Customer-managed keys for Azure Storage encryption
You can use your own encryption key to protect the data in your storage account. When you specify a customer-managed key, that key is used to protect and control access to the key that encrypts your data. Customer-managed keys offer greater flexibility to manage access controls.
You must use one of the following Azure key stores to store your customer-managed keys:
You can either create your own keys and store them in the key vault or managed HSM, or you can use the Azure Key Vault APIs to generate keys. The storage account and the key vault or managed HSM can be in different Microsoft Entra tenants, regions, and subscriptions.
Note
Azure Key Vault and Azure Key Vault Managed HSM support the same APIs and management interfaces for configuration of customer-managed keys. Any action that is supported for Azure Key Vault is also supported for Azure Key Vault Managed HSM.
The following diagram shows how Azure Storage uses Microsoft Entra ID and a key vault or managed HSM to make requests using the customer-managed key:
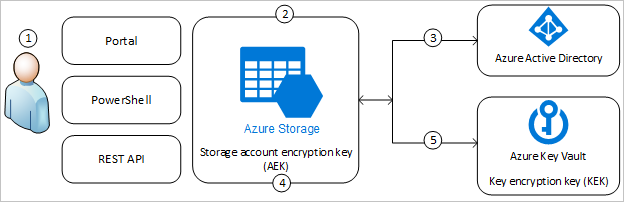
The following list explains the numbered steps in the diagram:
- An Azure Key Vault admin grants permissions to encryption keys to a managed identity. The managed identity may be either a user-assigned managed identity that you create and manage, or a system-assigned managed identity that is associated with the storage account.
- An Azure Storage admin configures encryption with a customer-managed key for the storage account.
- Azure Storage uses the managed identity to which the Azure Key Vault admin granted permissions in step 1 to authenticate access to Azure Key Vault via Microsoft Entra ID.
- Azure Storage wraps the account encryption key with the customer-managed key in Azure Key Vault.
- For read/write operations, Azure Storage sends requests to Azure Key Vault to unwrap the account encryption key to perform encryption and decryption operations.
The managed identity that is associated with the storage account must have these permissions at a minimum to access a customer-managed key in Azure Key Vault:
- wrapkey
- unwrapkey
- get
For more information about key permissions, see Key types, algorithms, and operations.
Azure Policy provides a built-in policy to require that storage accounts use customer-managed keys for Blob Storage and Azure Files workloads. For more information, see the Storage section in Azure Policy built-in policy definitions.
Data stored in Queue and Table storage isn't automatically protected by a customer-managed key when customer-managed keys are enabled for the storage account. You can optionally configure these services to be included in this protection at the time that you create the storage account.
For more information about how to create a storage account that supports customer-managed keys for queues and tables, see Create an account that supports customer-managed keys for tables and queues.
Data in Blob storage and Azure Files is always protected by customer-managed keys when customer-managed keys are configured for the storage account.
When you configure customer-managed keys for a storage account, Azure Storage wraps the root data encryption key for the account with the customer-managed key in the associated key vault or managed HSM. The protection of the root encryption key changes, but the data in your Azure Storage account remains encrypted at all times. There is no additional action required on your part to ensure that your data remains encrypted. Protection by customer-managed keys takes effect immediately.
You can switch between customer-managed keys and Microsoft-managed keys at any time. For more information about Microsoft-managed keys, see About encryption key management.
The key vault or managed HSM that stores the key must have both soft delete and purge protection enabled. Azure storage encryption supports RSA and RSA-HSM keys of sizes 2048, 3072 and 4096. For more information about keys, see About keys.
Using a key vault or managed HSM has associated costs. For more information, see Key Vault pricing.
You can configure customer-managed keys with the key vault and storage account in the same tenant or in different Microsoft Entra tenants. To learn how to configure Azure Storage encryption with customer-managed keys when the key vault and storage account are in the same tenants, see one of the following articles:
- Configure customer-managed keys in an Azure key vault for a new storage account
- Configure customer-managed keys in an Azure key vault for an existing storage account
When you enable customer-managed keys with a key vault in the same tenant, you must specify a managed identity that is to be used to authorize access to the key vault that contains the key. The managed identity may be either a user-assigned or system-assigned managed identity:
- When you configure customer-managed keys at the time that you create a storage account, you must use a user-assigned managed identity.
- When you configure customer-managed keys on an existing storage account, you can use either a user-assigned managed identity or a system-assigned managed identity.
To learn more about system-assigned versus user-assigned managed identities, see Managed identities for Azure resources. To learn how to create and manage a user-assigned managed identity, see Manage user-assigned managed identities.
To learn how to configure Azure Storage encryption with customer-managed keys when the key vault and storage account are in different Microsoft Entra tenants, see one of the following articles:
- Configure cross-tenant customer-managed keys for a new storage account
- Configure cross-tenant customer-managed keys for an existing storage account
You can configure customer-managed keys with an Azure Key Vault Managed HSM for a new or existing account. And you can configure customer-managed keys with a managed HSM that's in the same tenant as the storage account, or in a different tenant. The process for configuring customer-managed keys in a managed HSM is the same as for configuring customer-managed keys in a key vault, but the permissions are slightly different. For more information, see Configure encryption with customer-managed keys stored in Azure Key Vault Managed HSM.
Following cryptographic best practices means rotating the key that is protecting your storage account on a regular schedule, typically at least every two years. Azure Storage never modifies the key in the key vault, but you can configure a key rotation policy to rotate the key according to your compliance requirements. For more information, see Configure cryptographic key auto-rotation in Azure Key Vault.
After the key is rotated in the key vault, the customer-managed keys configuration for your storage account must be updated to use the new key version. Customer-managed keys support both automatic and manual updating of the key version for the key that is protecting the account. You can decide which approach you want to use when you configure customer-managed keys, or when you update your configuration.
When you modify the key or the key version, the protection of the root encryption key changes, but the data in your Azure Storage account remains encrypted at all times. There is no additional action required on your part to ensure that your data is protected. Rotating the key version doesn't impact performance. There is no downtime associated with rotating the key version.
Important
To rotate a key, create a new version of the key in the key vault or managed HSM, according to your compliance requirements. Azure Storage does not handle key rotation, so you will need to manage rotation of the key in the key vault.
When you rotate the key used for customer-managed keys, that action is not currently logged to the Azure Monitor logs for Azure Storage.
To automatically update a customer-managed key when a new version is available, omit the key version when you enable encryption with customer-managed keys for the storage account. If the key version is omitted, then Azure Storage checks the key vault or managed HSM daily for a new version of a customer-managed key. If a new key version is available, then Azure Storage automatically uses the latest version of the key.
Azure Storage checks the key vault for a new key version only once daily. When you rotate a key, be sure to wait 24 hours before disabling the older version.
If the storage account was previously configured for manual updating of the key version and you want to change it to update automatically, you might need to explicitly change the key version to an empty string. For details on how to do this, see Configure encryption for automatic updating of key versions.
To use a specific version of a key for Azure Storage encryption, specify that key version when you enable encryption with customer-managed keys for the storage account. If you specify the key version, then Azure Storage uses that version for encryption until you manually update the key version.
When the key version is explicitly specified, then you must manually update the storage account to use the new key version URI when a new version is created. To learn how to update the storage account to use a new version of the key, see Configure encryption with customer-managed keys stored in Azure Key Vault or Configure encryption with customer-managed keys stored in Azure Key Vault Managed HSM.
To revoke access to a storage account that uses customer-managed keys, disable the key in the key vault. To learn how to disable the key, see Revoke access to a storage account that uses customer-managed keys.
After the key has been disabled, clients can't call operations that read from or write to a resource or its metadata. Attempts to call these operations will fail with error code 403 (Forbidden) for all users.
To call these operations again, restore access to the customer-managed key.
All data operations that aren't listed in the following sections may proceed after customer-managed keys are revoked or after a key is disabled or deleted.
To revoke access to customer-managed keys, use PowerShell or Azure CLI.
- List Blobs, when called with the
include=metadataparameter on the request URI - Get Blob
- Get Blob Properties
- Get Blob Metadata
- Set Blob Metadata
- Snapshot Blob, when called with the
x-ms-meta-namerequest header - Copy Blob
- Copy Blob From URL
- Set Blob Tier
- Put Block
- Put Block From URL
- Append Block
- Append Block From URL
- Put Blob
- Put Page
- Put Page From URL
- Incremental Copy Blob
- Create Permission
- Get Permission
- List Directories and Files
- Create Directory
- Get Directory Properties
- Set Directory Properties
- Get Directory Metadata
- Set Directory Metadata
- Create File
- Get File
- Get File Properties
- Set File Properties
- Put Range
- Put Range From URL
- Get File Metadata
- Set File Metadata
- Copy File
- Rename File
Customer-managed keys are also available for managing encryption of Azure managed disks. Customer-managed keys behave differently for managed disks than for Azure Storage resources. For more information, see Server-side encryption of Azure managed disks for Windows or Server side encryption of Azure managed disks for Linux.