Deploy containerized applications to AKS Edge Essentials cluster
AKS Edge Essentials makes it easier to get started with your containerized application, bringing cloud-native best practices to your edge application.
In the industrial factory scenario, we need to seamlessly integrate software that needs ongoing human supervision, without constant update feature disturbances.
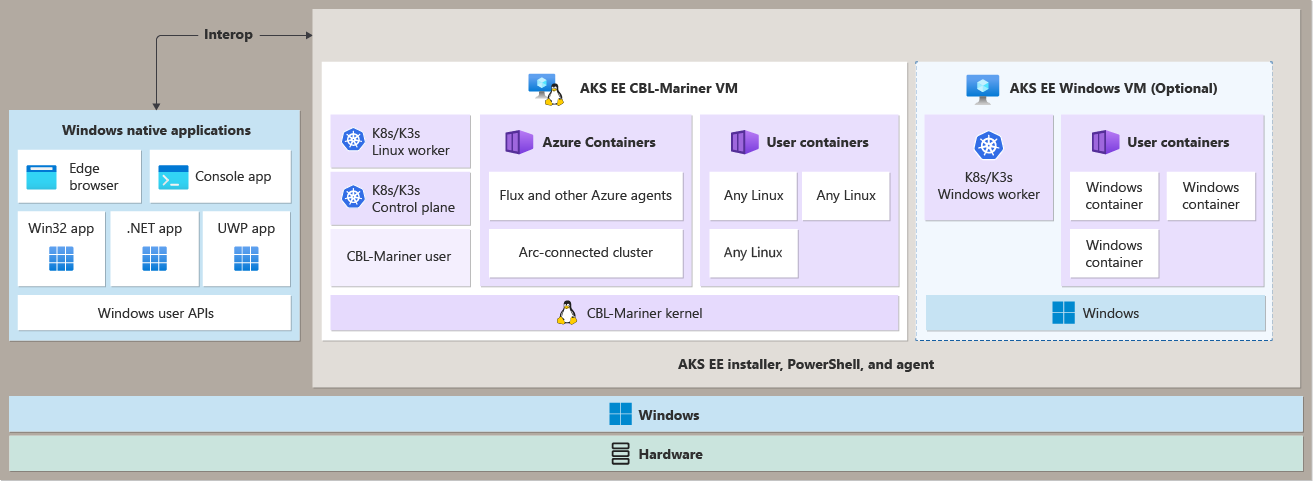
Here, you will learn how containerized applications can be deployed on AKS Edge Essentials Linux and Windows worker nodes, leveraging interoperability with Windows applications on a specialized device.
Deploy Linux and Windows applications on the AKS Edge Essentials cluster
Worker nodes
To run your applications and supporting services, you need a Kubernetes node. Worker nodes act as virtual machines (VMs) that run the Kubernetes node components, and host the pods and services that make up the application workload. Each machine in an AKS Edge Essentials cluster can only have one Linux and/or Windows VM. The Linux VM acts as the control node and worker node for Linux workloads in the Kubernetes cluster.
Pods
Kubernetes uses pods to run an instance of your application. A pod represents a single instance of your application, and typically, pods have a 1:1 mapping with a container. AKS Edge Essentials enables mixed-OS clusters, which means you can run Linux and Windows containers on the same cluster. This is useful when you have a Linux application that needs to communicate with a Windows application, or vice versa.
Deployments
A deployment represents one or more identical pods, managed by the Kubernetes Deployment Controller. A deployment defines the number of replicas (pods) to create, and the Kubernetes Scheduler ensures that if pods or nodes encounter problems, additional pods are scheduled on healthy nodes.
Manifest files
A Kubernetes manifest file allows you to describe your workloads in the YAML format declaratively and simplify Kubernetes object management. For example you can use a manifest file to ensure your pods get scheduled on nodes with the corresponding OS by adding nodeSelector to your deployment files. See linux-sample.yaml in the GitHub repo package for an example of a deployment manifest. Note that in the YAML we specified a nodeSelector tag as Linux.
Deploy the application
To deploy your application, you use the kubectl apply command. This command parses the manifest file and creates the defined Kubernetes objects. This is how you would deploy a linux application in AKS Edge Essentials:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/AKS-Edge/main/samples/others/linux-sample.yaml
Deploy applications remotely to your Arc-enabled AKS Edge Essentials cluster
When you have a large number of devices and you want to deploy the same application to all of them, you can use GitOps and Flux to deploy applications to your Arc-enabled AKS Edge Essentials cluster.
GitOps on Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes uses Flux. Flux is a tool for keeping Kubernetes clusters in sync with sources of configuration (like Git repositories) and automating updates to the configuration when there is new code to deploy.
Interoperability with Windows applications
Many of the cloud-native workloads are built on Linux, and you're faced with the challenge of having to introduce Linux systems to take advantage of cloud-native solutions. AKS Edge Essentials offers interoperability between native Windows applications and containerized Linux or Windows workloads.
To establish a communication channel between the Windows host OS and the Linux and Windows virtual machines, we use a Hyper-V networking stack. For more information about AKS Edge Essentials networking, see AKS Edge Essentials networking.
Specialized devices with Windows IoT Enterprise
In the industrial factory scenario, we are looking for creating a specialized device that don’t need functionality and feature updates as frequently as other general purpose devices in the organization. We need our application to run on a device that is built for a specific purpose and is not intended to be changed or upgraded.
Windows powers many ATM machines, point-of-sale terminals, industrial automation systems, thin clients, medical devices, digital signage, kiosks, and other fixed purpose devices like the ones in our industrial factory scenario. Windows IoT Enterprise allows you to build these fixed purpose devices with specific allowances and restrictions in the license agreement.
When targeting fixed purpose devices that often require a longer servicing option and don’t need feature updates as frequently as other devices in the organization, then you shall consider running AKS Edge Essentials on Windows IoT Enterprise with a 10-year Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC).