How to disable optimizations when debugging Reference Source
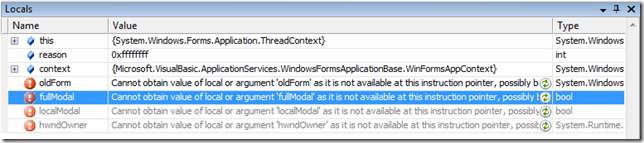
When you debug code in the .NET Framework using the newly available Reference Source functionality in VS 2008, you may notice that many variables are not available for inspection.
This is because you're debugging against retail-optimized code. In many cases, since you can still step through, this is something that's manageable.
But what if you really need to get a better idea of what's going on? Fortunately, there is a way.
What you need to do is to tell the CLR not to load the pre-JIT (aka NGEN) images. Here is how to do it.
First, create a CMD file that sets an environment variable, then launches Visual Studio. I called mine "NoOptDevEnv.cmd", and it's contents are as follows:
set COMPLUS_ZapDisable=1
cd /d "%ProgramFiles%\Microsoft Visual Studio 9.0\Common7\ide\"
start devenv.exe
exit
I put this cmd file on my desktop. When I want to disable optimizations, and only when I want to do this, I launch VS from this command.
Once in my Visual Studio project, do the following steps:
1) Right click on your project file and choose "Properties"
2) Choose the "Debug" tab and uncheck "Enable the Visual Studio Hosting Process"
3) Launch your application in the debugger.
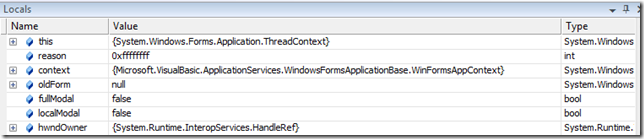
Now, you'll see full local and member variable information:
Finally, you may be asking yourself "What is the Visual Studio Hosting Process (aka VSHost), and what happens if I turn it off?" And this is a good question.
For the most part, disabling VSHost won't have any major impacts, but it will disable two features that you may be using.
First, you will not be able to do "Debug In Zone", which allows you to debug a process in the context of a security zone such as "Internet" or "Intranet". That won't work without VSHost.
Second, Design Time Expression Evaluation for class libraries will also not work. What that means, for example, is that if you are developing a Class Library, you won't be able to execute code from it in the Immediate Window while under the debugger.
In general, I recommend re-enabling VSHost (undo step 2 above) when you are finished with your debugging.
Hope that helps!
Comments
Anonymous
January 29, 2008
Wow, it's amazing!!, very good job, i love Microsoft.Anonymous
January 29, 2008
Reference Source デバッグ時に最適化を殺すにはAnonymous
January 30, 2008
You've been kicked (a good thing) - Trackback from DotNetKicks.comAnonymous
February 01, 2008
Kudos to Brian for editing everything last night, I think he's sleeping on my couch right now, but ourAnonymous
February 01, 2008
Kudos to Brian for editing everything last night, I think he's sleeping on my couch right now, butAnonymous
February 01, 2008
This is Episode #1 of <insert.name.here>, a weekly recap show of our favorite things for developersAnonymous
February 21, 2008
BTW, what does the "ZAP" acronym stand for?Anonymous
March 03, 2008
ZAP is an old name we had for the JIT'd assemblies. It's no longer in use - just like the name COMPLUS in reference to the CLR - but gives you an idea of how long this switch has been around!Anonymous
January 12, 2009
At one point or another, you run in the situation where you need to debug an application that makes useAnonymous
January 27, 2009
Sooner or later you may run into a situation where you need to evaluate a local variable under debuggerAnonymous
November 22, 2009
I cannot see the debug tab under project properties. I am using VS 2008, any ideas?Anonymous
October 06, 2010
Hi, Thank you for the absolutely great article, very useful. I would like to question though. I want to disable optimisations while debugging an ASP.NET application. I can't use the Visual Studio Internal Web Server (Cassini) because we use virtual host names extensively and (I think) Cassini doesn't support virtual host names. So the question is, can we disable optimisations while debugging IIS? Thanks, GeorgesAnonymous
December 23, 2010
To do this in VS 2010, right-click the project, Properties, Build, uncheck "Optimize code"