What's New in System Center Service Manager
Important
Service Provider Foundation (SPF) is discontinued from System Center 2025. However, SPF 2022 will continue to work with System Center 2025 components.
This article details the new features supported in System Center 2025 - Service Manager.
See the following sections for information about the new features/features updated in Service Manager (SM) 2025.
Service Manager 2025 now supports Windows Server 2025. Learn more.
Service Manager 2025 also includes the following updates:
Supports the following newer browsers Chrome and Edge:
- Microsoft Edge version 121 and later with IE compatibility mode.
- Google Chrome version 121 and later.
There are no new features introduced in Service Manager 2022. For issues fixed in SM 2022, see release notes.
This article details the new features supported in System Center 2019 - Service Manager.
See the following sections for information about the new features/features updated in Service Manager (SM) 2019.
SM 2019 supports new installation of SQL Server 2017. Learn more.
Service Manager supports SQL Server 2019 with Cumulative Update 8 (CU8) or later, as detailed here.
Note
- Service Manager 2019 supports SQL 2019 with CU8 or later; however, it doesn't support SQL 2019 RTM.
- Use ODBC 17.3 to 17.10.4.1, and MSOLEDBSQL 18.2 to 18.6.6.
The Active Directory (AD) connector has been improvised to synchronize with a specific domain controller. You may now specify the domain controller in the LDAP query of the Active Directory connector.
The user interface is made responsive by addressing memory leak problems.
In earlier releases, during the setup of Service Manager Management Server and Service Manager Data Warehouse Management Server, various credentials are asked for SM accounts. These accounts had been interactive (accounts having Allow log on locally (SetInteractiveLogonRight) permission).
With SM 2019, we've enabled Service Logon type to make Service Manager more secure, and the default logon type is set to Service Logon. For information on how to grant service logon permissions to the Run As accounts, see enable service logon feature. Learn more.
This release of System Center Service Manager contains all the bug fixes shipped until the Update Rollup 5 of SCSM 2016.
Note
The following feature was introduced in Service Manager 1807, enhanced in 2019.
You can upgrade SQL server 2016 to SQL 2017. Learn more.
Note
The following feature was introduced in Service Manager 1801, included in 2019.
SM supports an enhanced experience for evaluating Service Manager and activating the product for retail use.
The evaluation version of Service Manager can be installed and used for 180 days. In SM 2016, after an evaluation version is installed, there was no option to view the remaining days for the evaluation period. With Service Manager 1801 and later, you can view the information about the evaluation period, and accordingly activate your SM. Learn more.
The following new feature is supported with Service Manager Update Rollup 2.
Service Manager UR2 supports SQL Server 2019 with Cumulative Update 8 (CU8) or later, as detailed here.
This support is applicable for Service Manager 2019.
Note
- Service Manager 2019 doesn't support SQL 2019 RTM, and supports SQL 2019 with CU8 or later.
- Use ODBC 17.3 to 17.10.4.1, and MSOLEDBSQL 18.2 to 18.6.6.
This article details the new features supported in System Center 2016 - Service Manager (SM).
The following sections summarize the new features released in SM 2016.
SQL Server 2014 SP2 is supported to host your Service Manager database and your data warehouse database.
Windows 7 is supported with the Service Manager console. However, you need .NET 4.5.1 as a prerequisite. Download the offline installer with language pack from the Microsoft Support site at https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/2858728. The new spell check feature, which was introduced in the Service Manager 2016 console, has limited language support for Windows 7 installations. The supported languages on Windows 7 include English, French, German, and Spanish.
To help simplify upgrades, you can use the following Service Manager 2016 connectors with System Center 2012 R2 components.
- System Center 2012 R2 Virtual Machine manager
- System Center 2012 R2 Orchestrator
- System Center 2012 R2 Operations Manager
- System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager (including SCCM 1511, 1602 and 1606)
In System Center 2016 - Service Manager, data processing throughout has been increased by four times. With this improvement, Service Manager better utilizes SQL Server. These results are from testing at Microsoft by stressing test systems heavily using the standard recommended topology.
Performance improvements are realized in the following ways:
- Time to create and update work items was greatly reduced using this improvement.
- Workflows in Service Manager should have less latency and should catch up faster when you do experience latency.
- Service Manager can more easily handle a large inflow of 45 work items per minute.
- The internal testing results have shown 50% improvement. For example, the time was reduced by half for a work item or configuration item to show up for associated users or workflows. In Service Manager 2012 R2 where a stressed environment would take 30 minutes to refresh the groups and queues, Service Manager 2016 can refresh the groups/queues within 15 minutes for the same load.
Here's a summary of the performance improvement metrics:
Here's how the test bed looks like which we've used for testing:
- 400 simultaneous client connections
- Inflow of 45 work-items per minute
- Two secondary Service Manager management servers handling 200 client connections each
- 216 subscription workflows
- 42 queues
- Service Manager Data Warehouse registered
- AD connector was running syncing 100K users
- All computers had standard recommended configurations
Improved work-item creation and update commit performance
Time to create and update work items was greatly reduced using this improvement.
| action | Service Manager 2012 R2 | Service Manager 2016 | improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| incident creation time | 2-6 seconds | 0.5 second | 4 times |
| incident creation time during connector sync | 8-10 seconds | less than 1 second | 8 times |
Improved workflow processing
Workflows in Service Manager should have less latency and should catch up faster when you do experience latency.
Here are the times for workflows to catch up after 2 hours of latency at a 45 work item per minute rate:
| action | Service Manager 2012 R2 | Service Manager 2016 | improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| workflow catch-up time | 2 hours 50 mins | 1 hour 46 mins | 1.5 times |
Higher work-item per second processing capacity
Service Manager can more easily handle a large inflow of 45 work items per minute.
| action | Service Manager 2012 R2 | Service Manager 2016 | improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| average incident creation time | 2.2 seconds | 0.5 second | 4 times |
The Active Directory and SCCM connectors in Service Manager can import large amounts of data into the Service Manager database. In doing so, they not only increase the size of the data table, which is where the data from the connectors are stored, but they also increase the size of the EntityChangeLog (ECL) table and history tables considerably. A large ECL table size can be a problem - in some cases, it can slow down the system significantly.
The ECL table, and the history tables in this case, store details about when the data was brought into Service Manager and the properties that were added or updated for each data item. Disabling ECL logging doesn't affect importing data from connectors. Instead, most logging data doesn't get written to the ECL and history tables, which can result in significant performance improvement. Disabled ECL logging isn't available by default. In other words, by default, ECL logging is enabled. However, you can easily turn on Disabled ECL logging by using a simple PowerShell cmdlet. For more information, see Optionally Disable ECL Logging for Faster Connector Synchronization.
During ECL log grooming, Service Manager doesn't groom the latest change to an entity, even if the retention history period of that entity has elapsed.
Grooming eventually leaves one entry for every object ever created in the ECL table for the lifetime of your Service Manager deployment. In order to keep the last entry in the ECL table, the execution of the stored procedure (p_GroomChangeLog) can take a time. In some cases, longer than 30 minutes when the ECL entry is very large. As part of the optimization, Service Manager doesn't keep the entry, which results in a performance improvement for the grooming stored procedure. Typically, the grooming stored procedure runs 3 to 4 times faster.
As a result, the history tab wouldn't show any entry for an entity if its history retention period has elapsed, as opposed to seeing one entry earlier.
The following incident-related workflows included in Service Manager have been optimized to reduce the amount of time to update incidents, especially when many work items are created simultaneously.
WorkItem_SetFirstAssingedTo_RelationhsipAdd_Rule
Incident_Adjust_PriorityAndResolutionTime_Custom_Rule.Update
Incident_Adjust_PriorityAndResolutionTime_Custom_Rule.Add
ServiceManager.IncidentManagement.ParentIncidentActivated.UpdateRule
The batch sizes were increased for each workflow, which results in better performance and allows an increased number of incidents to update simultaneously.
The AD GroupExpansion functionality is now part of the ADConnector, as opposed to a separate workflow in the previous release.
GroupExpansion functionality runs in the same schedule as ADConnector.
The time required to sync group membership changes has been reduced.
With System Center 2016 - Service Manager, the Service Manager Data Warehouse cubes contain new date dimensions which help you to create rich reports and slice data based on Year, Quarter, Month, Day, etc.
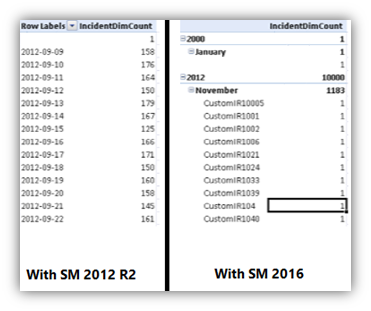
The following new dimensions have been added to Service Manager data warehouse cubes:
Cube Name: Service Manager Work Items Cube
- Content: Incident, Problem management
- New date dimensions:
- Incident ClosedDate
- Incident CreatedDate
- Incident ResolvedDate
- Problem ClosedDate
- Problem CreatedDate
- Problem ResolvedDate
- Incident ClosedDate
Cube Name: Change and Activity Management Cube
- Content: Change and Activity management
- New Date Dimensions:
- Activity ActualEndDate
- Activity ActualStartDate
- Activity CreatedDate
- Activity ScheduledEndDate
- Activity ScheduledStartDate
- ChangeRequest ActualEndDate
- ChangeRequest ActualStartDate
- ChangeRequest CreatedDate
- ChangeRequest ScheduledEndDate
- ChangeRequest ScheduledStartDate
- Activity ActualEndDate
Cube Name: Service Manager Service Catalog library cube
- Content: Service Catalog
- New Date Dimensions:
- Activity ActualEndDate
- Activity ActualStartDate
- Activity CreatedDate
- Activity ScheduledEndDate
- Activity ScheduledStartDate
- ReviewActivity ActualEndDate
- ReviewActivity ActualStartDate
- ReviewActivity CreatedDate
- ReviewActivity ScheduledEndDate
- ReviewActivity ScheduledStartDate
- ServiceRequest ActualEndDate
- ServiceRequest ActualStartDate
- ServiceRequest CreatedDate
- ServiceRequest CompletedDate
- ServiceRequest ClosedDate
- ServiceRequest ScheduledEndDate
- ServiceRequest ScheduledStartDate
All these dimensions have the following attributes, which you can use for slicing your data:
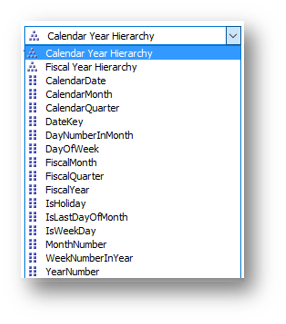
In the management pack defining the cube definition, add the named Calculations for the required field like mentioned below:
<NamedCalculation ID="Incident_CreatedDate__DateKey" Target="IncidentDW!IncidentDim" ColumnType="Int"> <Calculation>isNull(CONVERT(nvarchar(8), CreatedDate, 112),'20000101')</Calculation> </NamedCalculation>The NamedCalculation ID should have string
__DateKeyin the end, and this field in the data warehouse shouldn't be NULL or 0.Seal the management pack and import it into Service Manager.
Run the MPSyncJob on the data warehouse and wait until the management pack is marked Completed.
Process all the cubes, or wait for automatic processing overnight.
Cubes are updated with new date dimensions, as defined above.
This release contains a new HTML based Self Service Portal, which offers the following enhancements:
- Updated modern UI with easy-to-use navigation
- Multiple browsers support
- Announcements are now supported in the portal
- New Service Catalog
- Rich browser for help articles
- My Activities and My Request management
- Server caching to reduce database calls and improve portal performance
- Support of direct URLs for Self Service Portal pages
- Rich customization options
For more information and installing and customizing the portal, see Deploy the Self-Service Portal for Service Manager.
Note
The older Silverlight and SharePoint-based Self-Service portal has been removed.
Spell check is now enabled for work item forms. It's enabled for 17 out of the 21 Service Manager supported languages [Chinese (Simplified), Chinese (Traditional), Japanese and Korean are currently not supported]. To use this feature, install your desired language pack and set the keyboard IME for your desired language. This feature is enabled by default, but can be switched by navigating to View > spell check.
A new console task Open Activity in Progress was added for service requests and change requests. This console task’s link is enabled when a work item moves to the in progress state. Clicking this task’s link opens the current in-progress activity. For work items that don’t have any in-progress activity, the localized message No Activity with In Progress state is found for the work item. is displayed. In previous versions of Service Manager, it required to open the work item, navigate to the Activities tab, and then selecting the In progress activity. Now In progress activity can be accessed with a single click.
System Center 2016 - Service Manager includes the updates that support integration with Lync 2013 and Skype for Business in Microsoft Office suite 2013 and 2016. For information about contacting a user using Lync or Skype for Business, see Contact a User from an Incident Form.
Note
Lync versions earlier to 2013 are not supported.
The Setup wizard allows you to easily install Service Manager in complex configurations such as a SQL AlwaysOn configuration with different named instances.
Now you can configure the SQL management server, instance name and port number together.

Service Manager 2016 now supports the .NET framework 4.5.1
- To understand hardware and software requirements and software roles you need to prepare for Service Manager before you deploy it in your company or organization, see Planning for Service Manager.
- See the fixed issues.