Security Considerations: Event Settings on Windows
Introduction
When configuring a Windows system for a specific role it is a good practice that you apply the correct security template to hardening the system in a supported manner. By using the Security Configuration Wizard (SCW) you can accomplish this goal. However, it is very common for system administrators to customize their security policies according to their business need. You must be aware that system service hardening is not only about disabling services that you don’t need for a specific role, it is also about optimizing the server to perform in a secure manner. If System Administrator tightens the security of a server it is possible that the side effects will be as bad as leaving the system without hardening. A classic example of that is when the system administrator changes the system to operate in a certain way that dependency services will fail to start because another service was disabled.
One particular setting that is often overlooked or changed is the event setting. This article will describe the core event viewer settings for Application, System and Security events and how to configure these options with security in mind.
Understanding Event Options
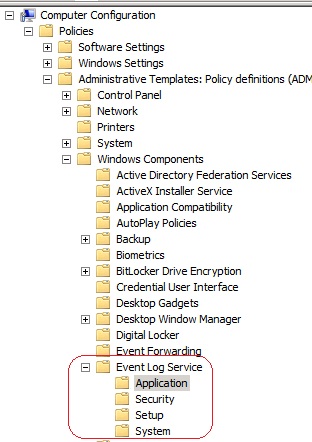
The event settings are located at Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Event Log Service. There you have Application, Security, Setup and System as you can see below:
Within each option (except Setup which will have one more option ) you will also have:
- Log File – controls the location for the log file.
- Maximum Log Size (KB) – specify the maximum size of the log file in KB.
- Backup log automatically when full – controls event log behavior when the log file reaches its maximum size.
- Log Access – specifies to use the security descriptor for the log using the Security Descriptor Define Language.
- Retain old events – controls event log behavior when the log file reaches its maximum size.
Security Considerations
There are two main options among those that should be carefully evaluated before any making any changes, these options are: Maximum Log Size (KB) and Retain old events. To better understand why you should be aware of the security considerations while changing those settings are described below.
Vulnerability
By knowing the potential vulnerability that this option can expose you will have a better understanding of the impact that changing this setting can have on your environment. Review the vulnerabilities below per option and per event type:
Event Type: Application and System
- Maximum Log Size (KB) and Retain old events - If events are not recorded it may be difficult or impossible to determine the root cause of system problems or the unauthorized activities of malicious users.
Event Type: Security
- Maximum Log Size (KB) - If you significantly increase the number of objects to audit in your organization, there is a risk that the Security log will reach its capacity and force the computer to shut down if you enabled the Audit: Shut down system immediately if unable to log security audits.
- Retain old events - If new events are not recorded it may be difficult or impossible to determine the root cause of system problems or the unauthorized activities of malicious users.
Countermeasure
In order to mitigate those vulnerabilities the following countermeasures are recommended:
Event Type: Application, System and Security
- Maximum Log Size (KB) - You should enable sensible log size policies for all computers in your organization so that legitimate users can be held accountable for their actions, unauthorized activity can be detected and tracked, and computer problems can be detected and diagnosed.
- Retain old events - Configure this setting to Disabled.
Conclusion
When planning your system hardening strategy make sure to cover all settings that will be affected by those customizations. Always perform these changes in a custom template and use the Security Compliance Manager to compare your own template to the recommended one based on the OS version and server role. Make sure to perform those changes in a lab environment and test it before putting in production. By accessing those options and evaluate the security impact that each option will have, you are reducing the potential risk that your hardening will cause negative impact to the server.
Additional Resources
Audit Policy
Security Configuration Wizard
Microsoft Security Compliance Manager