Drive remediation with governance rules
While the security team is responsible for improving the security posture, team members might not actually implement security recommendations.
Using governance rules driven by the security team helps you to drive accountability and an SLA around the remediation process.
To learn more, watch this episode of the Defender for Cloud in the Field video series.
Governance rules
You can define rules that assign an owner and a due date for addressing recommendations for specific resources. This provides resource owners with a clear set of tasks and deadlines for remediating recommendations.
For tracking, you can review the progress of the remediation tasks by subscription, recommendation, or owner so you can follow up with tasks that need more attention.
- Governance rules can identify resources that require remediation according to specific recommendations or severities.
- The rule assigns an owner and due date to ensure the recommendations are handled. Many governance rules can apply to the same recommendations, so the rule with lower priority value is the one that assigns the owner and due date.
- The due date set for the recommendation to be remediated is based on a timeframe of 7, 14, 30, or 90 days from when the recommendation is found by the rule.
- For example, if the rule identifies the resource on March 1 and the remediation timeframe is 14 days, March 15 is the due date.
- You can apply a grace period so that the resources given a due date don't affect your secure score.
- You can also set the owner of the resources that are affected by the specified recommendations.
- In organizations that use resource tags to associate resources with an owner, you can specify the tag key and the governance rule reads the name of the resource owner from the tag.
- The owner is shown as unspecified when the owner wasn't found on the resource, the associated resource group, or the associated subscription based on the specified tag.
- By default, email notifications are sent to the resource owners weekly to provide a list of the on time and overdue tasks.
- If an email for the owner's manager is found in the organizational Microsoft Entra ID, the owner's manager receives a weekly email showing any overdue recommendations by default.
- Conflicting rules are applied in priority order. For example, rules on a management scope (Azure management groups, AWS accounts and GCP organizations), take effect before rules on scopes (for example, Azure subscriptions, AWS accounts, or GCP projects).
Before you begin
- The Defender Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) plan must be enabled.
- You need Contributor, Security Admin, or Owner permissions on the Azure subscriptions.
- For AWS accounts and GCP projects, you need Contributor, Security Admin, or Owner permissions on the Defender for Cloud AWS or GCP connectors.
Define a governance rule
You can define a governance rule as follows:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Navigate to Microsoft Defender for Cloud > Environment settings > Governance rules.
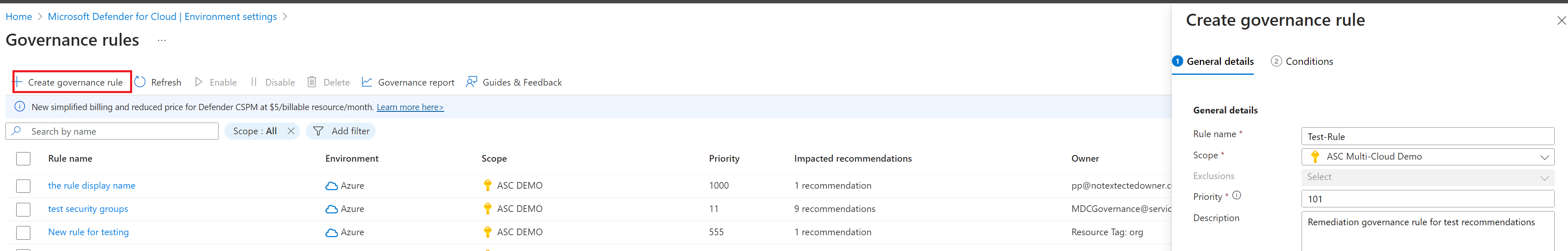
Select Create governance rule.
Specify a rule name and scope in which to apply the rule.
- Rules for management scope (Azure management groups, AWS master accounts, GCP organizations) are applied prior to the rules on a single scope.
- You can define exclusions within the scope as needed.
Set a priority level.
Rules are run in priority order from the highest (1) to the lowest (1000).
Specify a description to help you identify the rule.
Select Next
Specify how recommendations are impacted by the rule.
- By severity - The rule assigns the owner and due date to any recommendation in the subscription that doesn't already have them assigned.
- By specific recommendations - Select the specific built-in or custom recommendations that the rule applies to.
Set the owner to specify who's responsible for fixing recommendations covered by the rule.
- By resource tag - Enter the resource tag on your resources that defines the resource owner.
- By email address - Enter the email address of the owner to assign to the recommendations.
Specify remediation time frame to set the time that can elapse between when resources are identified as requiring remediation, and the time that the remediation is due.
For recommendations issued by MCSB, if you don't want the resources to affect your secure score until they're overdue, select Apply grace period.
(Optional) By default owners and their managers are notified weekly about open and overdue tasks. If you don't want them to receive these weekly emails, clear the notification options.
Select Create.
If there are existing recommendations that match the definition of the governance rule, you can either:
Assign an owner and due date to recommendations that don't already have an owner or due date.
Overwrite the owner and due date of existing recommendations.
When you delete or disable a rule, all existing assignments and notifications remain.
View effective rules
You can view the effect of government rules in your environment.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Navigate to Microsoft Defender for Cloud > Environment settings > Governance rules.
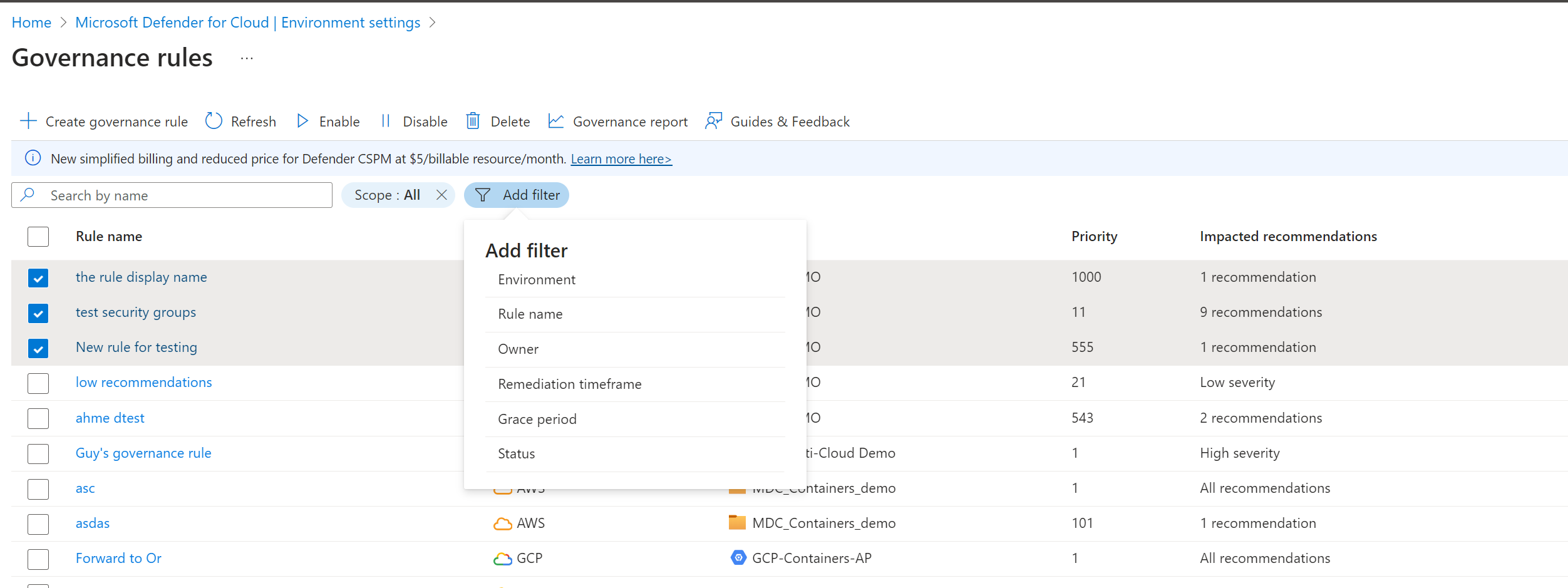
Review governance rules. The default list shows all the governance rules applicable in your environment.
You can search for rules, or filter rules.
Review the governance report
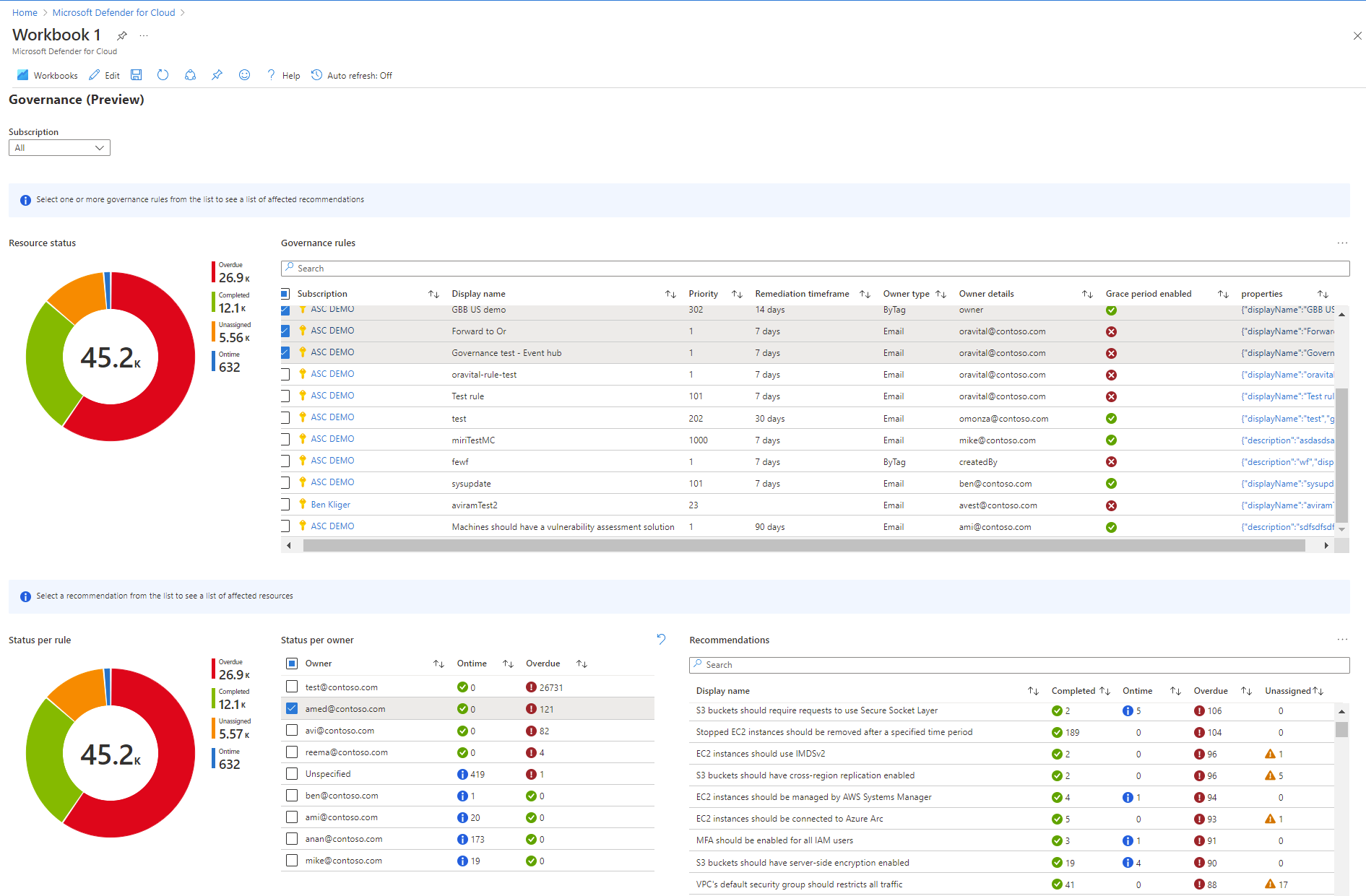
The governance report lets you select subscriptions that have governance rules and, for each rule and owner, shows you how many recommendations are completed, on time, overdue, or unassigned.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Navigate to Microsoft Defender for Cloud > Environment settings > Governance rules >Governance report.
Select a subscription.
From the governance report, you can drill down into recommendations by scope, display name, priority, remediation timeframe, owner type, owner details, grace period and cloud.
Next step
Learn how to Implement security recommendations.