Manual removal of Conficker
Conficker Clean batch file including MSRT
================================
Microsoft support has created a simple batch file, ConfickerClean.txt, that can be used to help removal of the malware on workstations and remediate some of the collateral damage that was done by the malware. The batch file is attached, but a Microsoft Security Support engineer will need to provide the supporting files via another method as they are executables. The batch file has details about what changes and files are needed.
ConfickClean-v10.zip msrtrun-v2.txt
Manual Steps
===========
The following are detailed steps that will help us manually remove the malware from a system if your current Anti-Virus software is not able to or the automated methods provided are not used.
1. Do NOT log onto the system with a Domain account, if at all possible. Especially NOT a Domain Admin account. Log on as a local user account. The malware appears to impersonate the logged on user and access network resources under those users credentials so it can spread.
2. Stop the Server service and Task Scheduler service. This removes the Admin shares from the system so the malware cannot spread via this method and disables the scheduled task that gets added to the system by the malware. Please note that the Server service should only be disabled temporarily, especially on production servers as this will impact network resource availability.
a) You may not be able to disable the Task Scheduler service via the UI in Vista and WS2008. To disable it do the following
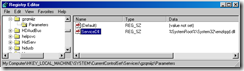
1. Open Regedit
2. Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Schedule
3. Open the value called Start
4. Change the setting from 0x2 to 0x4
5. After the reboot, the service will be disabled
3. Download and manually install MS08-067 - https://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/Bulletin/MS08-067.mspx
4. Reset any local admin and domain admin passwords to a complex password using guidance located here - https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc875814.aspx
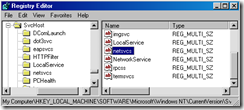
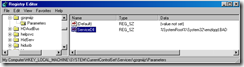
5. Run Regedit and drill down to the following key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SvcHost
On the right-hand pane, open netsvcs (highlited below) to see all the service names listed..
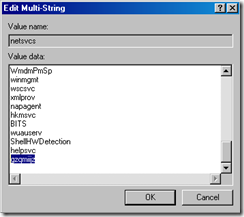
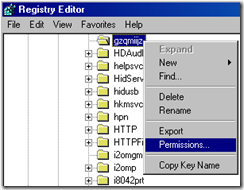
6. In the netsvcs listing, scroll down to the last couple entries in the list… if the machine is infected you will see a random looking name like the one below
In the example below, gzqmiijz is the name of the malware service…
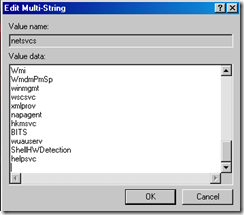
7. Delete the malware entry (make sure you have a blank line feed under the last legitimate entry as below)
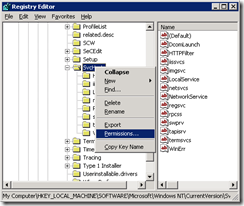
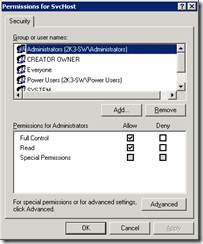
8. Now ACL down the SVCHOST registry key so it cannot be written to again
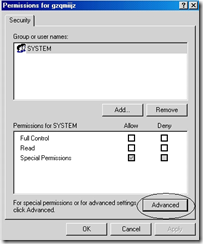
9. Right Click on the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Svchost and choose Permissions
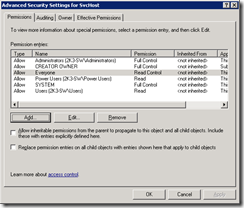
10. On Permissions Click on the Advanced button
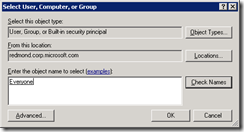
11. On the Advanced, click on the Add button
12. In the Select User, Computer or Group selection box, enter Everyone and click Check Names and click Okay after it resolves the Everyone group
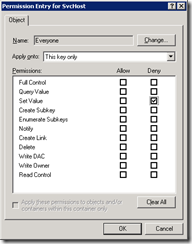
13. On the Permissions Entry window, change “Apply onto” setting to “This key only” and check the Deny column for Set Value
14. Click OK, Click OK again
15. Click Yes on the prompt
16. Click OK.
17. Now that you know the name of the malware service, go to the following registry key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ %BadServiceName%
In our example:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ gzqmiijz
18. Right click on the above malware service key and choose Permissions (note on Win2k you must use Regedt32 to set permissions):
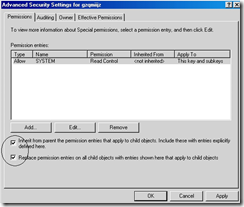
19. Click “Advanced”
20. Place a check on the following two items and click OK
- Inherit from parent entries that apply to child objects..
- Replace permission entries on all child objects…
21. After refreshing regedit (by hitting the F5 key) you will be able to see and edit the malware dll loading as a ServiceDll
22. At this point you can edit the above key so that the malware dll does not load…
23. There may be an entry under HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run that launches the malware that needs to be removed.
24. Check for Autorun.inf on any drives on the system, open with Notepad and verify it is really an Autorun.inf or not. Here is a sample of what a normal autorun.inf would look like the following and be 1-2kb in size –
[autorun]
shellexecute=Servers\splash.hta *DVD*
icon=Servers\autorun.ico
25. Remove the Autorun.inf if not valid.
26. Reboot the system.
27. Go to the path of the malware listed above
28. Edit the permissions on the file to include Full Control for Everyone
29. Then remove the file, in this example - %systemroot%\system32\emzlqqd.dll
30. Enable the BITS and Automatic Updates services via the Services.msc.
31. Remove all AT created scheduled tasks. Do this by running “AT /Delete /Yes”
32. Turn on the viewing of hidden files with the following command:
reg.exe add HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\Folder\Hidden\SHOWALL /v CheckedValue /t REG_DWORD /d 0x1 /f
33. Turn off Autorun to help mitigate any reinfection:
a) First download and install update https://support.microsoft.com/kb/953252, for Vista and WS2008, apply https://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/bulletin/ms08-038.mspx
b) The reference to MS08-038 for Vista and WS2008 has nothing to do with the malware exploiting this vulnerability. The security update contains the same fix as listed in KB953252, which is needed for the following registry key to function properly.
c) Then run the following command -
reg.exe add HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer /v NoDriveTypeAuto /t REG_DWORD /d 0xff /f
34. If the machine appears to be reinfected, then it is likely that one of the auto start locations did not get removed, such as the AT job or the Autorun.inf.
35. If possible, update the machine with all other missing Security Updates using Windows Update, WSUS, SMS, SCCM or your 3rd party patch management product. If you use SMS or SCCM, you will need to re-enable the Server service otherwise it may not be able to update the system.
36. There are other collateral damage items that this malware has caused. Please review the write up listed above for Conficker.b.
Comments
- Anonymous
May 19, 2009
The comment has been removed