Understand SQL database hyperscale
Azure SQL Database has been limited to 4 TB of storage per database for many years. This restriction is due to a physical limitation of the Azure infrastructure. Azure SQL Database Hyperscale changes the paradigm and allows for databases to be 100 TB or more. Hyperscale introduces new horizontal scaling techniques to add compute nodes as the data sizes grow. The cost of Hyperscale is the same as the cost of Azure SQL Database; however, there's a per terabyte cost for storage. You should note that once an Azure SQL Database is converted to Hyperscale, you can't convert it back to a “regular” Azure SQL Database. Hyperscale is the ability for an architecture to scale appropriately as demanded.
Azure SQL Database Hyperscale is a great option for most business workloads as it provides great flexibility and high performance with independently scalable compute and storage resources.
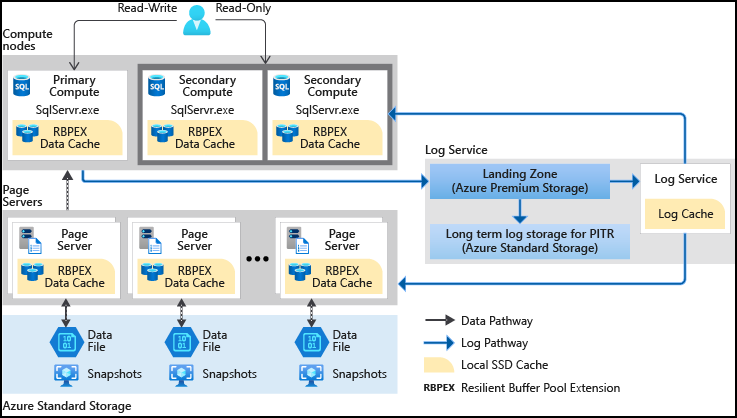
Hyperscale separates the query processing engine, where the semantics of various data engines diverge, from the components that provide long-term storage and durability for the data. In this way, storage capacity can be smoothly scaled out as far as needed.
The Hyperscale service tier in Azure SQL Database is the newest service tier in the vCore-based purchasing model. This service tier is a highly scalable storage and compute performance tier that uses Azure to scale out the storage and compute resources for an Azure SQL Database substantially beyond the limits available for the General Purpose and Business Critical service tiers.
Benefits
The Hyperscale service tier removes many of the practical limits traditionally seen in cloud databases. Where most other databases are limited by the resources available in a single node, databases in the Hyperscale service tier have no such limits. With its flexible storage architecture, storage grows as needed. In fact, Hyperscale databases aren't created with a defined max size. A Hyperscale database grows as needed - and you're billed only for the capacity you use. For read-intensive workloads, the Hyperscale service tier provides rapid scale-out by provisioning extra replicas as needed for offloading read workloads.
Additionally, the time required to create database backups or to scale up or down is no longer tied to the volume of data in the database. Hyperscale databases can be backed up instantaneously. You can also scale a database in the tens of terabytes up or down in minutes. This capability frees you from concerns about being boxed in by your initial configuration choices. Hyperscale also provides fast database restores which runs in minutes rather than hours or days.
Hyperscale provides rapid scalability based on your workload demand.
Scaling Up/Down – You can scale up the primary compute size in terms of resources like CPU and memory, and then scale down, in constant time. Because the storage is shared, scaling up and scaling down isn't linked to the volume of data in the database.
Scaling In/Out – You also get the ability to provision one or more compute replicas that you can use to serve your read requests. This means that you can use extra compute replicas as read-only replicas to offload your read workload from the primary compute. In addition to read-only, these replicas also serve as hot-standbys to failover from the primary.
Provisioning of each of these extra compute replicas can be done in constant time and is an online operation. You can connect to read-only compute replicas by setting the ApplicationIntent argument on your connection string to ReadOnly. Any connections with the ReadOnly application intent are automatically routed to one of the read-only compute replicas.
Hyperscale separates the query processing engine from the components that provide long-term storage and durability for the data. This architecture provides the ability to smoothly scale storage capacity as far as needed (initial target is 100 TB), and the ability to scale compute resources rapidly.
Security considerations
Security for Hyperscale service tier shares the same great capabilities as the other Azure SQL Database tiers. They're protected by the layered defense-in-depth approach as shown in the picture below, and moves from the outside in:
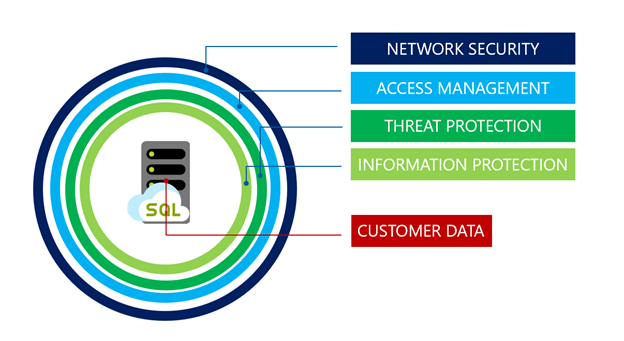
Network Security is the first layer of defense and uses IP firewall rules to allow access based on the originating IP address and Virtual Network firewall rules to allow the ability to accept communications that are sent from selected subnets inside a virtual network.
Access Management is provided through the below authentication methods to ensure a user is whom they claim to be:
- SQL Authentication
- Microsoft Entra authentication
- Windows Authentication for Microsoft Entra Principals (Preview)
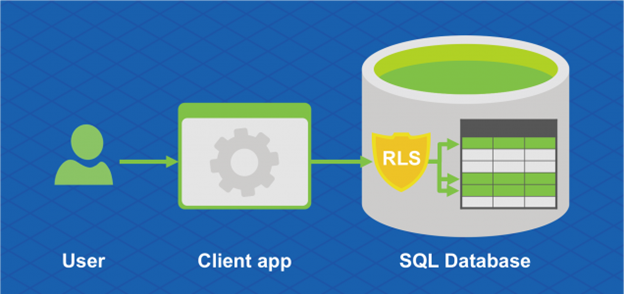
Azure SQL Database Hyperscale also supports Row-Level security. Row-Level Security enables customers to control access to rows in a database table based on the characteristics of the user executing a query (for example, group membership or execution context).
Threat Protection abilities in auditing and threat detection capabilities. SQL Database and SQL Managed Instance auditing tracks database activities and helps maintain compliance with security standards by recording database events to an audit log in a customer-owned Azure storage account. Advanced Threat Protection can be enabled per server for an extra fee and analyzes your logs to detect unusual behavior and potentially harmful attempts to access or exploit databases. Alerts are created for suspicious activities such as SQL injection, potential data infiltration, and brute force attacks or for anomalies in access patterns to catch privilege escalations and breached credentials use.
Information Protection is provided in the following various ways:
- Transport Layer Security (Encryption-in-transit)
- Transparent Data Encryption (Encryption-at-rest)
- Key management with Azure Key Vault
- Always Encrypted (Encryption-in-use)
- Dynamic data masking
Performance considerations
The Hyperscale service tier is intended for customers who have large on-premises SQL Server databases and want to modernize their applications by moving to the cloud, or for customers who are already using Azure SQL Database and want to significantly expand the potential for database growth. Hyperscale is also intended for customers who seek both high performance and high scalability.
Hyperscale provides the following performance capabilities:
- Nearly instantaneous database backups (based on file snapshots stored in Azure Blob storage) regardless of size with no IO effect on compute resources.
- Fast database restores (based on file snapshots) in minutes rather than hours or days (not a size of data operation).
- Higher overall performance due to higher transaction log throughput and faster transaction commit times regardless of data volumes.
- Rapid scale out - you can provision one or more read-only replicas for offloading your read workload and for use as hot-standbys.
- Rapid Scale up - you can, in constant time, scale up your compute resources to accommodate heavy workloads when needed, and then scale the compute resources back down when not needed.
Note
SQL Database Hyperscale does not support the following features:
- SQL Managed Instance
- Elastic Pools
- Geo-replication
- Query Performance Insights
Deploying Azure SQL Database Hyperscale
To deploy Azure SQL Database with the Hyperscale tier:
Browse to the Select SQL Deployment option page.
Under SQL databases, leave Resource type set to Single database, and select Create.
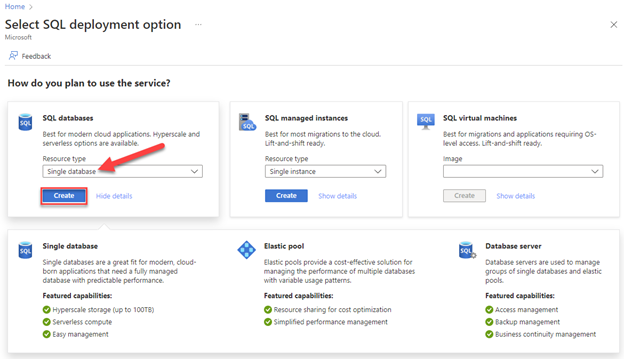
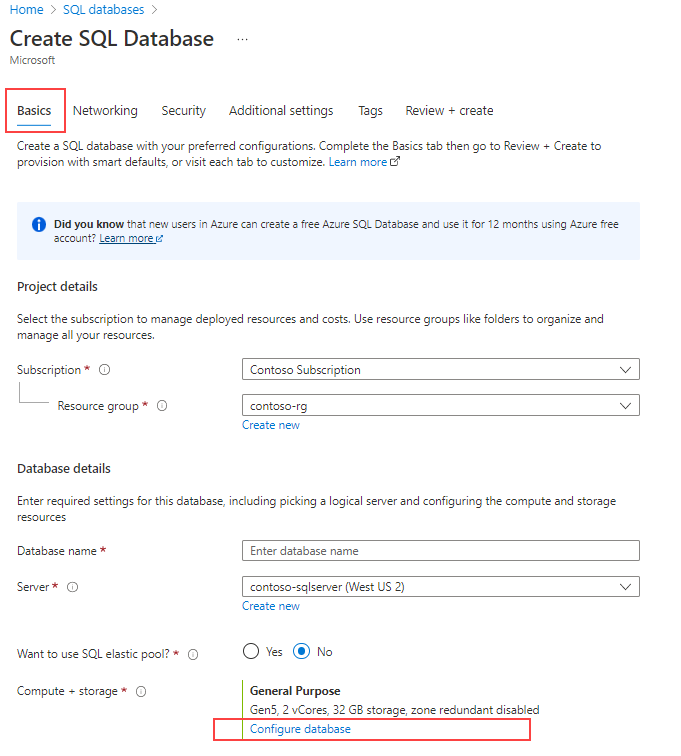
From the Basics tab of the Create SQL Database page, select the desired subscription, resource group, and database name.
Select the Create new link for the Server, and fill out the new server information, such as server name, server admin login and password, and location.
Under Compute + storage, select the Configure database link.
For Service tier, select Hyperscale.
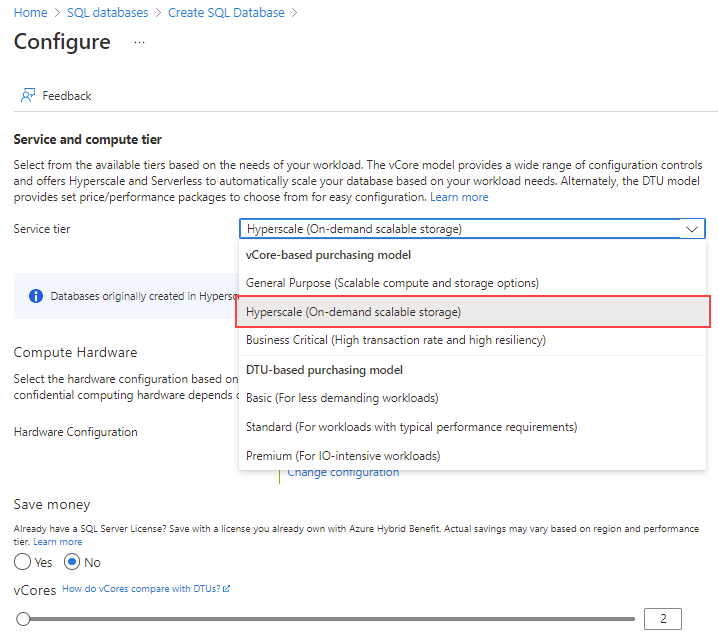
Under Hardware Configuration, select the Change configuration link. Review the available hardware configurations and select the most appropriate configuration for your database. For this example, we'll select the Gen5 configuration.
Select OK to confirm the hardware generation.
Optionally, adjust the vCores slider if you would like to increase the number of vCores for your database. For this example, we'll select 2 vCores.
Adjust the High-Availability Secondary Replicas slider to create one High Availability (HA) replica. Select Apply.
Select Next: Networking at the bottom of the page.
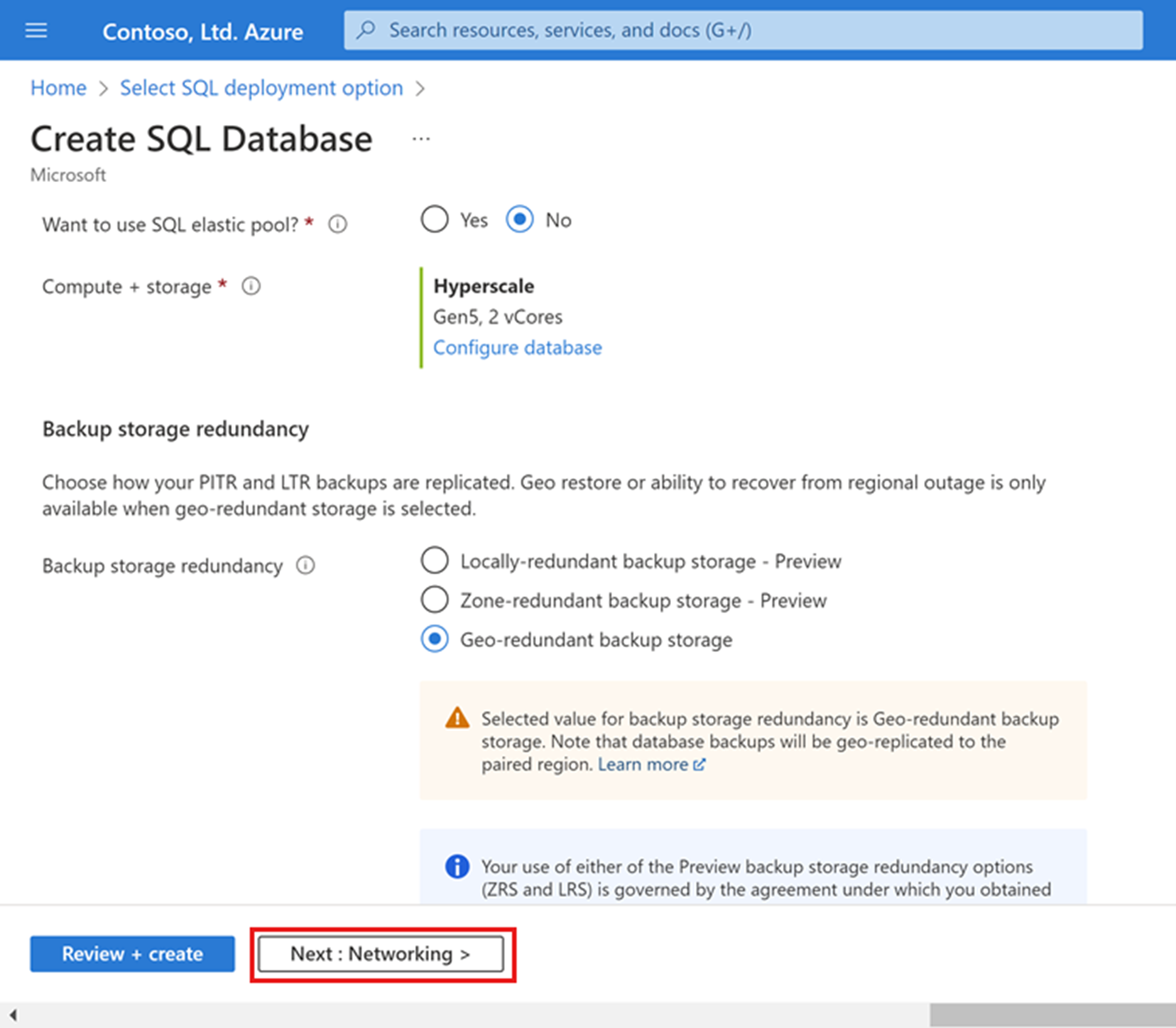
For Firewall rules on the Networking tab, set Add current client IP address to Yes. Leave Allow Azure services and resources to access this server set to No.
Select Next: Security at the bottom of the page.
On the Review + create tab, select Create.