Deploy Azure IoT Operations to an Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster
Learn how to deploy Azure IoT Operations to a Kubernetes cluster using the Azure portal.
In this article, we discuss Azure IoT Operations deployments and instances, which are two different concepts:
An Azure IoT Operations deployment describes all of the components and resources that enable the Azure IoT Operations scenario. These components and resources include:
- An Azure IoT Operations instance
- Arc extensions
- Custom locations
- Resources that you can configure in your Azure IoT Operations solution, like assets and asset endpoints.
An Azure IoT Operations instance is the parent resource that bundles the suite of services that are defined in What is Azure IoT Operations? like MQTT broker, data flows, and connector for OPC UA.
When we talk about deploying Azure IoT Operations, we mean the full set of components that make up a deployment. Once the deployment exists, you can view, manage, and update the instance.
Prerequisites
Cloud resources:
An Azure subscription.
Azure access permissions. For more information, see Deployment details > Required permissions.
Development resources:
Azure CLI installed on your development machine. This scenario requires Azure CLI version 2.53.0 or higher. Use
az --versionto check your version andaz upgradeto update if necessary. For more information, see How to install the Azure CLI.The Azure IoT Operations extension for Azure CLI. Use the following command to add the extension or update it to the latest version:
az extension add --upgrade --name azure-iot-ops
A cluster host:
Have an Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster with the custom location and workload identity features enabled. If you don't have one, follow the steps in Prepare your Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster.
If you deployed Azure IoT Operations to your cluster previously, uninstall those resources before continuing. For more information, see Update Azure IoT Operations.
(Optional) Prepare your cluster for observability before deploying Azure IoT Operations: Configure observability.
(Optional) Configure your own certificate authority issuer before deploying Azure IoT Operations: Bring your own issuer.
Deploy
The Azure portal deployment experience is a helper tool that generates a deployment command based on your resources and configuration. The final step is to run an Azure CLI command, so you still need the Azure CLI prerequisites described in the previous section.
In the Azure portal, search for and select Azure IoT Operations.
Select Create.
On the Basics tab, provide the following information:
Parameter Value Subscription Select the subscription that contains your Arc-enabled cluster. Resource group Select the resource group that contains your Arc-enabled cluster. Cluster name Select the cluster that you want to deploy Azure IoT Operations to. Custom location name Optional: Replace the default name for the custom location. 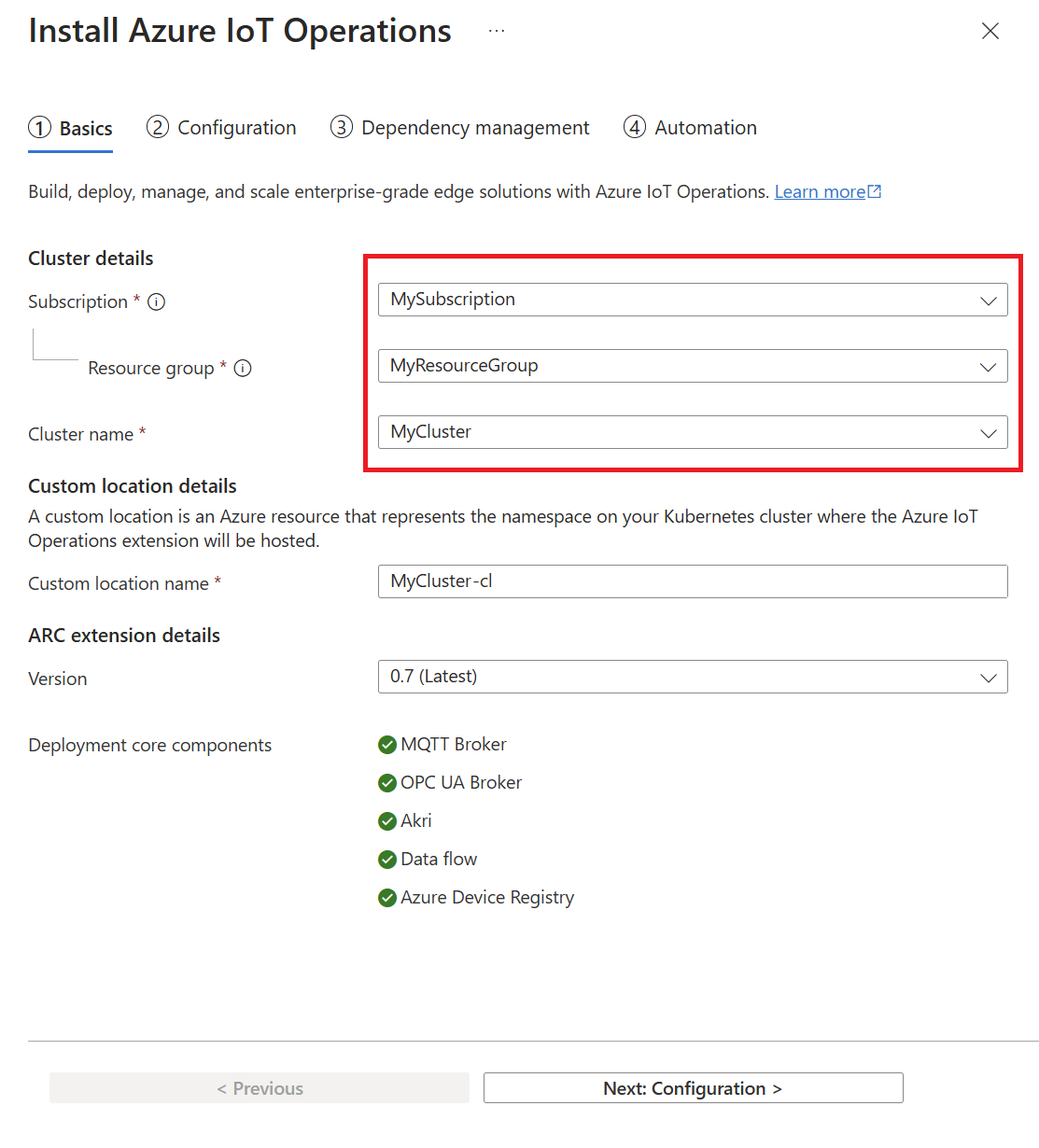
Select Next: Configuration.
On the Configuration tab, provide the following information:
Parameter Value Azure IoT Operations name Optional: Replace the default name for the Azure IoT Operations instance. MQTT broker configuration Optional: Edit the default settings for the MQTT broker. In Azure portal it's possible to configure cardinality and memory profile settings. To configure other settings including disk-backed message buffer and advanced MQTT client options, see Azure CLI support for advanced MQTT broker configuration. Data flow profile configuration Optional: Edit the default settings for data flows. For more information, see Configure data flow profile. 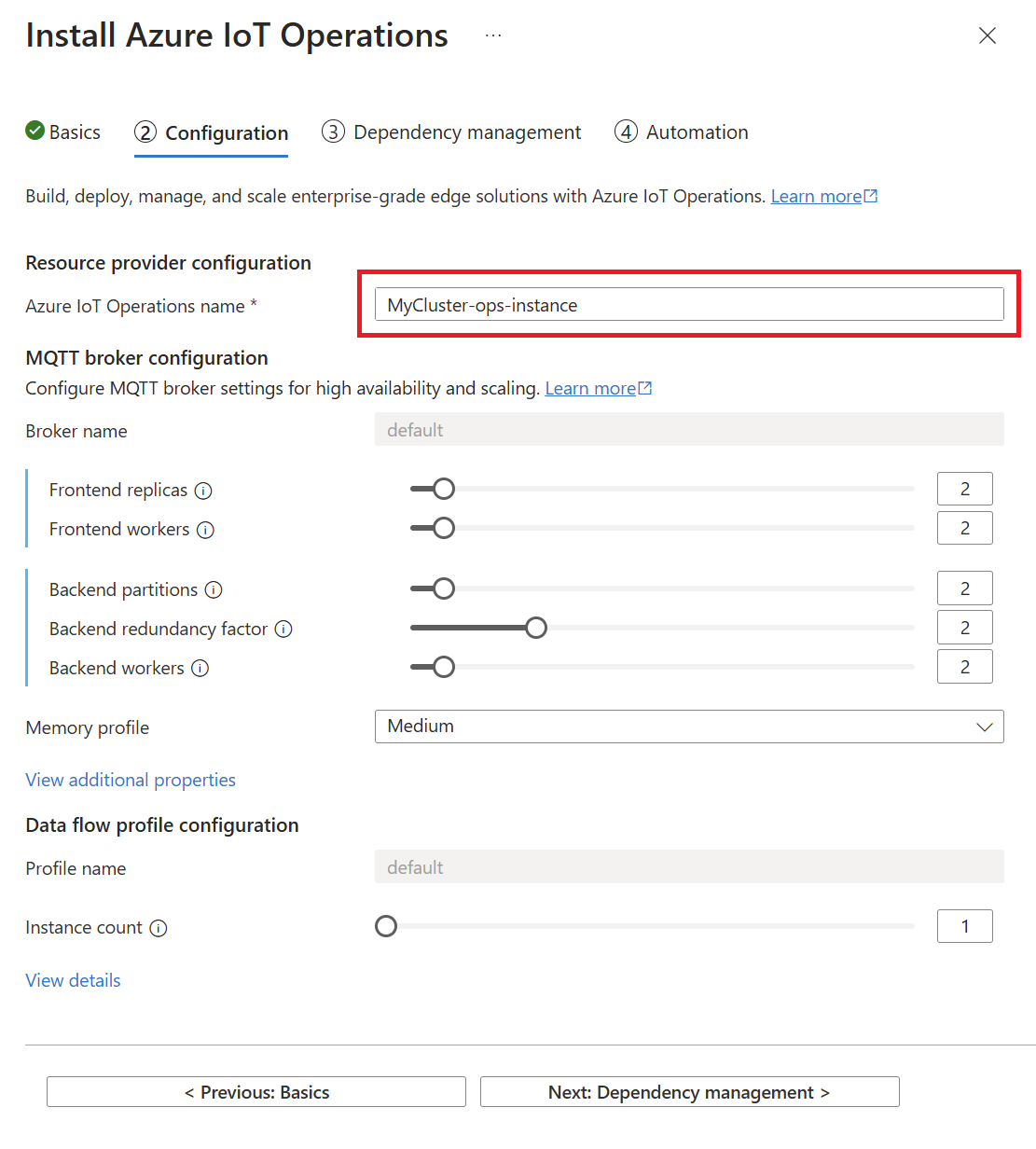
Select Next: Dependency management.
On the Dependency management tab, select an existing schema registry or use these steps to create one:
Select Create new.
Provide a Schema registry name and Schema registry namespace.
Select Select Azure Storage container.
Choose a storage account from the list of hierarchical namespace-enabled accounts, or select Create to create one.
Schema registry requires an Azure Storage account with hierarchical namespace and public network access enabled. When creating a new storage account, choose a General purpose v2 storage account type and set Hierarchical namespace to Enabled.
Select a container in your storage account or select Container to create one.
Select Apply to confirm the schema registry configurations.
On the Dependency management tab, select either the Test settings or the Secure settings deployment option. If you aren't sure which is right for your scenario, review the guidance in Deployment details > Choose your features.
Depending on your choice, follow the steps to either:
Deploy with test settings
Use these steps if you chose the Test settings option on the Dependency management tab.
Select Next: Automation.
One at a time, run each Azure CLI command on the Automation tab in a terminal:
Sign in to Azure CLI interactively with a browser even if you already signed in before. If you don't sign in interactively, you might get an error that says Your device is required to be managed to access your resource.
az loginInstall the latest Azure IoT Operations CLI extension.
az upgrade az extension add --upgrade --name azure-iot-opsCreate a schema registry which will be used by Azure IoT Operations components. Copy and run the provided az iot ops schema registry create command.
If you chose to use an existing schema registry, this command isn't displayed on the Automation tab.
Prepare the cluster for Azure IoT Operations deployment. Copy and run the provided az iot ops init command.
Tip
The
initcommand only needs to be run once per cluster. If you're reusing a cluster that already had Azure IoT Operations version 0.8.0 deployed on it, you can skip this step.If you followed the optional prerequisite to set up your own certificate authority issuer, add the
--user-trustflag to theinitcommand.This command might take several minutes to complete. You can watch the progress in the deployment progress display in the terminal.
Deploy Azure IoT Operations. Copy and run the provided az iot ops create command.
If you followed the optional prerequisites to prepare your cluster for observability, add the following parameters to the
createcommand:Parameter Value Description --ops-configobservability.metrics.openTelemetryCollectorAddress=<FULLNAMEOVERRIDE>.azure-iot-operations.svc.cluster.local:<GRPC_ENDPOINT>Provide the OpenTelemetry (OTel) collector address you configured in the otel-collector-values.yaml file.
The sample values used in Configure observability are fullnameOverride=aio-otel-collector and grpc.endpoint=4317.--ops-configobservability.metrics.exportInternalSeconds=<CHECK_INTERVAL>Provide the check_interval value you configured in the otel-collector-values.yaml file.
The sample value used in Configure observability is check_interval=60.If you followed the optional prerequisites to set up your own certificate authority issuer, add the
--trust-settingsparameters to thecreatecommand:--trust-settings configMapName=<CONFIGMAP_NAME> configMapKey=<CONFIGMAP_KEY_WITH_PUBLICKEY_VALUE> issuerKind=<CLUSTERISSUER_OR_ISSUER> issuerName=<ISSUER_NAME>
This command might take several minutes to complete. You can watch the progress in the deployment progress display in the terminal.
Once all of the Azure CLI commands complete successfully, you can close the Install Azure IoT Operations wizard.
Once the create command completes successfully, you have a working Azure IoT Operations instance running on your cluster. At this point, your instance is configured for most testing and evaluation scenarios.
If at any point in the future you want to prepare your instance for production scenarios, follow the steps in Enable secure settings on an existing Azure IoT Operations instance.
Deploy with secure settings
Use these steps if you chose the Secure settings option on the Dependency management tab.
In the Deployment options section, provide the following information:
Parameter Value Subscription Select the subscription that contains your Azure key vault. Azure Key Vault Select an Azure key vault or select Create new.
Ensure that your key vault has Azure role-based access control as its permission model. To check this setting, select Manage selected vault > Settings > Access configuration.
Ensure to give your user account permissions to manage secrets with theKey Vault Secrets Officerrole.User assigned managed identity for secrets Select an identity or select Create new. User assigned managed identity for AIO components Select an identity or select Create new. Don't use the same managed identity as the one you selected for secrets. 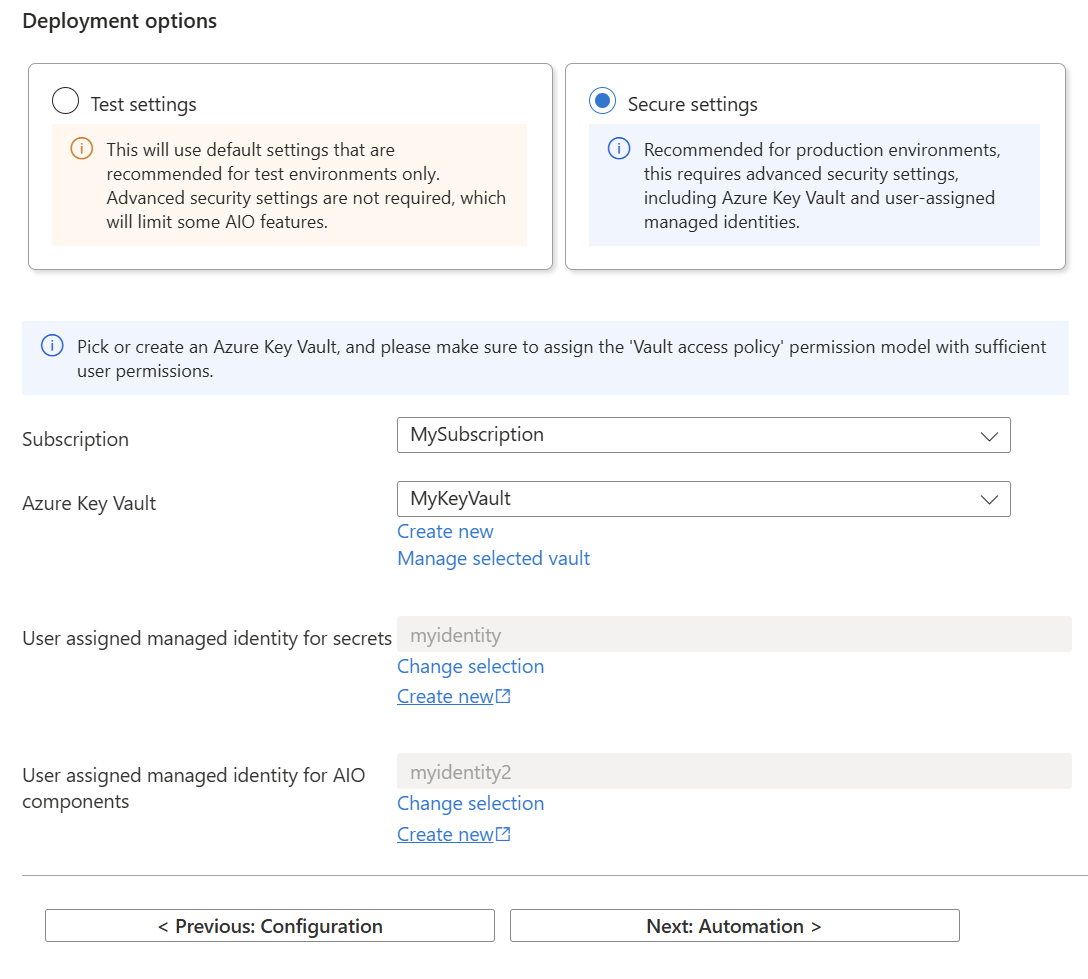
Select Next: Automation.
One at a time, run each Azure CLI command on the Automation tab in a terminal:
Sign in to Azure CLI interactively with a browser even if you already signed in before. If you don't sign in interactively, you might get an error that says Your device is required to be managed to access your resource when you continue to the next step to deploy Azure IoT Operations.
az loginInstall the latest Azure IoT Operations CLI extension.
az upgrade az extension add --upgrade --name azure-iot-opsCreate a schema registry which will be used by Azure IoT Operations components. Copy and run the provided az iot ops schema registry create command.
If you chose to use an existing schema registry, this command isn't displayed on the Automation tab.
Note
This command requires that you have role assignment write permissions because it assigns a role to give schema registry access to the storage account. By default, the role is the built-in Storage Blob Data Contributor role, or you can create a custom role with restricted permissions to assign instead. For more information, see az iot ops schema registry create.
Prepare the cluster for Azure IoT Operations deployment. Copy and run the provided az iot ops init command.
Tip
The
initcommand only needs to be run once per cluster. If you're reusing a cluster that already had Azure IoT Operations version 0.8.0 deployed on it, you can skip this step.This command might take several minutes to complete. You can watch the progress in the deployment progress display in the terminal.
Deploy Azure IoT Operations. Copy and run the provided az iot ops create command.
If you followed the optional prerequisites to prepare your cluster for observability, add the following optional parameters to the
createcommand:Optional parameter Value Description --ops-configobservability.metrics.openTelemetryCollectorAddress=<FULLNAMEOVERRIDE>.azure-iot-operations.svc.cluster.local:<GRPC_ENDPOINT>Provide the OpenTelemetry (OTel) collector address you configured in the otel-collector-values.yaml file.
The sample values used in Configure observability are fullnameOverride=aio-otel-collector and grpc.endpoint=4317.--ops-configobservability.metrics.exportInternalSeconds=<CHECK_INTERVAL>Provide the check_interval value you configured in the otel-collector-values.yaml file.
The sample value used in Configure observability is check_interval=60.This command might take several minutes to complete. You can watch the progress in the deployment progress display in the terminal.
Enable secret sync for the deployed Azure IoT Operations instance. Copy and run the provided az iot ops secretsync enable command.
This command:
- Creates a federated identity credential using the user-assigned managed identity.
- Adds a role assignment to the user-assigned managed identity for access to the Azure Key Vault.
- Adds a minimum secret provider class associated with the Azure IoT Operations instance.
Assign a user-assigned managed identity to the deployed Azure IoT Operations instance. Copy and run the provided az iot ops identity assign command.
This command creates a federated identity credential using the OIDC issuer of the indicated connected cluster and the Azure IoT Operations service account.
Once all of the Azure CLI commands complete successfully, you can close the Install Azure IoT Operations wizard.
Once the create command completes successfully, you have a working Azure IoT Operations instance running on your cluster. At this point, your instance is configured for production scenarios.
Verify deployment
After the deployment is complete, use az iot ops check to evaluate IoT Operations service deployment for health, configuration, and usability. The check command can help you find problems in your deployment and configuration.
az iot ops check
The check command displays a warning about missing data flows, which is normal and expected until you create a data flow. For more information, see Process and route data with data flows.
You can check the configurations of topic maps, QoS, and message routes by adding the --detail-level 2 parameter to the check command for a verbose view.
Next steps
If your components need to connect to Azure endpoints like SQL or Fabric, learn how to Manage secrets for your Azure IoT Operations deployment.