Quickstart: Join a room call
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
- An active Communication Services resource and connection string. Create a Communication Services resource.
- Two or more Communication User Identities. Create and manage access tokens or Quick-create identities for testing.
- A created room and participant added to it. Create and manage rooms
Obtain user access token
If you have already created users and have added them as participants in the room following the "Set up room participants" section in this page, then you can directly use those users to join the room.
Otherwise, you'll need to create a User Access Token for each call participant. Learn how to create and manage user access tokens. You can also use the Azure CLI and run the command below with your connection string to create a user and an access token. After the users have been created, you'll need to add them to the room as participants before they can join the room.
az communication identity token issue --scope voip --connection-string "yourConnectionString"
For details, see Use Azure CLI to Create and Manage Access Tokens.
Note
Rooms can be accessed using the Azure Communication Services UI Library. The UI Library enables developers to add a call client that is Rooms enabled into their application with only a couple lines of code.
Join a room call
To follow along with this quickstart, you can download the Room Call quickstart on GitHub.
Pre-requisites
- You need to have Node.js 18. You can use the msi installer to install it.
Setting up
Create a new Node.js application
Open your terminal or command window create a new directory for your app, and navigate to it.
mkdir calling-rooms-quickstart && cd calling-rooms-quickstart
Run npm init -y to create a package.json file with default settings.
npm init -y
Install the package
Use the npm install command to install the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK for JavaScript.
Important
This quickstart uses the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK version 1.14.1. The ability to join a room call and display the roles of call participants is available in the Calling JavaScript SDK for web browsers version 1.13.1 and above.
npm install @azure/communication-common --save
npm install @azure/communication-calling@1.14.1 --save
Set up the app framework
This quickstart uses webpack to bundle the application assets. Run the following command to install the webpack, webpack-cli and webpack-dev-server npm packages and list them as development dependencies in your package.json:
npm install copy-webpack-plugin@^11.0.0 webpack@^5.88.2 webpack-cli@^5.1.4 webpack-dev-server@^4.15.1 --save-dev
Here's the code:
Create an index.html file in the root directory of your project. We use this file to configure a basic layout that allows the user to join a rooms call.
<!-- index.html-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Azure Communication Services - Rooms Call Sample</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<h4>Azure Communication Services - Rooms Call Sample</h4>
<input id="user-access-token"
type="text"
placeholder="User access token"
style="margin-bottom:1em; width: 500px;"/>
<button id="initialize-call-agent" type="button">Initialize Call Agent</button>
<br>
<br>
<input id="acs-room-id"
type="text"
placeholder="Enter Room Id"
style="margin-bottom:1em; width: 500px; display: block;"/>
<button id="join-room-call-button" type="button" disabled="true">Join Room Call</button>
<button id="hangup-call-button" type="button" disabled="true">Hang up Call</button>
<button id="start-video-button" type="button" disabled="true">Start Video</button>
<button id="stop-video-button" type="button" disabled="true">Stop Video</button>
<br>
<br>
<div id="connectedLabel" style="color: #13bb13;" hidden>Room Call is connected!</div>
<br>
<div id="remoteVideosGallery" style="width: 40%;" hidden>Remote participants' video streams:</div>
<br>
<div id="localVideoContainer" style="width: 30%;" hidden>Local video stream:</div>
<!-- points to the bundle generated from client.js -->
<script src="./main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Create a file in the root directory of your project called index.js to contain the application logic for this quickstart. Add the following code to index.js:
// Make sure to install the necessary dependencies
const { CallClient, VideoStreamRenderer, LocalVideoStream } = require('@azure/communication-calling');
const { AzureCommunicationTokenCredential } = require('@azure/communication-common');
const { AzureLogger, setLogLevel } = require("@azure/logger");
// Set the log level and output
setLogLevel('verbose');
AzureLogger.log = (...args) => {
console.log(...args);
};
// Calling web sdk objects
let callAgent;
let deviceManager;
let call;
let localVideoStream;
let localVideoStreamRenderer;
// UI widgets
let userAccessToken = document.getElementById('user-access-token');
let acsRoomId = document.getElementById('acs-room-id');
let initializeCallAgentButton = document.getElementById('initialize-call-agent');
let startCallButton = document.getElementById('join-room-call-button');
let hangUpCallButton = document.getElementById('hangup-call-button');
let startVideoButton = document.getElementById('start-video-button');
let stopVideoButton = document.getElementById('stop-video-button');
let connectedLabel = document.getElementById('connectedLabel');
let remoteVideosGallery = document.getElementById('remoteVideosGallery');
let localVideoContainer = document.getElementById('localVideoContainer');
/**
* Using the CallClient, initialize a CallAgent instance with a CommunicationUserCredential which enable us to join a rooms call.
*/
initializeCallAgentButton.onclick = async () => {
try {
const callClient = new CallClient();
tokenCredential = new AzureCommunicationTokenCredential(userAccessToken.value.trim());
callAgent = await callClient.createCallAgent(tokenCredential)
// Set up a camera device to use.
deviceManager = await callClient.getDeviceManager();
await deviceManager.askDevicePermission({ video: true });
await deviceManager.askDevicePermission({ audio: true });
startCallButton.disabled = false;
initializeCallAgentButton.disabled = true;
} catch(error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
startCallButton.onclick = async () => {
try {
const localVideoStream = await createLocalVideoStream();
const videoOptions = localVideoStream ? { localVideoStreams: [localVideoStream] } : undefined;
const roomCallLocator = { roomId: acsRoomId.value.trim() };
call = callAgent.join(roomCallLocator, { videoOptions });
// Subscribe to the call's properties and events.
subscribeToCall(call);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* Subscribe to a call obj.
* Listen for property changes and collection updates.
*/
subscribeToCall = (call) => {
try {
// Inspect the initial call.id value.
console.log(`Call Id: ${call.id}`);
//Subscribe to call's 'idChanged' event for value changes.
call.on('idChanged', () => {
console.log(`Call Id changed: ${call.id}`);
});
// Inspect the initial call.state value.
console.log(`Call state: ${call.state}`);
// Subscribe to call's 'stateChanged' event for value changes.
call.on('stateChanged', async () => {
console.log(`Call state changed: ${call.state}`);
if(call.state === 'Connected') {
connectedLabel.hidden = false;
startCallButton.disabled = true;
hangUpCallButton.disabled = false;
startVideoButton.disabled = false;
stopVideoButton.disabled = false;
remoteVideosGallery.hidden = false;
} else if (call.state === 'Disconnected') {
connectedLabel.hidden = true;
startCallButton.disabled = false;
hangUpCallButton.disabled = true;
startVideoButton.disabled = true;
stopVideoButton.disabled = true;
remoteVideosGallery.hidden = true;
console.log(`Call ended, call end reason={code=${call.callEndReason.code}, subCode=${call.callEndReason.subCode}}`);
}
});
call.on('isLocalVideoStartedChanged', () => {
console.log(`isLocalVideoStarted changed: ${call.isLocalVideoStarted}`);
});
console.log(`isLocalVideoStarted: ${call.isLocalVideoStarted}`);
call.localVideoStreams.forEach(async (lvs) => {
localVideoStream = lvs;
await displayLocalVideoStream();
});
call.on('localVideoStreamsUpdated', e => {
e.added.forEach(async (lvs) => {
localVideoStream = lvs;
await displayLocalVideoStream();
});
e.removed.forEach(lvs => {
removeLocalVideoStream();
});
});
// Inspect the call's current remote participants and subscribe to them.
call.remoteParticipants.forEach(remoteParticipant => {
subscribeToRemoteParticipant(remoteParticipant);
});
// Subscribe to the call's 'remoteParticipantsUpdated' event to be
// notified when new participants are added to the call or removed from the call.
call.on('remoteParticipantsUpdated', e => {
// Subscribe to new remote participants that are added to the call.
e.added.forEach(remoteParticipant => {
subscribeToRemoteParticipant(remoteParticipant)
});
// Unsubscribe from participants that are removed from the call
e.removed.forEach(remoteParticipant => {
console.log('Remote participant removed from the call.');
});
});
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* Subscribe to a remote participant obj.
* Listen for property changes and collection updates.
*/
subscribeToRemoteParticipant = (remoteParticipant) => {
try {
// Inspect the initial remoteParticipant.state value.
console.log(`Remote participant state: ${remoteParticipant.state}`);
// Subscribe to remoteParticipant's 'stateChanged' event for value changes.
remoteParticipant.on('stateChanged', () => {
console.log(`Remote participant state changed: ${remoteParticipant.state}`);
});
// Inspect the remoteParticipants's current videoStreams and subscribe to them.
remoteParticipant.videoStreams.forEach(remoteVideoStream => {
subscribeToRemoteVideoStream(remoteVideoStream)
});
// Subscribe to the remoteParticipant's 'videoStreamsUpdated' event to be
// notified when the remoteParticipant adds new videoStreams and removes video streams.
remoteParticipant.on('videoStreamsUpdated', e => {
// Subscribe to new remote participant's video streams that were added.
e.added.forEach(remoteVideoStream => {
subscribeToRemoteVideoStream(remoteVideoStream)
});
// Unsubscribe from remote participant's video streams that were removed.
e.removed.forEach(remoteVideoStream => {
console.log('Remote participant video stream was removed.');
})
});
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* Subscribe to a remote participant's remote video stream obj.
* You have to subscribe to the 'isAvailableChanged' event to render the remoteVideoStream. If the 'isAvailable' property
* changes to 'true', a remote participant is sending a stream. Whenever availability of a remote stream changes
* you can choose to destroy the whole 'Renderer', a specific 'RendererView' or keep them, but this will result in displaying blank video frame.
*/
subscribeToRemoteVideoStream = async (remoteVideoStream) => {
let renderer = new VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream);
let view;
let remoteVideoContainer = document.createElement('div');
remoteVideoContainer.className = 'remote-video-container';
const createView = async () => {
// Create a renderer view for the remote video stream.
view = await renderer.createView();
// Attach the renderer view to the UI.
remoteVideoContainer.appendChild(view.target);
remoteVideosGallery.appendChild(remoteVideoContainer);
}
// Remote participant has switched video on/off
remoteVideoStream.on('isAvailableChanged', async () => {
try {
if (remoteVideoStream.isAvailable) {
await createView();
} else {
view.dispose();
remoteVideosGallery.removeChild(remoteVideoContainer);
}
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
});
// Remote participant has video on initially.
if (remoteVideoStream.isAvailable) {
try {
await createView();
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
}
}
/**
* Start your local video stream.
* This will send your local video stream to remote participants so they can view it.
*/
startVideoButton.onclick = async () => {
try {
const localVideoStream = await createLocalVideoStream();
await call.startVideo(localVideoStream);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* Stop your local video stream.
* This will stop your local video stream from being sent to remote participants.
*/
stopVideoButton.onclick = async () => {
try {
await call.stopVideo(localVideoStream);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* To render a LocalVideoStream, you need to create a new instance of VideoStreamRenderer, and then
* create a new VideoStreamRendererView instance using the asynchronous createView() method.
* You may then attach view.target to any UI element.
*/
createLocalVideoStream = async () => {
const camera = (await deviceManager.getCameras())[0];
if (camera) {
return new LocalVideoStream(camera);
} else {
console.error(`No camera device found on the system`);
}
}
/**
* Display your local video stream preview in your UI
*/
displayLocalVideoStream = async () => {
try {
localVideoStreamRenderer = new VideoStreamRenderer(localVideoStream);
const view = await localVideoStreamRenderer.createView();
localVideoContainer.hidden = false;
localVideoContainer.appendChild(view.target);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* Remove your local video stream preview from your UI
*/
removeLocalVideoStream = async() => {
try {
localVideoStreamRenderer.dispose();
localVideoContainer.hidden = true;
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* End current room call
*/
hangUpCallButton.addEventListener("click", async () => {
await call.hangUp();
});
Add the webpack local server code
Create a file in the root directory of your project called webpack.config.js to contain the local server logic for this quickstart. Add the following code to webpack.config.js:
const path = require('path');
const CopyPlugin = require("copy-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
entry: './index.js',
output: {
filename: 'main.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
},
devServer: {
static: {
directory: path.join(__dirname, './')
},
},
plugins: [
new CopyPlugin({
patterns: [
'./index.html'
]
}),
]
};
Run the code
Use the webpack-dev-server to build and run your app. Run the following command to bundle the application host in a local webserver:
`npx webpack serve --config webpack.config.js`
- Open your browser navigate to http://localhost:8080/.
- On the first input field, enter a valid user access token.
- Click on the "Initialize Call Agent" and enter your Room ID.
- Click "Join Room Call"
You have now successfully joined a Rooms call!
Understanding joining a Room call
All the code that you have added in your QuickStart app allowed you to successfully start and join a room call. Here is more information about what more methods/handlers you can access for Rooms to extend functionality in your application.
To display the role of the local or remote call participants, subscribe to the handler below.
// Subscribe to changes for your role in a call
const callRoleChangedHandler = () => {
console.log(call.role);
};
call.on('roleChanged', callRoleChangedHandler);
// Subscribe to role changes for remote participants
const subscribeToRemoteParticipant = (remoteParticipant) => {
remoteParticipant.on('roleChanged', () => {
console.log(remoteParticipant.role);
});
}
You can learn more about roles of room call participants in the rooms concept documentation.
Join a Room call
To follow along with this quickstart, you can download the Room Call quickstart on GitHub.
Setting up
Creating the Xcode project
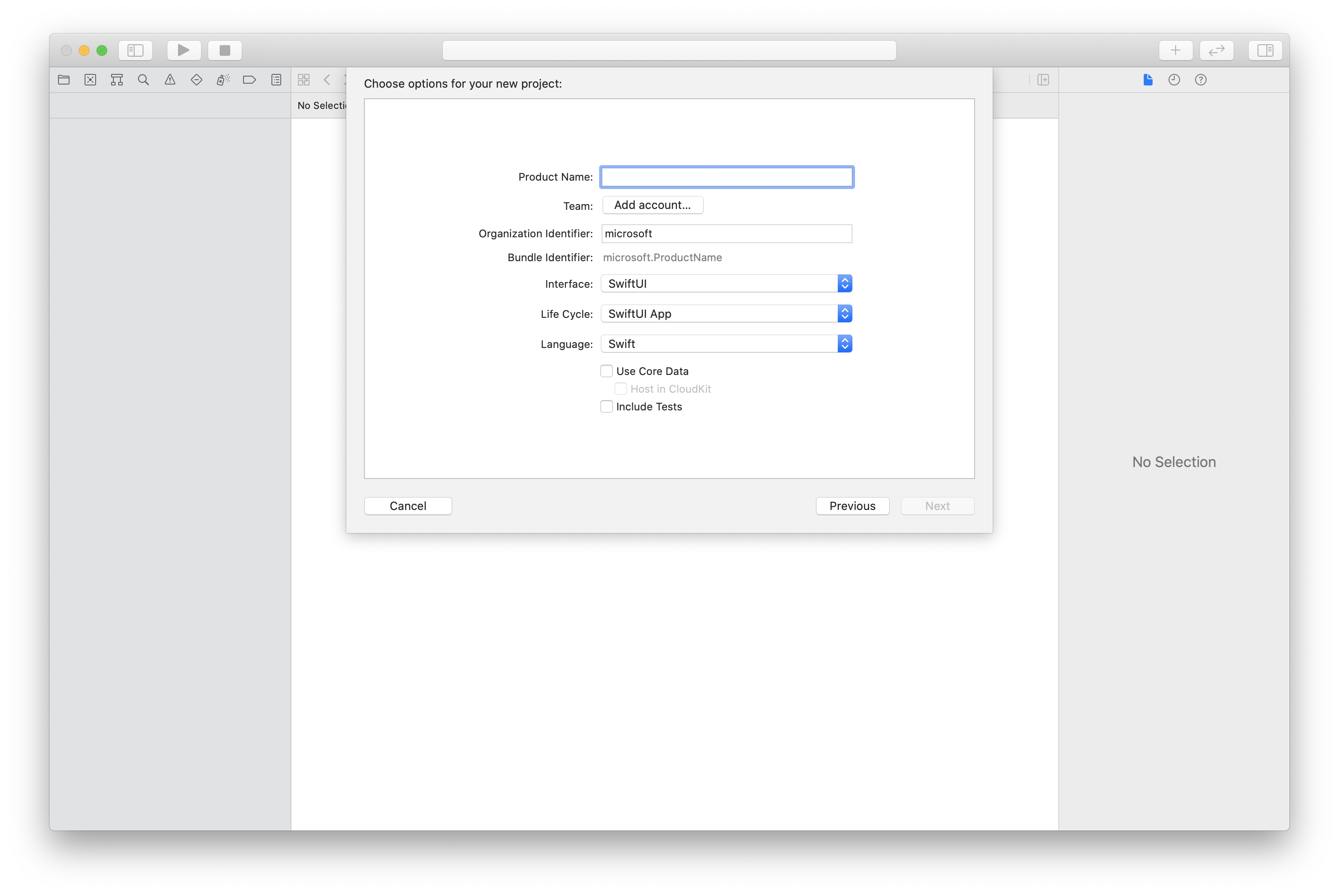
In Xcode, create a new iOS project and select the Single View App template. This tutorial uses the SwiftUI framework, so you should set the Language to Swift and the User Interface to SwiftUI.
Installing CocoaPods
Use this guide to install CocoaPods on your Mac.
Install the package and dependencies with CocoaPods
To create a Podfile for your application, open the terminal and navigate to the project folder and run pod init.
Add the following code to the Podfile and save:
platform :ios, '13.0'
use_frameworks!
target 'roomsquickstart' do
pod 'AzureCommunicationCalling', '~> 2.5.0'
end
Run pod install.
Open the
.xcworkspacefile with Xcode.
Request access to the microphone and camera
To access the device's microphone and camera, you need to update your app's Information Property List with NSMicrophoneUsageDescription and NSCameraUsageDescription. Set the associated value to a string that will be included in the dialog the system uses to request access from the user.
Right-click the Info.plist entry of the project tree and select Open As > Source Code. Add the following lines the top level <dict> section, and then save the file.
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>Need microphone access for VOIP calling.</string>
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Need camera access for video calling</string>
Set up the app framework
Open your project's ContentView.swift file and add an import declaration to the top of the file to import the AzureCommunicationCalling library and AVFoundation. AVFoundation is used to capture audio permission from code.
import AzureCommunicationCalling
import AVFoundation
Object model
The following classes and interfaces handle some of the major features of the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK for iOS.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CallClient | The CallClient is the main entry point to the Calling SDK. |
| CallAgent | The CallAgent is used to start and manage calls. |
| CommunicationTokenCredential | The CommunicationTokenCredential is used as the token credential to instantiate the CallAgent. |
| CommunicationIdentifier | The CommunicationIdentifier is used to represent the identity of the user, and can have one of the following values: CommunicationUserIdentifier/PhoneNumberIdentifier/CallingApplication. |
| RoomCallLocator | The RoomCallLocator is used by CallAgent to join a Room call |
Create the Call Agent
Replace the implementation of the ContentView struct with some simple UI controls that enable a user to initiate and end a call. We'll attach business logic to these controls in this quickstart.
struct ContentView: View {
@State var roomId: String = ""
@State var callObserver:CallObserver?
@State var previewRenderer: VideoStreamRenderer? = nil
@State var previewView: RendererView? = nil
@State var sendingLocalVideo: Bool = false
@State var speakerEnabled: Bool = false
@State var muted: Bool = false
@State var callClient: CallClient?
@State var call: Call?
@State var callHandler: CallHandler?
@State var callAgent: CallAgent?
@State var deviceManager: DeviceManager?
@State var localVideoStreams: [LocalVideoStream]?
@State var callState: String = "Unknown"
@State var showAlert: Bool = false
@State var alertMessage: String = ""
@State var participants: [[Participant]] = [[]]
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
ZStack {
if (call == nil) {
Form {
Section {
TextField("Room ID", text: $roomId)
Button(action: joinRoomCall) {
Text("Join Room Call")
}
}
}
.navigationBarTitle("Rooms Quickstart")
} else {
ZStack {
VStack {
ForEach(participants, id:\.self) { array in
HStack {
ForEach(array, id:\.self) { participant in
ParticipantView(self, participant)
}
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: 200, alignment: .topLeading)
}
}
.background(Color.black)
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: .infinity, alignment: .topLeading)
VStack {
if (sendingLocalVideo) {
HStack {
RenderInboundVideoView(view: $previewView)
.frame(width:90, height:160)
.padding(10)
.background(Color.green)
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, alignment: .trailing)
}
HStack {
Button(action: toggleMute) {
HStack {
Text(muted ? "Unmute" : "Mute")
}
.frame(width:80)
.padding(.vertical, 10)
.background(Color(.lightGray))
}
Button(action: toggleLocalVideo) {
HStack {
Text(sendingLocalVideo ? "Video-Off" : "Video-On")
}
.frame(width:80)
.padding(.vertical, 10)
.background(Color(.lightGray))
}
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, alignment: .leading)
.padding(.horizontal, 10)
.padding(.vertical, 5)
HStack {
Button(action: leaveRoomCall) {
HStack {
Text("Leave Room Call")
}
.frame(width:80)
.padding(.vertical, 10)
.background(Color(.red))
}
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, alignment: .leading)
.padding(.horizontal, 10)
.padding(.vertical, 5)
HStack {
Text("Status:")
Text(callState)
}
.padding(.vertical, 10)
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: .infinity, alignment: .bottomLeading)
}
}
}
}
.onAppear{
// Authenticate the client
// Initialize the CallAgent and access Device Manager
// Ask for permissions
}
}
}
//Functions and Observers
struct HomePageView_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
HomePageView()
}
}
Authenticate the client
In order to initialize a CallAgent instance, we need a User Access Token which will enable us to join Room calls.
Once you have a token, add the following code to the onAppear callback in ContentView.swift. You need to replace <USER ACCESS TOKEN> with a valid user access token for your resource:
var userCredential: CommunicationTokenCredential?
do {
userCredential = try CommunicationTokenCredential(token: "<USER ACCESS TOKEN>")
} catch {
print("ERROR: It was not possible to create user credential.")
return
}
Initialize the CallAgent and access the Device Manager
To create a CallAgent instance from a CallClient, use the callClient.createCallAgent method that asynchronously returns a CallAgent object once it's initialized. DeviceManager lets you enumerate local devices that can be used in a call to transmit audio/video streams. It also allows you to request permission from a user to access microphone/camera.
self.callClient = CallClient()
self.callClient?.createCallAgent(userCredential: userCredential!) { (agent, error) in
if error != nil {
print("ERROR: It was not possible to create a call agent.")
return
} else {
self.callAgent = agent
print("Call agent successfully created.")
self.callAgent!.delegate = callHandler
self.callClient?.getDeviceManager { (deviceManager, error) in
if (error == nil) {
print("Got device manager instance")
self.deviceManager = deviceManager
} else {
print("Failed to get device manager instance")
}
}
}
}
Ask for permissions
We need to add the following code to the onAppear callback to ask for permissions for audio and video.
AVAudioSession.sharedInstance().requestRecordPermission { (granted) in
if granted {
AVCaptureDevice.requestAccess(for: .video) { (videoGranted) in
/* NO OPERATION */
}
}
}
Joining a Room call
The joinRoomCall method is set as the action that will be performed when the Join Room Call button is tapped. In this quickstart, calls are audio only by default but can have video enabled once a Room has been joined.
func joinRoomCall() {
if self.callAgent == nil {
print("CallAgent not initialized")
return
}
if (self.roomId.isEmpty) {
print("Room ID not set")
return
}
// Join a call with a Room ID
let options = JoinCallOptions()
let audioOptions = AudioOptions()
audioOptions.muted = self.muted
options.audioOptions = audioOptions
let roomCallLocator = RoomCallLocator(roomId: roomId)
self.callAgent!.join(with: roomCallLocator, joinCallOptions: options) { (call, error) in
self.setCallAndObserver(call: call, error: error)
}
}
CallObserver is used to manage mid-call events and remote participants. We'll set the observers in the setCallAndObserver function.
func setCallAndObserver(call:Call!, error:Error?) {
if (error == nil) {
self.call = call
self.callObserver = CallObserver(view:self)
self.call!.delegate = self.callObserver
if (self.call!.state == CallState.connected) {
self.callObserver!.handleInitialCallState(call: call)
}
} else {
print("Failed to get call object")
}
}
Leaving a Room call
The leaveRoomCall method is set as the action that will be performed when the Leave Room Call button is tapped. It handles leaving a call and cleans up any resources that were created.
private func leaveRoomCall() {
if (self.sendingLocalVideo) {
self.call!.stopVideo(stream: self.localVideoStreams!.first!) { (error) in
if (error != nil) {
print("Failed to stop video")
} else {
self.sendingLocalVideo = false
self.previewView = nil
self.previewRenderer?.dispose()
self.previewRenderer = nil
}
}
}
self.call?.hangUp(options: nil) { (error) in }
self.participants.removeAll()
self.call?.delegate = nil
self.call = nil
}
Broadcasting video
During a Room call, we can use startVideo or stopVideo to start or stop sending LocalVideoStream to remote participants.
func toggleLocalVideo() {
if (self.sendingLocalVideo) {
self.call!.stopVideo(stream: self.localVideoStreams!.first!) { (error) in
if (error != nil) {
print("Cannot stop video")
} else {
self.sendingLocalVideo = false
self.previewView = nil
self.previewRenderer!.dispose()
self.previewRenderer = nil
}
}
} else {
let availableCameras = self.deviceManager!.cameras
let scalingMode:ScalingMode = .crop
if (self.localVideoStreams == nil) {
self.localVideoStreams = [LocalVideoStream]()
}
self.localVideoStreams!.append(LocalVideoStream(camera: availableCameras.first!))
self.previewRenderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(localVideoStream: self.localVideoStreams!.first!)
self.previewView = try! previewRenderer!.createView(withOptions: CreateViewOptions(scalingMode:scalingMode))
self.call!.startVideo(stream: self.localVideoStreams!.first!) { (error) in
if (error != nil) {
print("Cannot start video")
}
else {
self.sendingLocalVideo = true
}
}
}
}
Muting local audio
During a Room call we can use mute or unMute to mute or unmute our microphone.
func toggleMute() {
if (self.muted) {
call!.unmuteOutgoingAudio(completionHandler: { (error) in
if error == nil {
self.muted = false
}
})
} else {
call!.muteOutgoingAudio(completionHandler: { (error) in
if error == nil {
self.muted = true
}
})
}
}
Handling call updates
To deal with call updates, implement an CallHandler to handle update events. Put the following implementation in CallHandler.swift.
final class CallHandler: NSObject, CallAgentDelegate {
public var owner: ContentView?
private static var instance: CallHandler?
static func getOrCreateInstance() -> CallHandler {
if let c = instance {
return c
}
instance = CallHandler()
return instance!
}
private override init() {}
public func callAgent(_ callAgent: CallAgent, didUpdateCalls args: CallsUpdatedEventArgs) {
if let removedCall = args.removedCalls.first {
owner?.call = nil
}
}
}
We need to create an instance of CallHandler by adding the following code to the onAppear callback in ContentView.swift:
self.callHandler = CallHandler.getOrCreateInstance()
self.callHandler.owner = self
Set a delegate to the CallAgent after the CallAgent being successfully created:
self.callAgent!.delegate = callHandler
Remote participant management
All remote participants are represented by the RemoteParticipant type and are available through the remoteParticipants collection on a call instance. We can implement a Participant class to manage the updates on remote video streams of remote participants among other things.
class Participant: NSObject, RemoteParticipantDelegate, ObservableObject {
private var videoStreamCount = 0
private let innerParticipant:RemoteParticipant
private let call:Call
private var renderedRemoteVideoStream:RemoteVideoStream?
@Published var state:ParticipantState = ParticipantState.disconnected
@Published var isMuted:Bool = false
@Published var isSpeaking:Bool = false
@Published var hasVideo:Bool = false
@Published var displayName:String = ""
@Published var videoOn:Bool = true
@Published var renderer:VideoStreamRenderer? = nil
@Published var rendererView:RendererView? = nil
@Published var scalingMode: ScalingMode = .fit
init(_ call: Call, _ innerParticipant: RemoteParticipant) {
self.call = call
self.innerParticipant = innerParticipant
self.displayName = innerParticipant.displayName
super.init()
self.innerParticipant.delegate = self
self.state = innerParticipant.state
self.isMuted = innerParticipant.isMuted
self.isSpeaking = innerParticipant.isSpeaking
self.hasVideo = innerParticipant.videoStreams.count > 0
if(self.hasVideo) {
handleInitialRemoteVideo()
}
}
deinit {
self.innerParticipant.delegate = nil
}
func getMri() -> String {
Utilities.toMri(innerParticipant.identifier)
}
func set(scalingMode: ScalingMode) {
if self.rendererView != nil {
self.rendererView!.update(scalingMode: scalingMode)
}
self.scalingMode = scalingMode
}
func handleInitialRemoteVideo() {
renderedRemoteVideoStream = innerParticipant.videoStreams[0]
renderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream: renderedRemoteVideoStream!)
rendererView = try! renderer!.createView()
}
func toggleVideo() {
if videoOn {
rendererView = nil
renderer?.dispose()
videoOn = false
}
else {
renderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream: innerParticipant.videoStreams[0])
rendererView = try! renderer!.createView()
videoOn = true
}
}
func remoteParticipant(_ remoteParticipant: RemoteParticipant, didUpdateVideoStreams args: RemoteVideoStreamsEventArgs) {
let hadVideo = hasVideo
hasVideo = innerParticipant.videoStreams.count > 0
if videoOn {
if hadVideo && !hasVideo {
// Remote user stopped sharing
rendererView = nil
renderer?.dispose()
} else if hasVideo && !hadVideo {
// remote user started sharing
renderedRemoteVideoStream = innerParticipant.videoStreams[0]
renderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream: renderedRemoteVideoStream!)
rendererView = try! renderer!.createView()
} else if hadVideo && hasVideo {
if args.addedRemoteVideoStreams.count > 0 {
if renderedRemoteVideoStream?.id == args.addedRemoteVideoStreams[0].id {
return
}
// remote user added a second video, so switch to the latest one
guard let rendererTemp = renderer else {
return
}
rendererTemp.dispose()
renderedRemoteVideoStream = args.addedRemoteVideoStreams[0]
renderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream: renderedRemoteVideoStream!)
rendererView = try! renderer!.createView()
} else if args.removedRemoteVideoStreams.count > 0 {
if args.removedRemoteVideoStreams[0].id == renderedRemoteVideoStream!.id {
// remote user stopped sharing video that we were rendering but is sharing
// another video that we can render
renderer!.dispose()
renderedRemoteVideoStream = innerParticipant.videoStreams[0]
renderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream: renderedRemoteVideoStream!)
rendererView = try! renderer!.createView()
}
}
}
}
}
func remoteParticipant(_ remoteParticipant: RemoteParticipant, didChangeDisplayName args: PropertyChangedEventArgs) {
self.displayName = innerParticipant.displayName
}
}
class Utilities {
@available(*, unavailable) private init() {}
public static func toMri(_ id: CommunicationIdentifier?) -> String {
if id is CommunicationUserIdentifier {
let communicationUserIdentifier = id as! CommunicationUserIdentifier
return communicationUserIdentifier.identifier
} else {
return "<nil>"
}
}
}
Remote participant video streams
We can create a ParticipantView to handle the rendering of video streams of remote participants. Put the implementation in ParticipantView.swift
struct ParticipantView : View, Hashable {
static func == (lhs: ParticipantView, rhs: ParticipantView) -> Bool {
return lhs.participant.getMri() == rhs.participant.getMri()
}
private let owner: HomePageView
@State var showPopUp: Bool = false
@State var videoHeight = CGFloat(200)
@ObservedObject private var participant:Participant
var body: some View {
ZStack {
if (participant.rendererView != nil) {
HStack {
RenderInboundVideoView(view: $participant.rendererView)
}
.background(Color(.black))
.frame(height: videoHeight)
.animation(Animation.default)
} else {
HStack {
Text("No incoming video")
}
.background(Color(.red))
.frame(height: videoHeight)
}
}
}
func hash(into hasher: inout Hasher) {
hasher.combine(participant.getMri())
}
init(_ owner: HomePageView, _ participant: Participant) {
self.owner = owner
self.participant = participant
}
func resizeVideo() {
videoHeight = videoHeight == 200 ? 150 : 200
}
func showAlert(_ title: String, _ message: String) {
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 0.1) {
self.owner.alertMessage = message
self.owner.showAlert = true
}
}
}
struct RenderInboundVideoView: UIViewRepresentable {
@Binding var view:RendererView!
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> UIView {
return UIView()
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: UIView, context: Context) {
for view in uiView.subviews {
view.removeFromSuperview()
}
if (view != nil) {
uiView.addSubview(view)
}
}
}
Subscribe to events
We can implement a CallObserver class to subscribe to a collection of events to be notified when values, like remoteParticipants, change during the call.
public class CallObserver : NSObject, CallDelegate
{
private var owner: ContentView
private var firstTimeCallConnected: Bool = true
init(view: ContentView) {
owner = view
super.init()
}
public func call(_ call: Call, didChangeState args: PropertyChangedEventArgs) {
let state = CallObserver.callStateToString(state:call.state)
owner.callState = state
if (call.state == CallState.disconnected) {
owner.leaveRoomCall()
}
else if (call.state == CallState.connected) {
if(self.firstTimeCallConnected) {
self.handleInitialCallState(call: call);
}
self.firstTimeCallConnected = false;
}
}
public func handleInitialCallState(call: Call) {
// We want to build a matrix with max 2 columns
owner.callState = CallObserver.callStateToString(state:call.state)
var participants = [Participant]()
// Add older/existing participants
owner.participants.forEach { (existingParticipants: [Participant]) in
participants.append(contentsOf: existingParticipants)
}
owner.participants.removeAll()
// Add new participants to the collection
for remoteParticipant in call.remoteParticipants {
let mri = Utilities.toMri(remoteParticipant.identifier)
let found = participants.contains { (participant) -> Bool in
participant.getMri() == mri
}
if !found {
let participant = Participant(call, remoteParticipant)
participants.append(participant)
}
}
// Convert 1-D array into a 2-D array with 2 columns
var indexOfParticipant = 0
while indexOfParticipant < participants.count {
var newParticipants = [Participant]()
newParticipants.append(participants[indexOfParticipant])
indexOfParticipant += 1
if (indexOfParticipant < participants.count) {
newParticipants.append(participants[indexOfParticipant])
indexOfParticipant += 1
}
owner.participants.append(newParticipants)
}
}
public func call(_ call: Call, didUpdateRemoteParticipant args: ParticipantsUpdatedEventArgs) {
var participants = [Participant]()
// Add older/existing participants
owner.participants.forEach { (existingParticipants: [Participant]) in
participants.append(contentsOf: existingParticipants)
}
owner.participants.removeAll()
// Remove deleted participants from the collection
args.removedParticipants.forEach { p in
let mri = Utilities.toMri(p.identifier)
participants.removeAll { (participant) -> Bool in
participant.getMri() == mri
}
}
// Add new participants to the collection
for remoteParticipant in args.addedParticipants {
let mri = Utilities.toMri(remoteParticipant.identifier)
let found = participants.contains { (view) -> Bool in
view.getMri() == mri
}
if !found {
let participant = Participant(call, remoteParticipant)
participants.append(participant)
}
}
// Convert 1-D array into a 2-D array with 2 columns
var indexOfParticipant = 0
while indexOfParticipant < participants.count {
var array = [Participant]()
array.append(participants[indexOfParticipant])
indexOfParticipant += 1
if (indexOfParticipant < participants.count) {
array.append(participants[indexOfParticipant])
indexOfParticipant += 1
}
owner.participants.append(array)
}
}
private static func callStateToString(state:CallState) -> String {
switch state {
case .connected: return "Connected"
case .connecting: return "Connecting"
case .disconnected: return "Disconnected"
case .disconnecting: return "Disconnecting"
case .none: return "None"
default: return "Unknown"
}
}
}
Run the code
You can build and run your app on iOS simulator by selecting Product > Run or by using the (⌘-R) keyboard shortcut.
The ability to join a room call and display the roles of call participants is available in the iOS Mobile Calling SDK version 2.5.0 and above.
You can learn more about roles of room call participants in the rooms concept documentation.
Sample app
To follow along with this quickstart, you can download the Room Call quickstart on GitHub.
Setting up project
Create an Android app with an empty activity
From Android Studio, create a new project:
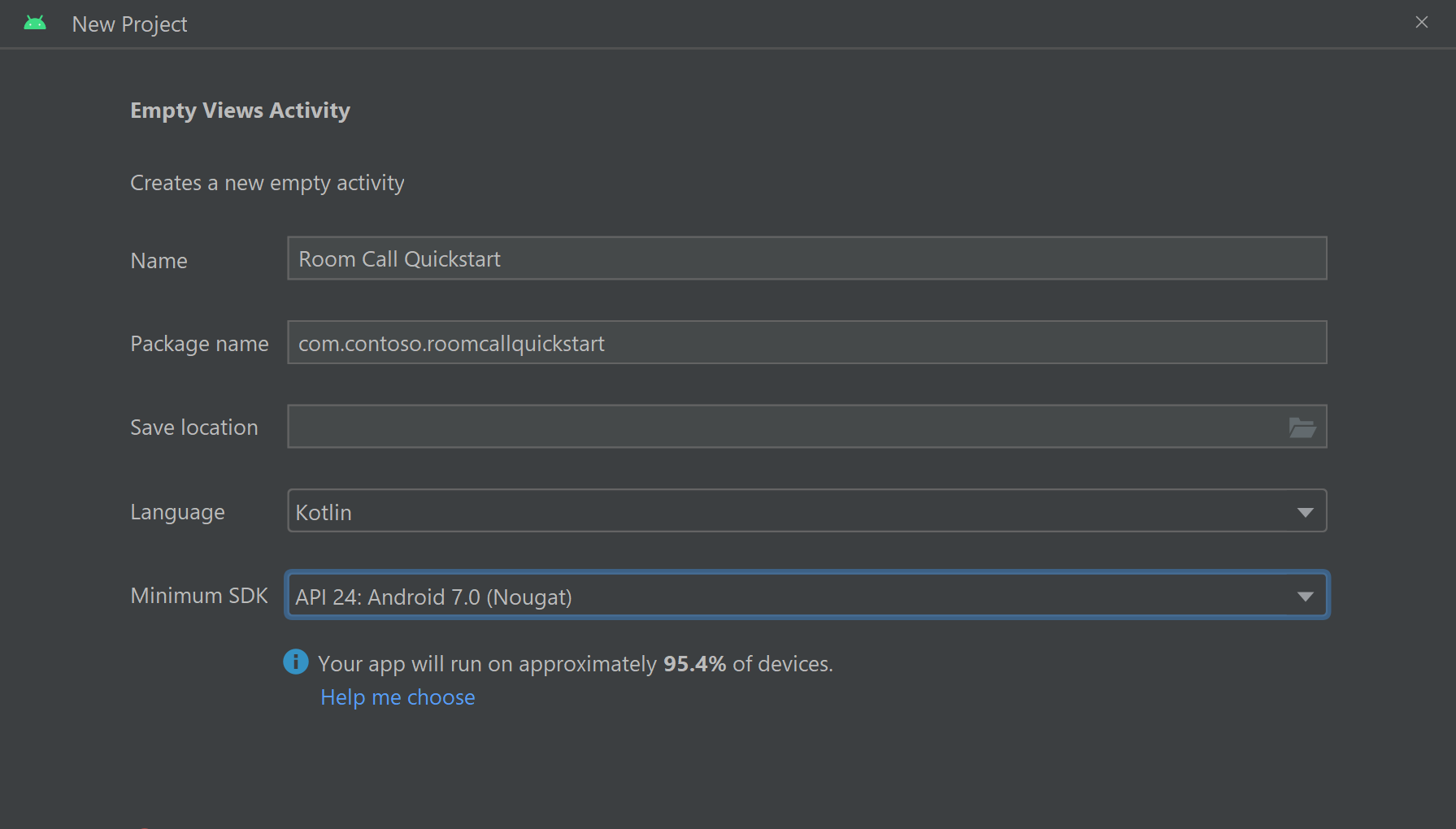
Name your project Room Call Quickstart and select Kotlin.
Install the package
In your module level build.gradle, add the following line to the dependencies section.
dependencies {
...
//Ability to join a Rooms calls is available in 2.4.0 or above.
implementation 'com.azure.android:azure-communication-calling:2.4.0'
...
}
Add permissions to application manifest
To request permissions required to make a call, you must first declare the permissions in the application manifest (app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml). Copy the following to your manifest file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<uses-feature
android:name="android.hardware.camera"
android:required="false" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.AppTheme">
<!--Our Calling SDK depends on the Apache HTTP SDK.
When targeting Android SDK 28+, this library needs to be explicitly referenced.
See https://developer.android.com/about/versions/pie/android-9.0-changes-28#apache-p-->
<uses-library android:name="org.apache.http.legacy" android:required="false"/>
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Set up the layout for the app
You need a text input for the room ID, a button for placing the call, and extra button for hanging up the call.
Go to app/src/main/res/layout/activity_main.xml, and replace the content of file with the following code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_role"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Role:"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_call_status"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Call Status"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
android:layout_marginTop="48dp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/room_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="Room ID"
android:inputType="textPersonName"
android:layout_marginTop="100dp"
android:layout_marginHorizontal="20dp"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="260dp"
android:gravity="center"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/call_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="32dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Start Call" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/hangup_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hangup" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Create the main activity
With the layout created, you can add the logic to start a Room call. The activity handles requesting runtime permissions, creating the call agent, and placing the call when the button is pressed.
The onCreate method invokes getAllPermissions and createAgent, and adds the bindings for the call button.
This event occurs only once when the activity is created. For more information about onCreate, see the guide Understand the activity lifecycle.
Go to MainActivity.kt file, and replace the content with the following code:
package com.contoso.roomscallquickstart
import android.Manifest
import android.annotation.SuppressLint
import android.content.pm.PackageManager
import android.media.AudioManager
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.EditText
import android.widget.TextView
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.Call
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.CallAgent
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.CallClient
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.HangUpOptions
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.JoinCallOptions
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.RoomCallLocator
import com.azure.android.communication.common.CommunicationTokenCredential
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val allPermissions = arrayOf(
Manifest.permission.RECORD_AUDIO,
Manifest.permission.CAMERA,
Manifest.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE
)
private val userToken = "<ACS_USER_TOKEN>"
private lateinit var callAgent: CallAgent
private var call: Call? = null
private lateinit var roleTextView: TextView
private lateinit var statusView: TextView
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
getAllPermissions()
createCallAgent()
val callButton: Button = findViewById(R.id.call_button)
callButton.setOnClickListener { startCall() }
val hangupButton: Button = findViewById(R.id.hangup_button)
hangupButton.setOnClickListener { endCall() }
roleTextView = findViewById(R.id.text_role)
statusView = findViewById(R.id.text_call_status)
volumeControlStream = AudioManager.STREAM_VOICE_CALL
}
/**
* Start a call
*/
private fun startCall() {
if (userToken.startsWith("<")) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Please enter token in source code", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
return
}
val roomIdView: EditText = findViewById(R.id.room_id)
val roomId = roomIdView.text.toString()
if (roomId.isEmpty()) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Please enter room ID", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
return
}
val joinCallOptions = JoinCallOptions()
val roomCallLocator = RoomCallLocator(roomId)
call = callAgent.join(applicationContext, roomCallLocator, joinCallOptions)
call?.addOnStateChangedListener { setCallStatus(call?.state.toString()) }
call?.addOnRoleChangedListener { setRoleText(call?.callParticipantRole.toString()) }
}
/**
* Ends the call previously started
*/
private fun endCall() {
try {
call?.hangUp(HangUpOptions())?.get()
} catch (e: ExecutionException) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Unable to hang up call", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
/**
* Create the call callAgent
*/
private fun createCallAgent() {
try {
val credential = CommunicationTokenCredential(userToken)
callAgent = CallClient().createCallAgent(applicationContext, credential).get()
} catch (ex: Exception) {
Toast.makeText(
applicationContext,
"Failed to create call callAgent.",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT
).show()
}
}
/**
* Request each required permission if the app doesn't already have it.
*/
private fun getAllPermissions() {
val permissionsToAskFor = mutableListOf<String>()
for (permission in allPermissions) {
if (ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, permission) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
permissionsToAskFor.add(permission)
}
}
if (permissionsToAskFor.isNotEmpty()) {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, permissionsToAskFor.toTypedArray(), 1)
}
}
/**
* Ensure all permissions were granted, otherwise inform the user permissions are missing.
*/
override fun onRequestPermissionsResult(
requestCode: Int,
permissions: Array<out String>,
grantResults: IntArray
) {
super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults)
var allPermissionsGranted = true
for (result in grantResults) {
allPermissionsGranted = allPermissionsGranted && (result == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)
}
if (!allPermissionsGranted) {
Toast.makeText(this, "All permissions are needed to make the call.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
finish()
}
}
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
private fun setCallStatus(status: String?) {
runOnUiThread {
statusView.text = "Call Status: $status"
}
}
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
private fun setRoleText(role: String?) {
runOnUiThread {
roleTextView.text = "Role: $role"
}
}
}
Note
When you're designing your app, consider when these permissions should be requested. Permissions should be requested as they are needed, not ahead of time. For more information, see, the Android Permissions Guide.
Run your project
Before running your project, replace <ACS_USER_TOKEN> in MainActivity.kt with your Azure Communication Services User Access Token.
private val userToken = "<ACS_USER_TOKEN>"
Run the project on an emulator or a physical device.
You should see a field to enter your Room ID and a button to start the Room Call. Enter your Room ID and verify the Call status has changed along with your Role.
Understanding joining a Room call
All the code that you have added in your QuickStart app allowed you to successfully start and join a room call. We need to dive deep into how it all works and what more methods/handlers you can access for Rooms.
Room calls are joined through CallAgent which is created with a valid user token:
private fun createCallAgent() {
try {
val credential = CommunicationTokenCredential(userToken)
callAgent = CallClient().createCallAgent(applicationContext, credential).get()
} catch (ex: Exception) {
Toast.makeText(
applicationContext,
"Failed to create call callAgent.",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT
).show()
}
}
Using CallAgent and RoomCallLocator, we can join a room call using the CallAgent.join method which returns a Call object:
val joinCallOptions = JoinCallOptions()
val roomCallLocator = RoomCallLocator(roomId)
call = callAgent.join(applicationContext, roomCallLocator, joinCallOptions)
Further customization beyond the MainActivity.ktfile includes subscribing to Call events to get updates:
call.addOnRemoteParticipantsUpdatedListener { args: ParticipantsUpdatedEvent? ->
handleRemoteParticipantsUpdate(
args!!
)
}
call.addOnStateChangedListener { args: PropertyChangedEvent? ->
this.handleCallOnStateChanged(
args!!
)
}
You can extend MainActivity.kt further to display the role of the local or remote call participants by using these methods and handlers below.
// Get your role in the call
call.getCallParticipantRole();
// Subscribe to changes for your role in a call
private void isCallRoleChanged(PropertyChangedEvent propertyChangedEvent) {
// handle self-role change
}
call.addOnRoleChangedListener(isCallRoleChanged);
// Subscribe to role changes for remote participants
private void isRoleChanged(PropertyChangedEvent propertyChangedEvent) {
// handle remote participant role change
}
remoteParticipant.addOnRoleChangedListener(isRoleChanged);
// Get role of the remote participant
remoteParticipant.getCallParticipantRole();
The ability to join a room call and display the roles of call participants is available in the Android Mobile Calling SDK version 2.4.0 and above.
You can learn more about roles of room call participants in the rooms concept documentation.
Join a room call
To join a room call, set up your windows application using the Add video calling to your client app guide. Alternatively, you can download the video calling quickstart on GitHub.
Create a callAgent with a valid user token:
var creds = new CallTokenCredential("<user-token>");
CallAgentOptions callAgentOptions = new CallAgentOptions();
callAgentOptions.DisplayName = "<display-name>";
callAgent = await callClient.CreateCallAgentAsync(creds, callAgentOptions);
Use the callAgent and RoomCallLocator to join a room call, the CallAgent.JoinAsync method will return a CommunicationCall object:
RoomCallLocator roomCallLocator = new RoomCallLocator('<RoomId>');
CommunicationCall communicationCall = await callAgent.JoinAsync(roomCallLocator, joinCallOptions);
Subscribe to CommunicationCall events to get updates:
private async void CommunicationCall_OnStateChanged(object sender, PropertyChangedEventArgs args) {
var call = sender as CommunicationCall;
if (sender != null)
{
switch (call.State){
// Handle changes in call state
}
}
}
To display the role of call participants, subscribe to the role changes:
private void RemoteParticipant_OnRoleChanged(object sender, Azure.Communication.Calling.WindowsClient.PropertyChangedEventArgs args)
{
_ = Windows.ApplicationModel.Core.CoreApplication.MainView.CoreWindow.Dispatcher.RunAsync(CoreDispatcherPriority.Normal, () =>
{
System.Diagnostics.Trace.WriteLine("Raising Role change, new Role: " + remoteParticipant_.Role);
PropertyChanged(this, new System.ComponentModel.PropertyChangedEventArgs("RemoteParticipantRole"));
});
}
The ability to join a room call and display the roles of call participants is available in the Windows NuGet Release version 1.1.0 and above.
You can learn more about roles of room call participants in the rooms concept documentation.
Next steps
In this section you learned how to:
- Add video calling to your application
- Pass the room identifier to the calling SDK
- Join a room call from your application
You may also want to:
- Learn about rooms concept
- Learn about voice and video calling concepts
- Learn about authentication concepts