Spring Cloud Azure MySQL support
This article applies to: ✔️ Version 4.19.0 ✔️ Version 5.13.0
Azure Database for MySQL is a relational database service powered by the MySQL community edition. You can use either Single Server or Flexible Server to host a MySQL database in Azure. It's a fully managed database-as-a-service offering that can handle mission-critical workloads with predictable performance and dynamic scalability.
From version 4.5.0, Spring Cloud Azure supports various types of credentials for authentication to Azure Database for MySQL Flexible server.
Supported MySQL version
The current version of the starter should use Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server version 5.7 or 8.0.
Core features
Passwordless connection
Passwordless connection uses Microsoft Entra authentication for connecting to Azure services without storing any credentials in the application, its configuration files, or in environment variables. Microsoft Entra authentication is a mechanism for connecting to Azure Database for MySQL using identities defined in Microsoft Entra ID. With Microsoft Entra authentication, you can manage database user identities and other Microsoft services in a central location, which simplifies permission management.
How it works
Spring Cloud Azure will first build one of the following types of credentials depending on the application authentication configuration:
ClientSecretCredentialClientCertificateCredentialUsernamePasswordCredentialManagedIdentityCredentialDefaultAzureCredential
If none of these types of credentials are found, the DefaultAzureCredential credentials will be obtained from application properties, environment variables, managed identities, or the IDE. For more information, see Spring Cloud Azure authentication.
The following high-level diagram summarizes how authentication works using OAuth credential authentication with Azure Database for MySQL. The arrows indicate communication pathways.
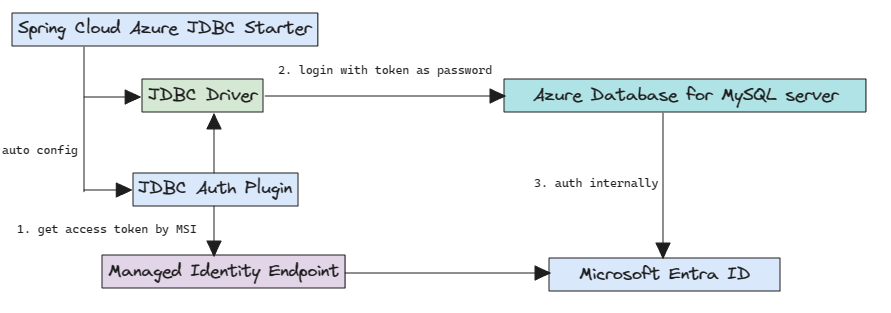
Configuration
Spring Cloud Azure for MySQL supports the following two levels of configuration options:
The global authentication configuration options of
credentialandprofilewith prefixes ofspring.cloud.azure.Spring Cloud Azure for MySQL common configuration options.
The following table shows the Spring Cloud Azure for MySQL common configuration options:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| spring.datasource.azure.passwordless-enabled | Whether to enable passwordless connections to Azure databases by using OAuth2 Microsoft Entra token credentials. |
| spring.datasource.azure.credential.client-certificate-password | Password of the certificate file. |
| spring.datasource.azure.credential.client-certificate-path | Path of a PEM certificate file to use when performing service principal authentication with Azure. |
| spring.datasource.azure.credential.client-id | Client ID to use when performing service principal authentication with Azure. This is a legacy property. |
| spring.datasource.azure.credential.client-secret | Client secret to use when performing service principal authentication with Azure. This is a legacy property. |
| spring.datasource.azure.credential.managed-identity-enabled | Whether to enable managed identity to authenticate with Azure. If true and the client-id is set, will use the client ID as user assigned managed identity client ID. The default value is false. |
| spring.datasource.azure.credential.password | Password to use when performing username/password authentication with Azure. |
| spring.datasource.azure.credential.username | Username to use when performing username/password authentication with Azure. |
| spring.datasource.azure.profile.cloud-type | Name of the Azure cloud to connect to. |
| spring.datasource.azure.profile.environment.active-directory-endpoint | The Microsoft Entra endpoint to connect to. |
| spring.datasource.azure.profile.tenant-id | Tenant ID for Azure resources. The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. |
Dependency setup
Add the following dependency to your project. This will automatically include the spring-boot-starter dependency in your project transitively.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-azure-starter-jdbc-mysql</artifactId>
</dependency>
Note
Passwordless connections have been supported since version 4.5.0.
Remember to add the BOM spring-cloud-azure-dependencies along with the above dependency. For more information, see the Getting started section of the Spring Cloud Azure developer guide.
Basic usage
The following sections show the classic Spring Boot application usage scenarios.
Important
Passwordless connection uses Microsoft Entra authentication. To use Microsoft Entra authentication, you should set the Microsoft Entra admin user first. Only a Microsoft Entra admin user can create and enable users for Microsoft Entra ID-based authentication. For more information, see Use Spring Data JDBC with Azure Database for MySQL.
Connect to Azure MySQL locally without password
To create users and grant permission, see the Create a MySQL non-admin user and grant permission section of Use Spring Data JDBC with Azure Database for MySQL.
Configure the following properties in your application.yml file:
spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://${AZURE_MYSQL_SERVER_NAME}.mysql.database.azure.com:3306/${AZURE_MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME} username: ${AZURE_MYSQL_AD_NON_ADMIN_USERNAME} azure: passwordless-enabled: true
Connect to Azure MySQL using a service principal
Create a Microsoft Entra user for service principal and grant permission.
First, use the following commands to set up some environment variables.
export AZURE_MYSQL_AZURE_AD_SP_USERID=$(az ad sp list \ --display-name <service_principal-name> \ --query '[0].appId' --output tsv) export AZURE_MYSQL_AZURE_AD_SP_USERNAME=<YOUR_MYSQL_AZURE_AD_USERNAME> export AZURE_MYSQL_SERVER_NAME=<YOUR_MYSQL_SERVER_NAME> export AZURE_MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME=<YOUR_MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME> export CURRENT_USERNAME=$(az ad signed-in-user show \ --query userPrincipalName \ --output tsv)Then, create a SQL script called create_ad_user_sp.sql for creating a non-admin user. Add the following contents and save it locally:
cat << EOF > create_ad_user_sp.sql SET aad_auth_validate_oids_in_tenant = OFF; CREATE AADUSER '$AZURE_MYSQL_AZURE_AD_SP_USERNAME' IDENTIFIED BY '$AZURE_MYSQL_AZURE_AD_SP_USERID'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON $AZURE_MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME.* TO '$AZURE_MYSQL_AZURE_AD_SP_USERNAME'@'%'; FLUSH privileges; EOFUse the following command to run the SQL script to create the Microsoft Entra non-admin user:
mysql -h $AZURE_MYSQL_SERVER_NAME.mysql.database.azure.com --user $CURRENT_USERNAME --enable-cleartext-plugin --password=$(az account get-access-token --resource-type oss-rdbms --output tsv --query accessToken) < create_ad_user_sp.sqlNow use the following command to remove the temporary SQL script file:
rm create_ad_user_sp.sql
Configure the following properties in your application.yml file:
spring: cloud: azure: credential: client-id: ${AZURE_CLIENT_ID} client-secret: ${AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET} profile: tenant-id: <tenant> datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://${AZURE_MYSQL_SERVER_NAME}.mysql.database.azure.com:3306/${AZURE_MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME} username: ${AZURE_MYSQL_AD_SP_USERNAME} azure: passwordless-enabled: true
Note
The values allowed for tenant-id are: common, organizations, consumers, or the tenant ID. For more information about these values, see the Used the wrong endpoint (personal and organization accounts) section of Error AADSTS50020 - User account from identity provider does not exist in tenant. For information on converting your single-tenant app, see Convert single-tenant app to multitenant on Microsoft Entra ID.
Connect to Azure MySQL with Managed Identity in Azure Spring Apps
To enable managed identity, see the Assign the managed identity using the Azure portal section of Migrate an application to use passwordless connections with Azure Database for MySQL.
To grant permissions, see the Assign roles to the managed identity section of Migrate an application to use passwordless connections with Azure Database for MySQL.
Configure the following properties in your application.yml file:
spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://${AZURE_MYSQL_SERVER_NAME}.mysql.database.azure.com:3306/${AZURE_MYSQL_DATABASE_NAME} username: ${AZURE_MYSQL_AD_MI_USERNAME} azure: passwordless-enabled: true
Samples
See the azure-spring-boot-samples repository on GitHub.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for