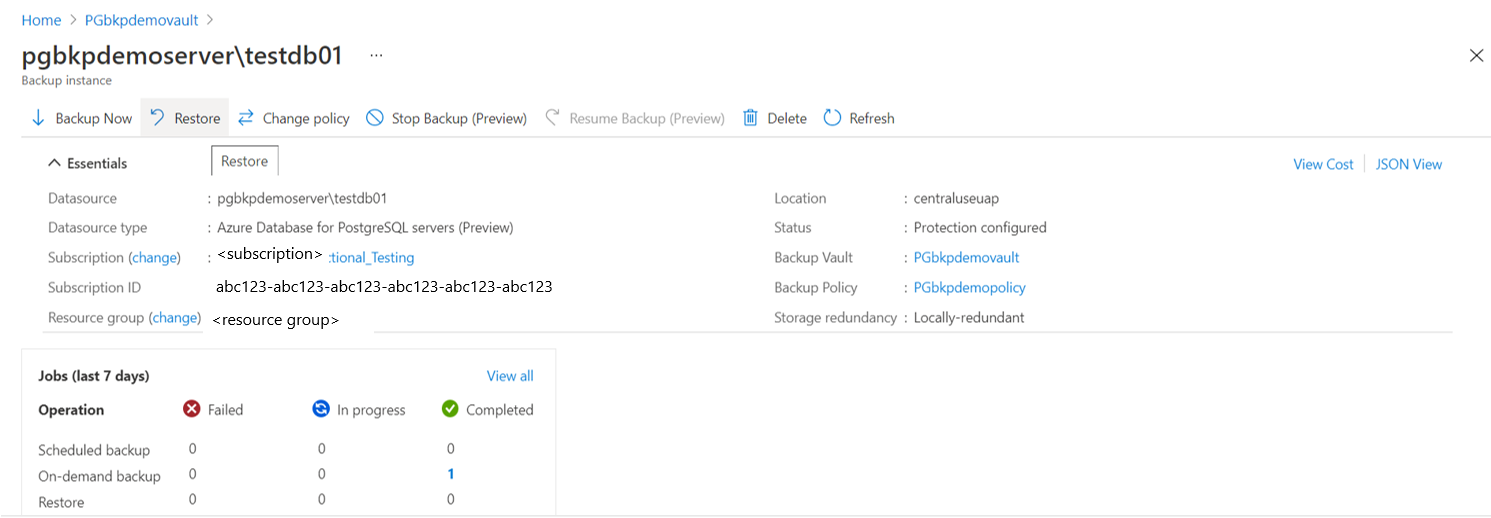
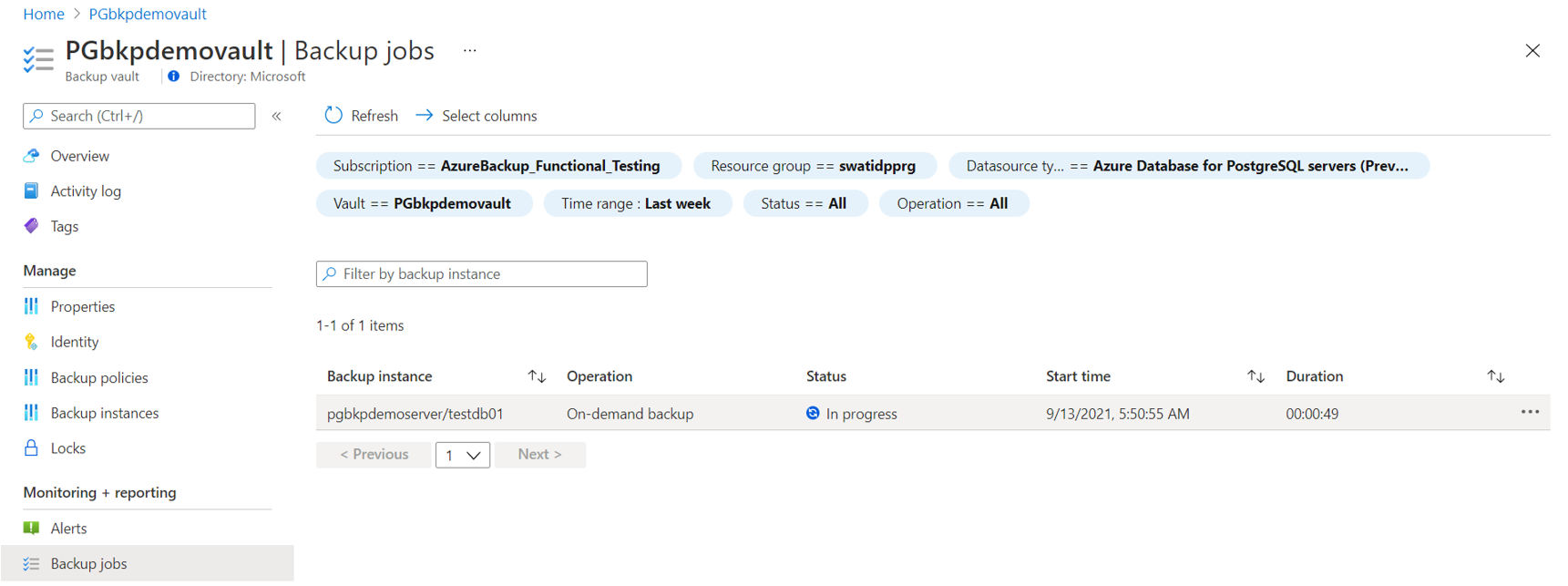
Go to Backup vault -> Backup Instances. Select a database and click Restore.
Alternatively, you can navigate to this page from the Backup center.
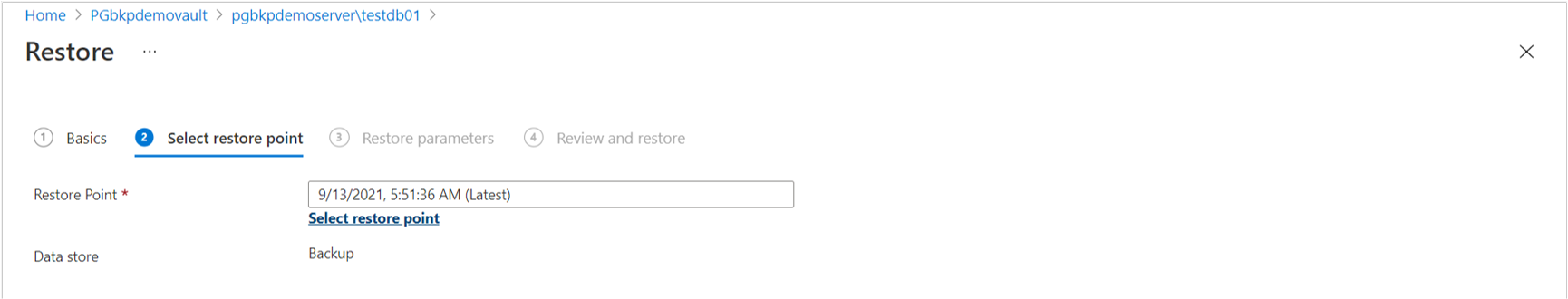
On the Select restore point page, select a recovery point from the list of all full backups available for the selected backup instance. By default, the latest recovery point is selected.
If the restore point is in the archive tier, you must rehydrate the recovery point before restoring. Provide the following additional parameters required for rehydration:
- Rehydration priority: Default is Standard.
- Rehydration duration: The maximum rehydration duration is 30 days, and the minimum rehydration duration is 10 days. Default value is 15 days. The recovery point is stored in the Backup data store for this duration.
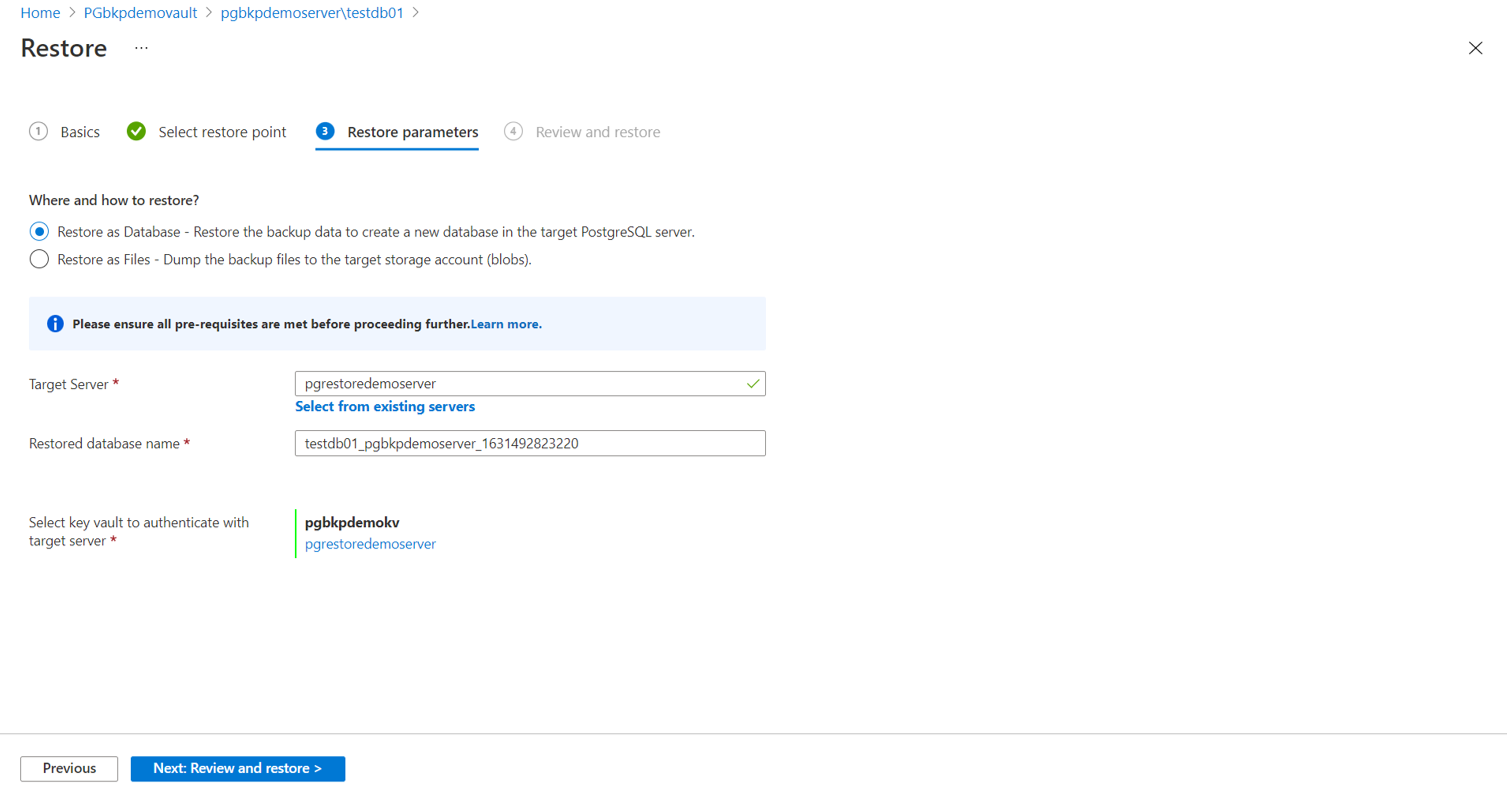
On the Restore parameters page, select one of the following restore types: Restore as Database or Restore as Files.
Restore as Database
The target server can be same as the source server. However, overwriting the original database isn't supported. You can choose from the server across all subscriptions, but in the same region as that of the vault.
In the Select key vault and the secret drop-down list, select a vault that stores the credentials to connect to the target server.
Select Review + Restore to trigger validation to check if the service has restore permissions on the target server. These permissions must be granted manually.
Important
The DB user whose credentials were chosen via the key vault will have all the privileges over the restored database and any existing DB user boundaries will be overridden. For eg: If the backed up database had any DB user specific permissions/constraints such as DB user A can access few tables, and DB user B can access few other tables, such permissions will not be preserved after restore. If you want to preserve those permissions, use restore as files and use the pg_restore command with the relevant switch.
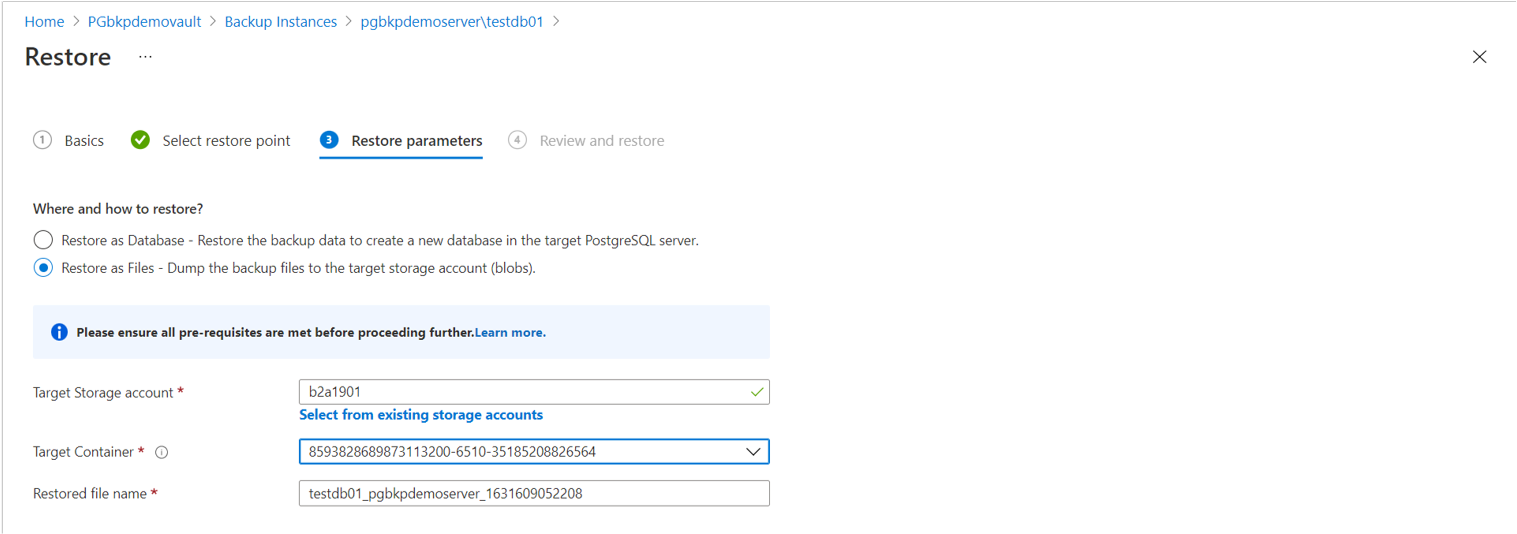
Restore as Files: Dump the backup files to the target storage account (blobs).
You can choose from the storage accounts across all subscriptions, but in the same region as that of the vault.
- In the Select the target container drop-down list, select one of the containers filtered for the selected storage account.
- Select Review + Restore to trigger validation to check if the backup service has the restore permissions on the target storage account.
Note
Archive support for Azure Database for PostgreSQL is in limited public preview.
Restore permissions on the target storage account
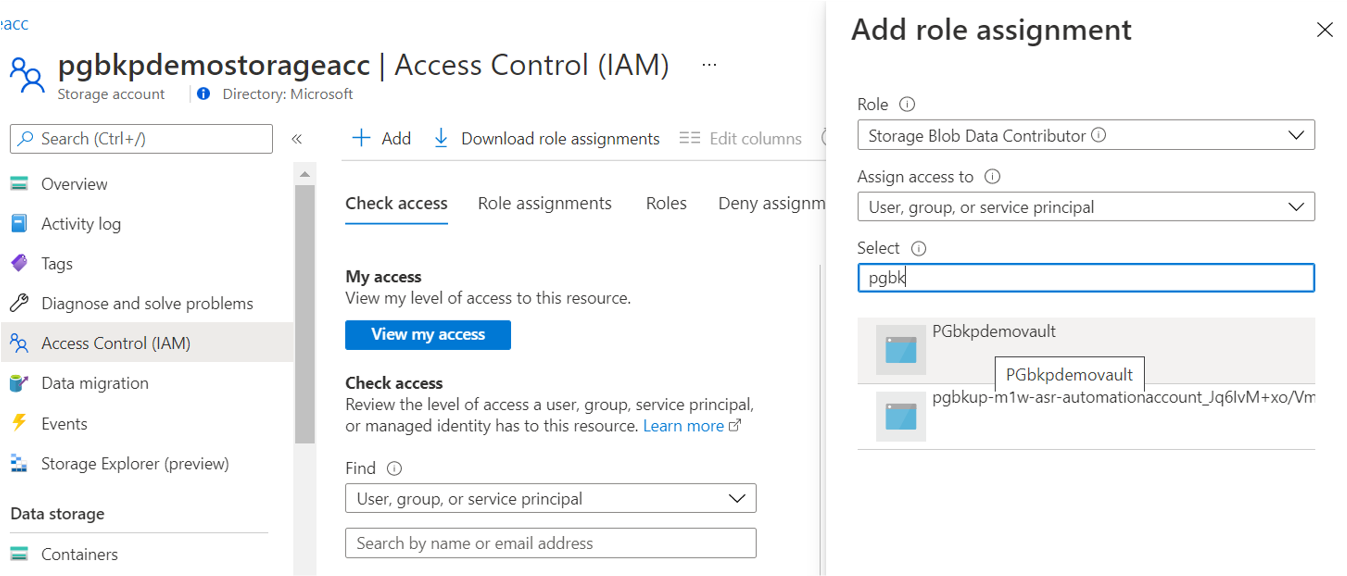
Assign the Backup vault MSI the permission to access the storage account containers using the Azure portal.
Go to Storage Account -> Access Control -> Add role assignment.
Select the Storage Blob Data Contributor role in the Role drop-down list to the Backup vault MSI.
Alternatively, give granular permissions to the specific container you're restoring to by using the Azure CLI az role assignment create command.
az role assignment create --assignee $VaultMSI_AppId --role "Storage Blob Data Contributor" --scope $id
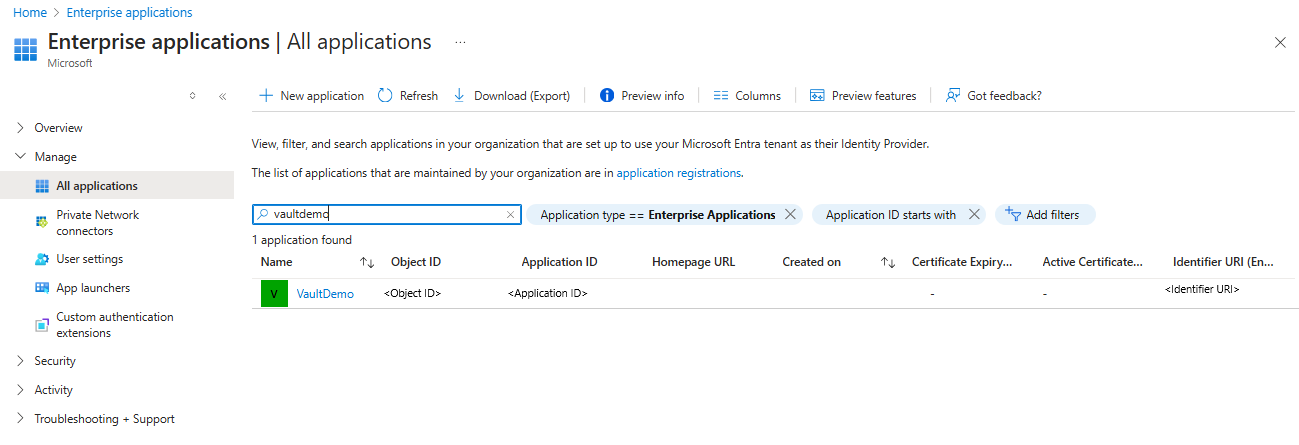
Replace the assignee parameter with the Application ID of the vault's MSI and the scope parameter to refer to your specific container. To get the Application ID of the vault MSI, select All applications under Application type. Search for the vault name and copy the Application ID.
Restore databases across regions
As one of the restore options, Cross Region Restore (CRR) allows you to restore Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers in a secondary region, which is an Azure-paired region.
Considerations
- To begin using the feature, read the Before you start section.
- To check if Cross Region Restore is enabled, see the Configure Cross Region Restore section.
View backup instances in secondary region
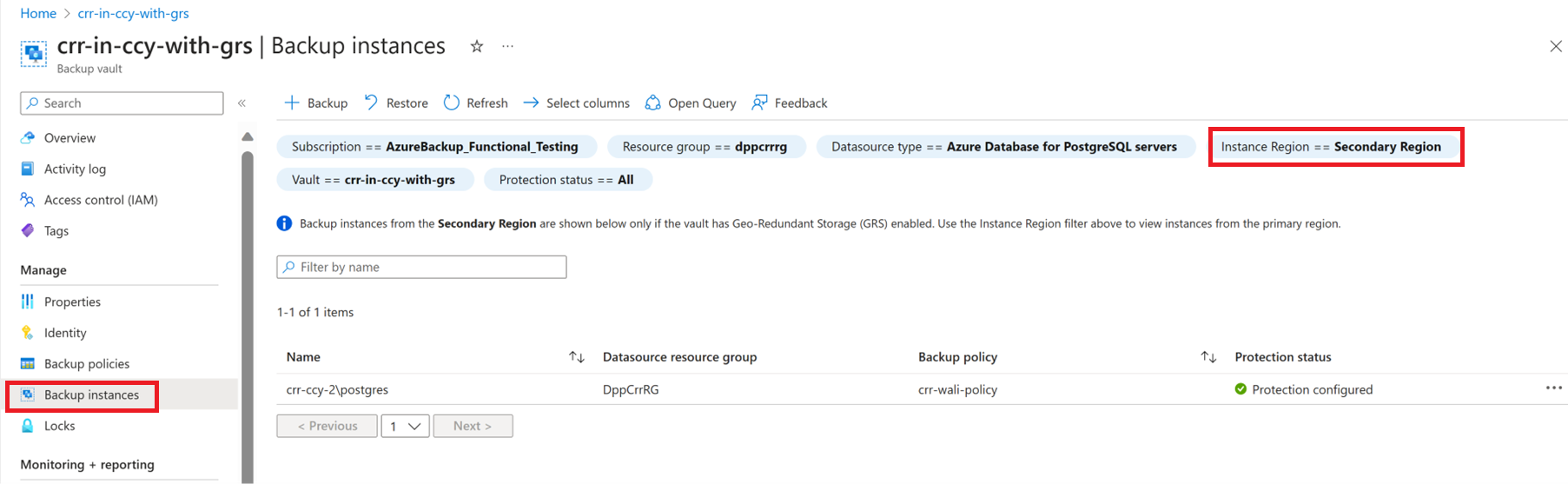
If CRR is enabled, you can view the backup instances in the secondary region.
From the Azure portal, go to Backup Vault > Backup Instances.
Select the filter as Instance Region == Secondary Region.
Note
Only Backup Management Types supporting the CRR feature are listed. Currently, the restoration of primary region data to a secondary region for PostgreSQL servers is only supported.
Restore in secondary region
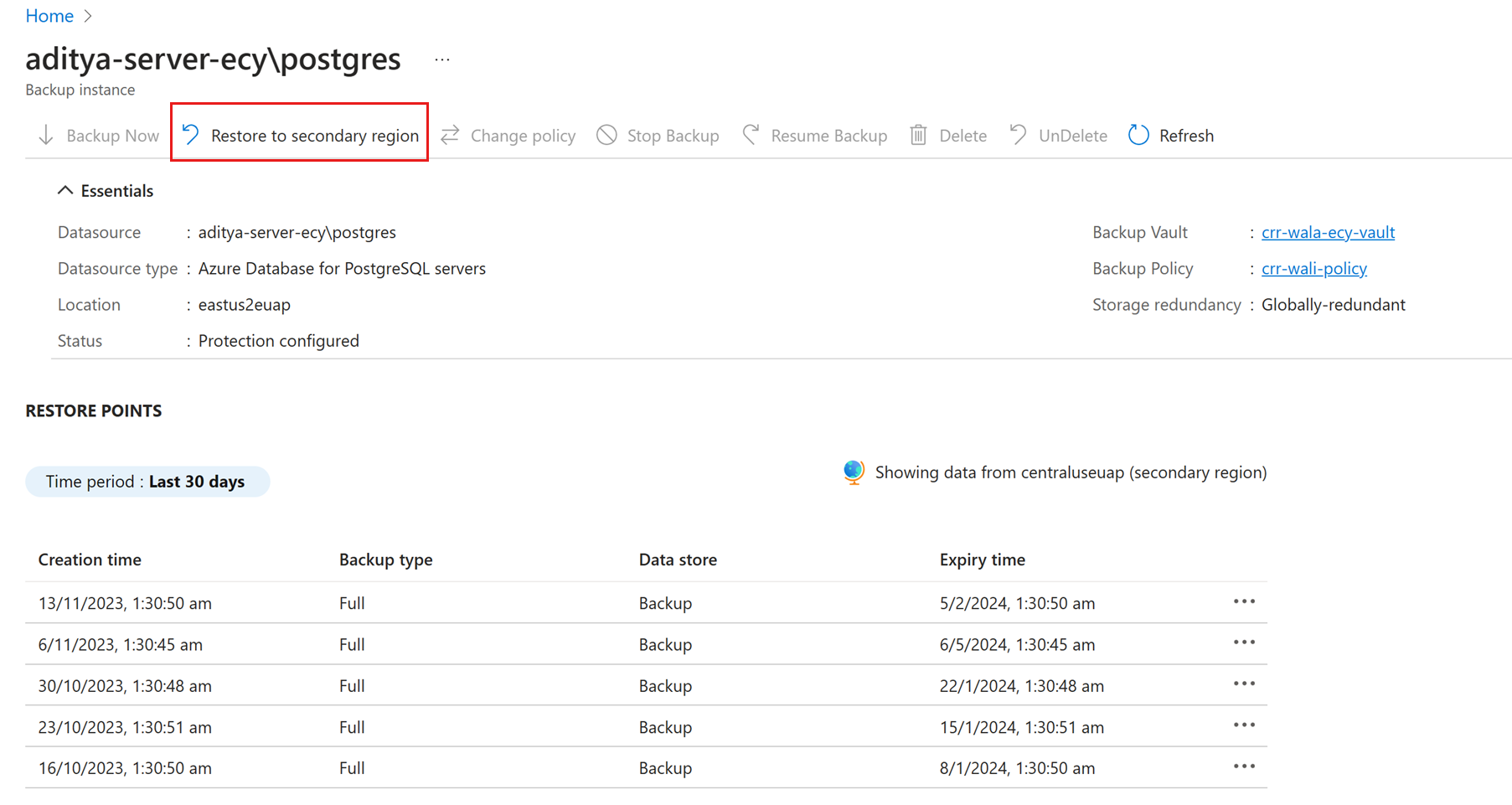
The secondary region restore experience is similar to the primary region restore.
When configuring details in the Restore Configuration pane to configure your restore, you’re prompted to provide only secondary region parameters. So, a vault should already exist in the secondary region and the PostgreSQL server should be registered to the vault in the secondary region.
Follow these steps:
Select Backup Instance name to view details.
Select Restore to secondary region.
Select the restore point, the region, and the resource group.
Select Restore.
Note
- After the restore is triggered in the data transfer phase, the restore job can't be canceled.
- The role/access level required to perform restore operation in cross-regions are Backup Operator role in the subscription and Contributor (write) access on the source and target virtual machines. To view backup jobs, Backup reader is the minimum permission required in the subscription.
- The RPO for the backup data to be available in secondary region is 12 hours. Therefore, when you turn on CRR, the RPO for the secondary region is 12 hours + log frequency duration (that can be set to a minimum of 15 minutes).
Monitoring secondary region restore jobs
In the Azure portal, go to Monitoring + Reporting > Backup Jobs.
Filter Instance Region for Secondary Region to view the jobs in the secondary region.
Next steps
Troubleshoot PostgreSQL database backup by using Azure Backup