Configure Azure Database for PostgreSQL in a copy activity
This article outlines how to use the copy activity in Data pipeline to copy data from and to Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
Supported configuration
For the configuration of each tab under copy activity, go to the following sections respectively.
General
Refer to the General settings guidance to configure the General settings tab.
Source
Go to Source tab to configure your copy activity source. See the following content for the detailed configuration.
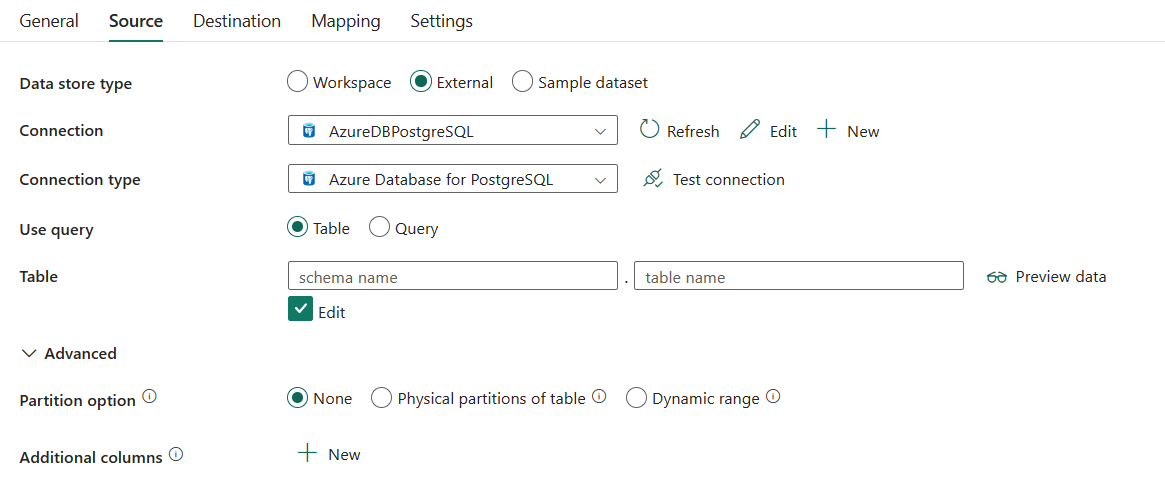
The following three properties are required:
- Data store type: Select External.
- Connection: Select an Azure Database for PostgreSQL connection from the connection list. If no connection exists, then create a new Azure Database for PostgreSQL connection by selecting New.
- Connection type: Select Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
- Use query: Select Table to read data from the specified table or select Query to read data using queries.
If you select Table:
Table: Select the table from the drop-down list or select Edit to manually enter it to read data.
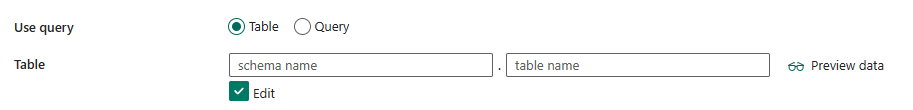
If you select Query:
Query: Specify the custom SQL query to read data. For example:
SELECT * FROM mytableorSELECT * FROM "MyTable".Note
In PostgreSQL, the entity name is treated as case-insensitive if not quoted.
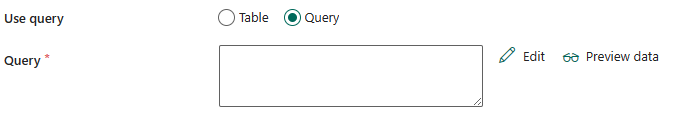
Under Advanced, you can specify the following fields:
Partition option: Specifies the data partitioning options used to load data from Azure Database for PostgreSQL. When a partition option is enabled (that is, not None), the degree of parallelism to concurrently load data from an Azure Database for PostgreSQL is controlled by the Degree of copy parallelism in the copy activity settings tab.
If you select None, you choose not to use partition.
If you select Physical partitions of table:
Partition names: Specify the list of physical partitions that needs to be copied.
If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook
?AdfTabularPartitionNamein the WHERE clause. For an example, see the Parallel copy from Azure Database for PostgreSQL section.
If you select Dynamic range:
Partition column name: Specify the name of the source column in integer or date/datetime type (
int,smallint,bigint,date,timestamp without time zone,timestamp with time zoneortime without time zone) that will be used by range partitioning for parallel copy. If not specified, the primary key of the table is auto-detected and used as the partition column.If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook
?AdfRangePartitionColumnNamein the WHERE clause. For an example, see the Parallel copy from Azure Database for PostgreSQL section.Partition upper bound: Specify the maximum value of the partition column to copy data out.
If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook
?AdfRangePartitionUpboundin the WHERE clause. For an example, see the Parallel copy from Azure Database for PostgreSQL section. .Partition lower bound: Specify the minimum value of the partition column to copy data out.
If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook
?AdfRangePartitionLowboundin the WHERE clause. For an example, see the Parallel copy from Azure Database for PostgreSQL section.
Additional columns: Add additional data columns to store source files' relative path or static value. Expression is supported for the latter.
Destination
Go to Destination tab to configure your copy activity destination. See the following content for the detailed configuration.
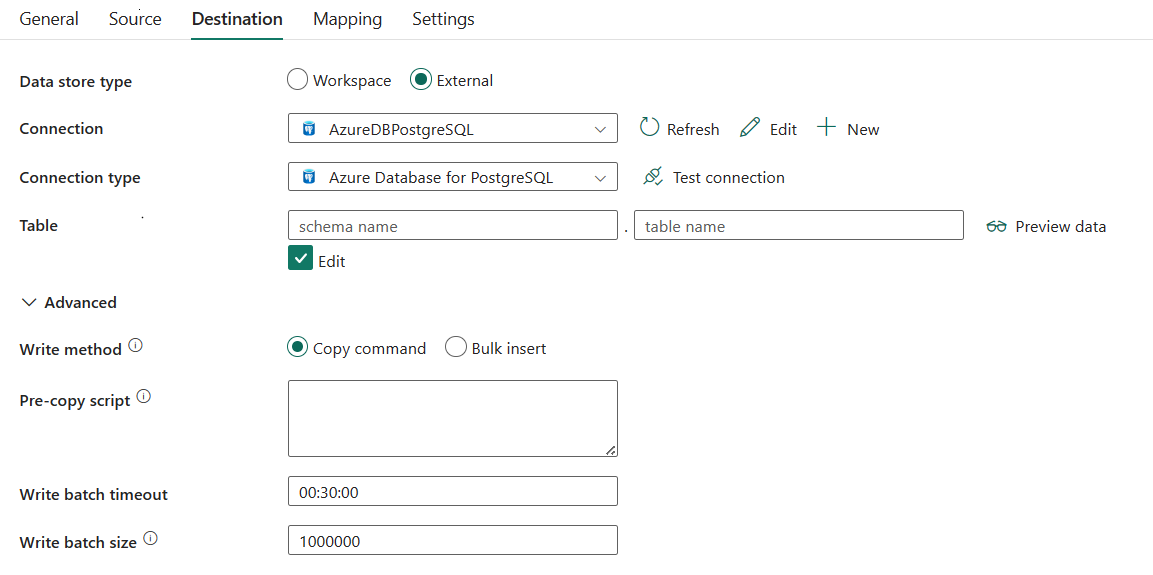
The following three properties are required:
- Data store type: Select External.
- Connection: Select an Azure Database for PostgreSQL connection from the connection list. If no connection exists, then create a new Azure Database for PostgreSQL connection by selecting New.
- Connection type: Select Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
- Table: Select the table from the drop-down list or select Edit to manually enter it to write data.
Under Advanced, you can specify the following fields:
Write method: Select the method used to write data into Azure Database for PostgreSQL. Select from Copy command (default, which is more performant) and Bulk insert.
Pre-copy script: Specify a SQL query for the copy activity to execute before you write data into Azure Database for PostgreSQL in each run. You can use this property to clean up the preloaded data.
Write batch timeout: Specify the wait time for the batch insert operation to finish before it times out. The allowed value is timespan. The default value is 00:30:00 (30 minutes).
Write batch size: Specify the number of rows loaded into Azure Database for PostgreSQL per batch. Allowed value is an integer that represents the number of rows. The default value is 1,000,000.
Mapping
For Mapping tab configuration, see Configure your mappings under mapping tab.
Settings
For Settings tab configuration, go to Configure your other settings under settings tab.
Parallel copy from Azure Database for PostgreSQL
The Azure Database for PostgreSQL connector in copy activity provides built-in data partitioning to copy data in parallel. You can find data partitioning options on the Source tab of the copy activity.
When you enable partitioned copy, copy activity runs parallel queries against your Azure Database for PostgreSQL source to load data by partitions. The parallel degree is controlled by the Degree of copy parallelism in the copy activity settings tab. For example, if you set Degree of copy parallelism to four, the service concurrently generates and runs four queries based on your specified partition option and settings, and each query retrieves a portion of data from your Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
You are suggested to enable parallel copy with data partitioning especially when you load large amount of data from your Azure Database for PostgreSQL. The following are suggested configurations for different scenarios. When copying data into file-based data store, it's recommended to write to a folder as multiple files (only specify folder name), in which case the performance is better than writing to a single file.
| Scenario | Suggested settings |
|---|---|
| Full load from large table, with physical partitions. | Partition option: Physical partitions of table. During execution, the service automatically detects the physical partitions, and copies data by partitions. |
| Full load from large table, without physical partitions, while with an integer column for data partitioning. | Partition options: Dynamic range. Partition column: Specify the column used to partition data. If not specified, the primary key column is used. |
| Load a large amount of data by using a custom query, with physical partitions. | Partition option: Physical partitions of table. Query: SELECT * FROM ?AdfTabularPartitionName WHERE <your_additional_where_clause>.Partition name: Specify the partition name(s) to copy data from. If not specified, the service automatically detects the physical partitions on the table you specified in the PostgreSQL dataset. During execution, the service replaces ?AdfTabularPartitionName with the actual partition name, and sends to Azure Database for PostgreSQL. |
| Load a large amount of data by using a custom query, without physical partitions, while with an integer column for data partitioning. | Partition options: Dynamic range. Query: SELECT * FROM ?AdfTabularPartitionName WHERE ?AdfRangePartitionColumnName <= ?AdfRangePartitionUpbound AND ?AdfRangePartitionColumnName >= ?AdfRangePartitionLowbound AND <your_additional_where_clause>.Partition column: Specify the column used to partition data. You can partition against the column with integer or date/datetime data type. Partition upper bound and Partition lower bound: Specify if you want to filter against partition column to retrieve data only between the lower and upper range. During execution, the service replaces ?AdfRangePartitionColumnName, ?AdfRangePartitionUpbound, and ?AdfRangePartitionLowbound with the actual column name and value ranges for each partition, and sends to Azure Database for PostgreSQL. For example, if your partition column "ID" is set with the lower bound as 1 and the upper bound as 80, with parallel copy set as 4, the service retrieves data by 4 partitions. Their IDs are between [1,20], [21, 40], [41, 60], and [61, 80], respectively. |
Best practices to load data with partition option:
- Choose distinctive column as partition column (like primary key or unique key) to avoid data skew.
- If the table has built-in partition, use partition option "Physical partitions of table" to get better performance.
Table summary
The following table contains more information about the copy activity in Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
Source information
| Name | Description | Value | Required | JSON script property |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data store type | Your data store type. | External | Yes | / |
| Connection | Your connection to the source data store. | < your Azure Database for PostgreSQL connection > | Yes | connection |
| Connection type | Your source connection type. | Azure Database for PostgreSQL | Yes | / |
| Use query | The way to read data. Apply Table to read data from the specified table or apply Query to read data using queries. | • Table • Query |
Yes | • typeProperties (under typeProperties -> source)- schema - table • query |
| Partition names | The list of physical partitions that needs to be copied. If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook ?AdfTabularPartitionName in the WHERE clause. |
< your partition names > | No | partitionNames |
| Partition column name | The name of the source column in integer or date/datetime type (int, smallint, bigint, date, timestamp without time zone, timestamp with time zone or time without time zone) that will be used by range partitioning for parallel copy. If not specified, the primary key of the table is auto-detected and used as the partition column. |
< your partition column names > | No | partitionColumnName |
| Partition upper bound | The maximum value of the partition column to copy data out. If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook ?AdfRangePartitionUpbound in the WHERE clause. |
< your partition upper bound > | No | partitionUpperBound |
| Partition lower bound | The minimum value of the partition column to copy data out. If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook ?AdfRangePartitionLowbound in the WHERE clause. |
< your partition lower bound > | No | partitionLowerBound |
| Additional columns | Add additional data columns to store source files' relative path or static value. Expression is supported for the latter. | • Name • Value |
No | additionalColumns: • name • value |
Destination information
| Name | Description | Value | Required | JSON script property |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data store type | Your data store type. | External | Yes | / |
| Connection | Your connection to the destination data store. | < your Azure Database for PostgreSQL connection > | Yes | connection |
| Connection type | Your destination connection type. | Azure Database for PostgreSQL | Yes | / |
| Table | Your destination data table to write data. | < name of your destination table > | Yes | typeProperties (under typeProperties -> sink):- schema - table |
| Write method | The method used to write data into Azure Database for PostgreSQL. | • Copy command (default) • Bulk insert |
No | writeMethod: • CopyCommand • BulkInsert |
| Pre-copy script | A SQL query for the copy activity to execute before you write data into Azure Database for PostgreSQL in each run. You can use this property to clean up the preloaded data. | < your pre-copy script > | No | preCopyScript |
| Write batch timeout | The wait time for the batch insert operation to finish before it times out. | timespan (the default is 00:30:00 - 30 minutes) |
No | writeBatchTimeout |
| Write batch size | The number of rows loaded into Azure Database for PostgreSQL per batch. | integer (the default is 1,000,000) |
No | writeBatchSize |
Related content
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for