Basic store operations
An in-game store typically will involve three basic operations:
This document will illustrate sample code involved with each operation. This is derived from the InGameStore sample which is continuously updated to reflect best practices.
Preparing to call XStore APIs
All XStore APIs operate over an XStoreContextHandle created using XStoreCreateContext.
This context allows you to perform store operations in the context of the specified user on console and the default user available on PCs. On consoles, the context is invalided after a Suspend or Quick Resume event. To safely handle these conditions we recommend closing a XStoreContextHandle and recreating it whenever the game resumes from a suspended state.
1. Determining what can be purchased
What a game usually offers for purchase is their add-ons. The following code demonstrates the basic XStoreQueryAssociatedProductsAsync API call needed for the game to know what products are available.
Only purchasable add-ons associated with the game are automatically returned in this query. Unrelated products associated with the same publisher (i.e. configured with the same Partner Center account) can also be made to return in this call so long as the game is set with a "can sell" relationship to this product in the Product relationship setup section in Partner Center.
Note
It is important to handle paging using XStoreProductsQueryHasMorePages and XStoreProductsQueryNextPageAsync, even if the number of expected products is less than the page size specified in the initial query.
This is because the Store services reserves the right to split the results across multiple pages of less than the specified page size.
struct QueryContext
{
Sample* pThis;
uint32_t count; // used to accumulate count of products returned across pages
XStoreProductQueryHandle handle; // handle to reuse for paged operations
};
bool CALLBACK ProductEnumerationCallback(const XStoreProduct* product, void* context)
{
// Handle adding the product to the game
printf("%s %s %u\n", product->title, product->storeId, product->productKind);
count++;
return true;
}
void CALLBACK QueryAssociatedProductsCallback(XAsyncBlock* async)
{
auto&[pThis, count, queryHandle] = *reinterpret_cast<QueryContext*>(async->context);
HRESULT hr = XStoreQueryAssociatedProductsResult(async, &queryHandle);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
hr = XStoreEnumerateProductsQuery(queryHandle, async->context, ProductEnumerationCallback);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
if (XStoreProductsQueryHasMorePages(queryHandle))
{
printf("Has more pages!\n");
pThis->QueryNextPage(async);
}
else
{
printf("Enumeration complete, %u products found\n", count);
delete async;
}
}
else
{
delete async;
}
}
}
void Sample::QueryCatalog()
{
auto async = new XAsyncBlock{};
async->context = new QueryContext{ this, 0, nullptr };
async->queue = m_asyncQueue;
async->callback = QueryAssociatedProductsCallback;
XStoreProductKind typeFilter =
XStoreProductKind::Consumable |
XStoreProductKind::Durable |
XStoreProductKind::Game;
HRESULT hr = XStoreQueryAssociatedProductsAsync(
m_xStoreContext,
typeFilter,
25, // Products per page (25 is good default)
async);
if (FAILED(hr))
{
delete async;
}
}
void Sample::QueryNextPage(XAsyncBlock *async)
{
async->callback = [](XAsyncBlock* async)
{
if (SUCCEEDED(XStoreProductsQueryNextPageResult(async, &queryHandle)))
{
auto&[pThis, count, queryHandle] = *reinterpret_cast<QueryContext*>(async->context);
HRESULT hr = XStoreEnumerateProductsQuery(queryHandle, async->context, ProductEnumerationCallback);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
if (XStoreProductsQueryHasMorePages(queryHandle))
{
printf("Has more pages!\n");
pThis->QueryNextPage(async);
}
else
{
printf("Enumeration complete, %u products found\n", count);
delete async;
}
}
else
{
delete async;
}
}
};
HRESULT result = XStoreProductsQueryNextPageAsync(queryHandle, async);
if (FAILED(result))
{
delete async;
}
}
Things to note
- Only purchasable products are returned with
XStoreQueryAssociatedProductsAsync; products that are only granted in bundles or otherwise not set to be independently purchasable will not return. For these useXStoreQueryProductsAsyncdescribed below. - Ensure the query handle is passed down through the paging recursion so as not to leak.
- There is no upfront knowledge of the number of products that will be returned, therefore the count must be accumulated.
Other options
XStoreQueryProductsAsync can be used to query specific products, if the store IDs are known or if other actionFilters are desired. "Actions" are usage scenarios that apply to a product, which include verbs like Purchase, License, and Redeem.
XStoreQueryProductForCurrentGameAsync is to query just the product for the currently running game.
XStoreShowAssociatedProductsUIAsync will transition the user to the Microsoft Store app to a view of associated products, which can be filtered by product kind. This is an alternative to enumerating and presenting the available products within the game.
Note
Note, this API opens the store in a web browser and it is suggested to use XStoreShowProductPageUI or XStoreShowPurchaseUI if your games is appearing in the console, Xbox App on PC, or game streaming storefronts.
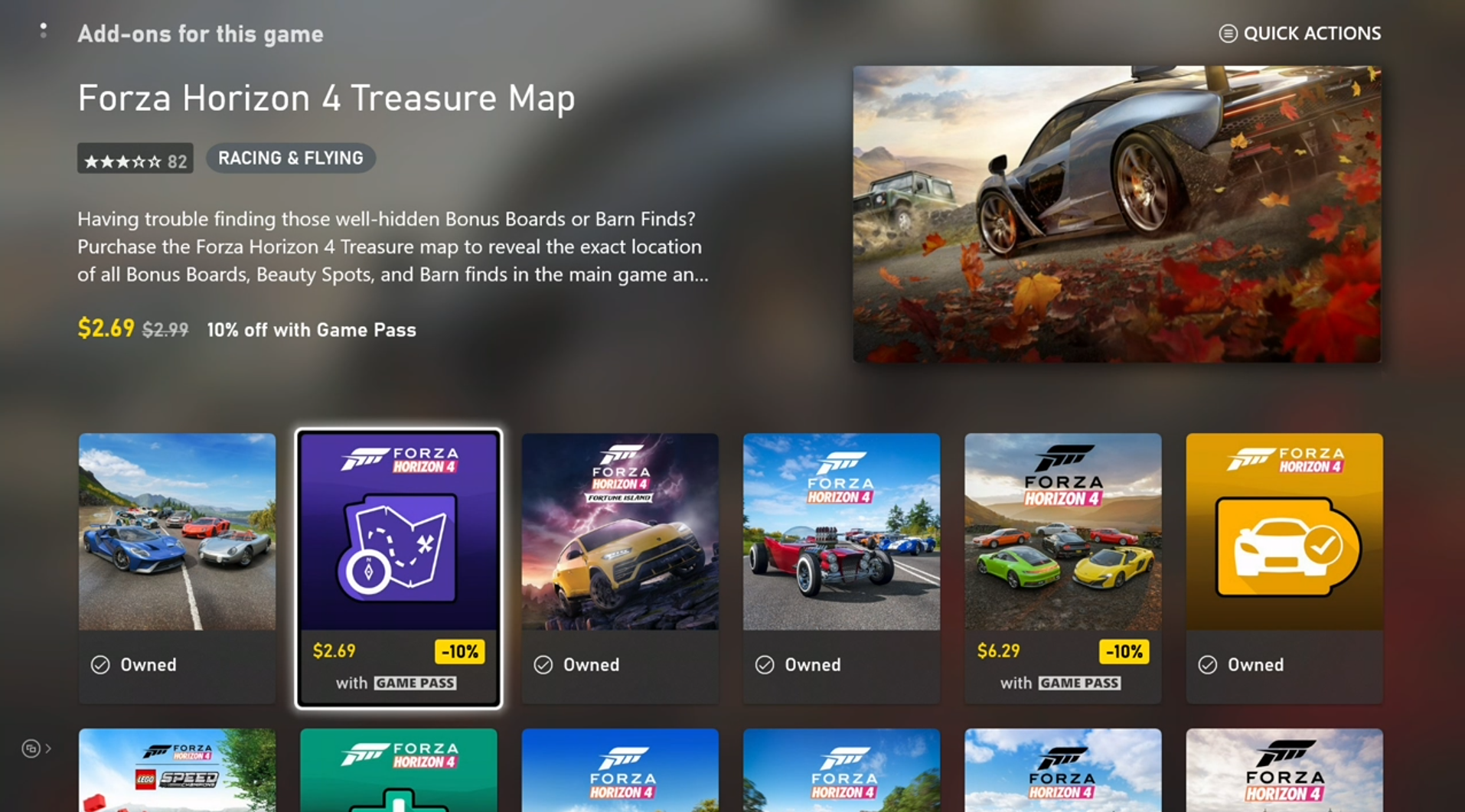
2. Evaluating what products are owned
This will involve essentially the same code as the above, including the need to manage pages, with these replacements:
- XStoreQueryAssociatedProductsAsync → XStoreQueryEntitledProductsAsync
- XStoreQueryAssociatedProductsResult → XStoreQueryEntitledProductsAsync
With these API, the results will comprise the products that are specifically entitled by the calling user's account. Entitled can mean directly owned, but also can mean satisfied by means of owning a parent bundle or subscription.
Note that this can also be determined by the results of XStoreQueryAssociatedProductsAsync as XStoreProduct contains an isInUserCollection field that is set to true when it is entitled.
Consumable ownership
Consumable quantity is noted in XStoreProduct.skus[i].collectionData.quantity.
Typically there is only one SKU for a consumable product.
Quantity can also be inquired independently by using XStoreQueryConsumableBalanceRemainingAsync, but this is discouraged for a large number of consumables individually as each will incur a service call.
Durable ownership
It is not enough to check if the account owns the product to determine that they should be entitled to use the product in-game. Durables must adhere to the content sharing policy that is described in Product sharing model for games.
XStoreAcquireLicenseForPackageAsync is used for durables with a package to determine if it is licensable according to the provisions of content sharing.
XStoreAcquireLicenseForDurablesAsync is used for durables without a package to do the same.
XStoreQueryAddOnLicensesAsync can be used for a digitally licensed game to return the list of licensable durables (without package).
More information can be found in Manage and license downloadable content and How to use a durable without a package.
3. Purchasing eligible products
Showing the purchase flow for a purchasable product is as simple as passing in the Store ID into the XStoreShowPurchaseUIAsync API:
void Sample::MakePurchase(const char* storeId)
{
struct PurchaseContext
{
Sample* pThis;
std::string storeId;
};
auto async = new XAsyncBlock{};
async->context = new PurchaseContext{ this, storeId };
async->queue = m_asyncQueue;
async->callback = [](XAsyncBlock *async)
{
auto &[pThis, storeId] = *reinterpret_cast<PurchaseContext*>(async->context);
HRESULT hr = XStoreShowPurchaseUIResult(async);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
printf("Purchase succeeded (%s)\n", storeId.c_str());
// Refresh ownership and update game
}
else
{
printf("Purchase failed (%s) 0x%x\n", storeId.c_str(), hr);
if (hr == E_GAMESTORE_ALREADY_PURCHASED)
{
printf("Already own this\n");
}
}
delete async;
};
HRESULT hr = XStoreShowPurchaseUIAsync(
m_xStoreContext,
storeId,
nullptr, // Can be used to override the title bar text
nullptr, // Can be used to provide extra details to purchase
async);
if (FAILED(hr))
{
delete async;
printf("Error calling XStoreShowPurchaseUIAsync : 0x%x\n", hr);
return;
}
}
In addition to handling the results of a potential purchase in the async callback, purchases can also be made outside of the game by explicitly switching to the Microsoft Store. They can also be made on Xbox.com, PC, mobile apps, or other outlets. It is recommended for there to be a flow the game that reliably refreshes product ownership on demand, such as a transition to the in-game store or somewhere in the settings, and not just solely as part of the initial sign-in flow.