Use index recommendations produced by index tuning in Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server (Preview)
Index tuning persists the recommendations it makes in a set of tables located under the intelligentperformance schema in the azure_sys database.
Currently, that information can be read using the Azure portal page build for this purpose or by executing queries to retrieve data from two views available inside the intelligent performance of the azure_sys database.
Consume index recommendations through the Azure portal
Sign in to the Azure portal and select your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance.
Select Index tuning (preview) in the Intelligent Performance section of the menu.
If the feature is enabled but no recommendations are produced yet, the screen looks like this:
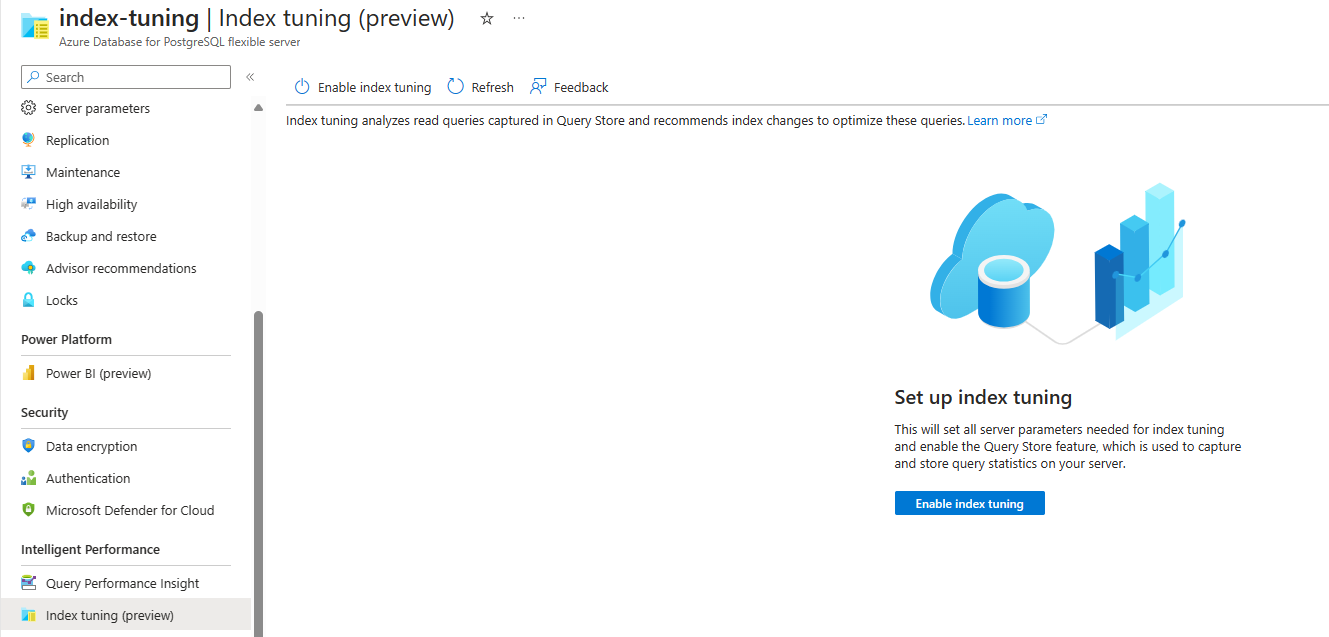
If the feature is currently disabled and it never produced recommendations in the past, the screen looks like this:
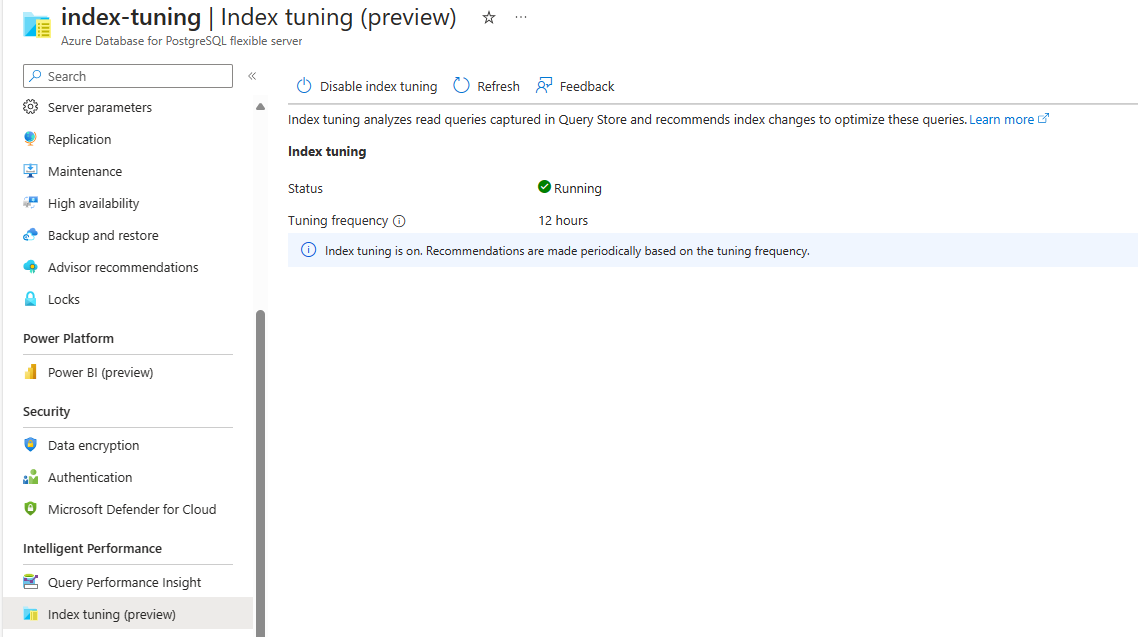
If the feature is enabled and no recommendations are produced yet, the screen looks like this:
If the feature is disabled but it ever produced recommendations, the screen looks like this:
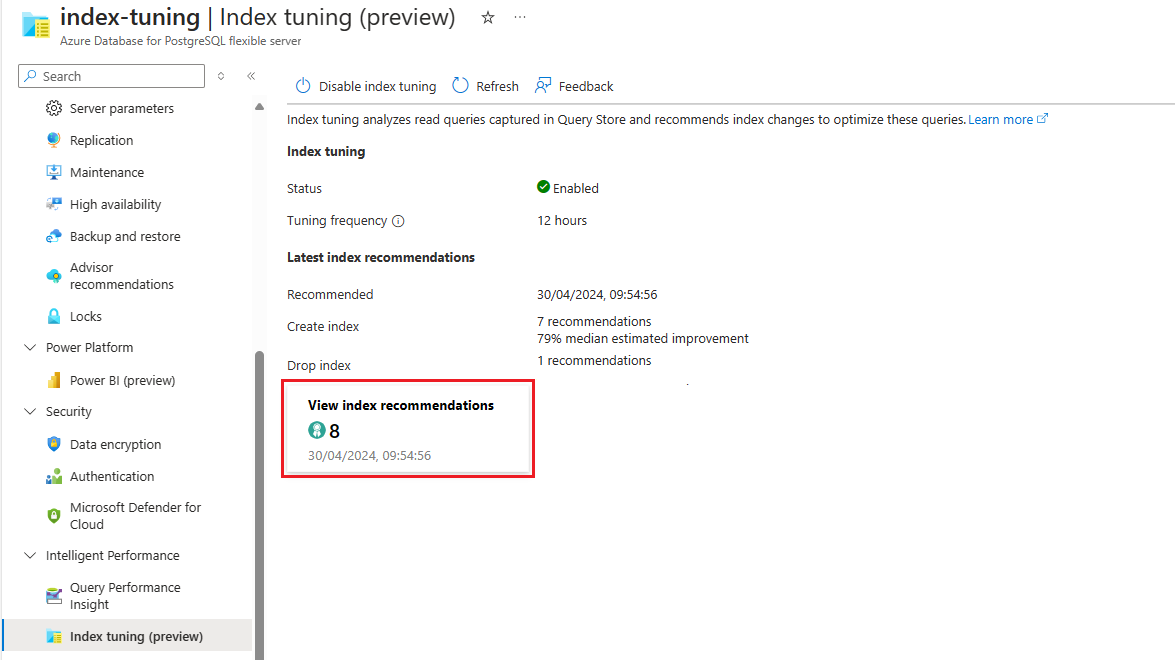
If there are recommendations available, select on the View index recommendations summarization to access to the full list:
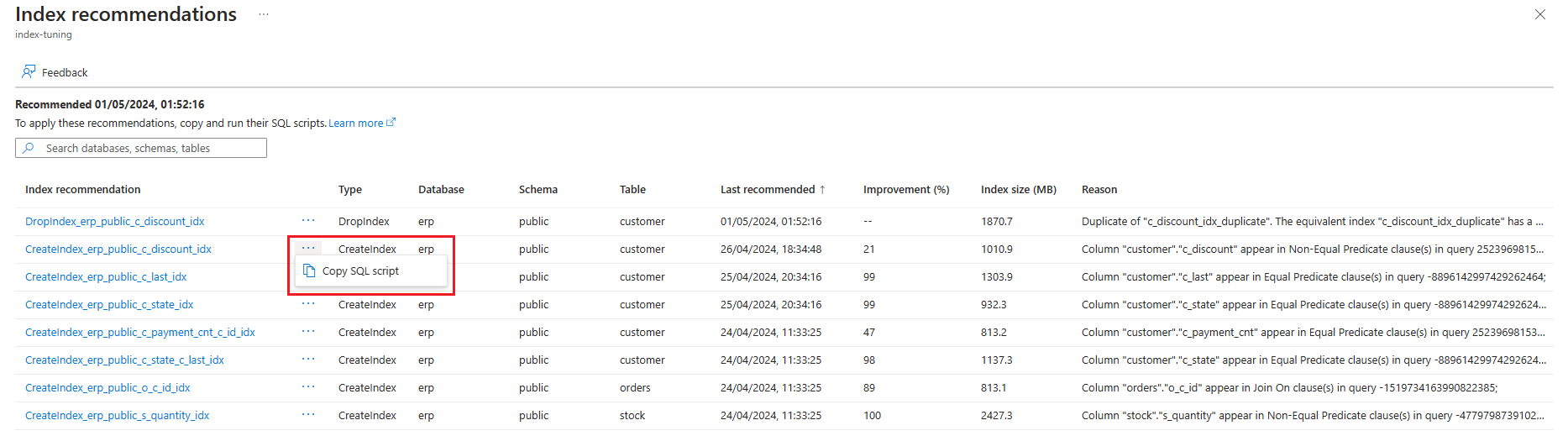
The list shows all available recommendations with some details for each of them. By default, the list is sorted by Last recommended in descending order, showing the most recent recommendations at the top. However, you can sort by any other column and can use the filtering box to reduce the list of items shown to those items whose database, schema, or table names contain the text that is provided:
To see further information about any specific recommendation, select on the name of that recommendation, and the Index recommendation details pane opens on the right side of the screen to surface all available details about the recommendation:
Consume index recommendations through views available in azure_sys database
- Connect to the
azure_sysdatabase available in your server with any role that has permission to connect to the instance. Members of thepublicrole can read from these views. - Execute queries on the
createindexrecommendationsanddropindexrecommendationsviews to retrieve the recommendations produced by index tuning for CREATE INDEX and DROP INDEX recommendations, respectively.
Views
Views in the azure_sys database provide a convenient way to access and retrieve index recommendations generated by index tuning. Specifically, the createindexrecommendations and dropindexrecommendations views contain detailed information about CREATE INDEX and DROP INDEX recommendations, respectively. These views expose data such as the session ID, database name, advisor type, start and stop times of the tuning session, recommendation ID, recommendation type, reason for the recommendation, and other relevant details. By querying these views, users can easily access and analyze the index recommendations produced by index tuning.
intelligentperformace.createindexrecommendations
The createindexrecommendations view exposes all the details for all CREATE INDEX recommendations generated on any tuning session whose data is still available in the underlying tables.
| column name | data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| session_id | char(36) | Globally Unique Identifier is assigned to every new tuning session. If a tuning session produces CREATE INDEX and DROP INDEX recommendations, there are rows in this view and dropindexrecommendations view with the same value. |
| database_name | varchar(64) | Name of the database in whose context was produced the recommendation. |
| advisor_type | varchar(64) | Constant value createindex. |
| start_time | timestamp | Timestamp at which the tuning session that produced this recommendation was started. |
| stop_time | timestamp | Timestamp at which the tuning session that produced this recommendation was started. NULL if the session is in progress or was aborted due to some failure. |
| session_context | json | Context describing details of the analyzed workload. In particular, it defines the time window that was the target for this particular session, the list of exceptions caught (if any), the total query count in the analyzed workload, and the list of examined query identifiers. |
| state | pg_recommendation_state_type | Represents whether the session failed, was completed successfully, or is still in progress. Error, Success, or InProgress. |
| recommendation_id | smallest | A monotonically increasing integer, starting at zero, is assigned to each recommendation produced within the context of a tuning session. Resets to zero for every new tuning session. |
| recommendation_type | varchar(64) | Constant value CreateIndex. |
| reason | varchar(1024) | Reason justifying why this recommendation was produced. Typically, one or more strings concatenated like "Column {columnName} appear in {Join On / Equal Predicate / Non-Equal Predicate / Group By / Order By} clause(s) in query {queryId}" |
| recommendation_context | json | Contains the list of query identifiers for the queries that are affected by the recommendation, the type of index being recommended, the name of the schema and the name of the table on which the index is being recommended, the index columns, the index name, and the estimated size in bytes of the recommended index. |
intelligentperformace.dropindexrecommendations
dropindexrecommendations exposes all the details for all DROP INDEX recommendations generated on any tuning session whose data is still available in the underlying tables.
| column name | data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| session_id | uuid | Globally Unique Identifier is assigned to every new tuning session. If a tuning session produces CREATE INDEX and DROP INDEX recommendations, there are rows in this view, and create index recommendations view with the same value. |
| database_name | text | Name of the database in whose context the recommendation was produced. |
| start_time | timestamp | Timestamp at which the tuning session that produced this recommendation was started. |
| end_time | timestamp | Timestamp at which the tuning session that produced this recommendation was started. NULL if the session is in progress or was aborted due to some failure. |
| message | text | Context describing details of the analyzed workload. In particular, it defines the time window that was the target for this particular session, the list of exceptions caught (if any), the total query count in the analyzed workload, and the list of examined query identifiers. |
| recommendation_id | int | A monotonically increasing integer, starting at 10000, is assigned to each recommendation produced within the context of all tuning sessions. Doesn't reset to zero for every new tuning session. |
| schema_name | text | Name of the schema in which the index exists. |
| table_name | text | Name of the table on which the index is created. |
| index_type | text | Type of index as described by the name of the access method exposed by pg_am. |
| index_name | text | Name of the index. |
| column_list | text | Names of the columns that make up the key of the index. |
| command | text | DROP INDEX statement to implement the recommended action. |
| benefit | double precision | Estimated benefit. |
| index_size | double precision | Estimated size of the index. |
| reason | text | Reason justifying why this recommendation was produced. Typically, for duplicate indexes it reports a message like "Duplicate of "{indexName}". The equivalent index "{IndexName}" {is a Primary Key, while / is a unique index, while / is a constraint, while / is a valid index, while / has been chosen as replica identity, while / was used to cluster the table, while / has a smaller estimated size compared to / has more tuples compared to / has more index scans compared to / has been fetched more times compared to / has been read more times compared to} {duplicateIndexName}". Optionally if the index isn't only identified as a duplicate, but also is determined that it wasn't used for more than index_tuning.unused_min_period days, the message "Also, the index is unused in the past {days} days." is appended to either of the previous ones. |
For unused indexes, the message would be like "The index is unused in the past {days} days."
Apply index recommendations
Index recommendations contain the SQL statement that you can execute to implement the recommendation.
The following sections will demonstrate how this statement can be obtained for a particular recommendation.
Once you have the statement, you can use any PostgreSQL client of your preference to connect to your server and apply the recommendation.
Obtain SQL statement through Index tuning (preview) page in Azure portal
Sign in to the Azure portal and select your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance.
Select Index tuning (preview) in the Intelligent Performance section of the menu.
Assuming index tuning has already produced recommendations, select the View index recommendations summarization to access the list of available recommendations.
From the list of recommendations, either:
Select the ellipsis to the right of the recommendation for which you want to obtain the SQL statement, and select Copy SQL script.
Or select the name of the recommendation to show its Index recommendation details, and select the copy to clipboard icon in the SQL script text box to copy the SQL statement.
Related content
- Index tuning in Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server (Preview)
- Configure index tuning in Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server (Preview)
- Monitor performance with Query Store
- Usage scenarios for Query Store - Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
- Best practices for Query Store - Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
- Query Performance Insight for Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server