RDP Direct Connection Process with NLA Enabled
Summary
This article is an overview of the Remote Desktop Protocol connection sequence for a direct connection (not through an RDS Gateway) from client machine to server machine. Please see parent article [[articles:Remote Desktop Services RDS Logon Connectivity Overview]] for additional information.
Environment
- Windows RDS 2012 r2 role installed only
- Using Remote Desktop Connection client (mstsc.exe) connecting directly to RDSH server
- No RD Gateway
Connection process
- User starts Remote Desktop Connection client (mstsc.exe) on client machine and enters machine to connect to. RDS client machine connects to Active Directory for Kerberos ticket for connecting to RDSH server.
- Connection is initialized to RDSH server.
- TCP connection over port 3389 is created from client to Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH) Remote Desktop Service
- By default client and server support multi transport (UDP) and two additional ports are also created
- RDS Server connects to Active Directory Domain Controller over LDAP 389 to authenticate user using Kerberos port 88 authentication
- RDS Server connects to Remote Desktop License Server (RDLS) over RPC port 135 to verify license
- RDS License server connects to AD to authenticate RDSH and verify / modify user object attributes for per user RDS CAL
- RDS License server responds to RDSH
- RDS Server connects to AD to request user Kerberos ticket for session logon
- Session is then allowed to logon and start initial application
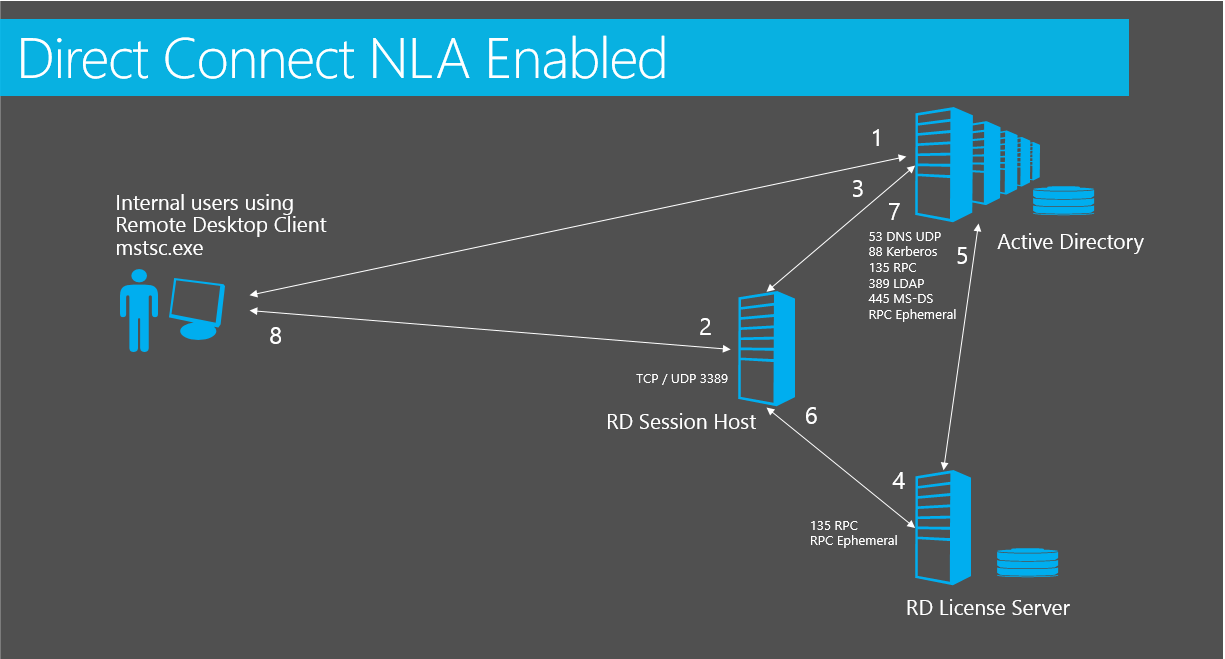
RDP Connectivity process for RDS Role Deployment with NLA enabled
The connectivity process when connecting directly to an RDS server that is installed as an 'RDS Role' with no RDS Connection Broker is as follows:
This is assuming both the RDS Session Host (RDSH) and the client are in an Active Directory domain and that Network Level Authentication (NLA) is enabled. Single Sign On is not enabled.
User logs on to client workstation launches Remote Desktop Connection application (mstsc.exe). The client machine connects to Active Directory to request Kerberos ticket to be used to connect to RDS server.
The client machine connects to the RDSH server by default on port 3389.
As NLA is enabled, the user authenticates before session is started to RDSH server. If NLA was disabled, the authentication would take place only on the RDSH server inside a windows session.
The RDSH server will then verify RDS per user / per device Client Access License (CAL) with the RDS License server.
The license server queries / updates Active Directory for user account license attributes and responds to RDSH server. If this is the first logon a temporary CAL will be issued. On the second logon, a permanent CAL will be issued.
RD License server responds to RDSH server.
RDS server authenticates user against Active Directory and gets kerberos token.
Once the Active Directory authentication process is complete, RDS CAL has been issued or verified, and Group Polices have been applied, the user will be presented with the Desktop.
For detailed events to look for in both event logs and network traces, click on the links below:
Client workstation
[[RDP Direct Connection with NLA Remote Desktop Client Event Logs]]
[[RDP Direct Connection with NLA Remote Desktop Client event Logs Debug]]
[[RDP Direct Connection with NLA Remote Desktop Client Network]]
Remote Desktop Session Host
[[RDP Direct Connection with NLA RDS Session Host Event Logs]]
[[RDP Direct Connection with NLA RDS Session Host Event Logs Debug]]
[[RDP Direct Connection with NLA RDS Session Host Network Trace]]
Remote Desktop License Server
[[RDP Direct Connection with NLA RDS License Server Event Logs]]
[[RDP Direct Connection with NLA DS License Server Network Trace]]
Active Directory Domain Controller
[[RDP Direct Connection with NLA Active Directory Domain Controller Event Logs]]
[[RDP Direct Connection with NLA Active Directory Network Trace]]