Scripting actions
Important
To prevent unauthorized access, Windows require administrator rights to access protected resources. To access protected resources (such as files) using the scripting actions, run Power Automate with administrator rights. To find more information regarding running Power Automate as an administrator, go to Run Power Automate with elevated rights.
Scripting actions enable you to run blocks of code and implement custom behavior in your desktop flows.
Important
As announced on October 2023, VBScript is deprecated from Windows. In future releases of Windows, VBScript will be available as a feature on demand before its removal from the operating system. For more information, see Resources for deprecated features.
All scripting actions follow the basic structure of the respective programming or scripting language: PowerShell, Python, VBScript, JavaScript and C#/VB.NET.
Note
Supported version for C#: v 5.0. For VB.NET: v 11.0
Natural language to script powered by copilot (preview)
[This topic is prerelease documentation and is subject to change.]
Natural language to code is a new copilot capability added in Power Automate for desktop. It lets you quickly generate code used in the scripting actions by describing it. This feature is available in the following scripting actions:
- Run PowerShell
- Run VBScript
- Run DOS command
- Run Python
- Run JavaScript
Important
- This is a preview feature.
- Preview features aren’t meant for production use and may have restricted functionality. These features are available before an official release so that customers can get early access and provide feedback.
Availability by region
Currently, copilot in Power Automate for desktop is only available in environments located in the United States.
Availability by account type
Currently, copilot in Power Automate for desktop is only available for users with a work or school account.
Note
If your environment is in the region listed above and you still need to see the copilot in Power Automate for desktop experience, contact your tenant administrator. They might have turned off the copilot functionality.
How to generate scripts using copilot and natural language
To generate scripts in one of the supported scripting actions drag and drop the action in the designer and select Generate script with Copilot.
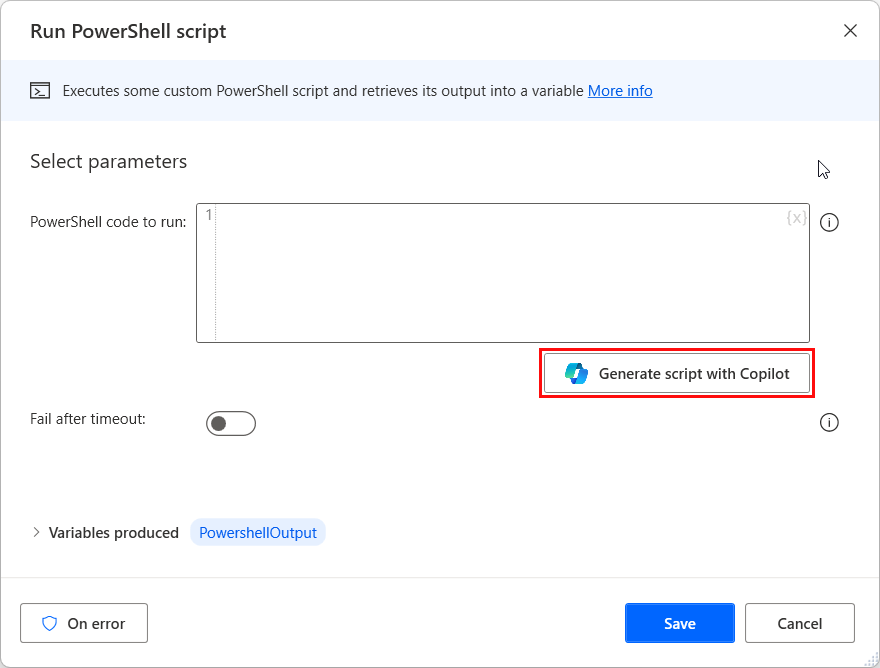
The create prompt screen opens where you can type your natural language prompt.
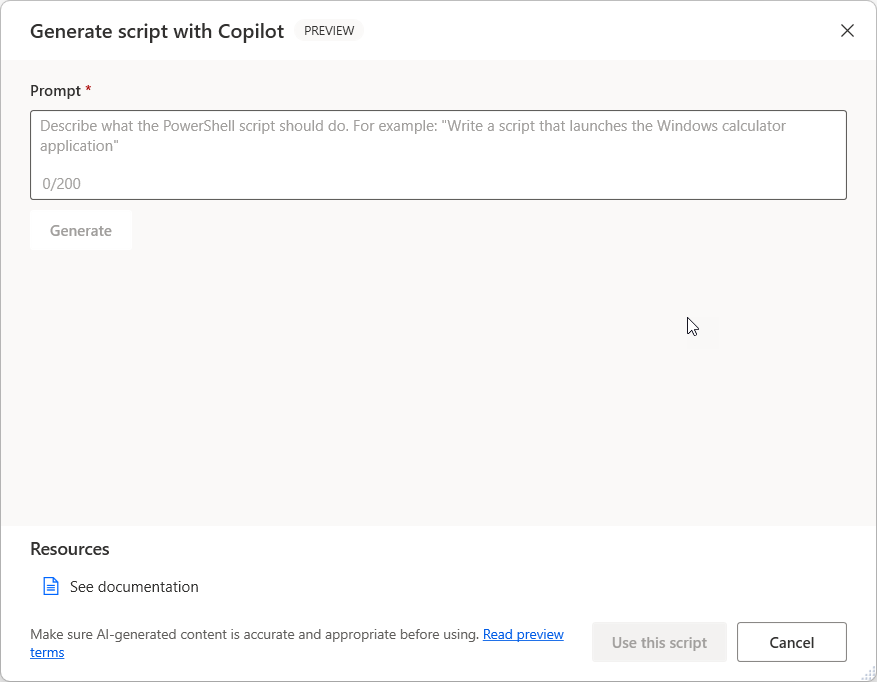
To create a script, write your prompt and select Generate. If you need to re-create it, you can change the prompt and select Regenerate. Otherwise, select Use this script to go back to the main action window, where you can modify it and add any necessary variables.
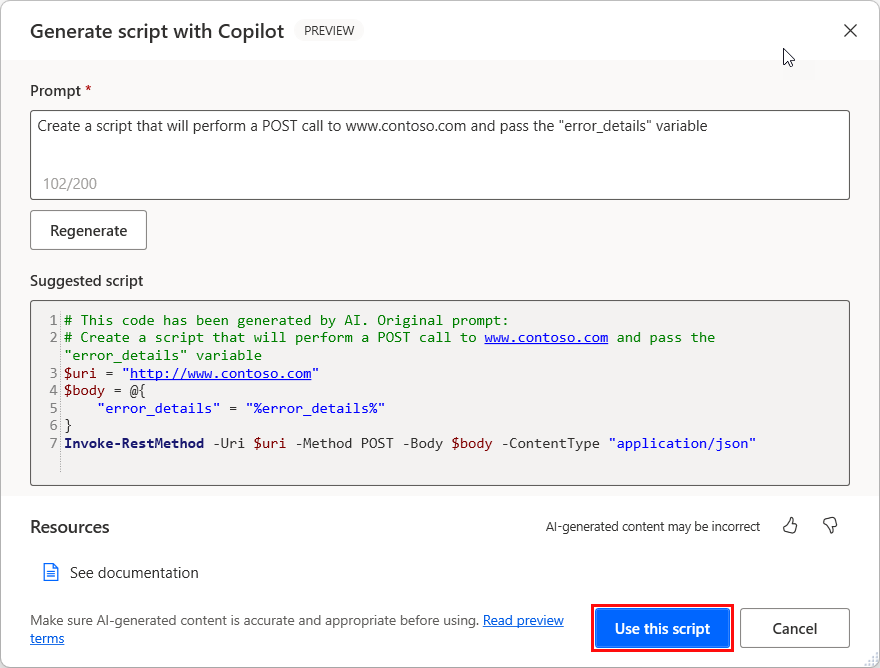
Important
Make sure that you always review the content generated by the AI model.
Help us improve this feature
Send feedback by selecting the thumb up or thumb down icon underneath the AI-generated content. Once you do, a feedback dialog appears, which you can use to submit feedback to Microsoft.
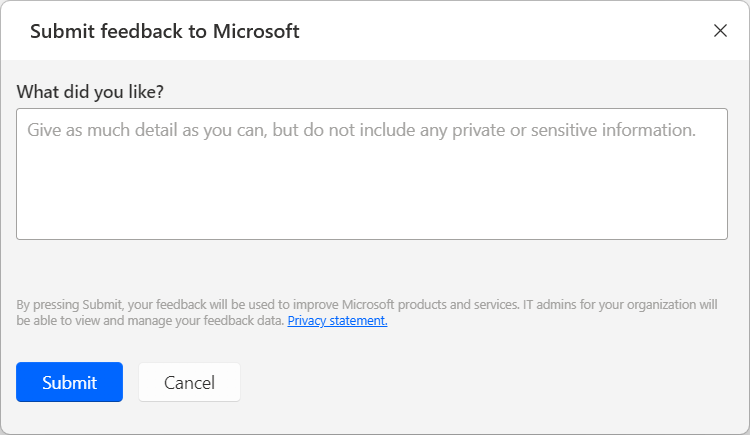
Note
If you can't see the dialog, your tenant admin might have turned it off. More information: Disabling the user feedback functionality
Disabling the user feedback functionality
As a tenant admin you can prevent your users from sending feedback to Microsoft by disabling the disableSurveyFeedback tenant setting. Find more information about viewing and setting tenant settings:
Data subject rights requests on user feedback
Tenant administrators can view, export, and delete the feedback from their users by signing in to the Microsoft 365 admin center, and then selecting Health > Product feedback.
AI with Power Automate resources
- FAQ for Generating scripts with natural language
- Responsible AI FAQs for Power Automate
- FAQ for Copilot data security and privacy in Microsoft Power Platform
Working with variables in scripting actions
To declare variables in scripting actions and return results in Power Automate, use the following commands:
To declare new variables in PowerShell scripts, use the $ notation. To return values from Run PowerShell script actions to Power Automate, use the Write-Output command.
$variableName = "variableValue" Write-Output $variableNamePython scripts don't require any special notation to declare new variables. To return values from Run Python script actions, use the print function.
variableName = "variableValue" print variableNameVBScript doesn't require any special notation to declare new variables. Use the WScript.Echo function to return values from Run VBScript actions to Power Automate.
variableName = "variableValue" WScript.Echo variableNameIn JavaScript scripts, use the var notation to declare new variables and the WScript.Echo function to return values from Run JavaScript actions.
var variableName = "variableValue"; WScript.Echo(variableName);For .NET scripts, use the Script Parameters window, accessed through the Run .NET script action's configuration card. You can set the type of the respective variable:
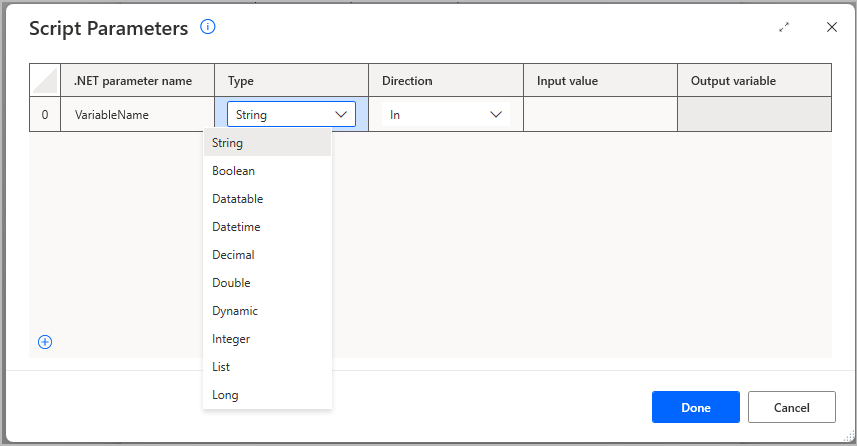
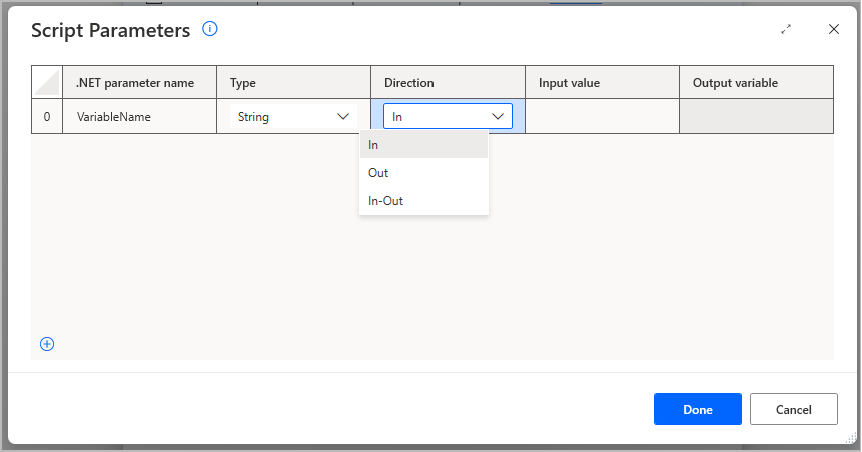
In addition, you can set whether it's an input to the .NET script (In option in Direction dropdown), an output of the script (Out option in Direction dropdown) or both (In-Out option in Direction dropdown).
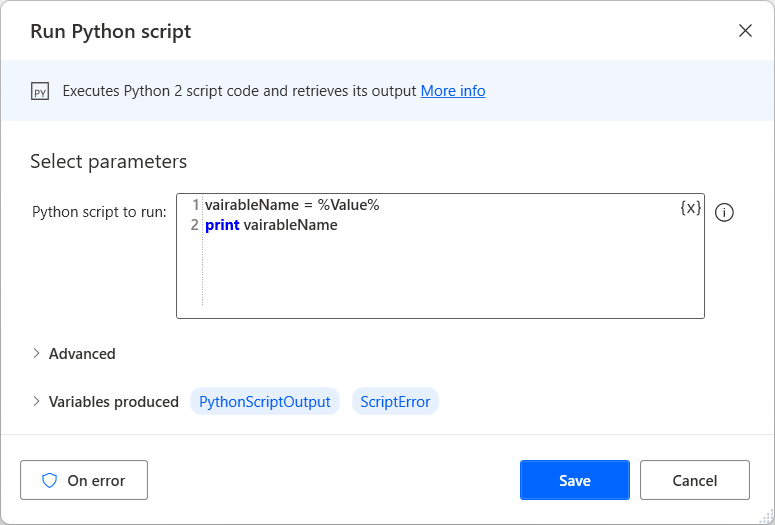
To use Power Automate variables in scripting actions, use the percentage notation (%) and handle the variables the same way as hardcoded values.
Run DOS command
Executes a DOS command or console application in invisible mode and retrieves its output upon completion.
Input parameters
| Argument | Optional | Accepts | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOS command or application | No | File | The name of DOS command or a console application, with arguments if applicable | |
| Working folder | Yes | Folder | The full path of the folder to work out of, if applicable | |
| Fail after timeout | Yes | Boolean value | Specify whether the DOS command or application will run indefinitely or fail after a set period of time | |
| Timeout | No | Numeric value | 10 | The maximum number of seconds to wait for the script to complete (-1 for indefinitely) |
| Change code page | N/A | Boolean value | False | Specifies whether to change the session's current code page |
| Encoding | No | ASMO-708: Arabic (ASMO 708), big5: Chinese Traditional (Big5), cp1025: IBM EBCDIC (Cyrillic Serbian-Bulgarian), cp866: Cyrillic (DOS), cp875: IBM EBCDIC (Greek Modern), csISO2022JP: Japanese (JIS-Allow 1 byte Kana), DOS-720: Arabic (DOS), DOS-862: Hebrew (DOS), EUC-CN: Chinese Simplified (EUC), EUC-JP: Japanese (JIS 0208-1990 and 0212-1990), euc-jp: Japanese (EUC), euc-kr: Korean (EUC), GB18030: Chinese Simplified (GB18030), gb2312: Chinese Simplified (GB2312), hz-gb-2312: Chinese Simplified (HZ), IBM-Thai: IBM EBCDIC (Thai), IBM00858: OEM Multilingual Latin I, IBM00924: IBM Latin-1, IBM01047: IBM Latin-1, IBM01140: IBM EBCDIC (US-Canada-Euro), IBM01141: IBM EBCDIC (Germany-Euro), IBM01142: IBM EBCDIC (Denmark-Norway-Euro), IBM01143: IBM EBCDIC (Finland-Sweden-Euro), IBM01144: IBM EBCDIC (Italy Euro), IBM01145: IBM EBCDIC (Spain-Euro), IBM01146: IBM EBCDIC (UK-Euro), IBM01147: IBM EBCDIC (France-Euro), IBM01148: IBM EBCDIC (International-Euro), IBM01149: IBM EBCDIC (Icelandic-Euro), IBM037: IBM EBCDIC (US-Canada), IBM1026: IBM EBCDIC (Turkish Latin-5), IBM273: IBM EBCDIC (Germany), IBM277: IBM EBCDIC (Denmark-Norway), IBM278: IBM EBCDIC (Finland-Sweden), IBM280: IBM EBCDIC (Italy), IBM284: IBM EBCDIC (Spain), IBM285: IBM EBCDIC (UK), IBM290: IBM EBCDIC (Japanese katakana), IBM297: IBM EBCDIC (France), IBM420: IBM EBCDIC (Arabic), IBM423: IBM EBCDIC (Greek), IBM424: IBM EBCDIC (Hebrew), IBM437: OEM United States, IBM500: IBM EBCDIC (International), ibm737: Greek (DOS), ibm775: Baltic (DOS), ibm850: Western European (DOS), ibm852: Central European (DOS), IBM855: OEM Cyrillic, ibm857: Turkish (DOS), IBM860: Portuguese (DOS), ibm861: Icelandic (DOS), IBM863: French Canadian (DOS), IBM864: Arabic (864), IBM865: Nordic (DOS), ibm869: Greek, Modern (DOS), IBM870: IBM EBCDIC (Multilingual Latin-2), IBM871: IBM EBCDIC (Icelandic), IBM880: IBM EBCDIC (Cyrillic Russian), IBM905: IBM EBCDIC (Turkish), iso-2022-jp: Japanese (JIS), iso-2022-jp: Japanese (JIS-Allow 1 byte Kana - SO/SI), iso-2022-kr: Korean (ISO), iso-8859-1: Western European (ISO), iso-8859-13: Estonian (ISO), iso-8859-15: Latin 9 (ISO), iso-8859-2: Central European (ISO), iso-8859-3: Latin 3 (ISO), iso-8859-4: Baltic (ISO), iso-8859-5: Cyrillic (ISO), iso-8859-6: Arabic (ISO), iso-8859-7: Greek (ISO), iso-8859-8: Hebrew (ISO-Visual), iso-8859-8-i: Hebrew (ISO-Logical), iso-8859-9: Turkish (ISO), Johab: Korean (Johab), koi8-r: Cyrillic (KOI8-R), koi8-u: Cyrillic (KOI8-U), ks_c_5601-1987: Korean, macintosh: Western European (Mac), shift_jis: Japanese (Shift-JIS), us-ascii: US-ASCII, utf-16: Unicode, utf-16BE: Unicode (Big-Endian), utf-32: Unicode (UTF-32), utf-32BE: Unicode (UTF-32 Big-Endian), utf-7: Unicode (UTF-7), utf-8: Unicode (UTF-8), windows-1250: Central European (Windows), windows-1251: Cyrillic (Windows), Windows-1252: Western European (Windows), windows-1253: Greek (Windows), windows-1254: Turkish (Windows), windows-1255: Hebrew (Windows), windows-1256: Arabic (Windows), windows-1257: Baltic (Windows), windows-1258: Vietnamese (Windows), windows-874: Thai (Windows), x-Chinese-CNS: Chinese Traditional (CNS), x-Chinese-Eten: Chinese Traditional (Eten), x-cp20001: TCA Taiwan, x-cp20003: IBM5550 Taiwan, x-cp20004: TeleText Taiwan, x-cp20005: Wang Taiwan, x-cp20261: T.61, x-cp20269: ISO-6937, x-cp20936: Chinese Simplified (GB2312-80), x-cp20949: Korean Wansung, x-cp50227: Chinese Simplified (ISO-2022), x-EBCDIC-KoreanExtended: IBM EBCDIC (Korean Extended), x-Europa: Europa, x-IA5: Western European (IA5), x-IA5-German: German (IA5), x-IA5-Norwegian: Norwegian (IA5), x-IA5-Swedish: Swedish (IA5), x-iscii-as: ISCII Assamese, x-iscii-be: ISCII Bengali, x-iscii-de: ISCII Devanagari, x-iscii-gu: ISCII Gujarati, x-iscii-ka: ISCII Kannada, x-iscii-ma: ISCII Malayalam, x-iscii-or: ISCII Oriya, x-iscii-pa: ISCII Punjabi, x-iscii-ta: ISCII Tamil, x-iscii-te: ISCII Telugu, x-mac-arabic: Arabic (Mac), x-mac-ce: Central European (Mac), x-mac-chinesesimp: Chinese Simplified (Mac), x-mac-chinesetrad: Chinese Traditional (Mac), x-mac-croatian: Croatian (Mac), x-mac-cyrillic: Cyrillic (Mac), x-mac-greek: Greek (Mac), x-mac-hebrew: Hebrew (Mac), x-mac-icelandic: Icelandic (Mac), x-mac-japanese: Japanese (Mac), x-mac-korean: Korean (Mac), x-mac-romanian: Romanian (Mac), x-mac-thai: Thai (Mac), x-mac-turkish: Turkish (Mac), x-mac-ukrainian: Ukrainian (Mac)` | utf-8: Unicode (UTF-8) | The encoding to use when reading the output |
Variables produced
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CommandOutput | Text value | The text output from the DOS command or application |
| CommandErrorOutput | Text value | The text describing the errors occurred (if any) during the execution of the DOS command or application |
| CommandExitCode | Numeric value | The command or application exit code. This value is numeric |
Exceptions
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| Can't execute command or console application | Indicates a problem executing the specified command or console application |
| Failed to run script in the allotted time | Indicates a problem running the provided script in the allotted time |
Run VBScript
Executes some custom VBScript code and retrieves its output into a variable.
You can use this action to include your own custom VBScript code in the desktop flow, while also having the ability to use variables therein, to generate dynamic VBScript content if needed.
Input parameters
| Argument | Optional | Accepts | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBScript to run | Yes | Text value | The VBScript code to execute. Variables may be included within the script since they evaluate prior to the execution of the VBScript | |
| Fail after timeout | Yes | Boolean value | N/A | Specify whether the VBScript script will run indefinitely or fail after a set period of time |
| Timeout | No | Numeric value | 10 | The maximum number of seconds to wait for the script to complete (-1 for indefinitely) |
Variables produced
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VBScriptOutput | Text value | The script's output |
| ScriptError | Text value | The errors that may occur during the execution of the VBScript code |
Exceptions
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| Failed to run script in the allotted time | Indicates a problem running the provided script in the allotted time |
Run JavaScript
Executes some custom JavaScript code and retrieves its output into a variable.
Input parameters
| Argument | Optional | Accepts | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JavaScript to run | Yes | Text value | The JavaScript code to execute. Variables may be included within the script since they evaluate prior to the JavaScript code's execution | |
| Fail after timeout | Yes | Boolean value | Specify whether the JavaScript script will run indefinitely or fail after a set period of time | |
| Timeout | No | Numeric value | 10 | The maximum number of seconds to wait for the script to complete (-1 for indefinitely) |
Variables produced
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| JavascriptOutput | Text value | The script's output |
| ScriptError | Text value | The errors that may occur during the execution of the JavaScript code |
Exceptions
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| Failed to run script in the allotted time | Indicates a problem running the provided script in the allotted time |
Run PowerShell script
Executes some custom PowerShell script and retrieves its output into a variable.
You can use this action to include your own custom PowerShell code in the desktop flow, while also having the ability to use variables therein, to generate dynamic PowerShell content if needed.
Input parameters
| Argument | Optional | Accepts | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PowerShell code to run | Yes | Text value | The PowerShell code to execute. Variables may be included within the script since they evaluate prior to the execution of the PowerShell code | |
| Fail after timeout | Yes | Boolean value | Specify whether the PowerShell script will run indefinitely or fail after a set period of time | |
| Timeout | No | Numeric value | 10 | The maximum number of seconds to wait for the script to complete (-1 for indefinitely) |
Variables produced
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PowershellOutput | Text value | The script's output |
| ScriptError | Text value | The errors that may occur during the execution of the PowerShell code |
Exceptions
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| Failed to run PowerShell script | Indicates a problem running the provided PowerShell script |
| Failed to run script in the allotted time | Indicates a problem running the provided script in the allotted time |
Run Python script
Executes Python script code and retrieves its output.
Input parameters
| Argument | Optional | Accepts | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Python script to run | No | Text value | The Python script code to execute | |
| Python version | No | Python 2.7, Python 3.4 | Python 2.7 | Specify which version of Python to use when executing the script |
| Module folder paths | Yes | List of Folders | The path(s) of folder(s) where external Python modules lie |
Variables produced
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PythonScriptOutput | Text value | The script's output |
| ScriptError | Text value | The errors that may occur during the execution of the Python script code |
Exceptions
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| Failed to run Python script | Indicates a problem running the provided Python script |
| Directory not found | Indicates that the directory wasn't found |
Run .NET script
Executes .NET (C#/VB.NET) script code and retrieves its output.
Input parameters
| Argument | Optional | Accepts | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | N/A | C#/ VB.NET | C# | The language of the script |
| .NET script imports | Yes | Text value | The .NET script imports to be included in the script | |
| References to be loaded | Yes | Folder | The root path where .NET dynamic link libraries (.dll files) references are located | |
| Script parameters | Yes | Script Parameters as defined by the user | Setting the values of the parameters that are defined in the script | |
| .NET code to run | No | Text value | The .NET code to run |
Variables produced
This action might produce variables, depending on the configuration made by the user when using the Script Parameters window.
Note
In the case the action is configured to produce output parameters (using the Out direction when configuring them), you should always ensure that the parameter inside the script is set to a value other than null. Otherwise, the script execution will result in an error since the output parameter has not been set.
Exceptions
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| Failed to run the .NET script | Indicates a problem running the provided .NET script |