Express.js app converts text to speech with Azure AI Speech
In this tutorial, add Azure AI Speech to an existing Express.js app to add conversion from text to speech using the Azure AI Speech service. Converting text to speech allows you to provide audio without the cost of manually generating the audio.
This tutorial shows 3 different ways to convert text to speech from Azure Azure AI Speech:
- Client JavaScript gets audio directly
- Server JavaScript gets audio from file (*.MP3)
- Server JavaScript gets audio from in-memory arrayBuffer
Application architecture
The tutorial takes a minimal Express.js app and adds functionality using a combination of:
- new route for the server API to provide conversion from text to speech, returning an MP3 stream
- new route for an HTML form to allow you to enter your information
- new HTML form, with JavaScript, provides a client-side call to the Speech service
This application provides three different calls to convert speech to text:
- The first server call creates a file on the server then returns it to the client. You would typically use this for longer text or text you know should be served more than once.
- The second server call is for shorter term text and is held in-memory before returned to the client.
- The client call demonstrates a direct call to the Speech service using the SDK. You may choose to make this call if you have a client-only application without a server.
Prerequisites
Node.js LTS - installed to your local machine.
Visual Studio Code - installed to your local machine.
The Azure App Service extension for VS Code (installed from within VS Code).
Git - used to push to GitHub - which activates the GitHub action.
Use Azure Cloud Shell using the bash
If you prefer, install the Azure CLI to run CLI reference commands.
- If you're using a local install, sign in with Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. See Sign in with Azure CLI for more sign-in options.
- When you're prompted, install Azure CLI extensions on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with Azure CLI.
- Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
Download sample Express.js repo
Using git, clone the Express.js sample repo to your local computer.
git clone https://github.com/Azure-Samples/js-e2e-express-serverChange to the new directory for the sample.
cd js-e2e-express-serverOpen the project in Visual Studio Code.
code .Open a new terminal in Visual Studio Code and install the project dependencies.
npm install
Install Azure AI Speech SDK for JavaScript
From the Visual Studio Code terminal, install the Azure AI Speech SDK.
npm install microsoft-cognitiveservices-speech-sdk
Create a Speech module for the Express.js app
To integrate the Speech SDK into the Express.js application, create a file in the
srcfolder namedazure-cognitiveservices-speech.js.Add the following code to pull in dependencies and create a function to convert text to speech.
// azure-cognitiveservices-speech.js const sdk = require('microsoft-cognitiveservices-speech-sdk'); const { Buffer } = require('buffer'); const { PassThrough } = require('stream'); const fs = require('fs'); /** * Node.js server code to convert text to speech * @returns stream * @param {*} key your resource key * @param {*} region your resource region * @param {*} text text to convert to audio/speech * @param {*} filename optional - best for long text - temp file for converted speech/audio */ const textToSpeech = async (key, region, text, filename)=> { // convert callback function to promise return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { const speechConfig = sdk.SpeechConfig.fromSubscription(key, region); speechConfig.speechSynthesisOutputFormat = 5; // mp3 let audioConfig = null; if (filename) { audioConfig = sdk.AudioConfig.fromAudioFileOutput(filename); } const synthesizer = new sdk.SpeechSynthesizer(speechConfig, audioConfig); synthesizer.speakTextAsync( text, result => { const { audioData } = result; synthesizer.close(); if (filename) { // return stream from file const audioFile = fs.createReadStream(filename); resolve(audioFile); } else { // return stream from memory const bufferStream = new PassThrough(); bufferStream.end(Buffer.from(audioData)); resolve(bufferStream); } }, error => { synthesizer.close(); reject(error); }); }); }; module.exports = { textToSpeech };- Parameters - The file pulls in the dependencies for using the SDK, streams, buffers, and the file system (fs). The
textToSpeechfunction takes four arguments. If a file name with local path is sent, the text is converted to an audio file. If a file name is not sent, an in-memory audio stream is created. - Speech SDK method - The Speech SDK method synthesizer.speakTextAsync returns different types, based on the configuration it receives.
The method returns the result, which differs based on what the method was asked to do:
- Create file
- Create in-memory stream as an array of Buffers
- Audio format - The audio format selected is MP3, but other formats exists, along with other Audio configuration methods.
The local method,
textToSpeech, wraps and converts the SDK call-back function into a promise.- Parameters - The file pulls in the dependencies for using the SDK, streams, buffers, and the file system (fs). The
Create a new route for the Express.js app
Open the
src/server.jsfile.Add the
azure-cognitiveservices-speech.jsmodule as a dependency at the top of the file:const { textToSpeech } = require('./azure-cognitiveservices-speech');Add a new API route to call the textToSpeech method created in the previous section of the tutorial. Add this code after the
/api/helloroute.// creates a temp file on server, the streams to client /* eslint-disable no-unused-vars */ app.get('/text-to-speech', async (req, res, next) => { const { key, region, phrase, file } = req.query; if (!key || !region || !phrase) res.status(404).send('Invalid query string'); let fileName = null; // stream from file or memory if (file && file === true) { fileName = `./temp/stream-from-file-${timeStamp()}.mp3`; } const audioStream = await textToSpeech(key, region, phrase, fileName); res.set({ 'Content-Type': 'audio/mpeg', 'Transfer-Encoding': 'chunked' }); audioStream.pipe(res); });This method takes the required and optional parameters for the
textToSpeechmethod from the querystring. If a file needs to be created, a unique file name is developed. ThetextToSpeechmethod is called asynchronously and pipes the result to the response (res) object.
Update the client web page with a form
Update the client HTML web page with a form that collects the required parameters. The optional parameter is passed in based on which audio control the user selects. Because this tutorial provides a mechanism to call the Azure Speech service from the client, that JavaScript is also provided.
Open the /public/client.html file and replace its contents with the following:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Microsoft Cognitive Services Demo</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="content" style="display:none">
<h1 style="font-weight:500;">Microsoft Cognitive Services Speech </h1>
<h2>npm: microsoft-cognitiveservices-speech-sdk</h2>
<table width="100%">
<tr>
<td></td>
<td>
<a href="https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/cognitive-services/speech-service/get-started" target="_blank">Azure
Cognitive Services Speech Documentation</a>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="right">Your Speech Resource Key</td>
<td>
<input id="resourceKey" type="text" size="40" placeholder="Your resource key (32 characters)" value=""
onblur="updateSrc()">
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="right">Your Speech Resource region</td>
<td>
<input id="resourceRegion" type="text" size="40" placeholder="Your resource region" value="eastus"
onblur="updateSrc()">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="right" valign="top">Input Text (max 255 char)</td>
<td><textarea id="phraseDiv" style="display: inline-block;width:500px;height:50px" maxlength="255"
onblur="updateSrc()">all good men must come to the aid</textarea></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="right">
Stream directly from Azure Cognitive Services
</td>
<td>
<div>
<button id="clientAudioAzure" onclick="getSpeechFromAzure()">Get directly from Azure</button>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="right">
Stream audio from file on server</td>
<td>
<audio id="serverAudioFile" controls preload="none" onerror="DisplayError()">
</audio>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td align="right">Stream audio from buffer on server</td>
<td>
<audio id="serverAudioStream" controls preload="none" onerror="DisplayError()">
</audio>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
<!-- Speech SDK reference sdk. -->
<script
src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/microsoft-cognitiveservices-speech-sdk@latest/distrib/browser/microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech.sdk.bundle-min.js">
</script>
<!-- Speech SDK USAGE -->
<script>
// status fields and start button in UI
var phraseDiv;
var resultDiv;
// subscription key and region for speech services.
var resourceKey = null;
var resourceRegion = "eastus";
var authorizationToken;
var SpeechSDK;
var synthesizer;
var phrase = "all good men must come to the aid"
var queryString = null;
var audioType = "audio/mpeg";
var serverSrc = "/text-to-speech";
document.getElementById('serverAudioStream').disabled = true;
document.getElementById('serverAudioFile').disabled = true;
document.getElementById('clientAudioAzure').disabled = true;
// update src URL query string for Express.js server
function updateSrc() {
// input values
resourceKey = document.getElementById('resourceKey').value.trim();
resourceRegion = document.getElementById('resourceRegion').value.trim();
phrase = document.getElementById('phraseDiv').value.trim();
// server control - by file
var serverAudioFileControl = document.getElementById('serverAudioFile');
queryString += `%file=true`;
const fileQueryString = `file=true®ion=${resourceRegion}&key=${resourceKey}&phrase=${phrase}`;
serverAudioFileControl.src = `${serverSrc}?${fileQueryString}`;
console.log(serverAudioFileControl.src)
serverAudioFileControl.type = "audio/mpeg";
serverAudioFileControl.disabled = false;
// server control - by stream
var serverAudioStreamControl = document.getElementById('serverAudioStream');
const streamQueryString = `region=${resourceRegion}&key=${resourceKey}&phrase=${phrase}`;
serverAudioStreamControl.src = `${serverSrc}?${streamQueryString}`;
console.log(serverAudioStreamControl.src)
serverAudioStreamControl.type = "audio/mpeg";
serverAudioStreamControl.disabled = false;
// client control
var clientAudioAzureControl = document.getElementById('clientAudioAzure');
clientAudioAzureControl.disabled = false;
}
function DisplayError(error) {
window.alert(JSON.stringify(error));
}
// Client-side request directly to Azure Cognitive Services
function getSpeechFromAzure() {
// authorization for Speech service
var speechConfig = SpeechSDK.SpeechConfig.fromSubscription(resourceKey, resourceRegion);
// new Speech object
synthesizer = new SpeechSDK.SpeechSynthesizer(speechConfig);
synthesizer.speakTextAsync(
phrase,
function (result) {
// Success function
// display status
if (result.reason === SpeechSDK.ResultReason.SynthesizingAudioCompleted) {
// load client-side audio control from Azure response
audioElement = document.getElementById("clientAudioAzure");
const blob = new Blob([result.audioData], { type: "audio/mpeg" });
const url = window.URL.createObjectURL(blob);
} else if (result.reason === SpeechSDK.ResultReason.Canceled) {
// display Error
throw (result.errorDetails);
}
// clean up
synthesizer.close();
synthesizer = undefined;
},
function (err) {
// Error function
throw (err);
audioElement = document.getElementById("audioControl");
audioElement.disabled = true;
// clean up
synthesizer.close();
synthesizer = undefined;
});
}
// Initialization
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
var clientAudioAzureControl = document.getElementById("clientAudioAzure");
var resultDiv = document.getElementById("resultDiv");
resourceKey = document.getElementById('resourceKey').value;
resourceRegion = document.getElementById('resourceRegion').value;
phrase = document.getElementById('phraseDiv').value;
if (!!window.SpeechSDK) {
SpeechSDK = window.SpeechSDK;
clientAudioAzure.disabled = false;
document.getElementById('content').style.display = 'block';
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Highlighted lines in the file:
- Line 74: The Azure Speech SDK is pulled into the client library, using the
cdn.jsdelivr.netsite to deliver the NPM package. - Line 102: The
updateSrcmethod updates the audio controls'srcURL with the querystring including the key, region, and text. - Line 137: If a user selects the
Get directly from Azurebutton, the web page calls directly to Azure from the client page and processes the result.
Create an Azure AI Speech resource
Create the Speech resource with Azure CLI commands in an Azure Cloud Shell.
Log in to the Azure Cloud Shell. This requires you to authenticate in a browser with your account, which has permission on a valid Azure Subscription.
Create a resource group for your Speech resource.
az group create \ --location eastus \ --name tutorial-resource-group-eastusCreate a Speech resource in the resource group.
az cognitiveservices account create \ --kind SpeechServices \ --location eastus \ --name tutorial-speech \ --resource-group tutorial-resource-group-eastus \ --sku F0This command will fail if your only free Speech resource has already been created.
Use the command to get the key values for the new Speech resource.
az cognitiveservices account keys list \ --name tutorial-speech \ --resource-group tutorial-resource-group-eastus \ --output tableCopy one of the keys.
You use the key by pasting it into the web form of the Express app to authenticate to the Azure Speech service.
Run the Express.js app to convert text to speech
Start the app with the following bash command.
npm startOpen the web app in a browser.
http://localhost:3000Paste your Speech key into the highlighted text box.
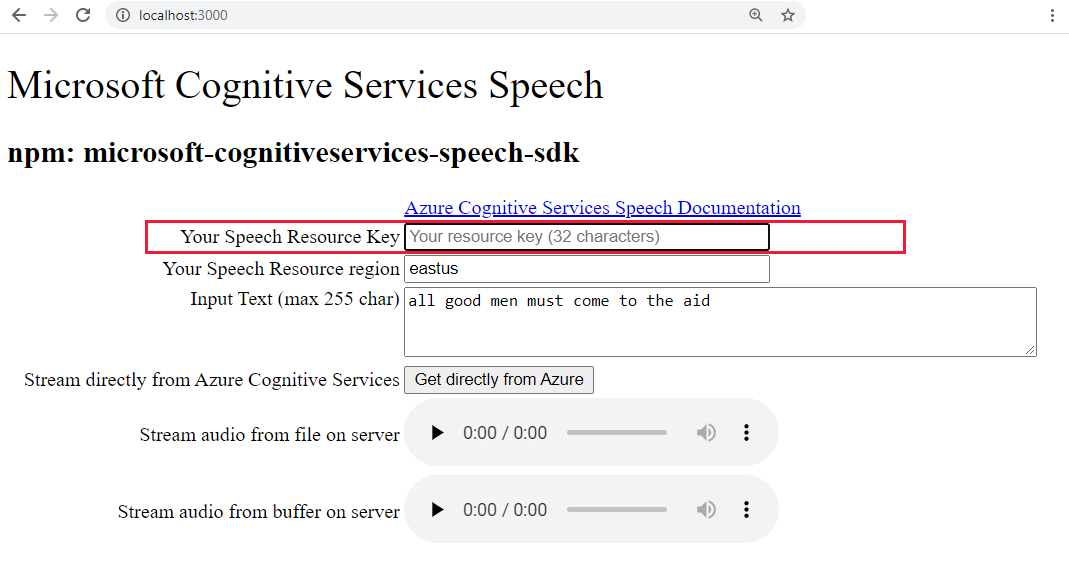
Optionally, change the text to something new.
Select one of the three buttons to begin the conversion to the audio format:
- Get directly from Azure - client-side call to Azure
- Audio control for audio from file
- Audio control for audio from buffer
You may notice a small delay between selecting the control and the audio playing.
Create new Azure App service in Visual Studio Code
From the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P), type "create web" and select Azure App Service: Create New Web App...Advanced. You use the advanced command to have full control over the deployment including resource group, App Service Plan, and operating system rather than use Linux defaults.
Respond to the prompts as follows:
- Select your Subscription account.
- For Enter a globally unique name like
my-text-to-speech-app.- Enter a name that's unique across all of Azure. Use only alphanumeric characters ('A-Z', 'a-z', and '0-9') and hyphens ('-')
- Select
tutorial-resource-group-eastusfor the resource group. - Select a runtime stack of a version that includes
NodeandLTS. - Select the Linux operating system.
- Select Create a new App Service plan, provide a name like
my-text-to-speech-app-plan. - Select the F1 free pricing tier. If your subscription already has a free web app, select the
Basictier. - Select Skip for now for the Application Insights resource.
- Select the
eastuslocation.
After a short time, Visual Studio Code notifies you that creation is complete. Close the notification with the X button.
Deploy local Express.js app to remote App service in Visual Studio Code
With the web app in place, deploy your code from the local computer. Select the Azure icon to open the Azure App Service explorer, expand your subscription node, right-click the name of the web app you just created, and select Deploy to Web App.
If there are deployment prompts, select the root folder of the Express.js app, select your subscription account again and then select the name of the web app,
my-text-to-speech-app, created earlier.If prompted to run
npm installwhen deploying to Linux, select Yes if prompted to update your configuration to runnpm installon the target server.
Once deployment is complete, select Browse Website in the prompt to view your freshly deployed web app.
(Optional): You can make changes to your code files, then use the Deploy to Web App, in the Azure App service extension, to update the web app.
Stream remote service logs in Visual Studio Code
View (tail) any output that the running app generates through calls to console.log. This output appears in the Output window in Visual Studio Code.
In the Azure App Service explorer, right-click your new app node and choose Start Streaming Logs.
Starting Live Log Stream ---
Refresh the web page a few times in the browser to see additional log output.
Clean up resources by removing resource group
Once you have completed this tutorial, you need to remove the resource group, which includes the resource, to make sure you are not billed for any more usage.
In the Azure Cloud Shell, use the Azure CLI command to delete the resource group:
az group delete --name tutorial-resource-group-eastus -y
This command may take a few minutes.
