Azure landing zones - Bicep modules design considerations
This article discusses the design considerations of the modularized Azure Landing Zones (ALZ) - Bicep solution you can use to deploy and manage the core platform capabilities of the Azure landing zone conceptual architecture as detailed in the Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF).
Bicep is a domain-specific language (DSL) that uses declarative syntax to deploy Azure resources. It has concise syntax, reliable type safety, and support for code reuse.
 An implementation of this architecture is available on GitHub: Azure Landing Zones (ALZ) - Bicep Implementation. You can use it as a starting point and configure it as per your needs.
An implementation of this architecture is available on GitHub: Azure Landing Zones (ALZ) - Bicep Implementation. You can use it as a starting point and configure it as per your needs.
Note
There are implementations for several deployment technologies, including portal-based, ARM templates and Terraform modules. The choice of deployment technology should not influence the resulting Azure landing zones deployment.
ALZ Bicep Accelerator
You can find step by step guidance around implementing, automating, and maintaining your ALZ Bicep module with the ALZ Bicep Accelerator.
The ALZ Bicep Accelerator framework was developed to provide end-users support to onboarding and deployment of ALZ Bicep using full-fledged CI/CD pipelines, support for GitHub Actions and Azure DevOps Pipelines, dedicated Framework to stay in-sync with new ALZ Bicep releases and modify or add custom modules, and provides branching strategy guidance and pull request pipelines for linting and validating Bicep modules.
Design
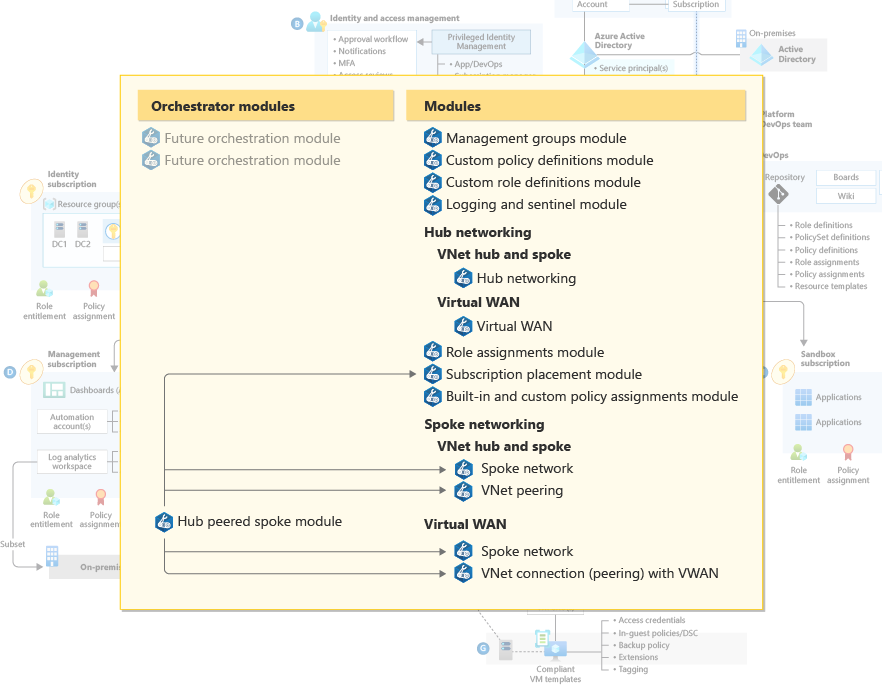
The architecture takes advantage of the modular nature of Azure Bicep and is composed of number of modules. Each module encapsulates a core capability of the Azure Landing Zones conceptual architecture. The modules can be deployed individually, but there are dependencies to be aware of.
The architecture proposes the inclusion of orchestrator modules to simplify the deployment experience. The orchestrator modules could be used to automate the deployment of the modules and to encapsulate differing deployment topologies.
Modules
A core concept in Bicep is the use of modules. Modules enable you to organize deployments into logical groupings. With modules, you improve the readability of your Bicep files by encapsulating complex details of your deployment. You can also easily reuse modules for different deployments.
The ability to re-use modules offers a real benefit when defining and deploying landing zones. It enables repeatable, consistent environments in code while reducing the effort required to deploy at scale.
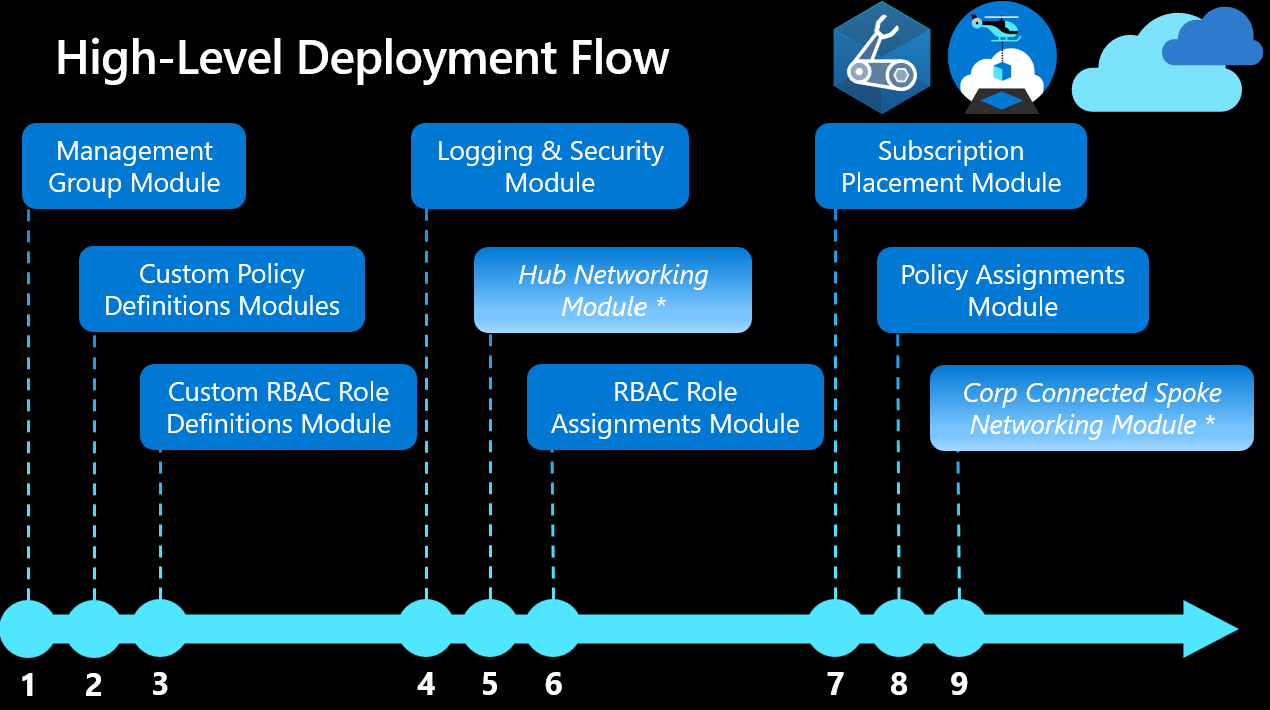
Layers and staging
In addition to modules, the Bicep landing zone architecture is structured using a concept of layers. Layers are groups of Bicep modules that are intended to be deployed together. Those groups form logical stages of the implementation.
A benefit of this layered approach is the ability to add to your environment incrementally over time. For example, you can start with a small number of the layers. You can add the remaining layers at a subsequent stage when you’re ready.
Module descriptions
This section provides a high-level overview of the core modules in this architecture.
| Layer | Module | Description | Useful Links |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core | Management Groups | Management groups are the highest level resources in an Azure tenant. Management groups allow you to more easily manage your resources. You can apply policy at the management group level and lower level resources will inherit that policy. Specifically, you can apply the following items at the management group level that will be inherited by subscriptions under the management group:
This module deploys the management group hierarchy as defined in the Azure landing zone conceptual architecture. |
|
| Core | Custom Policy Definitions | DeployIfNotExists (DINE) or Modify policies help ensure the subscriptions and resources that make up landing zones are compliant. The policies also ease the burden of management of landing zones. This module deploys custom policy definitions to management groups. Not all customers are able to use DINE or Modify policies. If that is the case for you, CAF guidance on custom policies provides guidance. |
|
| Core | Custom Role Definitions | Role-based access control (RBAC) simplifies the management of user rights within a system. Instead of managing the rights of individuals, you determine the rights required for different roles in your system. Azure RBAC has several built-in roles. Custom role definitions allow you to create custom roles for your environment. This module deploys custom role definitions. The module should follow CAF guidance on Azure role-based access control. |
|
| Management | Logging, Automation & Sentinel | Azure Monitor, Azure Automation and Microsoft Sentinel allow you monitor and manage your infrastructure and workloads. Azure Monitor is a solution that allows you to collect, analyze and act on telemetry from your environment. Microsoft Sentinel is a cloud-native security information and event management (SIEM). It allows you to:
Azure Automation is a cloud-based automation system. It includes:
This module deploys the tools necessary to monitor, manage and access threats to your environment. These tools should include Azure Monitor, Azure Automation and Microsoft Sentinel. |
|
| Connectivity | Networking | Network topology is a key consideration in Azure landing zone deployments. CAF focuses on 2 core networking approaches:
These modules deploy the network topology that you choose. |
|
| Identity | Role Assignments | Identity and access management (IAM) is the key security boundary in cloud computing. Azure RBAC allows you to perform role assignments of built-in roles or custom role definitions to security principals. This module deploys role assignments to Service Principals, Managed Identities or security groups across management groups and subscriptions. The module should follow CAF guidance on Azure identity and access management. |
|
| Core | Subscription Placement | Subscriptions that are assigned to a management group inherit:
This module moves subscriptions under the appropriate management group. |
|
| Core | Built-In and Custom Policy Assignments | This module deploys the default Azure landing zone Azure Policy assignments to management groups. It also creates role assignments for system-assigned Managed Identities created by policies. | |
| Management | Orchestrator Modules | Orchestrator modules can greatly improve the deployment experience. These modules encapsulate the deployment of multiple modules in a single module. This hides the complexity from the end user. |
Customizing the Bicep implementation
The Azure landing zone implementations provided as part of the Cloud Adoption Framework suit a wide variety of requirements and use cases. However, there are often scenarios where customization is required to meet specific business needs.
Tip
See Tailor the Azure landing zone architecture to meet requirements for further information.
Once the platform landing zone is implemented the next step is to deploy Application landing zones which enable application teams under the landing zones management group with the guardrails that Central IT or PlatformOps administrators require. The corp management group is for corporate connected applications, while the online management group is for applications that are primarily publicly facing, but may still connect to corporate applications via hub networks in some scenarios.
The Bicep Azure landing zone implementation can be used as the basis of your customized deployment. It provides you a way to accelerate your implementation by removing the need to start from scratch because of a specific required change that rules a ready-made option out.
 Information on customizing the modules is available in the GitHub repo wiki GitHub: Azure Landing Zones (ALZ) Bicep - Wiki- Consumer Guide. You can use it as a starting point and configure it as per your needs.
Information on customizing the modules is available in the GitHub repo wiki GitHub: Azure Landing Zones (ALZ) Bicep - Wiki- Consumer Guide. You can use it as a starting point and configure it as per your needs.