Tutorial: Use the Azure API Management extension for Visual Studio Code to import and manage APIs
APPLIES TO: Consumption | Developer | Basic | Standard | Premium
In this tutorial, you learn how to use the API Management extension for Visual Studio Code for common operations in API Management. Use the familiar Visual Studio Code environment to import, update, test, and manage APIs.
You learn how to:
- Import an API into API Management
- Edit the API
- Apply API Management policies
- Test the API
For an introduction to more API Management features, see the API Management tutorials using the Azure portal.
- Understand Azure API Management terminology.
- Ensure you've installed Visual Studio Code and the latest Azure API Management extension for Visual Studio Code.
- Create an API Management instance.
The following example imports an OpenAPI Specification in JSON format into API Management. For this example, you import the open source Petstore API.
- In Visual Studio Code, select the Azure icon from the Activity Bar.
- In the Explorer pane, expand the API Management instance you created.
- Right-click APIs, and select Import from OpenAPI Link.
- When prompted, enter the following values:
An OpenAPI link for content in JSON format. For this example:
https://petstore.swagger.io/v2/swagger.json.This file specifies the backend service that implements the example API and the operations it supports.
An API name, such as petstore, that is unique in the API Management instance. This name can contain only letters, number, and hyphens. The first and last characters must be alphanumeric. This name is used in the path to call the API.
After the API is imported successfully, it appears in the Explorer pane, and available API operations appear under the Operations node.
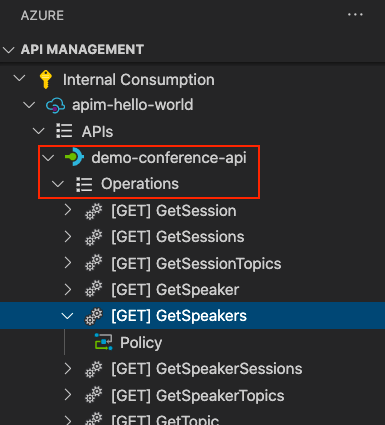
You can edit the API in Visual Studio Code. For example, edit the Resource Manager JSON description of the API in the editor window to remove the http protocol used to access the API, which is highlighted in the following snip:
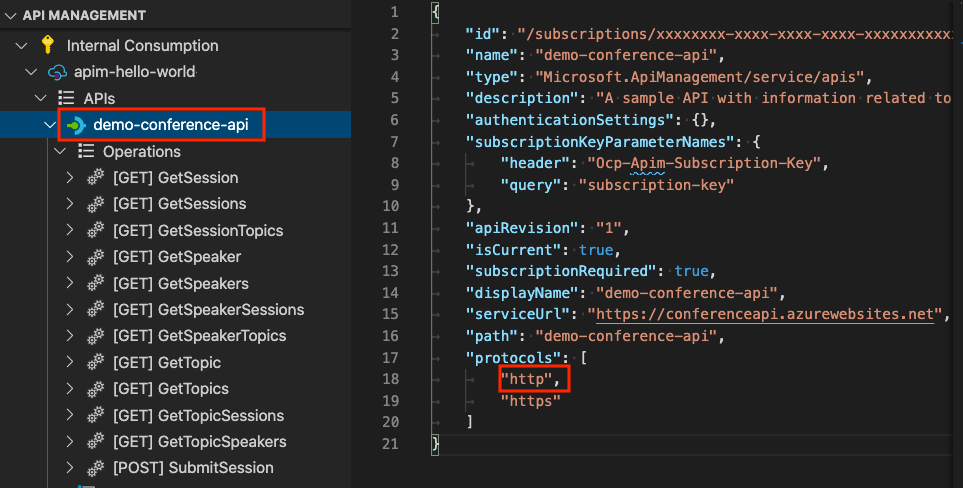
To edit the OpenAPI format, right-click the API name in the Explorer pane and select Edit OpenAPI. Make your changes, and then select File > Save.
API Management provides policies that you can configure for your APIs. Policies are a collection of statements. These statements are run sequentially on the request or response of an API. Policies can be global, which apply to all APIs in your API Management instance, or specific to a product, an API, or an API operation.
This section shows how to apply common inbound and outbound policies to your API.
In the Explorer pane, select Policy under the petstore API that you imported. The policy file opens in the editor window. This file configures policies for all operations in the API.
Update the file with the following content:
<policies> <inbound> <rate-limit calls="3" renewal-period="15" /> <base /> </inbound> <outbound> <set-header name="Custom" exists-action="override"> <value>"My custom value"</value> </set-header> <base /> </outbound> <on-error> <base /> </on-error> </policies>- The
rate-limitpolicy in theinboundsection limits the number of calls to the API to 3 every 15 seconds. - The
set-headerpolicy in theoutboundsection adds a custom response header for demonstration purposes.
- The
Save the file. If you're prompted, select Upload to upload the file to the cloud.
To test the API, get a subscription key and then make a request to the API Management gateway.
You need a subscription key for your API Management instance to test the imported API and the policies that are applied.
In the Explorer pane, right-click the name of your API Management instance.
Select Copy Subscription Key. This key is for the built-in all access subscription that is created when you create an API Management instance.
Caution
The all-access subscription enables access to every API in this API Management instance and should only be used by authorized users. Never use it for routine API access or embed the all-access key in client apps.
- In the Explorer pane, expand the Operations node under the petstore API that you imported.
- Select an operation such as [GET] Find pet by ID, and then right-click the operation and select Test Operation.
- In the editor window, substitute
5for thepetIdparameter in the request URL. - In the editor window, next to Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key, replace
{{SubscriptionKey}}with the subscription key that you copied. - Select Send request.
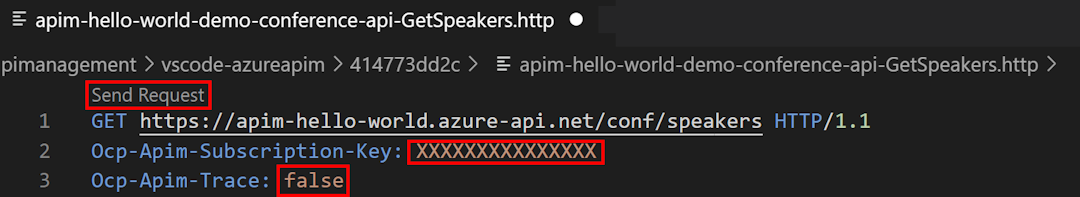
When the request succeeds, the backend responds with 200 OK and some data.
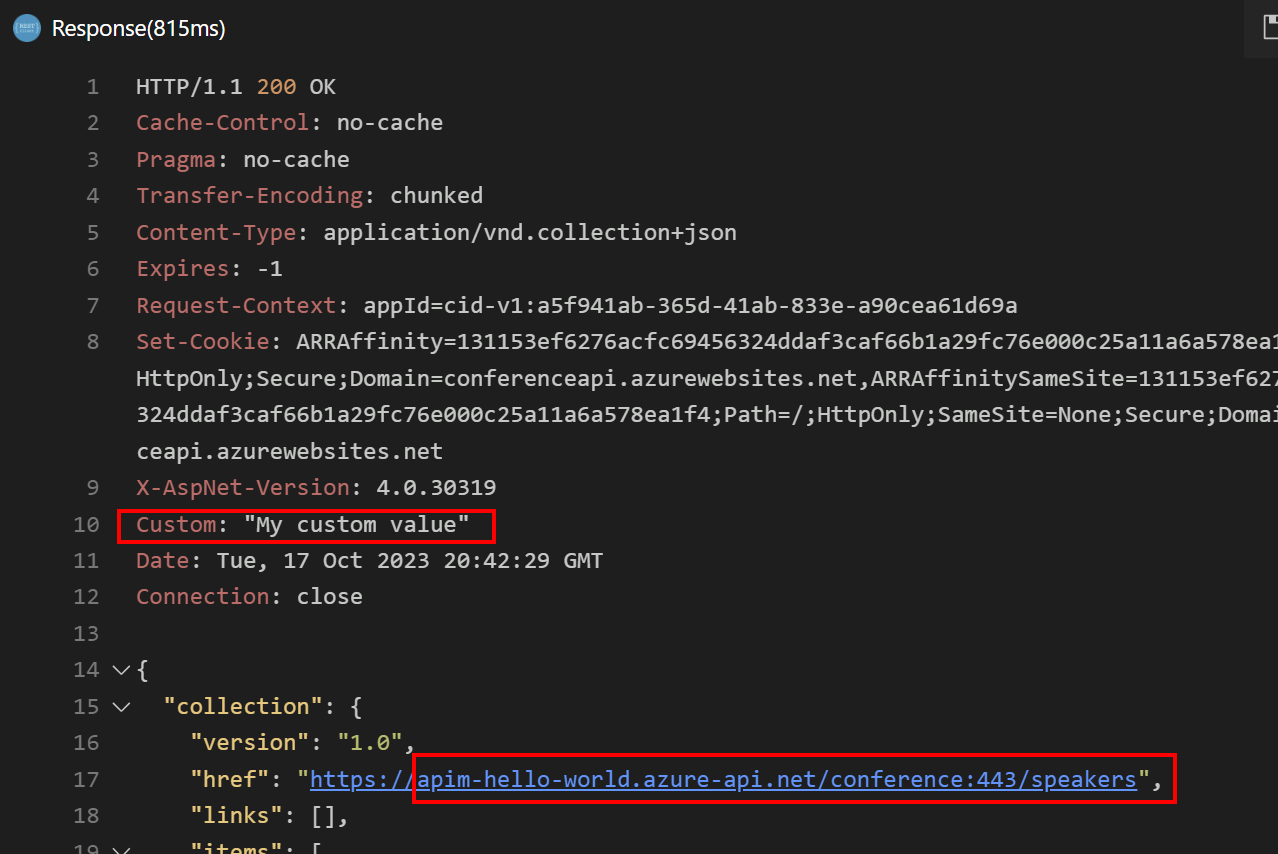
Notice the following detail in the response:
- The
Customheader is added to the response.
Now test the rate limiting policy. Select Send request several times in a row. After sending too many requests in the configured period, you get the 429 Too Many Requests response.
Optionally, you can get detailed request tracing information to help you debug and troubleshoot the API.
For steps to enable tracing for an API, see Enable tracing for an API. To limit unintended disclosure of sensitive information, tracing by default is allowed for only 1 hour.
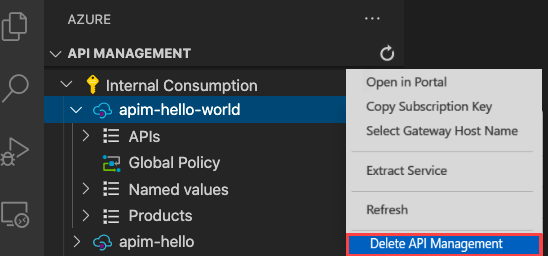
When no longer needed, remove the API Management instance by right-clicking and selecting Open in Portal to delete the API Management service and its resource group.
Alternately, you can select Delete API Management to only delete the API Management instance (this operation doesn't delete its resource group).
This tutorial introduced several features of the API Management extension for Visual Studio Code. You can use these features to import and manage APIs. You learned how to:
- Import an API into API Management
- Edit the API
- Apply API Management policies
- Test the API
The API Management extension provides more features to work with your APIs. For example, debug polices (available in the Developer service tier), or create and manage named values.