Tutorial: Connect to Virtual Machine Scale Set instances using Azure PowerShell
A Virtual Machine Scale Set allows you to deploy and manage a set of virtual machines. Throughout the lifecycle of a Virtual Machine Scale Set, you may need to run one or more management tasks. In this tutorial you learn how to:
- List connection information
- Connect to individual instances using Remote Desktop Connection
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Azure hosts Azure Cloud Shell, an interactive shell environment that you can use through your browser. You can use either Bash or PowerShell with Cloud Shell to work with Azure services. You can use the Cloud Shell preinstalled commands to run the code in this article, without having to install anything on your local environment.
To start Azure Cloud Shell:
| Option | Example/Link |
|---|---|
| Select Try It in the upper-right corner of a code or command block. Selecting Try It doesn't automatically copy the code or command to Cloud Shell. |  |
| Go to https://shell.azure.com, or select the Launch Cloud Shell button to open Cloud Shell in your browser. |  |
| Select the Cloud Shell button on the menu bar at the upper right in the Azure portal. |  |
To use Azure Cloud Shell:
Start Cloud Shell.
Select the Copy button on a code block (or command block) to copy the code or command.
Paste the code or command into the Cloud Shell session by selecting Ctrl+Shift+V on Windows and Linux, or by selecting Cmd+Shift+V on macOS.
Select Enter to run the code or command.
If you don't have a scale set already created, see Tutorial: Create and manage a Virtual Machine Scale Set with Azure PowerShell.
List all the instances in your Virtual Machine Scale Set using Get-AzVM.
Get-AzVM -ResourceGroup myResourceGroup
ResourceGroupName Name Location VmSize OsType NIC
----------------- ---- -------- ------ ------ ---
myResourceGroup myScaleSet_Instance1 eastus Standard_DS1_v2 Windows myScaleSet-instance1-nic
myResourceGroup myScaleSet_Instance2 eastus Standard_DS1_v2 Windows myScaleSet-instance2-nic
Using the NIC name, get the private IP address of the NIC, the backend address pool name and load balancer name with Get-AzNetworkInterface.
Get-AzNetworkInterface -Name myScaleSet-instance1-nic
Name : myScaleSet-instance1-nic
ResourceGroupName : myResourceGroup
Location : eastus
Id : /subscriptions//resourceGroups/myResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/myScaleSet-instance1-nic
ProvisioningState : Succeeded
Tags :
VirtualMachine : {
"Id": "/subscriptions//resourceGroups/myResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/myScaleSet_Instance1"
}
IpConfigurations : [
{
"Name": "myScaleSet",
"/subscriptions//resourceGroups/myResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/myScaleSet-instance1-nic/ipConfigurations/myScaleSet",
"PrivateIpAddress": "192.168.1.5",
"PrivateIpAllocationMethod": "Dynamic",
"Subnet": {
"Id": "/subscriptions//resourceGroups/myResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/myScaleSet/subnets/myScaleSet",
"IpAllocations": []
},
"ProvisioningState": "Succeeded",
"PrivateIpAddressVersion": "IPv4",
"LoadBalancerBackendAddressPools": [
{
"Id":
40.88.43.135"/subscriptions//resourceGroups/myResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.Network/loadBalancers/myScaleSet/backendAddressPools/myScaleSet",
"LoadBalancerBackendAddresses": []
}
],
"LoadBalancerInboundNatRules": [],
"Primary": true,
"ApplicationGatewayBackendAddressPools": [],
"ApplicationSecurityGroups": [],
"VirtualNetworkTaps": []
}
]
Using the backend pool name, load balancer name and private IP address, get the port for associated with private IP address of the instance you want to connect to using Get-AzLoadBalancerBackendAddressInboundNatRulePortMapping.
Get-AzLoadBalancerBackendAddressInboundNatRulePortMapping `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroup `
-LoadBalancerName myScaleSet `
-Name myScaleSet `
-IpAddress 192.168.1.5
If you run the above command and find your load balancer doesn't have any inbound NAT rules, you can add inbound NAT rules using Add-AzLoadBalancerInboundNatRuleConfig. Once complete, run Get-AzLoadBalancerBackendAddressInboundNatRulePortMapping again.
$slb = Get-AzLoadBalancer -Name "myScaleSet" -ResourceGroupName "MyResourceGroup"
$slb | Add-AzLoadBalancerInboundNatRuleConfig -Name "myNatRule" -FrontendIPConfiguration $slb.FrontendIpConfigurations[0] -Protocol "Tcp" -IdleTimeoutInMinutes 10 -FrontendPortRangeStart 50000 -FrontendPortRangeEnd 50099 -BackendAddressPool $slb.BackendAddressPools[0] -BackendPort 3389
$slb | Set-AzLoadBalancer
InboundNatRuleName : myNatRule
Protocol : Tcp
FrontendPort : 50001
BackendPort : 3389
Get the public IP of the load balancer using GetAzPublicIpAddress.
Get-AzPublicIpAddress -ResourceGroup myResourceGroup
Name : myScaleSet
ResourceGroupName : myResourceGroup
Location : eastus
Id : /subscriptions/resourceGroups/myResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses/myScaleSet
ProvisioningState : Succeeded
PublicIpAllocationMethod : Static
IpAddress : 40.88.43.135
PublicIpAddressVersion : IPv4
IdleTimeoutInMinutes : 4
IpConfiguration : {
"Id": "/subscriptions//resourceGroups/myResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.Network/loadBalancers/myScaleSet/frontendIPConfigurations/myScaleSet"
}
DnsSettings : {
"DomainNameLabel": "myscaleset-Instance1",
"Fqdn": "myscaleset-Instance1.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com"
}
Zones : {}
Sku : {
"Name": "Standard",
"Tier": "Regional"
}
Remote Desktop to your machine using the Public IP address of the load balancer and the Port mapping to the machine instance you want to connect to.
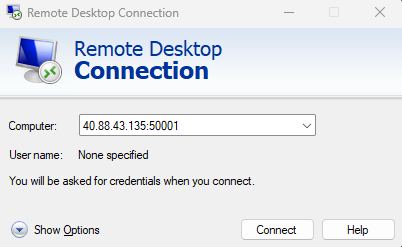
In this tutorial, you learned how to list the instances in your scale set and connect via SSH to an individual instance.
- List and view instances in a scale set
- Gather networking information for individual instances in a scale set
- Connect to individual VM instances inside a scale set