Microsoft Dynamics NAV: Architecture and Features
This article describe architecture, features and licensing model form Microsoft Dynamics NAV.
Architecture
NAV 2009&2013
The Microsoft Dynamics NAV software is composed of three major components (three-tier architecture):
- Data Tier: The Database Server, a database that stores the Microsoft Dynamics NAV data (as of NAV 2013 only Microsoft SQL Server)
- Middle or Server Tier: The Application Server (starting from NAV 2009 RTC), a service that managing all business logic and communication of Microsoft Dynamics NAV's operation
- Client Tier: The Client(s), the actual user interface into Microsoft Dynamics NAV.
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2009 has RTC (RoleTailored Client) and Classic Client.
- Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 has Windows Client (ex. named RTC), Web Client, Web Service Client, a SharePoint client through Microsoft Dynamics NAV Portal Framework, and a NAS services client for programmatic access.
Some common configurations are:
- All three components on the same computer. This is the configuration for a demo install, and is also typical for a development environment, so that a developer can work on Microsoft Dynamics NAV applications without worrying about network connections and inter-component security.
- Windows/RoleTailored client and Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server on the same computer, data tier on a separate computer.
- Each of the three tiers on a separate computer.
NAV2013R2
This version will come later until October 31st this year. This NAV version introduce better cloud environment with multi-tenancy system. You can read more about new architecture on [[Multi-tenancy in Dynamics NAV2013R2|Multi-tenancy page]].
Earlier versions
Previous Microsoft Dynamics NAV versions (before NAV 2009) has two-tier architecture. Two-tier architecture models are used in the true Client/Server Distributed Data solution. In two-tier architectures, the data and data manipulation layers reside on the server, whereas the application logic, presentation logic, and presentation layers reside on the client (we called 'Classic Client'). It puts the application logic (Business Logic) and presentation logic/layers (User Interface) on the client computer.
Features
Microsoft Dynamics NAV gives administrators the option of using either a Native database server or Microsoft SQL Server, as the DBMS (as of NAV 2013 only Microsoft SQL Server). SQL Server is better able to cope with large database sizes, but requires more maintenance than the classic database. The original database server is often referred to as 'C/SIDE' which refers to Client/Server Integrated Development Environment.
With NAV 2009, Microsoft introduced a completely new client interface which was named the RoleTailored Client (abbreviated RTC). Instead of a common experience for all users, the RTC improves efficiency by tailoring the NAV experience so users see only information pertinent to their role and day-to-day activities. Other notable improvements include several visual improvements such as support for charts, colorful reports, and adoption of a Microsoft Office style ribbon.
The NAV client interface previously available in versions 5 and older was retained in NAV 2009, but renamed the Classic Client.
While the Classic Client supports both Native and SQL databases, the RoleTailored Client requires a SQL database. Additionally, SQL database logins are not supported with the RoleTailored Client.
In October 2012, Microsoft released NAV 2013, which discontinued support for the Classic Client. The RoleTailored Client has been renamed the Windows Client. Additionally, a built-in Web Client and SharePoint Client were added. The Web Client does not require any special add-ins and works on computers and mobile devices alike.
Relative to Microsoft's other 3 ERP products, Dynamics NAV's sector is distribution and manufacturing companies that want more than “out of the box” functionality. The solution has a standard feature set, but it can also be thought of as an “ERP System construction set”. The Pascal-like development language is easily accessible to appropriate developers and is designed for rapidly customizing the software. There is no need for complex server side Transact-SQL stored procedures as the one language manages the application and database.
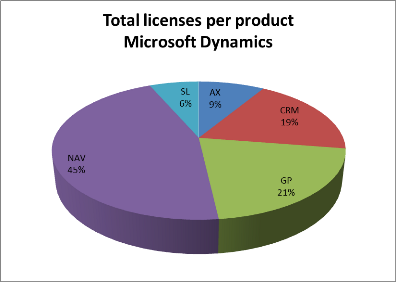
As per April 2013 Dynamics NAV is being used by 94,000 companies globally. The number of end users is estimated approx. two millions throughout the world. The facts show that Microsoft Dynamics NAV today represents 45% of the total installed Microsoft Dynamics licenses.
As a native International ERP, Microsoft Dynamics NAV is proposed with 43 official localizations and several unofficial ones (provided by local partners). These localizations ensure the full compliance of NAV with the local legal and fiscal rules. From 2013 version, Microsoft has changed the release cycle to make a major release every year, there is a product road map available for all the Dynamics products and the significant customer loyalty to all of the different Dynamics products will secure the focus on these many years ahead. The NAV solution is also compliant with IAS/IFRS.
Microsoft Dynamics NAV delivers integrated functionality to provide support for:
- Financial Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Manufacturing
- Distribution
- Customer Relationship Management
- Sales and Marketing
- Project and Resources Management
- Service Management
- Human Resource Management
As we said Microsoft Dynamics NAV is easy [[Customize Microsoft Dynamics NAV|Customize Solutions]], there are many Vertical Solutions for NAV.
Licensing model
Microsoft Dynamics NAV uses a concurrent user licensing model.
In 2006, Microsoft introduced the "Business Ready License" (BRL) model. The customer purchases user sessions, which have access to certain parts of the system included. There are two types of user - Business Essentials (BE) and Advanced Management (AM); AM provides access to more functionality than BE. Under the previous licensing model, "Module Based License" (MBL), users came with no functionality - this all had to be bought separately. Microsoft offers a path for customers to transition from MBL to BRL licensing.
With the arrival of NAV 2013, Microsoft introduced a new licensing model called "Perpetual Licensing", which considerably simplifies the pricing structure. When it comes to the user access/user types in NAV 2013, there are only 2 types of user licenses:
- Full User (full user license will have access to all the NAV data)
- Limited User (limited user will have read access to all the NAV data but with some write limitation)
All users are based on concurrent license model and both users can access NAV using any client (windows client, web Client, SharePoint client…).
[[Microsoft Dynamics NAV Overview|Return to Dynamics NAV Overview]]
Other Languages
This article is also available in other languages: