SQL Server: Getting Started with MS SQL Server on Ubuntu
1. Introduction
With Microsoft ❤ Linux ever so closely every day, Microsoft has released SQL Server vNext for public preview where you can deploy a SQL Server on a Linux operating system and still be able to be managed by SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) remotely. In this article, it will demonstrate how you can deploy the newly public preview release of SQL Server vNext on an Ubuntu Server to get you started.
2. Requirement
In this article, these will be requirements:
- Ubuntu Server 16.04 or higher
- SQL Server vNext CTP1 or higher
- SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) 16.5 or higher
3. Getting Started with Microsoft SQL Server on Ubuntu
To get started, you will have to deploy an Ubuntu Server with OpenSSH Server for SSH remote connectivity and the article will not be demonstrating or covering on how to deploy an Ubuntu Server nor OpenSSH Server into the server.
In general, you will be able to install SQL Server vNext using Bash shell commands on the terminal console and you may not require the OpenSSH Server but for this article it will provide examples on how to install the SQL Server vNext using Bash shell commands and PowerShell commands remotely through SSH as it is common practice for managing large enterprise environment.
So let us get started with deployment.
3.1. How to establishing SSH connectivity with Ubuntu Server?
In order to allow remote management of the Ubuntu server through SSH, you will need to install and setup OpenSSH Server on the Ubuntu server, and with that you will be able to establish SSH connectivity to issue Bash commands remotely.
3.1.1. Using PowerShell
In this example, it demonstrates the use of PosH-SSH PowerShell module to establish a SSH session with the Ubuntu server.
# Import Posh-SSH PowerShell Module
Import-Module `
-Global Posh-SSH ;
# Establish a SSH Session with the remote
# Linux Ubuntu server
New-SSHSession `
-ComputerName 192.168.150.235 `
-Credential (New-Object `
-TypeName System.Management.Automation.PSCredential `
-ArgumentList 'usr-ryen', `
(ConvertTo-SecureString `
-String 'myUbuntuPassword' `
-AsPlainText `
-Force) `
) `
-Force ;
# Display the remote Linux Ubuntu server's
# Operating System description
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'lsb_release -d' ;
3.1.2. Using PuTTY
In this example, it demonstrates the use of PuTTY to establish a SSH session with the Ubuntu server to issue the Bash shell commands.
# Download PuTTY to C:\Temp
Invoke-WebRequest `
-Uri 'https://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/latest/x86/putty.exe' `
-OutFile 'C:\Temp\putty.exe' ;
# Launch PuTTY and connect to
# the Ubuntu server using SSH
Start-Process `
-FilePath 'C:\Temp\putty.exe' `
-ArgumentList '192.168.150.235' ;
# Display the remote Linux Ubuntu server's
# Operating System description in Bash Shell
lsb_release -d
3.2. How to add the Public Repository GPG Key?
In order to access the Microsoft SQL Server Ubuntu repository, you will need to obtain the Public Repository GPG Key from Microsoft and add the key to the Ubuntu's Advanced Packaging Tool (APT).
3.2.1. Using PowerShell
In this example, it demonstrates the use of Invoke-SSHCommand PowerShell cmdlet to issue Bash shell command remotely to obtain and add the key into APT.
# Add the Microsoft Public Repository
# GPG Key into the Linux Ubuntu server
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo myUbuntuPassword | sudo -S curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo -S apt-key add -' ;
3.2.2. Using PuTTY
In this example, it demonstrates the use of PuTTY to issue Bash shell command remotely to obtain and add the key into APT.
# Add the Microsoft Public Repository
# GPG Key into the Linux Ubuntu server
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add -
3.3. How to register Microsoft SQL Server Ubuntu repository?
In order to download the Microsoft SQL Server from the repository, you will need to register the Microsoft SQL Server Ubuntu Repository to obtain the package.
3.3.1. Using PowerShell
In this example, it demonstrates the use of Invoke-SSHCommand PowerShell cmdlet to issue Bash shell command remotely to register the repository and initialize an update to the list of packages available.
# Register the Microsoft SQL Server
# Ubuntu repository
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo myUbuntuPassword | sudo -S curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/16.04/mssql-server.list | sudo -S tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mssql.list' ;
# Get Advanced Package Tool (APT) to
# initialize an update
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo myUbuntuPassword | sudo -S apt-get update' ;
3.3.2. Using PuTTY
In this example, it demonstrates the use of PuTTY to issue Bash shell command remotely to register the repository and initialize an update to the list of packages available.
# Register the Microsoft SQL Server
# Ubuntu repository
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/16.04/mssql-server.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mssql-server.list
# Get Advanced Package Tool (APT) to
# initialize an update
sudo apt-get update
3.4. How to install Microsoft SQL Server vNext on Ubuntu?
Now that Ubuntu's Advanced Packaging Tool (APT) has been configured, in this article you will be shown the example of installing the Microsoft SQL Server package and execute the setup to configure, start and register SQL Server as a service.
3.4.1. Using PowerShell
In this example, it demonstrates the use of Invoke-SSHCommand PowerShell cmdlet to issue Bash shell command remotely to install the Microsoft SQL Server package and complete the setup.
# Use Advanced Package Tool (APT) to
# initialize an install of mssql-server
# package
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo myUbuntuPassword | sudo -S apt-get install -y mssql-server' ;
# Create a SA_PASSWORD system-wide environment variable
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command "echo myUbuntuPassword | sudo -S echo SA_PASSWORD='""myMSSQLPa55w0rd""' | sudo -S tee --append /etc/environment" ;
# Verify if the SA_PASSWORD system-wide environment
# variable
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo $SA_PASSWORD' ;
# Remove the existing SSH Session
Remove-SSHSession `
-SessionId 0 ;
# Re-establish a SSH Session with the remote
# Linux Ubuntu server so that $SA_PASSWORD
# will be loaded in this new SSH session
New-SSHSession `
-ComputerName 192.168.150.235 `
-Credential (New-Object `
-TypeName System.Management.Automation.PSCredential `
-ArgumentList 'usr-ryen', `
(ConvertTo-SecureString `
-String 'myUbuntuPassword' `
-AsPlainText `
-Force) `
) `
-Force ;
# Re-verify if the SA_PASSWORD system-wide environment
# variable
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo $SA_PASSWORD' ;
# Use sqlservr-setup to initialize
# the setup from the mssql-server
# package
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo myUbuntuPassword | sudo -S /opt/mssql/bin/sqlservr-setup --accept-eula --start-service --enable-service --set-sa-password' ;
3.4.2. Using PuTTY
In this example, it demonstrates the use of PuTTY to issue Bash shell command remotely to install the Microsoft SQL Server package and complete the setup.
# Use Advanced Package Tool (APT) to
# initialize an install of mssql-server
# package
sudo apt-get install -y mssql-server
# Create a SA_PASSWORD system-wide environment variable
echo SA_PASSWORD="" | sudo tee --append /etc/environment
# Verify if the SA_PASSWORD system-wide environment
# variable
echo $SA_PASSWORD
# Exit the current SSH Session in PuTTY
# and reestablish a new SSH Session
# using PuTTY
exit
# Re-verify if the SA_PASSWORD system-wide environment
# variable
echo $SA_PASSWORD
# Use sqlservr-setup to initialize
# the setup from the mssql-server
# package
sudo /opt/mssql/bin/sqlservr-setup --accept-eula --start-service --enable-service --set-sa-password
3.5. How to register Microsoft Ubuntu repository?
With Microsoft SQL Server installed and configured on the Ubuntu server, you may want to know where you could obtain the Microsoft SQL Server tools for managing the database in Linux bash shell in Ubuntu server. In this section, you will need to register the Microsoft Ubuntu repository in order to obtain the Microsoft SQL Server tools.
3.5.1. Using PowerShell
In this example, it demonstrates the use of Invoke-SSHCommand PowerShell cmdlet to issue Bash shell command remotely to register the Microsoft Ubuntu repository and initialize an update to the list of packages available.
# Show a list of Public Repository
# GPG Key stored in the Linux Ubuntu server
# and verify you have the Microsoft Public Repository
# GPG Key
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo myUbuntuPassword | sudo -S apt-key list' | Select `
-ExpandProperty Output ;
# Add the Microsoft Public Repository
# GPG Key into the Linux Ubuntu server if
# you have not done this in section 3.2.1
<#
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo myUbuntuPassword | sudo -S curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo -S apt-key add -' ;
#>
# Register the Microsoft Ubuntu
# repository
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo myUbuntuPassword | sudo -S curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/16.04/prod.list | sudo -S tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/msprod.list' ;
# Get Advanced Package Tool (APT) to
# initialize an update
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo myUbuntuPassword | sudo -S apt-get update' ;
3.5.2. Using PuTTY
In this example, it demonstrates the use of PuTTY to issue Bash shell command remotely to register the Microsoft Ubuntu repository and initialize an update to the list of packages available.
# Show a list of Public Repository
# GPG Key stored in the Linux Ubuntu server
# and verify you have the Microsoft Public Repository
# GPG Key
sudo apt-key list
# Add the Microsoft Public Repository
# GPG Key into the Linux Ubuntu server if
# you have not done this in section 3.2.1
#
# sudo curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo -S apt-key add -
#
# Register the Microsoft Ubuntu
# repository
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/16.04/prod.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/msprod.list
# Get Advanced Package Tool (APT) to
# initialize an update
sudo apt-get update
3.6. How to install Microsoft SQL Server Tools on Ubuntu?
Now that Ubuntu's Advanced Packaging Tool (APT) has been configured, in this article you will be shown the example of installing the Microsoft SQL Server Tools package into the Ubuntu server.
3.6.1. Using PowerShell
In this example, it demonstrates the use of Invoke-SSHCommand PowerShell cmdlet to issue Bash shell command remotely to install the Microsoft SQL Server Tools package and query the version using sqlcmd Bash command.
# Use Advanced Package Tool (APT) to
# initialize an install of mssql-tools
# package
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'echo myUbuntuPassword | sudo -S ACCEPT_EULA=Y apt-get install mssql-tools -y -q' ;
# Use the sqlcmd Bash command from the
# installed mssql-tools package to
# establish a loopback connection to
# the the Microsoft SQL Server in Ubuntu
# and query the version
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-SessionId 0 `
-Command 'sqlcmd -S 127.0.0.1 -U sa -P myMSSQLPa55w0rd -Q "PRINT ''Hostname: '' + @@SERVERNAME ; PRINT @@Version" ' | Select `
-ExpandProperty Output ;
3.6.2. Using PuTTY
In this example, it demonstrates the use of PuTTY to issue Bash shell command remotely to install the Microsoft SQL Server Tools package and query the version using sqlcmd Bash command.
# Use Advanced Package Tool (APT) to
# initialize an install of mssql-tools
# package
sudo ACCEPT_EULA=Y apt-get install mssql-tools -y -q
# Use the sqlcmd Bash command from the
# installed mssql-tools package to
# establish a loopback connection to
# the the Microsoft SQL Server in Ubuntu
# and query the version
sqlcmd -S 127.0.0.1 -U sa -P myMSSQLPa55w0rd -Q "PRINT 'Hostname: ' + @@SERVERNAME ; PRINT @@Version"
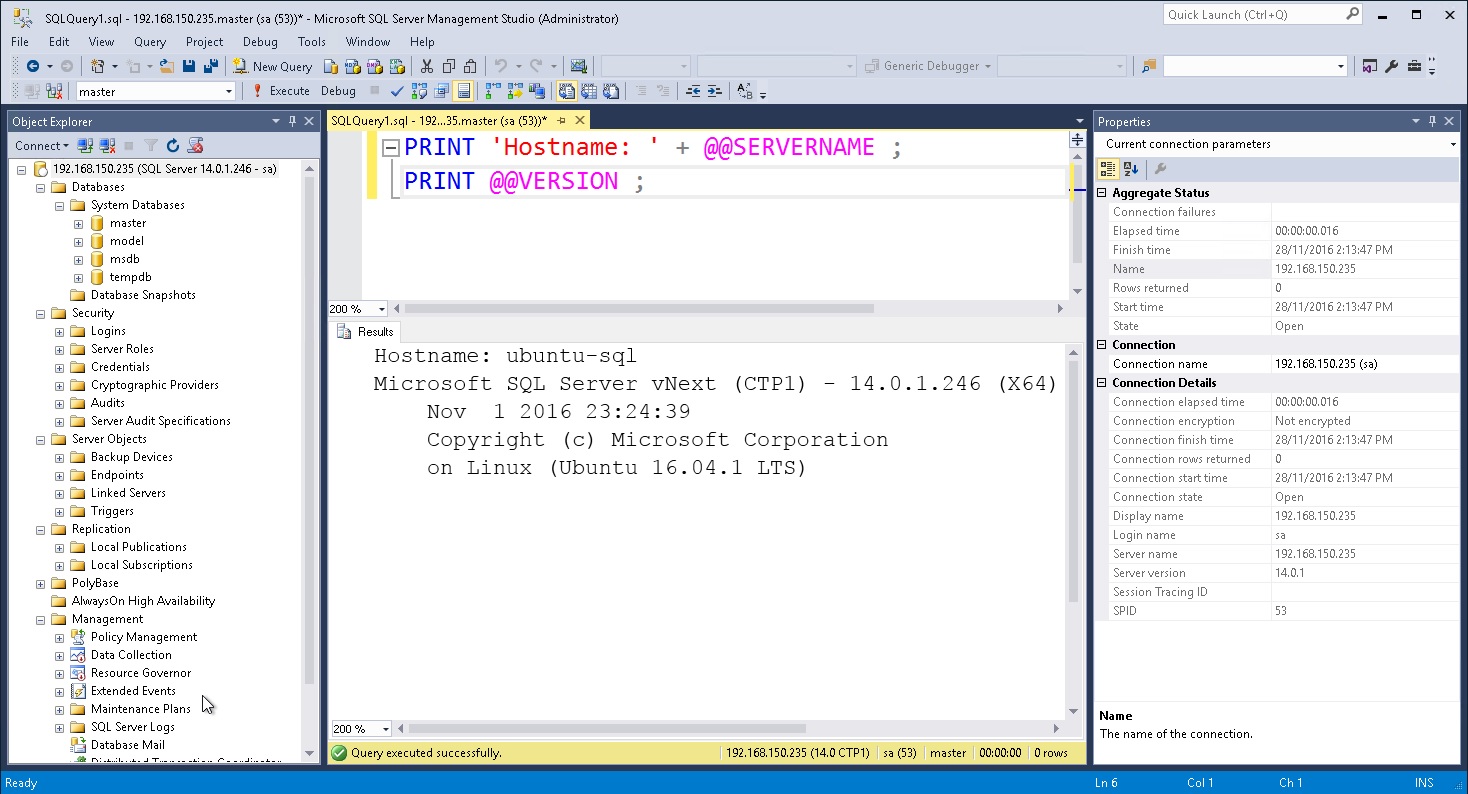
3.7 How to use Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to manage remotely?
In this section, it will demonstrate how you can use Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to manage your Microsoft SQL Server on Ubuntu remotely from a management server.
# Download SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) 16.5
# to C:\Temp
Invoke-WebRequest `
-Uri 'http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=832812' `
-OutFile 'C:\Temp\SSMS-Setup-ENU.exe' ;
# Install Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) 16.5
# on Management Server
Start-Process `
-FilePath 'C:\Temp\SSMS-Setup-ENU.exe' `
-ArgumentList '/install /quiet /log C:\Temp\SSMS-Setup-ENU_Installation.log' ;
# Launch Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) 16.5
# on Management Server to connect to SQL Server on Ubuntu
Start-Process `
-FilePath 'C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SQL Server\130\Tools\Binn\ManagementStudio\Ssms.exe' `
-ArgumentList '-S 192.168.150.235 -U sa -P myMSSQLPa55w0rd' ;
4. Conclusion
There you have it. After establishing connectivity using Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) with the SA credential, you can see if it get connected to the server and you can issue your SQL Transact-SQL Syntax Query statement to determine the version that you deployed on Ubuntu. If you happen to have a Firewall on the Ubuntu server, you will need to allow TCP Port 1433 traffic to the Ubuntu server to allow connection from the SSMS remotely.
5. Reference
- Microsoft SQL Server on Linux Public Preview Technical Whitepaper
- Microsoft Docs - SQL Server on Linux Documentation
- Microsoft Docs - Install SQL Server on Ubuntu by Jason Roth
- Microsoft Docs - Install SQL Server tools on Linux by Jason Roth
- Microsoft Docs - Use SSMS to Manage SQL Server on Linux by Sanjay Nagamangalam
- GitHub - PoSH-SSH by Carlos Perez
6. See Also