Microsoft Azure Automation
Automation within Microsoft Azure? Yes it’s real. Last week during the Microsoft Build conference Azure Automation was announced. Azure Automation allows you to do the following:
Azure Automation allows you to automate the creation, deployment, monitoring, and maintenance of resources in your Azure environment using a highly scalable and reliable workflow execution engine. Orchestrate time-consuming and frequently repeated tasks across Azure and third-party systems to decrease time to value for your cloud operations.
Source: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/automation/
I’ll walk through creating an automation runbook that pulls IP information from a virtual machine running in Microsoft Azure.
ASSUMPTIONS
- Microsoft Azure subscription
- Virtual Machine is already created
- Management Certificates are created
- Automation is enabled in the preview portal: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/preview/
LET’S GET STARTED
Login into your Microsoft Azure subscription and select AUTOMATION from the menu on the left:
From the menu at the bottom of the page, select CREATE. This will start the automation account creation process where the runbooks will be stored:
Give the automation account a name and select the check mark to complete:
Once an automation account has been created select it from the screen:
Select the runbook you created, mine is called “remotePScommand”, then select AUTHOR and then DRAFT:
Now we’re ready create or import automation scripts, I’ll need to use the following scripts first for my automation runbook to work properly:
- Connect-Azure: https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/Connect-to-an-Azure-f27a81bb - download this script
- Connect-AzureVM: https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/Connect-to-an-Azure-85f0782c - download this script
I’ll manually add the remote PowerShell command runbook for demonstration purposes in a later step.
To import scripts select RUNBOOKS at the top of the page, once there, select IMPORT at the bottom of the page:
Select one of the scripts previously downloaded from the links above, then select the check mark to start the import (import both scripts):
Once the imports are completed you will see them on the RUNBOOKS page:
Note: select each runbook and publish them as is under the AUTHORING page.
Alternatively, we can manually create runbooks. I’ll show how I completed the manual creation of a script next.
MANUALLY CREATING RUNBOOKS
Copy the code from the following runbook: https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/How-to-Use-a-PowerShell-59b2e28c
Now I’ll manually create a runbook instead of importing:
Select NEW at the bottom of the page, APP SERVICES, AUTOMATION, and RUNBOOK:
Finally, select QUICK CREATE and fill out the required boxes with information and select CREATE:
After the runbook is created, select RUNBOOKS from the portal to view all runbooks. The ones I imported and manually created are in the list:
Note: I changed the name slightly for my runbook
Now I’ll select “remotePScommand” runbook and then select AUTHOR from the top of the page and I’m put in DRAFT mode:
I’ll now paste the script code I copied in a previous step:
Note, the name of the script must match the workflow parameter name (feel free to change the name in the script to match the name of the runbook if needed as it won’t affect how it runs):
Before we move on, let’s summarize what we’ve completed so far:
- Created an automation account to store runbooks.
- Imported two runbooks (Connect-Azure & Connect-AzureVM) under the automation account.
- Manually created a runbook under the same automation account.
- Copied and pasted code into the manually created runbook.
Now we have to connect all the pieces together. Within the “remotePScommand” runbook you’ll see that there are a number of parameters that need information fed into them when the runbook is launched. Parameters can be called or manually entered when the runbook is launched. Some parameters are in the form of ASSETS.
Let’s take a look at what ASSETS are and how they’re used.
From the automation account portal select ASSETS:
At the bottom of the page select ADD SETTING:
Here we see several types of settings that can be consumed by runbooks:
ADD CONNECTION: To create a specific connection setting, you must import an integration module that contains the connection type definition.
ADD CREDENTIAL: Two types of credentials are available by default: Certificate and Windows PowerShell Credential.
ADD VARIABLE: the list below shows the list of available default variables:
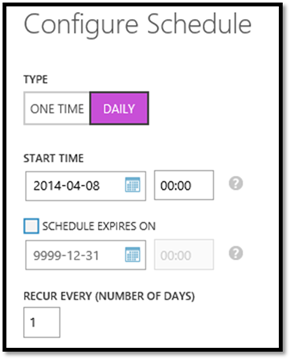
ADD SCHEDULE: schedule your runbooks to run at on specific days and times.
Let’s get back to the runbook where I’ll run a PowerShell command on an Azure VM.
I’ve defined a couple assets that I’ll reference when I launch the “remotePScommand” runbook.
The “Internal Subscription” is a connection to my Azure subscription and the “adminaccount” contains the administrator credentials that my Azure VM is configured to use for login:
EXECUTING A RUNBOOK
To test the runbook I created, I’ll navigate back to runbooks and select “remotePScommand”:
Then I'll select AUTHOR and DRAFT:
Now I’ll select TEST at the bottom of the page:
The following prompt is where we’ll use ASSETS as well as fill out other parameters:
After the runbooks executes, here is the final output it displays:
If you followed the steps above and created a similar automation runbook in Azure, Congratulations! If not, get started with Microsoft Azure Automation today.
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
Azure Automation Overview:
https://msdn.microsoft.com/library/azure/dn643629.aspx
Sample Azure Automation Scripts:
Comments
- Anonymous
January 01, 2003
Error:
27-04-2015 15:39:04, Error: [knswin.cloudapp.net] Connecting to remote server knswin.cloudapp.net failed with the following error message : Access
is denied. For more information, see the about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
+ CategoryInfo : OpenError: (knswin.cloudapp.net:String) [], PSRemotingTransportException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : AccessDenied,PSSessionStateBroken
27-04-2015 15:39:05, Error: Stop-AzureVM : Cannot validate argument on parameter 'ServiceName'. The argument is null or empty. Provide an argument
that is not null or empty, and then try the command again.
At knsremotepscommand:93 char:93
+
+ CategoryInfo : InvalidData: (:) [Stop-AzureVM], ParameterBindingValidationException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId :
ParameterArgumentValidationError,Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Commands.ServiceManagement.IaaS.StopAzureVMCommand
27-04-2015 15:39:06, Error: Backup-AzureVM : Cannot bind argument to parameter 'serviceName' because it is an empty string.
At knsremotepscommand:93 char:93
+
+ CategoryInfo : InvalidData: (:) [Backup-AzureVM], ParameterBindingValidationException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : ParameterArgumentValidationErrorEmptyStringNotAllowed,Backup-AzureVM
27-04-2015 15:39:06, Error: Start-AzureVM : Cannot validate argument on parameter 'ServiceName'. The argument is null or empty. Provide an argument
that is not null or empty, and then try the command again.
At knsremotepscommand:93 char:93
+
+ CategoryInfo : InvalidData: (:) [Start-AzureVM], ParameterBindingValidationException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId :
ParameterArgumentValidationError,Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Commands.ServiceManagement.IaaS.StartAzureVMCommand - Anonymous
April 28, 2014
Backing up a virtual machine in any cloud can be cumbersome. However with Microsoft Azure Automation - Anonymous
June 30, 2014
このポストは、6 月 26 日に投稿した Azure Automation: Your SQL Agent in the Cloud の翻訳です。
定期的なメンテナンスや管理ジョブをスケジュール設定できると