Send smtp email with Azure blob storage attachments
1 Introduction
Smtp is the most common protocol to send messages over the internet. Smtp stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. Smtp messages are secured using SSL by default, so no need to worry about security.
Azure Blob storage is going to store unstructured data as binary files, text files, any type of data in the cloud. It can store an image, document or a video as a blob, simply as an object. You can select a specific tier to store your blobs by referring to the pricing models of Azure blob storage.
Let's see how we can store a file in Azure blob storage and send it using smtp email.
2 Background
If you want to know how to send an email using smtp, Please go through this article, https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/36282.c-create-a-simple-smtp-email-with-html-body.aspx
If you want to know how to send an email concurrently using a windows service, check this article, https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/36288.how-to-fire-an-email-using-a-windows-service.aspx
3 Store files in the blob storage
This article is going to describe how to store an image, text file and a video in azure blob storage,
3.1 Create a storage account in Azure portal
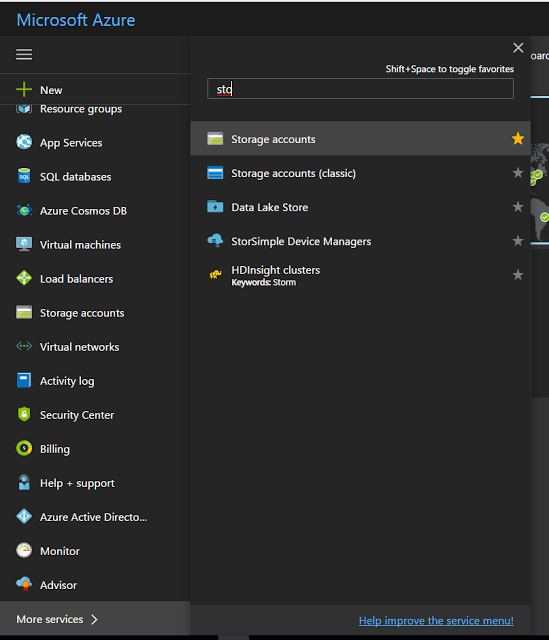
Log in to Azure portal, https://portal.azure.com Click on More Services link as below, It will open up all available services in azure portal. click on Storage accounts
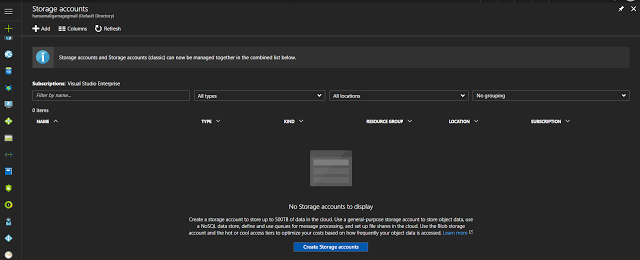
All storage accounts are displayed in here, currently this azure account doesn't have any storage accounts. Click on Create Storage accounts to create a new storage account.
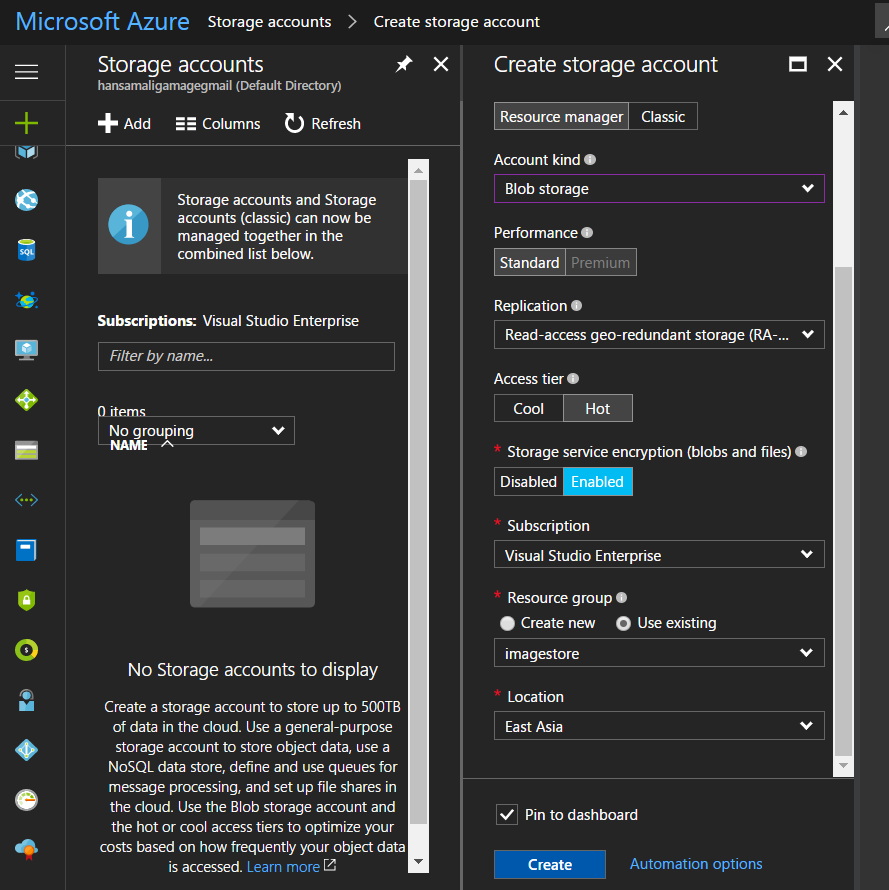
Add a name to the storage account, in this example, it's *mailfilestore
*Deployment model is going to tell how your storage account is going to deploy and manage, select Resource manager as Deployment model, storage accounts created by Azure portal is deployed under Resource manager Deployment model, it has newer features in Azure, and accounts created by Azure classic portal is deployed under classic.
In Account kind, it says what type of a storage account you want to use, General purpose accounts are going to store blobs, files, tables and queues,If you select account type as blob storage, it stores only blobs.
If you select Blob storage as account type, it's going to disable premium performance, You need to go for premium performance, when you need low latency performance like accessing virtual machine disks and databases. In here we are going to access files stored in a storage, We don't need to access stored images very frequently like accessing a database, so go for standard performance, that's enough.
You need to select a way to replicate storage account to maintain high availability and durability. Replication copies your data into a same data center or another data center. Let's select default replication method, Read access geo redundant storage (RA-GRS), in this replication method, it's going to replicate data into multiple data centers and data reads can be performed in secondary data center as well.
In Access tier, you can specify how you can access stored data. You can select Hot Access tier for more frequent data access, Cool access tier for less frequent access data like backups. In this example, let's select Hot access tier.
Storage service encryption is going to protect your data using encryption within data center,
Select your subscription for storage account,
Create a new resource group or use an existing resource group. When you use a resource group, you can deploy and manage all your resources in that group separately. You can redeploy all your resources in that resource group into another location.
select a region to store your storage account, let's select East Asia, since it's near to me
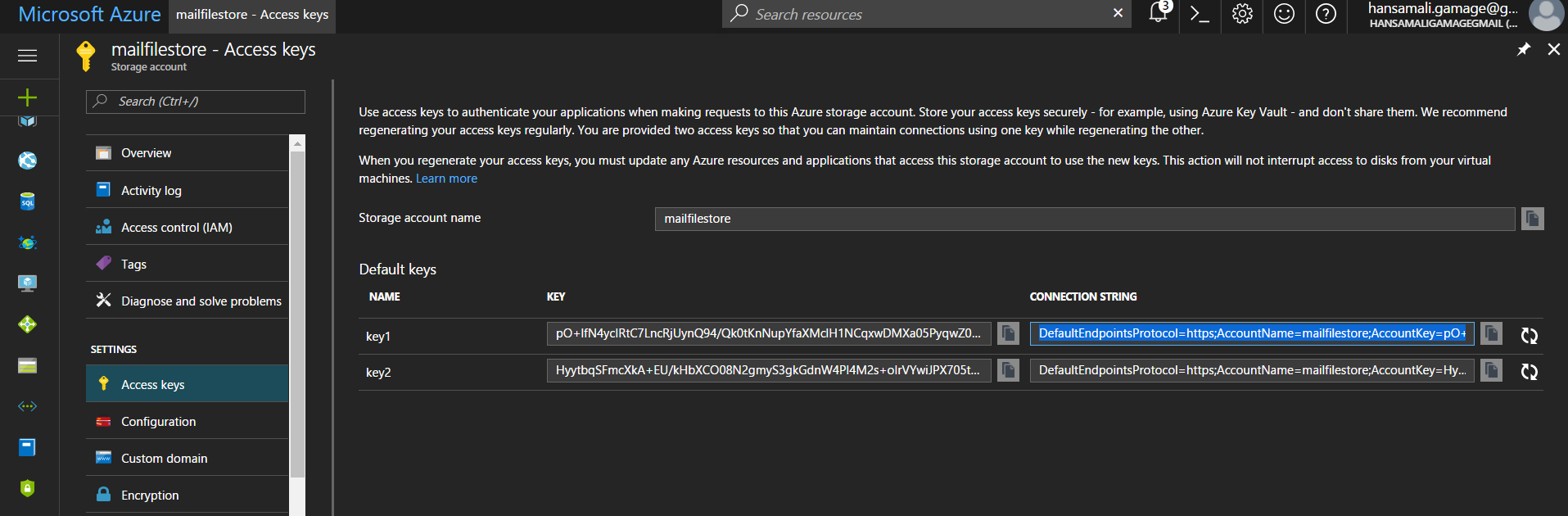
Go to storage account and search for Access Keys and copy connectionstring of key1 in access keys,
If you wonder why storage account has two access keys, Azure has recommended to regenerate access keys frequently in order to maintain security of your stored data. While you regenerating a one access key, you can use second access key to manage your storage without any issue, since you have two access keys.
3.2 Let's add some code to save your files in blob storage
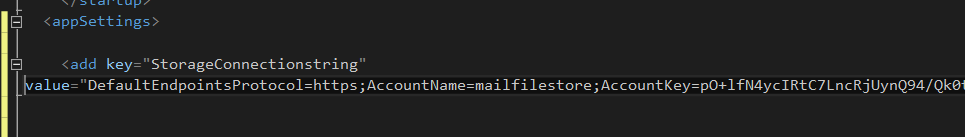
Create a console application in Visual studio, we want to store storage connection-string as a configuration in our application. Create a configuration setting in app.config file as below.
<appSettings>
<add key="StorageConnectionstring"
value="DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=mailfilestore;AccountKey=pO+lfN4ycIRtC7LncRjUynQ94/Qk0tKnNupYfaXMclH1NCqxwDMXa05PyqwZ0FVaWNgVfVARF4xvCKWq+POkSQ==;EndpointSuffix=core.windows.net"/>
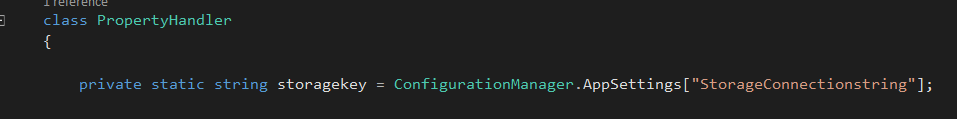
Create a class to handle blob storage saving, In this example PropertyHandler class is going to do that. In PropertyHandler class, initialize a private variable to hold the storage connection string
private static string storagekey = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["StorageConnectionstring"];
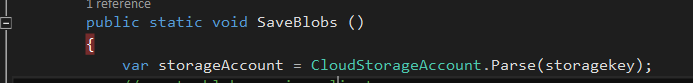
Create a method to save to blob storage, and create an Azure storage account by passing storage key parameter,
public static void SaveBlobs ()
{
var storageAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse(storagekey);
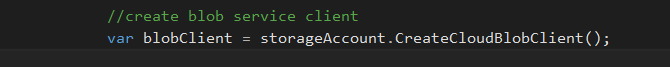
Create blob service client using azure storage account,
//create blob service client
var blobClient = storageAccount.CreateCloudBlobClient();
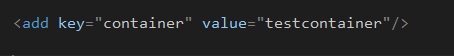
add a configuration into app.config file to define the container,
<add key="container" value="testcontainer"/>
Define a container name to store files in azure storage account
private static string containerstring = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["container"];
Create a reference to the container like this,
var container = blobClient.GetContainerReference(containerstring);
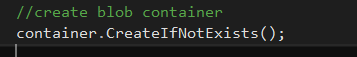
Create blob container if it doesn't exist,
//create blob container
container.CreateIfNotExists();
Set container permission to public, so any client can read your blob data, if you want to change access level, modify access policies on blob storage
container.SetPermissions( new BlobContainerPermissions { PublicAccess = BlobContainerPublicAccessType.Blob });
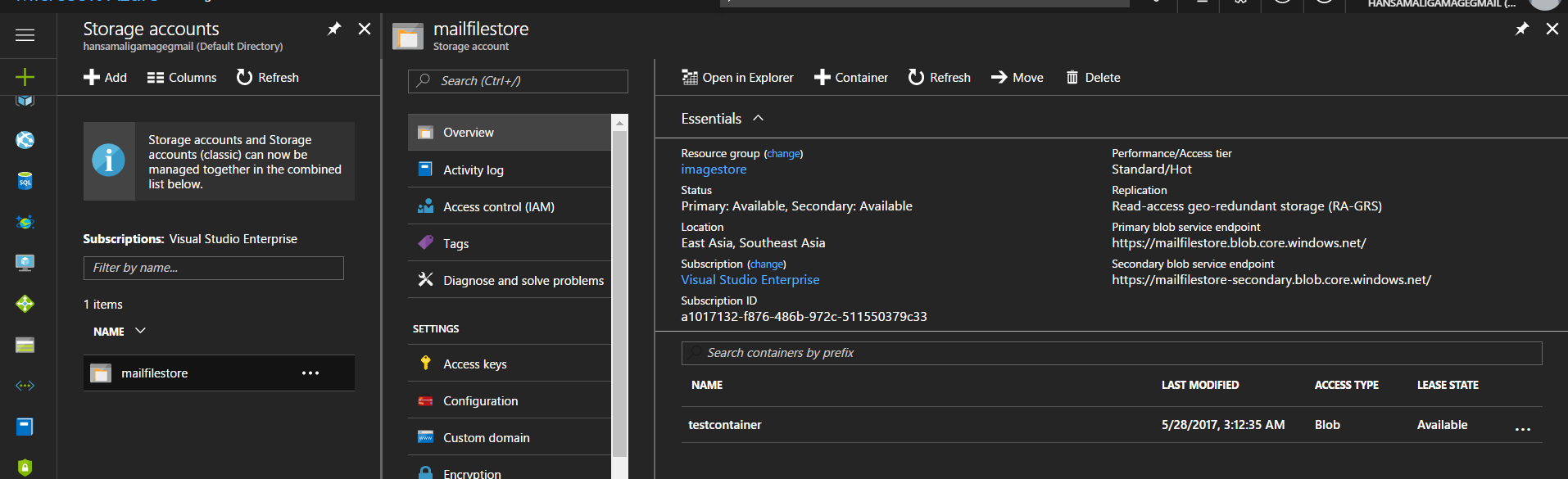
Go to created storage account and click on Overview section and you can see available containers, you'll see container you created as below, check access type of the container, it's *Blob type
3.2.1 Save image to a blob storage
Let's add more coding to save an image to a blob storage,
Create a configuration to hold image path in app.config file,
<add key="imagePath" value="C:\store\images.jpg"/>
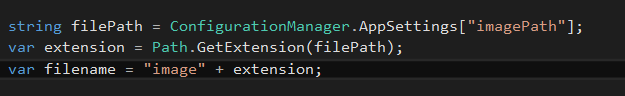
access imagepath to get path of an image, get file extension and append it to the file name.
string filePath = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["imagePath"];
var extension = Path.GetExtension(filePath);
var filename = "image" + extension;
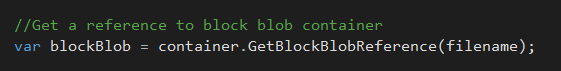
Get a reference to blob container,
//Get a reference to block blob container
var blockBlob = container.GetBlockBlobReference(filename);
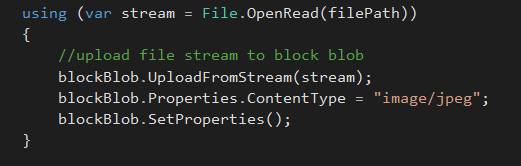
upload image to blob storage, don't forget to set the content type of the image as jpeg, and update blob properties after that.
using (var stream = File.OpenRead(filePath))
{
//upload file stream to block blob
blockBlob.UploadFromStream(stream);
blockBlob.Properties.ContentType = "image/jpeg";
blockBlob.SetProperties();
}
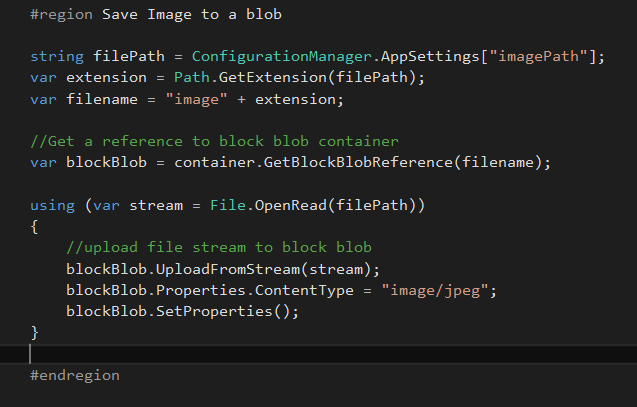
You can see complete code to save an image to a blob storage,
#region Save Image to a blob
string filePath = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["imagePath"];
var extension = Path.GetExtension(filePath);
var filename = "image" + extension;
//Get a reference to block blob container
var blockBlob = container.GetBlockBlobReference(filename);
using (var stream = File.OpenRead(filePath))
{
//upload file stream to block blob
blockBlob.UploadFromStream(stream);
blockBlob.Properties.ContentType = "image/jpeg";
blockBlob.SetProperties();
}
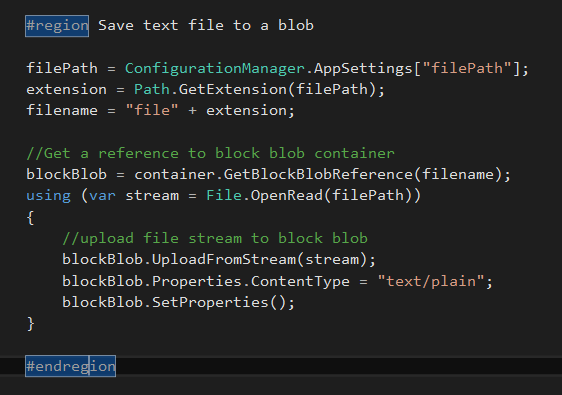
This code sample describes how to store a text file in blob storage, Get the configured file path, and store file in blob storage and set content type as text/plain
#region Save text file to a blob
filePath = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["filePath"];
extension = Path.GetExtension(filePath);
filename = "file" + extension;
//Get a reference to block blob container
blockBlob = container.GetBlockBlobReference(filename);
using (var stream = File.OpenRead(filePath))
{
//upload file stream to block blob
blockBlob.UploadFromStream(stream);
blockBlob.Properties.ContentType = "text/plain";
blockBlob.SetProperties();
}
#endregion
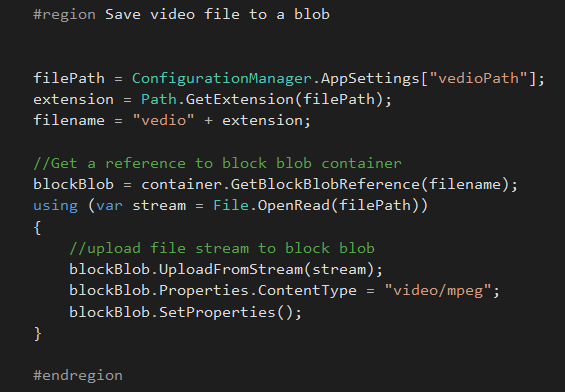
You can save a video file to a blob storage as below,
#region Save video file to a blob
filePath = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["vedioPath"];
extension = Path.GetExtension(filePath);
filename = "vedio" + extension;
//Get a reference to block blob container
blockBlob = container.GetBlockBlobReference(filename);
using (var stream = File.OpenRead(filePath))
{
//upload file stream to block blob
blockBlob.UploadFromStream(stream);
blockBlob.Properties.ContentType = "video/mpeg";
blockBlob.SetProperties();
}
#endregion
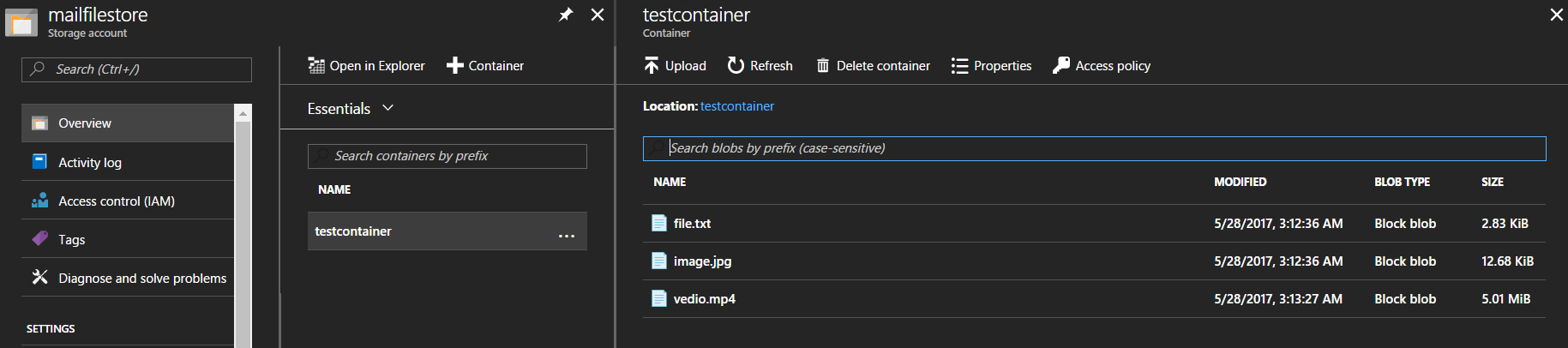
Go inside test container and view available files in it,
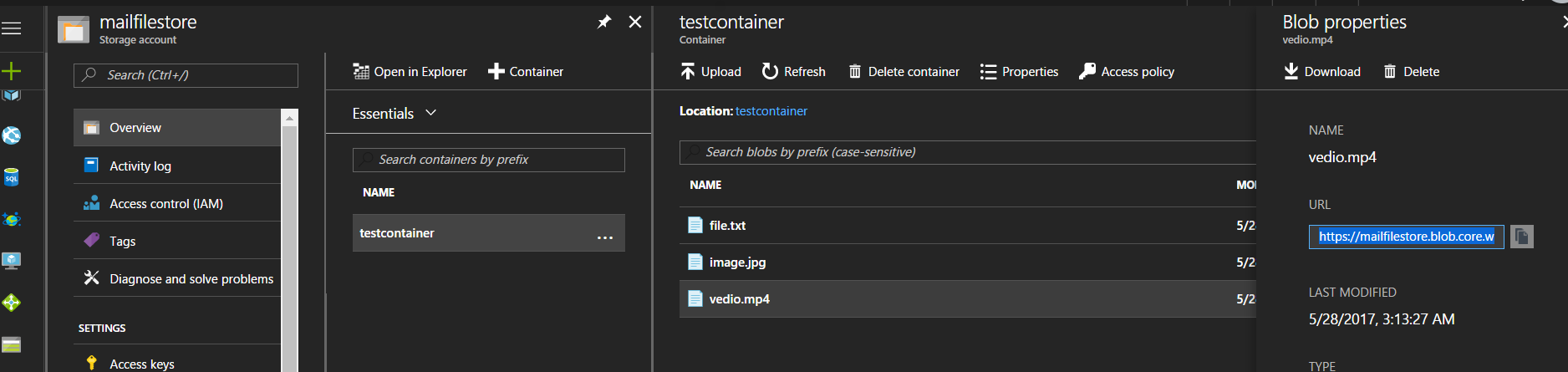
If you want to open one of this file, select a file and you can see the URL of it.
4 Send email with stored files as attachments
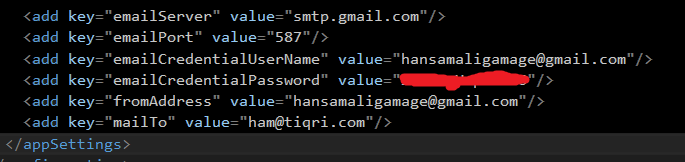
Define configuration settings used to send an email,
In this example, used gmail server as email server with specific port. email from and to addresses are also defined as a configurable setting.
<add key="emailServer" value="smtp.gmail.com"/>
<add key="emailPort" value="587"/>
<add key="emailCredentialUserName" value="hansamaligamage@gmail.com"/>
<add key="emailCredentialPassword" value=""/>
<add key="fromAddress" value="hansamaligamage@gmail.com"/>
<add key="mailTo" value="ham@tiqri.com"/>
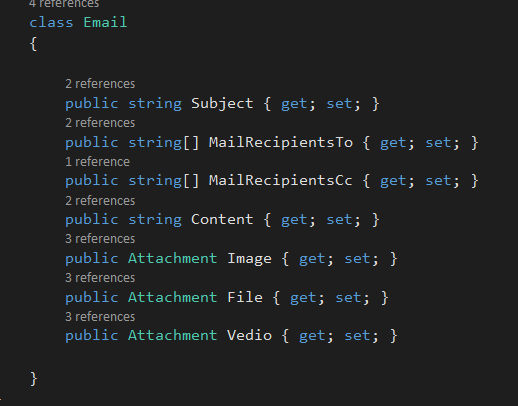
Create a class to set email properties as below,
class Email
{
public string Subject { get; set; }
public string[] MailRecipientsTo { get; set; }
public string[] MailRecipientsCc { get; set; }
public string Content { get; set; }
public Attachment Image { get; set; }
public Attachment File { get; set; }
public Attachment Vedio { get; set; }
}
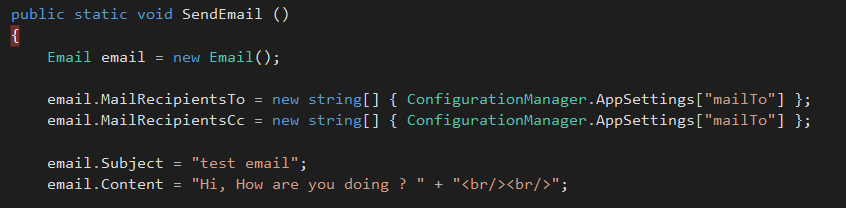
In sample application, create a separate class to send an email,
public static void SendEmail ()
{
Email email = new Email();
email.MailRecipientsTo = new string[] { ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["mailTo"] };
email.MailRecipientsCc = new string[] { ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["mailTo"] };
email.Subject = "test email";
email.Content = "Hi, How are you doing ? " + "<br/><br/>";
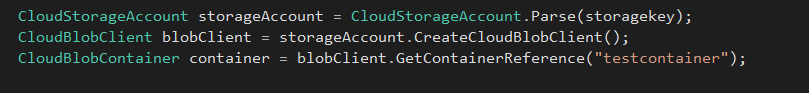
Get Azure storage account reference by passing storage account connection string, create the blob client and get a reference to storage container,
CloudStorageAccount storageAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse(storagekey);
CloudBlobClient blobClient = storageAccount.CreateCloudBlobClient();
CloudBlobContainer container = blobClient.GetContainerReference("testcontainer");
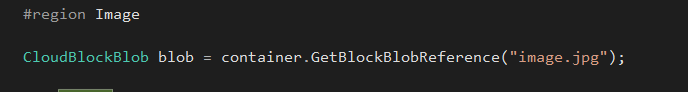
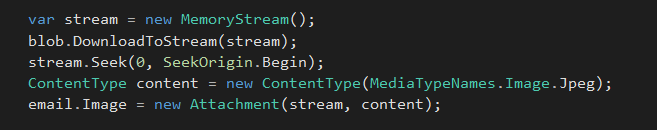
Get a reference to image, we stored in test container,
#region Image
CloudBlockBlob blob = container.GetBlockBlobReference("image.jpg");
Download file to memory stream, and set content type and create a new attachment object from it.
var stream = new MemoryStream();
blob.DownloadToStream(stream);
stream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
ContentType content = new ContentType(MediaTypeNames.Image.Jpeg);
email.Image = new Attachment(stream, content);
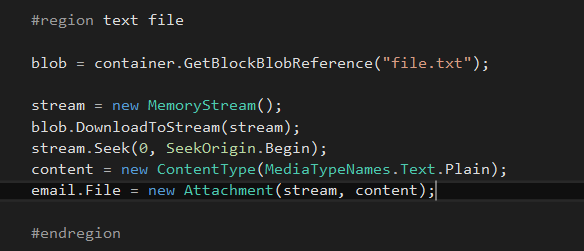
As same as image, create a new attachment from text file and set the content type as plain, if content type doesn't set properly, it will attach file as a invalid type of file.
#region text file
blob = container.GetBlockBlobReference("file.txt");
stream = new MemoryStream();
blob.DownloadToStream(stream);
stream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
content = new ContentType(MediaTypeNames.Text.Plain);
email.File = new Attachment(stream, content);
#endregion
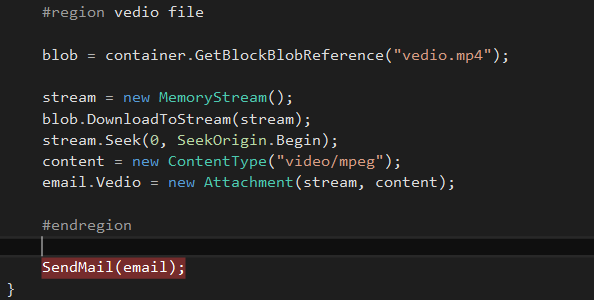
create the video attachment as well,
#region vedio file
blob = container.GetBlockBlobReference("vedio.mp4");
stream = new MemoryStream();
blob.DownloadToStream(stream);
stream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
content = new ContentType("video/mpeg");
email.Vedio = new Attachment(stream, content);
#endregion
SendMail(email);
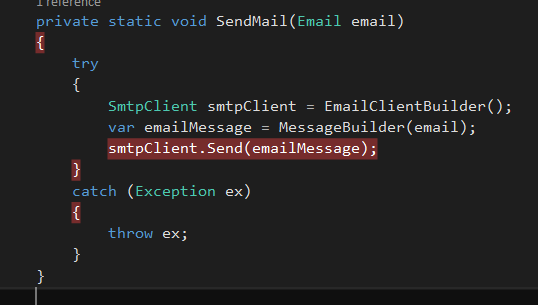
Create a method to send email as below, its going to construct the email and sends it
private static void SendMail(Email email)
{
try
{
SmtpClient smtpClient = EmailClientBuilder();
var emailMessage = MessageBuilder(email);
smtpClient.Send(emailMessage);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ex;
}
}
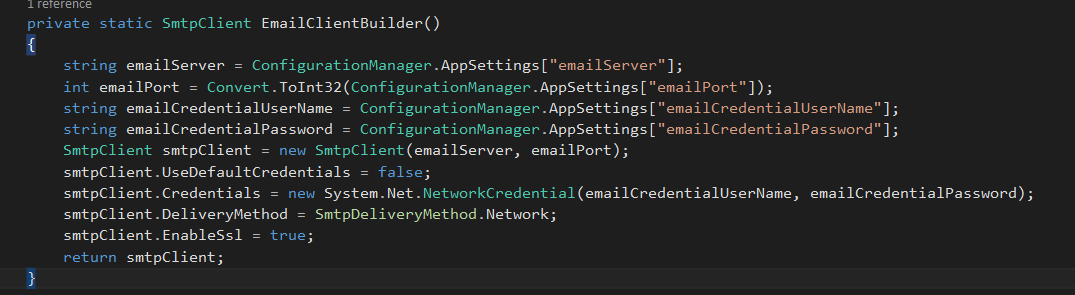
Create a method to return smtp client object, initialize a smtp client instance and set email configurations as below.
private static SmtpClient EmailClientBuilder()
{
string emailServer = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["emailServer"];
int emailPort = Convert.ToInt32(ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["emailPort"]);
string emailCredentialUserName = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["emailCredentialUserName"];
string emailCredentialPassword = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["emailCredentialPassword"];
SmtpClient smtpClient = new SmtpClient(emailServer, emailPort);
smtpClient.UseDefaultCredentials = false;
smtpClient.Credentials = new System.Net.NetworkCredential(emailCredentialUserName, emailCredentialPassword);
smtpClient.DeliveryMethod = SmtpDeliveryMethod.Network;
smtpClient.EnableSsl = true;
return smtpClient;
}
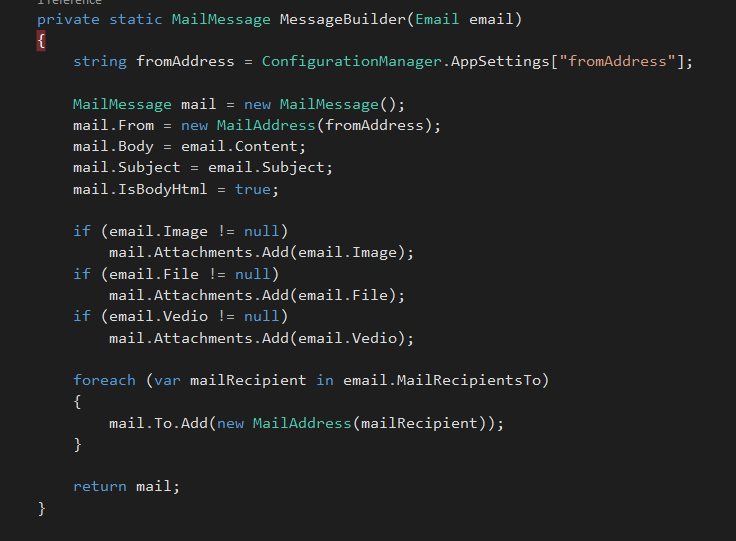
In Message Builder method, populate MailMessage object using Email object we constructed earlier.
private static MailMessage MessageBuilder(Email email)
{
string fromAddress = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["fromAddress"];
MailMessage mail = new MailMessage();
mail.From = new MailAddress(fromAddress);
mail.Body = email.Content;
mail.Subject = email.Subject;
mail.IsBodyHtml = true;
if (email.Image != null)
mail.Attachments.Add(email.Image);
if (email.File != null)
mail.Attachments.Add(email.File);
if (email.Vedio != null)
mail.Attachments.Add(email.Vedio);
foreach (var mailRecipient in email.MailRecipientsTo)
{
mail.To.Add(new MailAddress(mailRecipient));
}
return mail;
}
5 Download
5.1 Tech Net Gallery
You can download the source code from Microsoft tech net gallery, https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/Azure-blob-storage-files-985136db?redir=0
5.2 GitHub
You can clone git hub repository from here, https://github.com/hansamaligamage/blobstorageemailattatchment
6 Conclusion
This article has explained how to store a text file, image and video in Azure blob storage, Then how to attach blobs as an attachment to smtp email