Configure an expiration policy for shared access signatures
You can use a shared access signature (SAS) to delegate access to resources in your Azure Storage account. A SAS token includes the targeted resource, the permissions granted, and the interval over which access is permitted. Best practices recommend that you limit the interval for a SAS in case it's compromised. By setting a SAS expiration policy for your storage accounts, you can provide a recommended upper expiration limit when a user creates a user delegation SAS, a service SAS, or an account SAS.
For more information about shared access signatures, see Grant limited access to Azure Storage resources using shared access signatures (SAS).
Important
For scenarios where shared access signatures are used, Microsoft recommends using a user delegation SAS. A user delegation SAS is secured with Microsoft Entra credentials instead of the account key, which provides superior security.
About SAS expiration policies
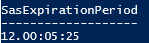
You can configure a SAS expiration policy on the storage account. The SAS expiration policy specifies the recommended upper limit for the signed expiry field on a user delegation SAS, a service SAS, or an account SAS. The recommended upper limit is specified as a date/time value that is a combined number of days, hours, minutes, and seconds.
The validity interval for the SAS is calculated by subtracting the date/time value of the signed start field from the date/time value of the signed expiry field. If the resulting value is less than or equal to the recommended upper limit, then the SAS is in compliance with the SAS expiration policy.
After you configure the SAS expiration policy, any user who creates a SAS with an interval that exceeds the recommended upper limit will see a warning.
A SAS expiration policy doesn't prevent a user from creating a SAS with an expiration that exceeds the limit recommended by the policy. When a user creates a SAS that violates the policy, they see a warning, along with the recommended maximum interval. If you've configured a diagnostic setting for logging with Azure Monitor, then Azure Storage writes a message to the SasExpiryStatus property in the logs whenever a user uses a SAS that expires after the recommended interval. The message indicates that the validity interval of the SAS exceeds the recommended interval.
When a SAS expiration policy is in effect for the storage account, the signed start field is required for every SAS. If the signed start field isn't included on the SAS, and you've configured a diagnostic setting for logging with Azure Monitor, then Azure Storage writes a message to the SasExpiryStatus property in the logs whenever a user uses a SAS without a value for the signed start field.
Configure a SAS expiration policy
When you configure a SAS expiration policy on a storage account, the policy applies to each type of SAS: user delegation SAS, service SAS, and account SAS. Service SAS and account SAS types are signed with the account key, while user delegation SAS is signed with Microsoft Entra credentials.
Note
A user delegation SAS is signed with a user delegation key, which is obtained using Microsoft Entra credentials. The user delegation key has its own expiry interval which isn't subject to the SAS expiration policy. The SAS expiration policy applies only to the user delegation SAS, not the user delegation key it's signed with.
A user delegation SAS has a maximum expiry interval of 7 days, regardless of the SAS expiration policy. If the SAS expiration policy is set to a value greater than 7 days, then the policy has no effect for a user delegation SAS. If the user delegation key expires, then any user delegation SAS signed with that key is invalid and any attempt to use the SAS returns an error.
Do I need to rotate the account access keys first?
This section applies to service SAS and account SAS types, which are signed with the account key. Before you can configure a SAS expiration policy, you might need to rotate each of your account access keys at least once. If the keyCreationTime property of the storage account has a null value for either of the account access keys (key1 and key2), you'll need to rotate them. To determine whether the keyCreationTime property is null, see Get the creation time of the account access keys for a storage account. If you attempt to configure a SAS expiration policy and the keys need to be rotated first, the operation fails.
How to configure a SAS expiration policy
You can configure a SAS expiration policy using the Azure portal, PowerShell, or Azure CLI.
To configure a SAS expiration policy in the Azure portal, follow these steps:
Navigate to your storage account in the Azure portal.
Under Settings, select Configuration.
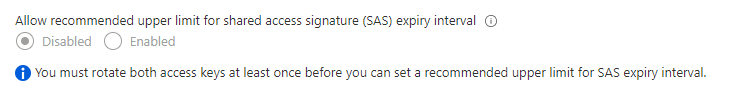
Locate the setting for Allow recommended upper limit for shared access signature (SAS) expiry interval, and set it to Enabled.
Note
If the setting is grayed out and you see the message shown in the image below, then you will need to rotate both account access keys before you can set the Recommended upper limit for SAS expiry interval values:
Specify the time values under Recommended upper limit for SAS expiry interval for the recommended interval for any new shared access signatures that are created on resources in this storage account.
Select Save to save your changes.
Query logs for policy violations
To log the use of a SAS that is valid over a longer interval than the SAS expiration policy recommends, first create a diagnostic setting that sends logs to an Azure Log Analytics workspace. For more information, see Send logs to Azure Log Analytics.
Next, use an Azure Monitor log query to monitor whether policy has been violated. Create a new query in your Log Analytics workspace, add the following query text, and press Run.
StorageBlobLogs
| where SasExpiryStatus startswith "Policy violated"
| summarize count() by AccountName, SasExpiryStatus
Use a built-in policy to monitor compliance
You can monitor your storage accounts with Azure Policy to ensure that storage accounts in your subscription have configured SAS expiration policies. Azure Storage provides a built-in policy for ensuring that accounts have this setting configured. For more information about the built-in policy, see Storage accounts should have shared access signature (SAS) policies configured in List of built-in policy definitions.
Assign the built-in policy for a resource scope
Follow these steps to assign the built-in policy to the appropriate scope in the Azure portal:
In the Azure portal, search for Policy to display the Azure Policy dashboard.
In the Authoring section, select Assignments.
Choose Assign policy.
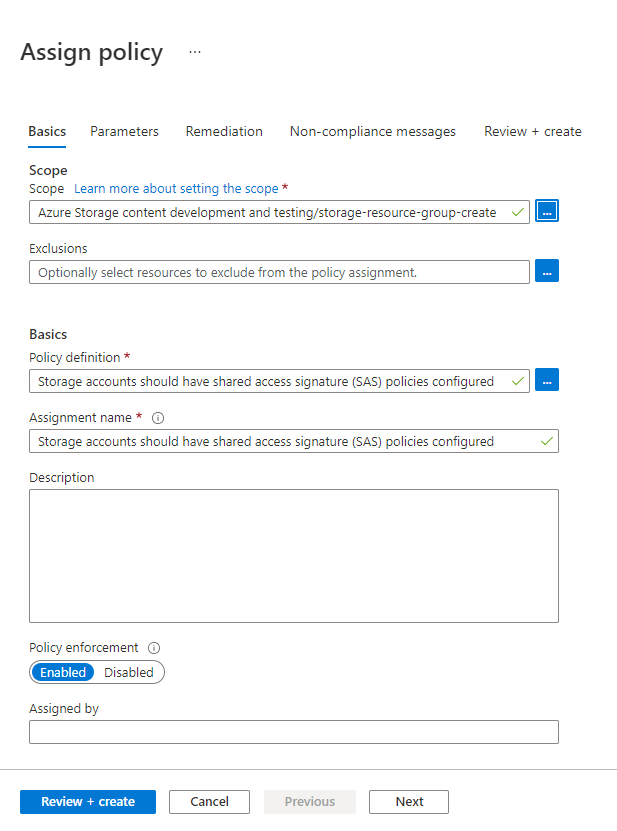
On the Basics tab of the Assign policy page, in the Scope section, specify the scope for the policy assignment. Select the More button to choose the subscription and optional resource group.
For the Policy definition field, select the More button, and enter storage account keys in the Search field. Select the policy definition named Storage account keys should not be expired.

Select Review + create to assign the policy definition to the specified scope.
Monitor compliance with the key expiration policy
To monitor your storage accounts for compliance with the key expiration policy, follow these steps:
On the Azure Policy dashboard, locate the built-in policy definition for the scope that you specified in the policy assignment. You can search for
Storage accounts should have shared access signature (SAS) policies configuredin the Search box to filter for the built-in policy.Select the policy name with the desired scope.
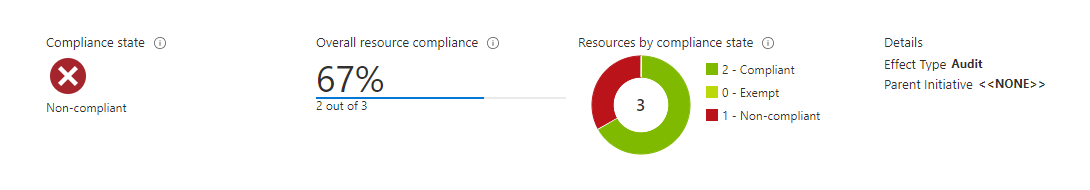
On the Policy assignment page for the built-in policy, select View compliance. Any storage accounts in the specified subscription and resource group that don't meet the policy requirements appear in the compliance report.
To bring a storage account into compliance, configure a SAS expiration policy for that account, as described in Configure a SAS expiration policy.