Use Copilot to analyze automation activity and ask product questions (preview)
[This topic is prerelease documentation and is subject to change.]
Understanding automation activity and performance are key to achieving operational excellence and reliability goals, regardless of the size of the automation estate, team, or role within the organization. To reach those goals requires advanced and dynamic monitoring capabilities that provide you with valuable insights that highlight areas of success and identify potential bottlenecks, trends and areas for improvement. Having more detailed insights allows you to make informed decisions that optimize your automation processes, leading to increased efficiency and effectiveness.
Important
- This is a preview feature.
- Preview features aren’t meant for production use and may have restricted functionality. These features are available before an official release so that customers can get early access and provide feedback.
- This capability is powered by Azure OpenAI Service.
- Copilot is a new technology that is still being developed. It is optimized for use with English language and has limited support with other languages. As such, parts of it might appear in English rather than your preferred language.
- Read the responsible AI FAQs for Copilot in automation center (preview) to learn more about this new Copilot experience.
- More FAQs: Responsible AI FAQs for Power Automate, FAQ for Copilot data security and privacy in Microsoft Power Platform
Prerequisites
- A work or school account with access to a Power Automate environment located in the United States.
- During initial preview, you must have an environment in the United States region to use this feature. If you don’t have access to an environment based in the United States, you can ask your administrator to create a new environment in Power Platform admin center and select United States as its region.
- Check known limitations for more information.
How does it work?
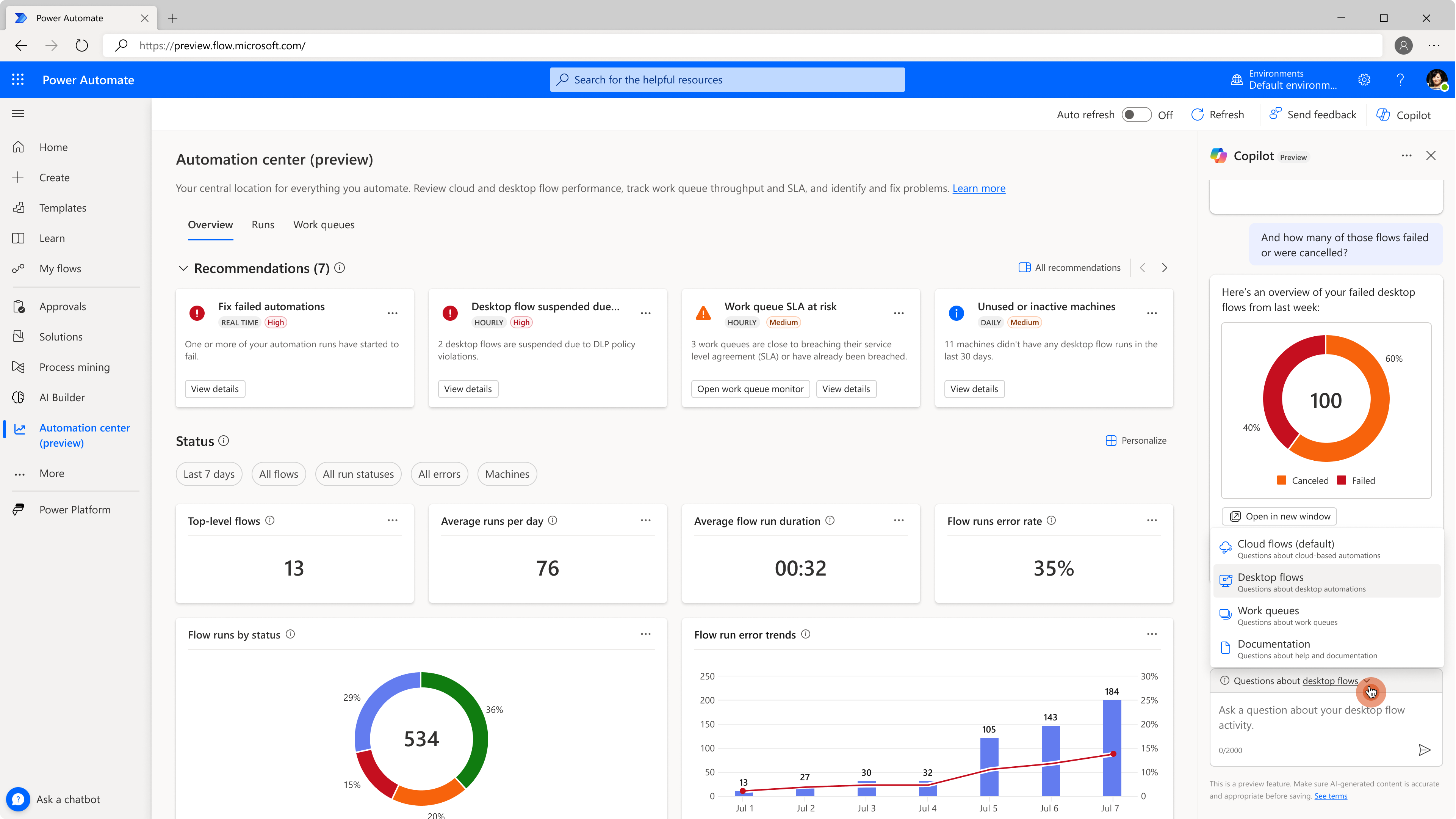
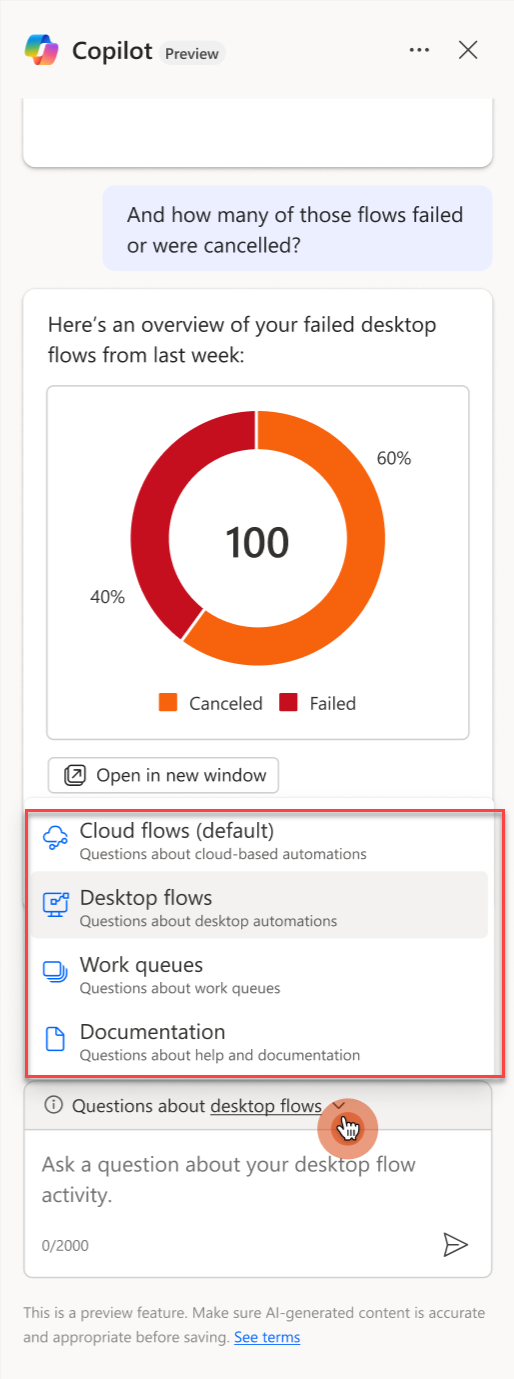
Copilot in automation center is able to answer questions about the following four skills:
| Index | Skill | Questions skill can answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cloud flow run logs | Cloud flow run status, trigger type, run duration, failure rate. |
| 2 | Desktop flow run logs | Desktop flow run status, used machine, run mode, failure rate. |
| 3 | Work queue data | Work queue items statuses, service level agreement (SLA) attainment, processor counts. |
| 4 | Documentation (generative answers) | General Power Automate feature questions such as how to analyze activity with Copilot. |
The first three skills in the above table translate natural language queries (questions) entered by users into Microsoft Dataverse FetchXML query syntax. This translation allows users to easily retrieve information about their automation data by asking questions in natural language. Additionally, Copilot determines the most suitable output visualization, such as a table, pie chart, bar chart, or line chart, to effectively present the insights and information to the user.
Copilot skill selector
When Copilot opens (per session) the first time, the "cloud flow" skill is preselected. You can modify the skill by choosing the dropdown next to the phrase Questions about and selecting your preferred skill. During the initial preview phase, the conversation history is reset each time you change the skill.
High-level process
- Once the user inputs a valid prompt, Copilot generates a FetchXML query based on the input.
- If the generated FetchXML is valid, the query is then executed against the Dataverse backend under the current user's security context to retrieve matching data. Retrieving the data as the user ensures that users only see data that they're already authorized to access.
- Copilot then determines the most suitable output visualization, such as a table, pie chart, bar chart, or line chart, to effectively present the insights and data to the user.
What are FetchXML queries?
Microsoft Dataverse FetchXML is a language used for retrieving data from a Dataverse database. FetchXML is designed to be easy to create, use, and understand. For example, you might want to ask Dataverse to give you a list of all flow runs for a specific flow. The FetchXML query is the way you phrase that question so the database understands it and can give you the right results.
Prompt best-practices
- Be specific:
- The more specific you are with your prompt, the better the AI understands and responds.
- If the AI isn't producing the desired output, don't worry. Try again by adjusting your prompt.
- Experiment with prompts:
- If you're not getting the results you were expecting, try rephrasing your prompt or provide more context.
- Provide feedback:
- If the AI produced great or unsatisfactory responses, let us know by selecting the thumbs up or down with an option to provide more feedback via the Tell Microsoft what you liked about this feature link that appears underneath.
Prompt examples
This section provides example prompts you can use as a starter prompt for your own use cases. Some of these prompts might not be applicable or return incorrect results. Model understanding or the actual prompt and the data available to you based on your permissions might influence the accuracy. We recommend that you review and validate the returned results and FetchXML query.
Cloud flow runs
Note
Cloud flow run history in Dataverse, which is built on the new Elastic Table feature, has different known limitations for querying and aggregating data compared to the desktop flow run history. These differences may impact the responses from Copilot. You can find out more about these known limitation here.
- How many runs last month were triggered by another cloud flow?
- Who initiated flow runs during the last month?
- How many flows failed yesterday?
Desktop flow runs
- Which flows ran the most last week?
- What were yesterday’s top five flows by number of completed runs?
- What is the distribution of flow run statuses?
Errors
- Show me the most frequent run errors last month.
- Show me a distribution of successful versus failed flows last quarter.
- What were the number of failed runs during the week before the last one?
Work queues
- Show me number of items that are on hold.
- Show me the number of items that are at risk of breaching SLA.
- What's the average handling time per processor (machine) and queue?
Machines
- Which bots had the most run failures today?
- Which machines are in maintenance mode?
- What are the machines with the most run failures?
Makers
- Show me the top flows by number of runs together with their owner info.
- Who were the top 10 users running flows last month?
- When and by whom were desktop flows modified last week?
Documentation (generative answers)
- How can I add a condition in Power Automate desktop?
- Can cloud flows handle approvals and decision-making processes?
- Where can I find deleted flows in Power Automate?
Multi-turn prompts
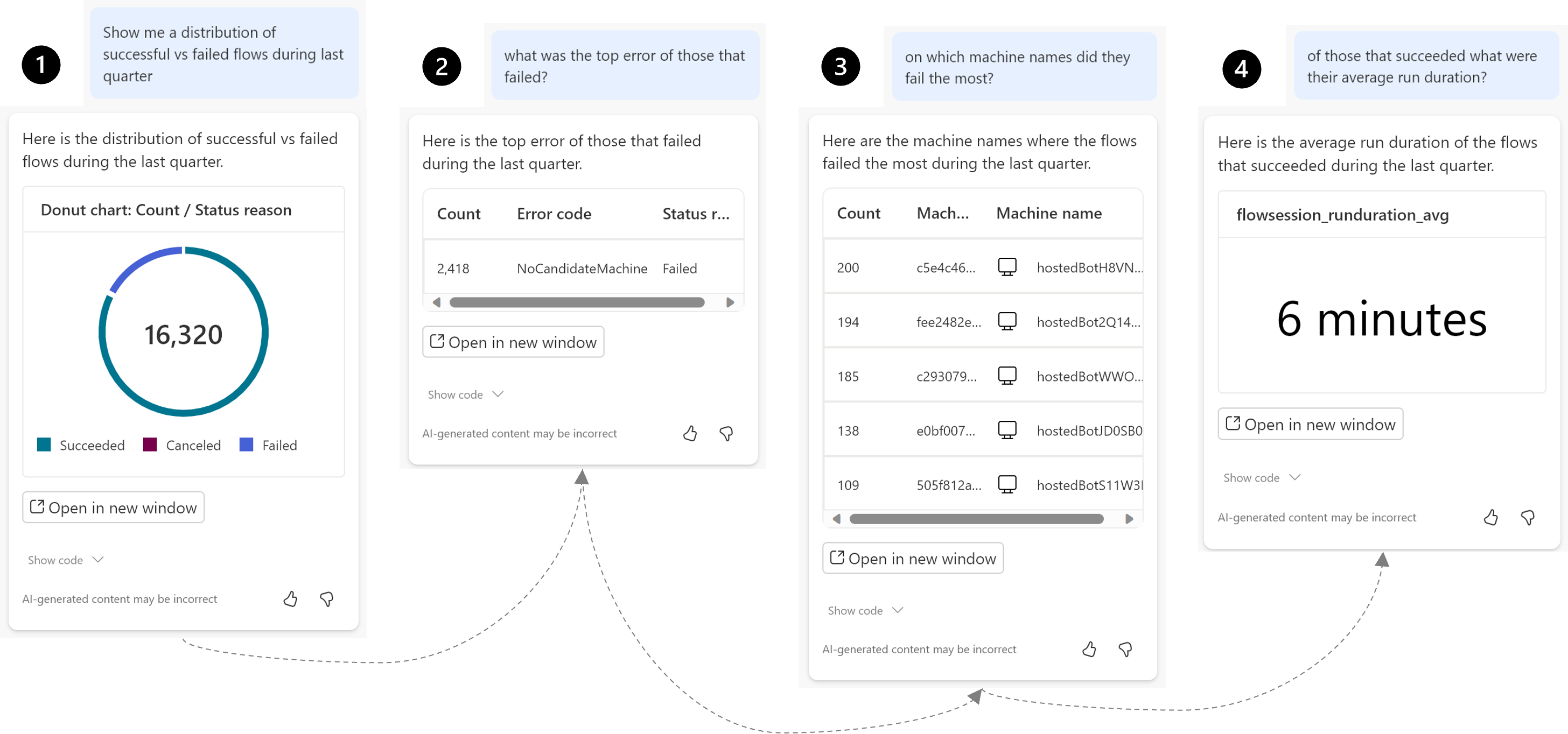
In the context of AI, multi-turn prompts allow you to have an ongoing conversation with Copilot, where it remembers the context of the previous messages in the conversation. It's not just answering one-off questions; it's engaging in a dialogue with you, where each response is based on what was said before.
Note
- Generative answers (documentation skill) does not support multi-turn conversations yet.
- When engaging in a multi-turn conversation, Copilot keeps track of the ten most recent questions only. This means that Copilot starts clearing the prompts that were entered first and only keeps the latest ten. To improve response quality, we suggest limiting your follow-up questions or more frequently restart the chat. For more information, see Clear previous prompt context to start over.
Example
| Turn | Prompt and reply |
|---|---|

|
User: Show me a distribution of successful vs failed flows last quarter |
| Copilot: Here's the distribution of successful vs failed flows during the last quarter. | |

|
User: What was the top error of the runs that failed? |
| Copilot: Here's the top error of the runs that failed. | |

|
User: On which machine names did they fail the most? |
| Copilot: Here are the machine names where the most failures occurred. | |

|
User: What was the average run duration of the flows that succeeded? |
| Copilot: Here's the average run duration of the flows that succeeded. |
Influencing the output format
You can influence Copilot's output format by asking for explicit output types like "show me failed vs succeeded flow run distribution as a bar chart." This prompt likely produces the following outcome:
Clear previous prompt context to start over
If you wish to reset the conversation with Copilot, select the three dots ... next to the copilot name, and then select New chat.
Edit and rerun FetchXML queries returned by Copilot
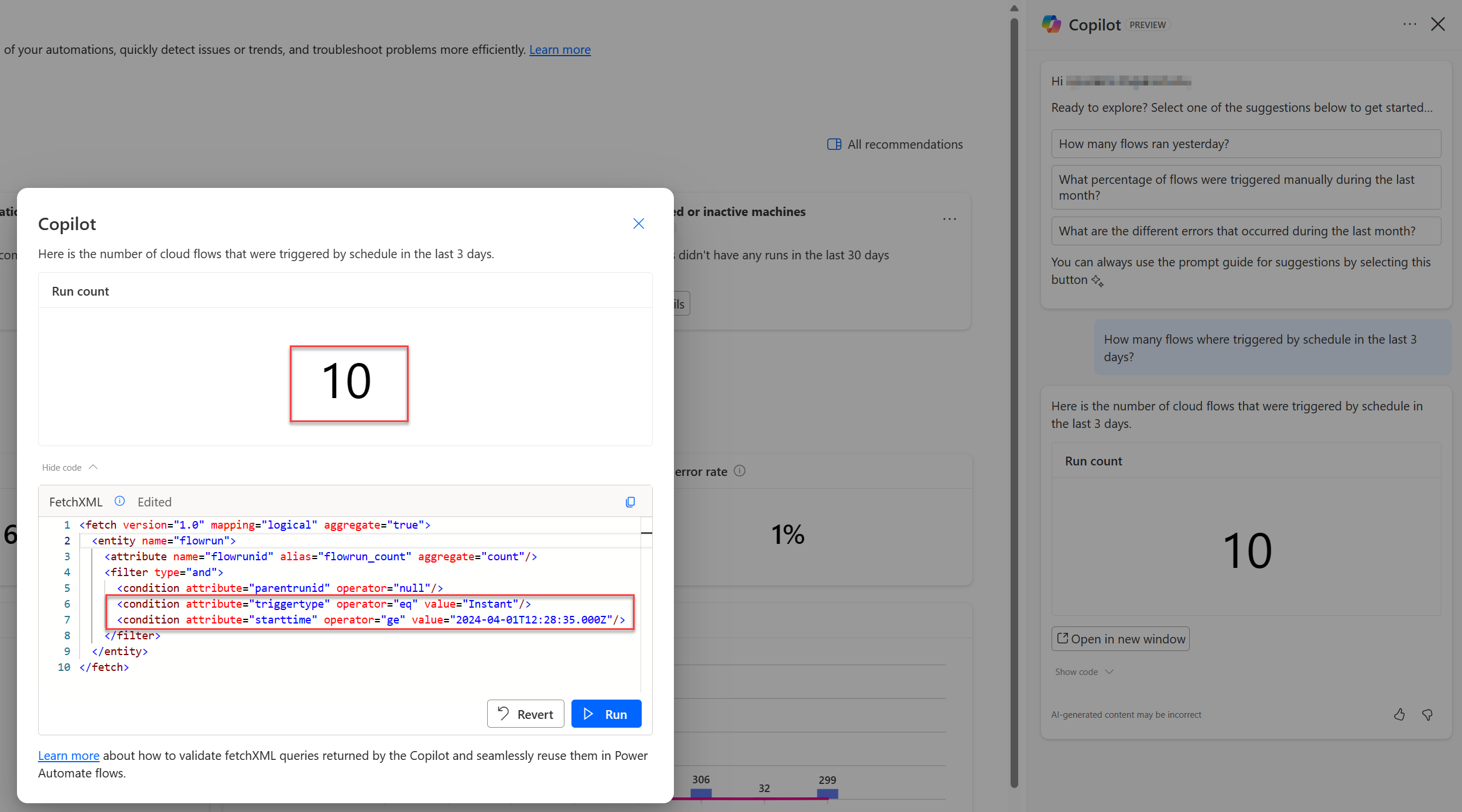
You can fine-tune the queries returned by Copilot through in-place edits in the code area. Just change the code to match your new search criteria and select Run. To illustrate, let's consider the following prompt:
- "How many flows were triggered by schedule in the last three days?"
Query results before any change
<fetch version="1.0" mapping="logical" aggregate="true">
<entity name="flowrun">
<attribute name="flowrunid" alias="flowrun_count" aggregate="count"/>
<filter type="and">
<condition attribute="parentrunid" operator="null"/>
<condition attribute="triggertype" operator="eq" value="Scheduled"/>
<condition attribute="starttime" operator="ge" value="2024-05-05T12:28:35.000Z"/>
</filter>
</entity>
</fetch>
Changed query results
<fetch version="1.0" mapping="logical" aggregate="true">
<entity name="flowrun">
<attribute name="flowrunid" alias="flowrun_count" aggregate="count"/>
<filter type="and">
<condition attribute="parentrunid" operator="null"/>
<condition attribute="triggertype" operator="eq" value="Instant"/>
<condition attribute="starttime" operator="ge" value="2024-04-01T12:28:35.000Z"/>
</filter>
</entity>
</fetch>
Validate FetchXML query results generated by Copilot
The following steps guide you through the process to validate (and potentially reuse) FetchXML queries in Power Automate cloud flows.
Step 1: Make a copy of the FetchXML query
After you submit your query to Copilot, you get a reply that includes a link labeled Show code. To copy the code, select this link and then select the copy icon located in the upper-right corner of the FetchXML box.
Step 2: Create a cloud flow and test the FetchXML query
- Navigate to the Power Automate portal and select My flows from the left navigation menu.
- Continue by selecting + New flow on the command bar, and then select Instant cloud flow from the dropdown menu.
- Enter a flow name, select Manually trigger a flow, and then select Create.
- The cloud flow designer appears. Find and then select the + New Step button.
- On the search bar that appears, enter Dataverse, and then select the Dataverse connector from the results.
- Various actions are displayed. Scroll through until you find and select the List rows action.
- Within the List rows action, select the Show advanced options link.
- A FetchXML query field appears. This field is where you input the copied FetchXML query that Copilot previously generated.
- After pasting in your FetchXML, select Save.
- Test your flow by selecting Test.
- Follow the prompts on your screen to start your flow manually to review its results.
Step 3: Understand the results
Let's assume you asked Copilot 'how many failed vs succeeded flows did we have last month?' This prompt produces a FetchXML query similar to the following example:
<fetch version="1.0" mapping="logical" aggregate="true" count="3" page="1">
<entity name="flowsession">
<attribute name="flowsessionid" alias="flowsession_count" aggregate="count" />
<attribute name="statuscode" alias="flowsession_statuscode" groupby="true" />
<filter type="and">
<condition attribute="completedon" operator="last-x-months" value="1" />
</filter>
</entity>
</fetch>
If data matches the given FetchXML query, the List rows Dataverse action configured in step 2 returns data in a format called JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), which is essentially a method used to present data in a well organized manner, making it easy to read and write digitally.
For distribution based questions like previously mentioned, data is grouped by one or more fields (statuscode), together with an aggregation (count) that returns the number for each group (that is, failed, succeeded, and so on).
Each record returned contains fields such as:
flowsession_count: The number of times the workflow ran.flowsession_regardingobjectid: The unique identifier for the flow run.flowsession_statuscode: The status of the flow run (for example, failed).workflow_name: The name of the flow.
If you want to know how many times a specific flow ran, look at the flowsession_count column of the record where workflow_name is your flow name.
Understand Copilot replies on problematic prompts
This table shows default responses that are returned when Copilot is unable to understand your question, intent, or generate a valid answer.
| Copilot reply | Details |
|---|---|
Sorry, something went wrong. Please try again. |
An unexpected error occurred. Rephrase your question and try again. |
Sorry, I couldn't find any results for that query. Please try again by refining your question, or consider using a sample suggestion from the prompt guide. |
The question was understood and a valid query was generated, but there's no data available to be returned. |
Sorry, I couldn’t understand your question. Rephrase it and try again. I’m able to answer questions that are about the data on this page. For more examples of prompts that you can ask Copilot, you can visit the prompt example section on our documentation page. |
Your question couldn't be translated into a valid FetchXML query. Rephrase your question and try again. |
Sorry, Copilot is at capacity and temporarily unavailable — please try again in a little while. |
There are resource constraints on the backend. Retry your question after a short time. |
Sorry, your message contains potentially harmful content. Please ensure your input is appropriate and try again. |
The backend service blocked your question because it might include potentially harmful content. Remove any potentially harmful content from your question and try again. |
Sorry, I was not able to generate a valid answer based on your question. Please rephrase it and try again. I’m able to answer questions that are about the data on this page. For more examples of prompts that you can ask Copilot, you can visit the prompt example section on our documentation page. |
The generated FetchXML is invalid or that the query failed when Copilot tried to execute it. Rephrase your question and try again. |
Sorry, your search includes too many results. Please refine your query and try again. For examples on how to limit search results returned by Copilot, visit our documentation page. |
The filters applied to your query exceed current aggregation limits in FetchXML. Add more appropriate filters such as only yesterday's or last month's data to ensure the query returns data within those limits. |
Known issues and limitations
The following list contains known limitations of Copilot in automation center.
- Copilot is a new technology that is still being developed. It's optimized for use with English language and support with other languages is limited. As such, parts of it might appear in English rather than your preferred language.
- Copilot is currently only available in Dataverse environments based in the United States.
- Copilot might return wrong or incomplete data and FetchXML queries.
- Copilot is initially only capable to answer questions about desktop flow activity, cloud flow activity, work queues and general product feature questions of Power Automate.
- In multi-turn conversations, Copilot keeps context of the last 10 question only. If you encounter wrong or incomplete results, consider resetting the conversation.
- Multi-turn conversations aren't supported for generative answers (documentation skill).
- For queries that return large result-sets, Copilot might not be able return or render the result.
See also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for