Deploy Spring Boot Application to Azure Kubernetes Service
Note
For Spring Boot applications, we recommend using Azure Container Apps. However, you can still choose to use Azure Kubernetes Service as a destination. For more information, see Choose the right Azure services for your Java applications.
This tutorial walks you through combining Kubernetes and Docker to develop and deploy a Spring Boot application to Microsoft Azure. More specifically, you use Spring Boot for application development, Kubernetes for container deployment, and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) to host your application.
Kubernetes and Docker are open-source solutions that help developers automate the deployment, scaling, and management of their applications running in containers.
Prerequisites
- An Azure subscription; if you don't already have an Azure subscription, you can activate your MSDN subscriber benefits or sign up for a free Azure account.
- The Azure Command-Line Interface (CLI).
- A supported Java Development Kit (JDK). For more information about the JDKs available for use when developing on Azure, see Java support on Azure and Azure Stack.
- Apache's Maven build tool (Version 3).
- A Git client.
- A Docker client.
- The ACR Docker credential helper.
Note
Due to the virtualization requirements of this tutorial, you cannot follow the steps in this article on a virtual machine; you must use a physical computer with virtualization features enabled.
Create the Spring Boot on Docker Getting Started web app
The following steps walk you through building a Spring Boot web application and testing it locally.
Open a command-prompt and create a local directory to hold your application, and change to that directory; for example:
mkdir C:\SpringBoot cd C:\SpringBoot-- or --
mkdir /users/$USER/SpringBoot cd /users/$USER/SpringBootClone the Spring Boot on Docker Getting Started sample project into the directory.
git clone https://github.com/spring-guides/gs-spring-boot-docker.gitChange directory to the completed project.
cd gs-spring-boot-docker cd completeUse Maven to build and run the sample app.
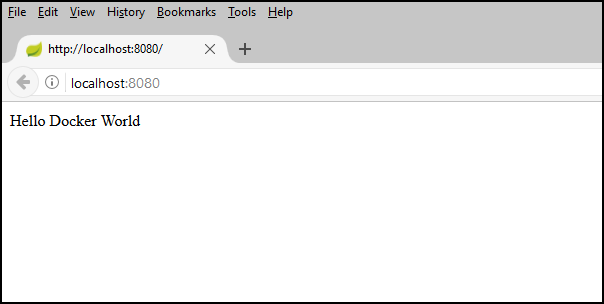
mvn package spring-boot:runTest the web app by browsing to
http://localhost:8080, or with the followingcurlcommand:curl http://localhost:8080You should see the following message displayed: Hello Docker World
Create an Azure Container Registry using the Azure CLI
Open a command prompt.
Log in to your Azure account:
az loginChoose your Azure Subscription:
az account set -s <YourSubscriptionID>Create a resource group for the Azure resources used in this tutorial.
az group create --name=wingtiptoys-kubernetes --location=eastusCreate a private Azure container registry in the resource group. The tutorial pushes the sample app as a Docker image to this registry in later steps. Replace
wingtiptoysregistrywith a unique name for your registry.az acr create --resource-group wingtiptoys-kubernetes --location eastus \ --name wingtiptoysregistry --sku Basic
Push your app to the container registry via Jib
Log in to your Azure Container Registry from the Azure CLI.
# set the default name for Azure Container Registry, otherwise you need to specify the name in "az acr login" az config set defaults.acr=wingtiptoysregistry az acr loginOpen the pom.xml file with a text editor; for example Visual Studio Code.
code pom.xmlUpdate the
<properties>collection in the pom.xml file with the registry name for your Azure Container Registry and the latest version of jib-maven-plugin.<properties> <!-- Note: If your ACR name contains upper case characters, be sure to convert them to lower case characters. --> <docker.image.prefix>wingtiptoysregistry.azurecr.io</docker.image.prefix> <jib-maven-plugin.version>2.5.2</jib-maven-plugin.version> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties>Update the
<plugins>collection in the pom.xml file so that the<plugin>element contains an entry for thejib-maven-plugin, as shown in the following example. Note that we are using a base image from the Microsoft Container Registry (MCR):mcr.microsoft.com/openjdk/jdk:11-ubuntu, which contains an officially supported JDK for Azure. For other MCR base images with officially supported JDKs, see Install the Microsoft Build of OpenJDK..<plugin> <artifactId>jib-maven-plugin</artifactId> <groupId>com.google.cloud.tools</groupId> <version>${jib-maven-plugin.version}</version> <configuration> <from> <image>mcr.microsoft.com/openjdk/jdk:11-ubuntu</image> </from> <to> <image>${docker.image.prefix}/gs-spring-boot-docker</image> </to> </configuration> </plugin>Navigate to the completed project directory for your Spring Boot application and run the following command to build the image and push the image to the registry:
az acr login && mvn compile jib:build
Note
Due to the security concern of Azure Cli and Azure Container Registry, the credential created by az acr login is valid for 1 hour. If you see a 401 Unauthorized error, you can run the az acr login --name <your registry name> command again to reauthenticate. If you see a Read timed out error, you can try increasing timeouts with mvn -Djib.httpTimeout=7200000 jib:dockerBuild, or -Djib.httpTimeout=0 for an infinite timeout.
Create a Kubernetes Cluster on AKS using the Azure CLI
Create a Kubernetes cluster in Azure Kubernetes Service. The following command creates a kubernetes cluster in the
wingtiptoys-kubernetesresource group, withwingtiptoys-aksclusteras the cluster name, with Azure Container Registry (ACR)wingtiptoysregistryattached, andwingtiptoys-kubernetesas the DNS prefix:az aks create --resource-group=wingtiptoys-kubernetes --name=wingtiptoys-akscluster \ --attach-acr wingtiptoysregistry \ --dns-name-prefix=wingtiptoys-kubernetes --generate-ssh-keysThis command may take a while to complete.
Install
kubectlusing the Azure CLI. Linux users may have to prefix this command withsudosince it deploys the Kubernetes CLI to/usr/local/bin.az aks install-cliDownload the cluster configuration information so you can manage your cluster from the Kubernetes web interface and
kubectl.az aks get-credentials --resource-group=wingtiptoys-kubernetes --name=wingtiptoys-akscluster
Deploy the image to your Kubernetes cluster
This tutorial deploys the app using kubectl, then allows you to explore the deployment through the Kubernetes web interface.
Deploy with kubectl
Open a command prompt.
Run your container in the Kubernetes cluster by using the
kubectl runcommand. Give a service name for your app in Kubernetes and the full image name. For example:kubectl run gs-spring-boot-docker --image=wingtiptoysregistry.azurecr.io/gs-spring-boot-docker:latestIn this command:
The container name
gs-spring-boot-dockeris specified immediately after theruncommandThe
--imageparameter specifies the combined login server and image name aswingtiptoysregistry.azurecr.io/gs-spring-boot-docker:latest
Expose your Kubernetes cluster externally by using the
kubectl exposecommand. Specify your service name, the public-facing TCP port used to access the app, and the internal target port your app listens on. For example:kubectl expose pod gs-spring-boot-docker --type=LoadBalancer --port=80 --target-port=8080In this command:
The container name
gs-spring-boot-dockeris specified immediately after theexpose podcommand.The
--typeparameter specifies that the cluster uses load balancer.The
--portparameter specifies the public-facing TCP port of 80. You access the app on this port.The
--target-portparameter specifies the internal TCP port of 8080. The load balancer forwards requests to your app on this port.
Once the app is deployed to the cluster, query the external IP address and open it in your web browser:
kubectl get services -o=jsonpath='{.items[*].status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}'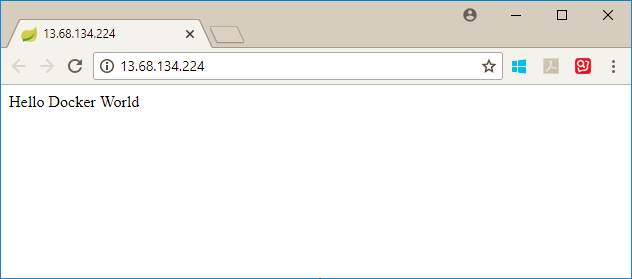
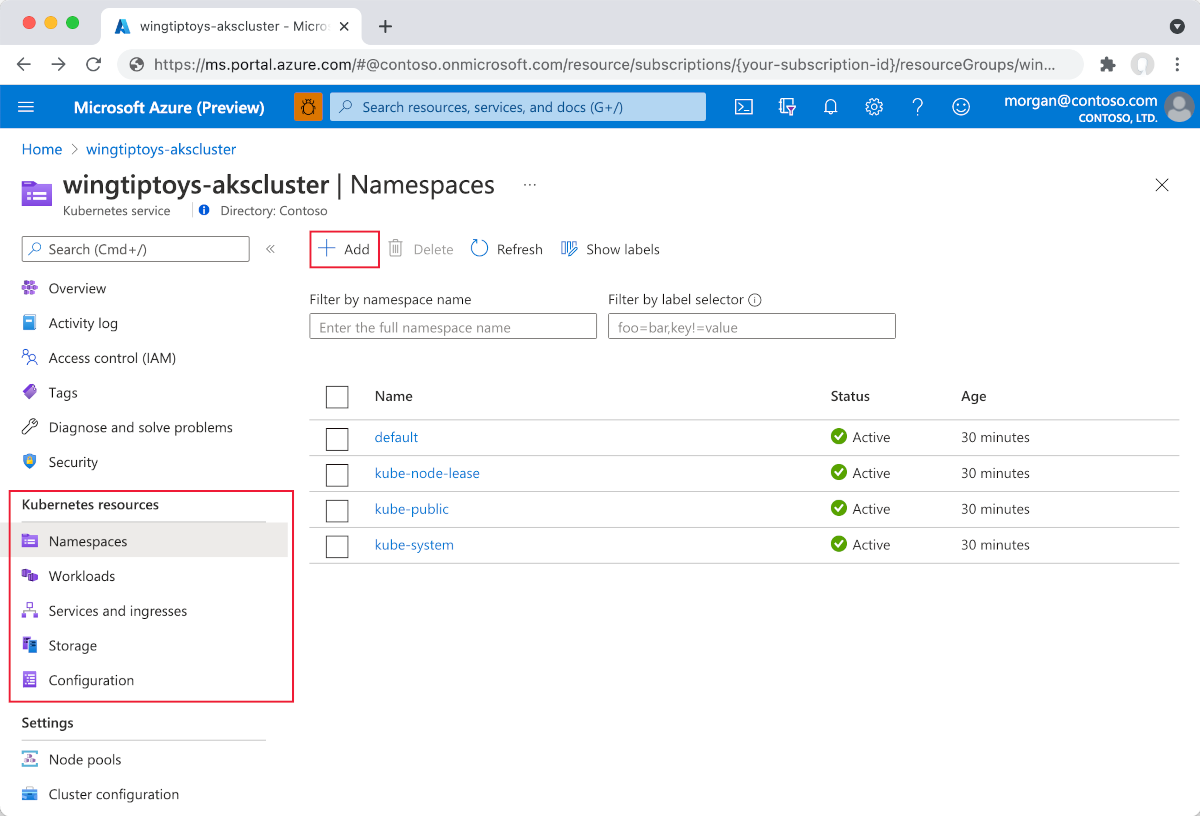
Deploy with the Kubernetes resource view
Select Add from any of the resource views (Namespace, Workloads, Services and ingresses, Storage, or Configuration).
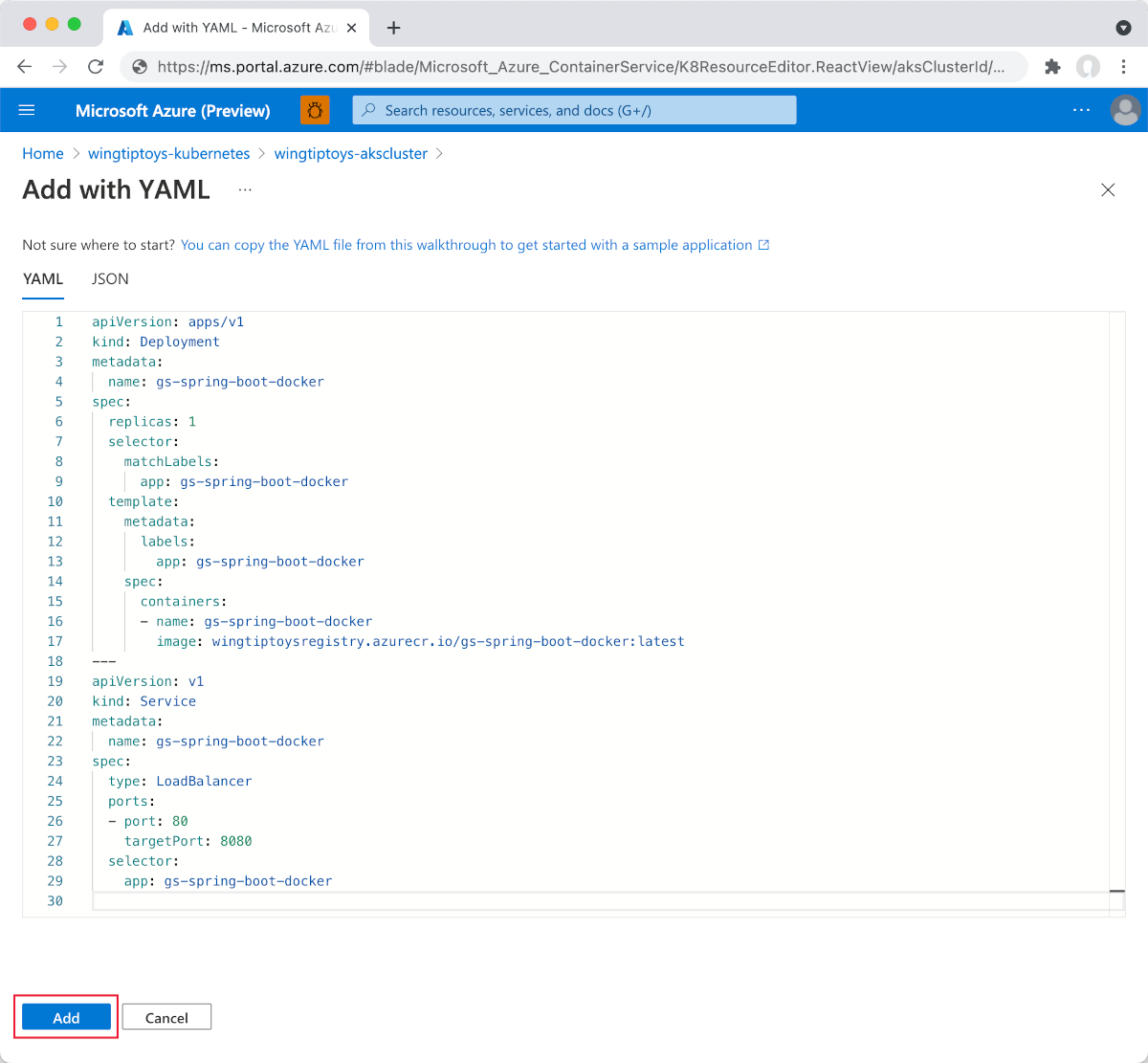
Paste in the following YAML:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: gs-spring-boot-docker spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: gs-spring-boot-docker template: metadata: labels: app: gs-spring-boot-docker spec: containers: - name: gs-spring-boot-docker image: wingtiptoysregistry.azurecr.io/gs-spring-boot-docker:latestSelect Add at the bottom of the YAML editor to deploy the application.
After deploying the
Deployment, just like above, select Add at the bottom of the YAML editor to deployServiceusing the following YAML:apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: gs-spring-boot-docker spec: type: LoadBalancer ports: - port: 80 targetPort: 8080 selector: app: gs-spring-boot-dockerOnce the YAML file is added, the resource viewer shows your Spring Boot application. The external service includes a linked external IP address so you can easily view the application in your browser.
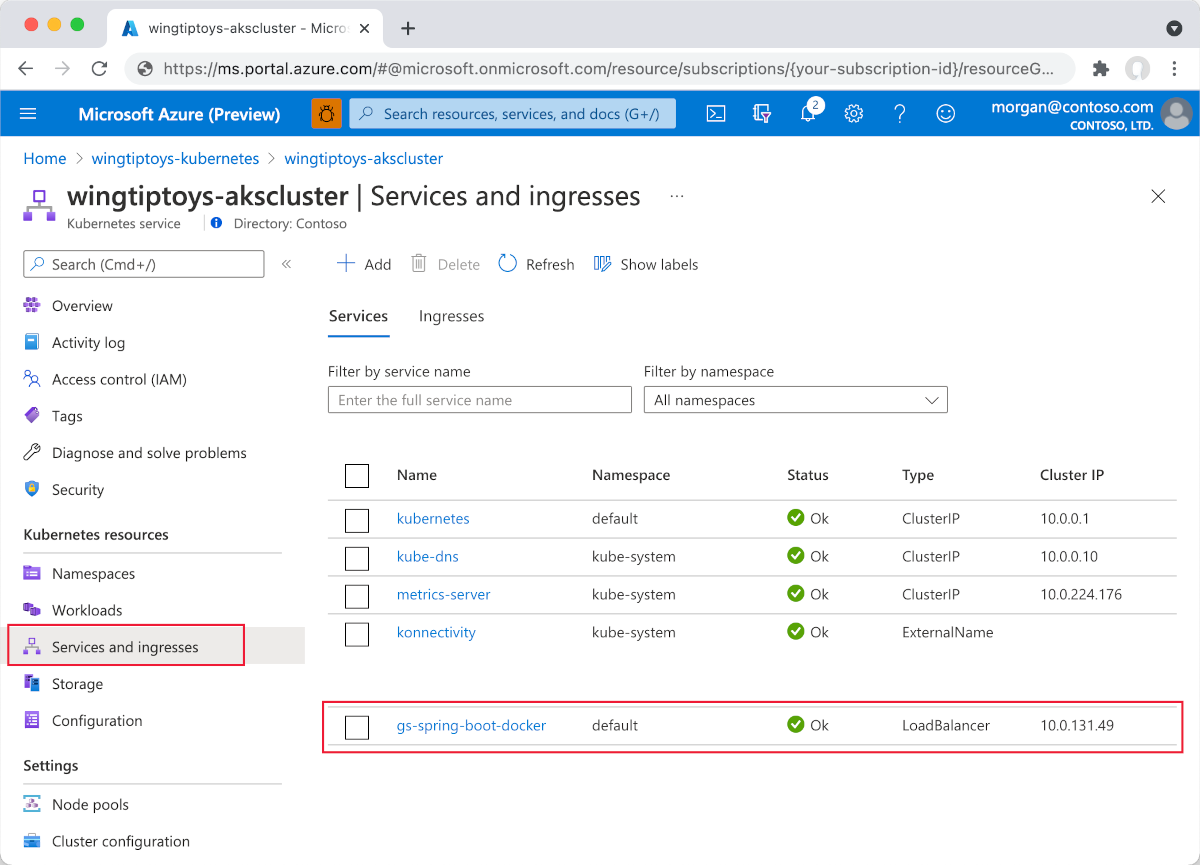
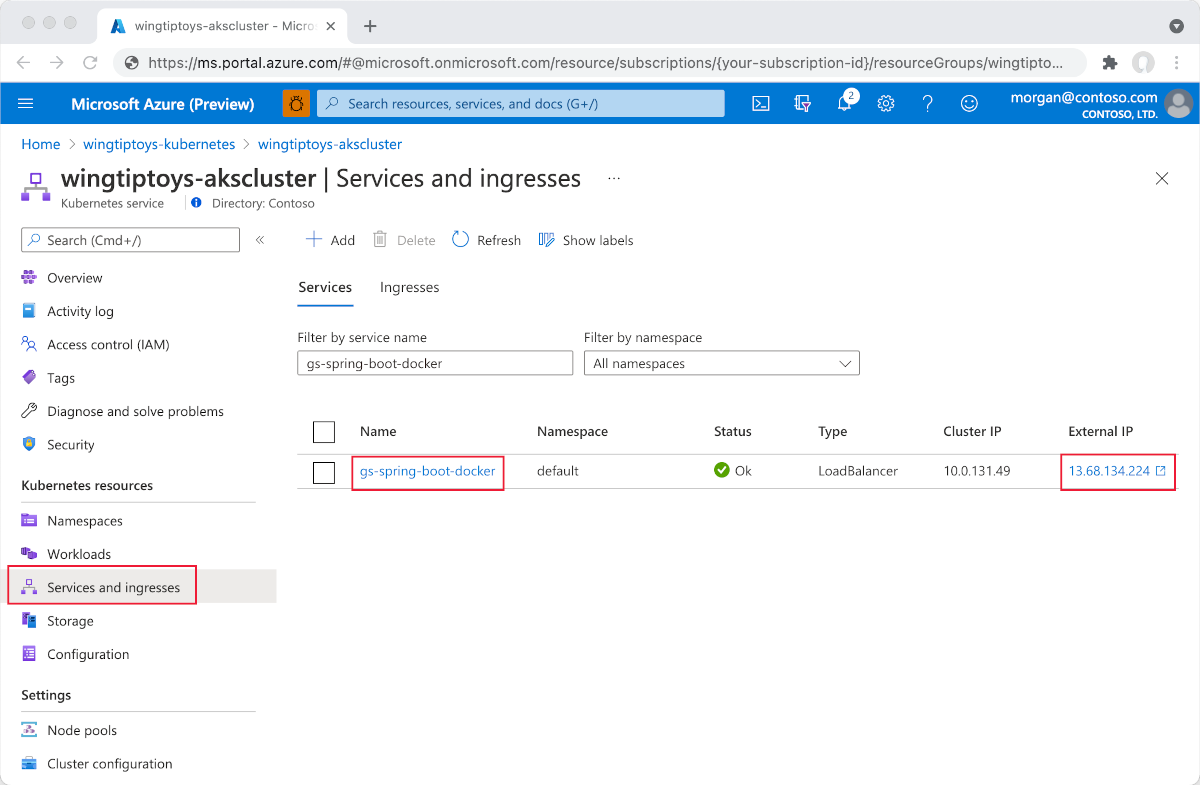
Select External IP. You'll then see your Spring Boot application running on Azure.

Next steps
To learn more about Spring and Azure, continue to the Spring on Azure documentation center.
See also
For more information about using Spring Boot on Azure, see the following article:
For more information about using Azure with Java, see the Azure for Java Developers and the Working with Azure DevOps and Java.
For more information about deploying a Java application to Kubernetes with Visual Studio Code, see Visual Studio Code Java Tutorials.
For more information about the Spring Boot on Docker sample project, see Spring Boot on Docker Getting Started.
The following links provide additional information about creating Spring Boot applications:
- For more information about creating a simple Spring Boot application, see the Spring Initializr at https://start.spring.io/.
The following links provide additional information about using Kubernetes with Azure:
More information about using Kubernetes command-line interface is available in the kubectl user guide at https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/.
The Kubernetes website has several articles that discuss using images in private registries:
For additional examples for how to use custom Docker images with Azure, see Using a custom Docker image for Azure Web App on Linux.
For more information about iteratively running and debugging containers directly in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) with Azure Dev Spaces, see Get started on Azure Dev Spaces with Java