Run scripts in your Linux VM by using action Run Commands
Applies to: ✔️ Linux VMs ✔️ Flexible scale sets
The Run Command feature uses the virtual machine (VM) agent to run shell scripts within an Azure Linux VM. You can use these scripts for general machine or application management. They can help you to quickly diagnose and remediate VM access and network issues and get the VM back to a good state.
Benefits
You can access your virtual machines in multiple ways. Run Command can run scripts on your virtual machines remotely by using the VM agent. You use Run Command through the Azure portal, REST API, or Azure CLI for Linux VMs.
This capability is useful in all scenarios where you want to run a script within a virtual machine. It's one of the only ways to troubleshoot and remediate a virtual machine that doesn't have the RDP or SSH port open because of network or administrative user configuration.
Prerequisites
Linux Distro’s Supported
| Linux Distro | x64 | ARM64 |
|---|---|---|
| Alma Linux | 9.x+ | 9.x+ |
| Debian | 10+ | 11.x+ |
| Flatcar Linux | 3374.2.x+ | 3374.2.x+ |
| Azure Linux | 2.x | 2.x |
| openSUSE | 12.3+ | Not Supported |
| Oracle Linux | 6.4+, 7.x+, 8.x+ | Not Supported |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux | 6.7+, 7.x+, 8.x+ | 8.6+, 9.0+ |
| Rocky Linux | 9.x+ | 9.x+ |
| SLES | 12.x+, 15.x+ | 15.x SP4+ |
| Ubuntu | 18.04+, 20.04+, 22.04+ | 20.04+, 22.04+ |
Restrictions
The following restrictions apply when you're using Run Command:
- Output is limited to the last 4,096 bytes.
- The minimum time to run a script is about 20 seconds.
- Scripts run by default as an elevated user on Linux.
- You can run one script at a time.
- Scripts that prompt for information (interactive mode) aren't supported.
- You can't cancel a running script.
- The maximum time a script can run is 90 minutes. After that, the script will time out.
- Outbound connectivity from the VM is required to return the results of the script.
Note
To function correctly, Run Command requires connectivity (port 443) to Azure public IP addresses. If the extension doesn't have access to these endpoints, the scripts might run successfully but not return the results. If you're blocking traffic on the virtual machine, you can use service tags to allow traffic to Azure public IP addresses by using the AzureCloud tag.
Available commands
This table shows the list of commands available for Linux VMs. You can use the RunShellScript command to run any custom script that you want. When you're using the Azure CLI or PowerShell to run a command, the value that you provide for the --command-id or -CommandId parameter must be one of the following listed values. When you specify a value that isn't an available command, you receive this error:
The entity was not found in this Azure location
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| RunShellScript | Runs a Linux shell script. |
| ifconfig | Gets the configuration of all network interfaces. |
Azure CLI
The following example uses the az vm run-command command to run a shell script on an Azure Linux VM.
az vm run-command invoke -g myResourceGroup -n myVm --command-id RunShellScript --scripts "apt-get update && apt-get install -y nginx"
Note
To run commands as a different user, enter sudo -u to specify a user account.
Azure portal
Go to a VM in the Azure portal and select Run command in the left menu, under Operations. You see a list of the available commands to run on the VM.
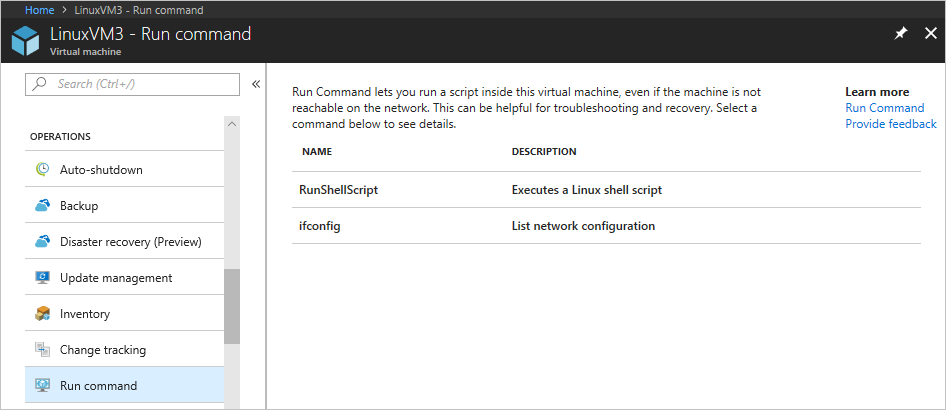
Choose a command to run. Some of the commands might have optional or required input parameters. For those commands, the parameters are presented as text fields for you to provide the input values. For each command, you can view the script that's being run by expanding View script. RunShellScript is different from the other commands, because it allows you to provide your own custom script.
Note
The built-in commands are not editable.
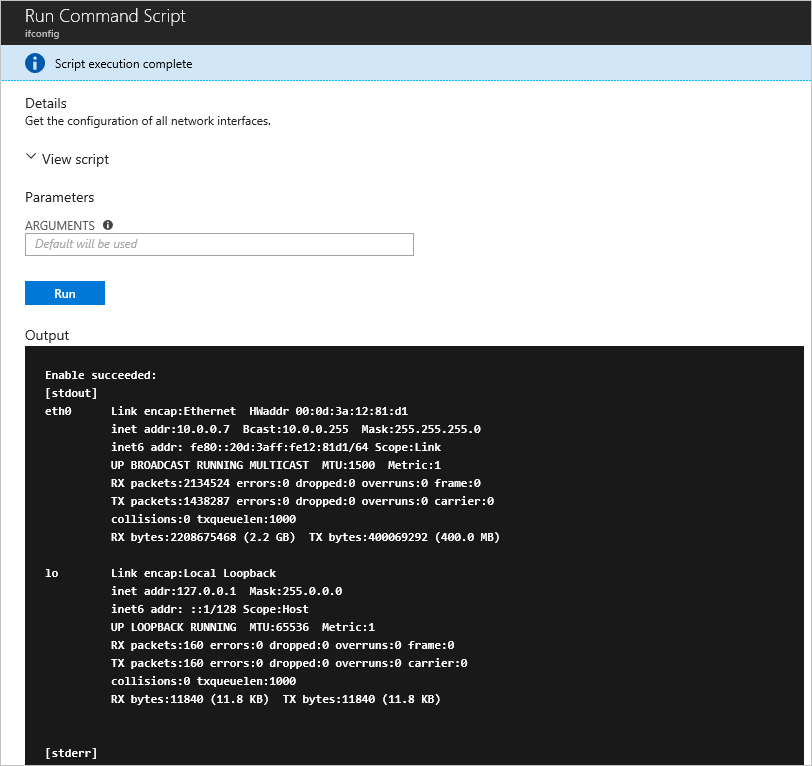
After you choose the command, select Run to run the script. After the script finishes, it returns the output and any errors in the output window. The following screenshot shows an example output from running the ifconfig command.
PowerShell
The following example uses the Invoke-AzVMRunCommand cmdlet to run a PowerShell script on an Azure VM. The cmdlet expects the script referenced in the -ScriptPath parameter to be local to where the cmdlet is being run.
Invoke-AzVMRunCommand -ResourceGroupName '<myResourceGroup>' -Name '<myVMName>' -CommandId 'RunShellScript' -ScriptPath '<pathToScript>' -Parameter @{"arg1" = "var1";"arg2" = "var2"}
Limiting access to Run Command
Listing the run commands or showing the details of a command requires the Microsoft.Compute/locations/runCommands/read permission on Subscription level. The built-in Reader role and higher levels have this permission.
Running a command requires the Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/runCommands/write permission. The Virtual Machine Contributor role and higher levels have this permission.
You can use one of the built-in roles or create a custom role to use Run Command.
Action Run Command Linux troubleshooting
When troubleshooting action run command for Linux environments, refer to the handler log file typically located in the following directory: /var/log/azure/run-command-handler/handler.log for further details.
Known issues
The Linux action run command logs have a few notable differences compared to the action run command Windows logs:
- The sequence number is reported with each line of the log as 'seq=#'
- There won't be a line that contains
Awaiting completion...as this will be in action run command Windows only. - The line
Command existed with code: #is also only present in action run command Windows logging.
Action Run Command Removal
If needing to remove your action run command Linux extension, refer to the below steps for Azure PowerShell and CLI:
Replace rgname and vmname with your relevant resource group name and virtual machine name in the following removal examples.
Invoke-AzVMRunCommand -ResourceGroupName 'rgname' -VMName 'vmname' -CommandId 'RemoveRunCommandLinuxExtension'
az vm run-command invoke --command-id RemoveRunCommandLinuxExtension --name vmname -g rgname
Note
When you apply a Run Command again, the extension will get installed automatically. You can use the extension removal command to troubleshoot any issues related to the extension.
Next steps
To learn about other ways to run scripts and commands remotely in your VM, see Run scripts in your Linux VM.