Describe SQL Edge
Many organizations have substantial investments in IoT infrastructure. A typical IoT solution architecture includes IoT devices responsible for reading environmental sensors to generate customer data. Commonly, this data gets processed on-site using Edge devices. In addition, an IoT Edge device can run Docker compatible containers containing custom business logic or light-weight versions of cloud services such as Azure Stream Analytics, Azure Machine Learning, Azure Functions, Azure SQL, and more. The benefit to IoT Edge is that processing happens on the local network resulting in a quicker feedback loop should any action need to be taken, at the same time minimizing cloud processing and bandwidth costs.
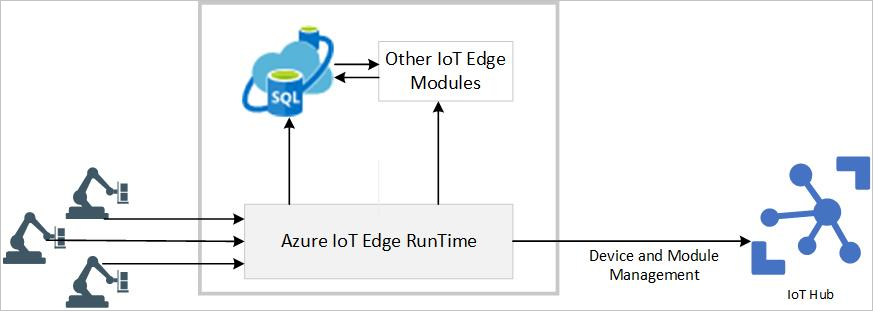
Azure SQL Edge is an optimized relational database engine purposefully designed for IoT workloads. It provides capabilities to stream, process, and analyze relational and non-relational data such as JSON, graph, and time-series data. Azure SQL Edge is built on the latest version of the SQL Server Database Engine – the same engine that serves as the foundation of SQL Server and Azure SQL. Azure SQL Edge brings T-SQL programming, industry-leading performance, security, and query processing capabilities to the Edge.
Benefits
Familiar T-SQL syntax and tooling
SQL Developers and administrators can continue to leverage familiar T-SQL syntax and tooling since Azure SQL Edge is based on the SQL Server Database Engine. Tooling available includes the Azure portal, SQL Server Management Studio, Azure Data Studio, Visual Studio Code, and SQL Server Data Tools in Visual Studio.
Portability
Azure SQL Edge is a containerized version of the SQL Server Database Engine optimized for IoT. Azure SQL Edge is deployable to various Windows and Linux-based servers capable of running the IoT Edge runtime, ranging from powerful full-fledged servers to smaller ARM-based devices.
Support for multiple connection states and data sync
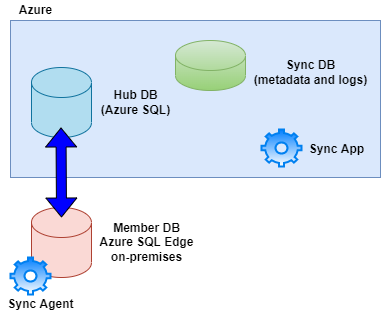
In IoT, internet connectivity isn't always possible or reliable. Therefore, IoT Edge modules need to support all states of connectivity. Azure SQL Edge supports connected, disconnected, and hybrid semi-connected scenarios. Incremental data synchronization is possible with the Azure SQL Data Sync service and configuring sync groups to synchronize the tables you choose bi-directionally across multiple databases in Azure SQL and SQL Server instances.
The diagram below depicts the synchronization process. The synchronization process uses a sync agent on the Azure SQL Edge to sync data with the Hub database. From the Hub perspective, the synchronization process is driven by a Sync app guided by details available in the Sync database, where the synchronization metadata and logs get stored.
Built-in data streaming and machine learning
Azure SQL Edge has built-in support for data streaming to and from multiple inputs and outputs. This functionality borrows the same technology that powers Azure Stream Analytics and allows introspection of incoming time-series data using anomaly detection, time-windowing, aggregation, and filtering. Azure SQL Edge also has T-SQL functions that support querying time-series data. Furthermore, Azure SQL Edge supports machine learning inference and the PREDICT statement.
Security considerations
Security on Azure SQL Edge brings data encryption, classification, and access controls from the SQL Server Database Engine. In addition, Azure SQL Edge provides row-level security, dynamic data masking, and transparent data encryption (TDE) as an extra security benefit. It's also beneficial to encrypt any backup files created using a certificate or asymmetric key.
As for network transport, Azure SQL Edge utilizes transport layer security (TLS) and certificates to encrypt all communication. Lastly, Microsoft Defender for IoT provides a centralized and unified security solution to discover and identify IoT devices, vulnerabilities, and threats. As with any data-related solution, it's also prudent to ensure that database users are granted the least privilege on database objects.
Deploying Azure SQL Edge from the Azure Marketplace
Azure SQL Edge is available in the Azure Marketplace with two plans, Azure SQL Edge Developer (for development only, limited to 4 cores and 32 GB of memory), and Azure SQL Edge (for production, limited to 8 cores and 64 GB of memory).
As a pre-requisite to deploy Azure SQL Edge, you need to have an IoT Hub provisioned with at least one IoT Edge device. In this example, an IoT Hub named org-iot-hub and a Linux-based IoT Edge device called iot-edge-device-1 have been pre-provisioned.
Locate the Azure SQL Edge module in the Azure Marketplace, and select the Get It Now button.

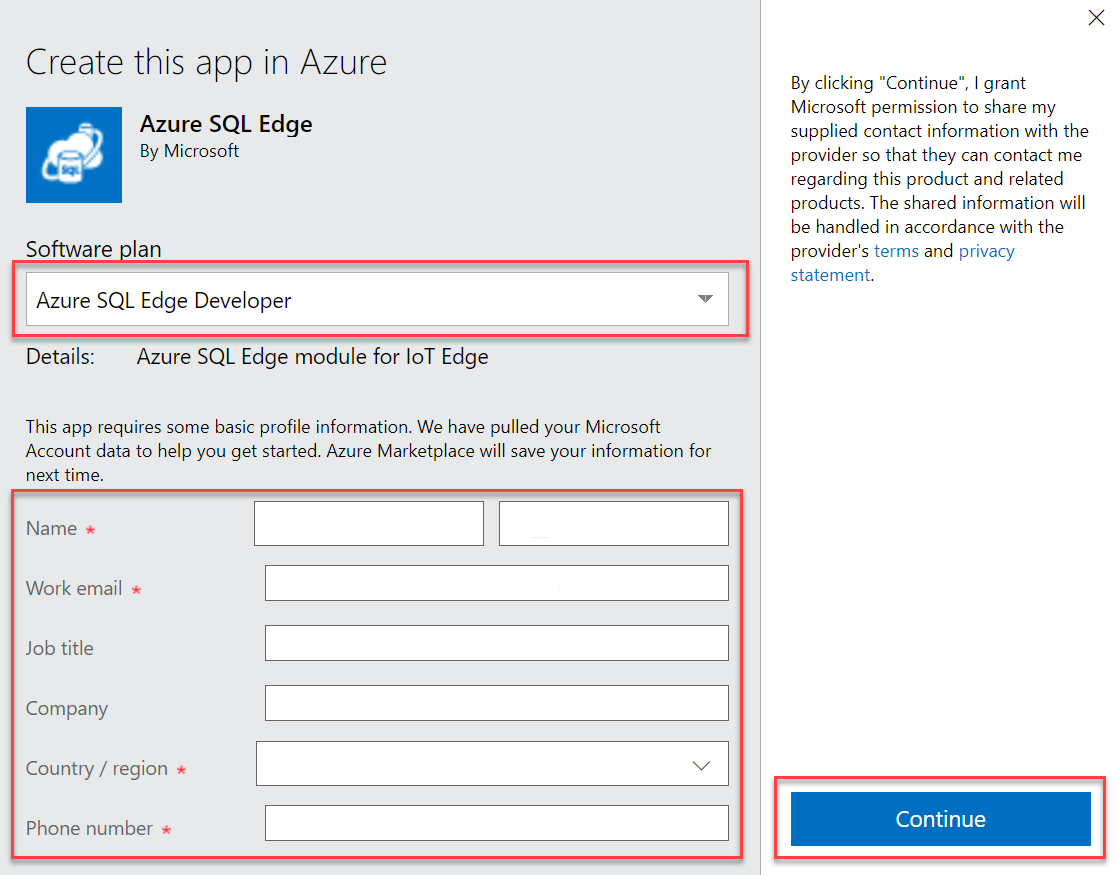
In the modal form, select the desired software plan SKU. In this example, Azure SQL Edge Developer is chosen. Next, fill in any other profile information required by the form and select Continue.
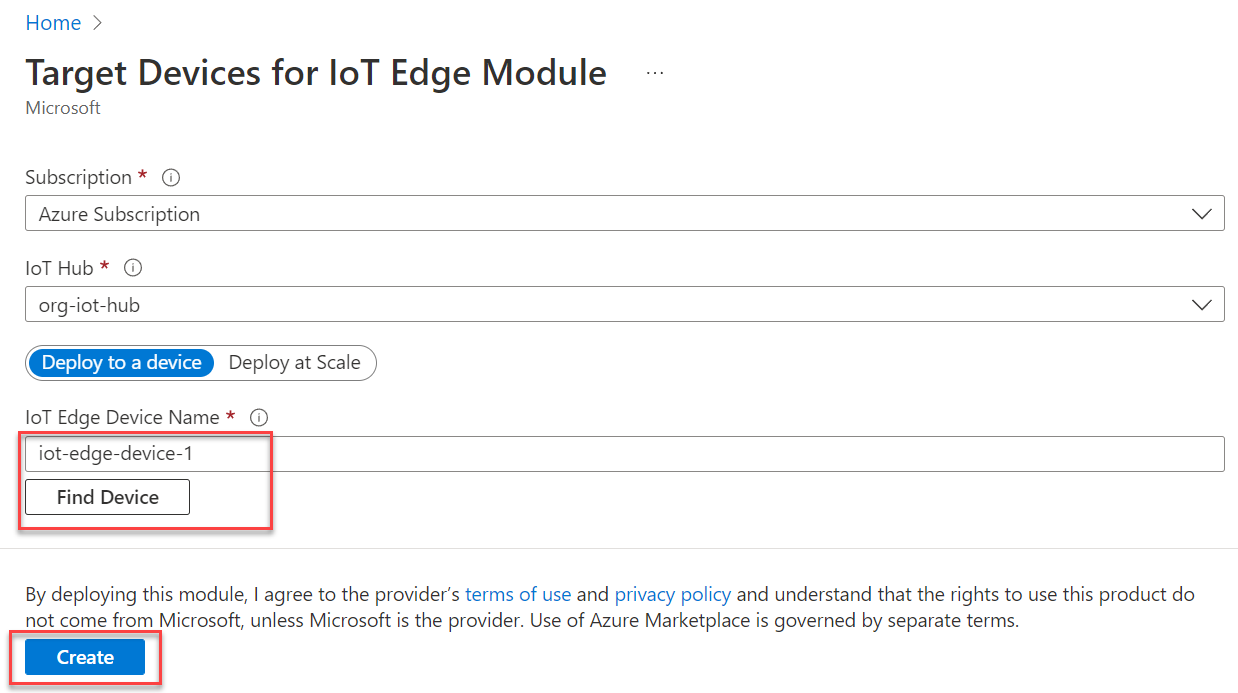
In the Target Devices for IoT Edge Module screen, enter the IoT Edge Device Name value manually or use the Find Device functionality to locate the Edge device from the selected IoT Hub. In this example, the Edge device name is iot-device-edge-1. Next, select the Create button.
On the Set modules on device blade, choose the AzureSQLEdge item under IoT Edge Modules.
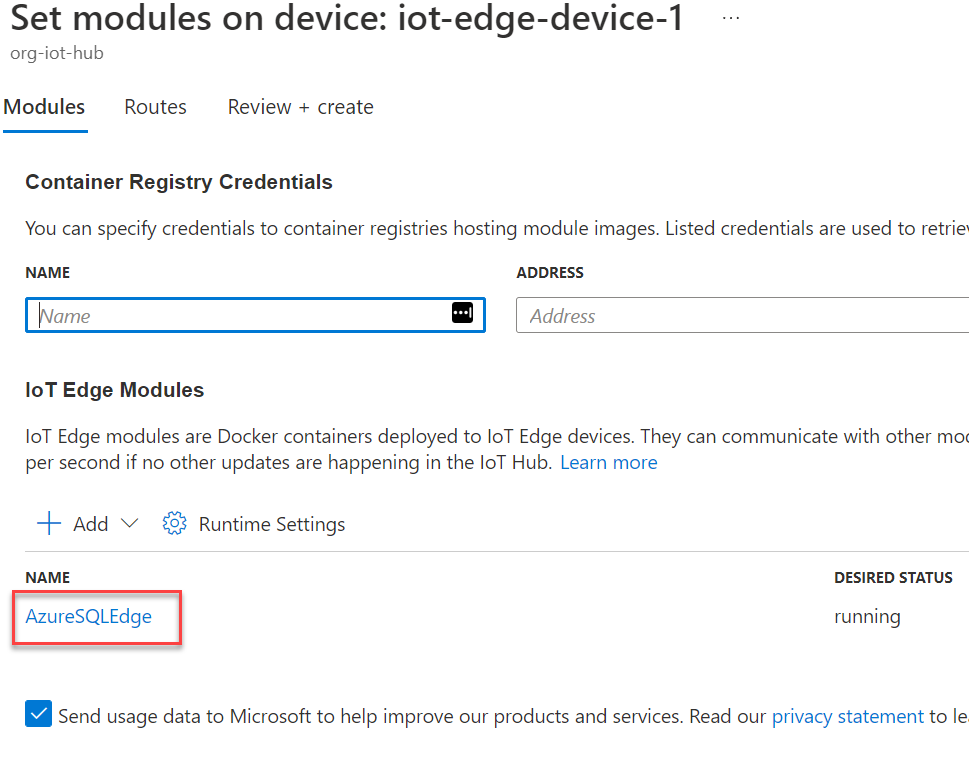
On the Update IoT Edge Module blade, select the Environment Variables tab. Next, replace the SQL Edge admin account password by setting the value for the MSSQL_SA_PASSWORD variable. Optionally add configuration options under theContainer Create Options tab. Once complete, select the Update button.
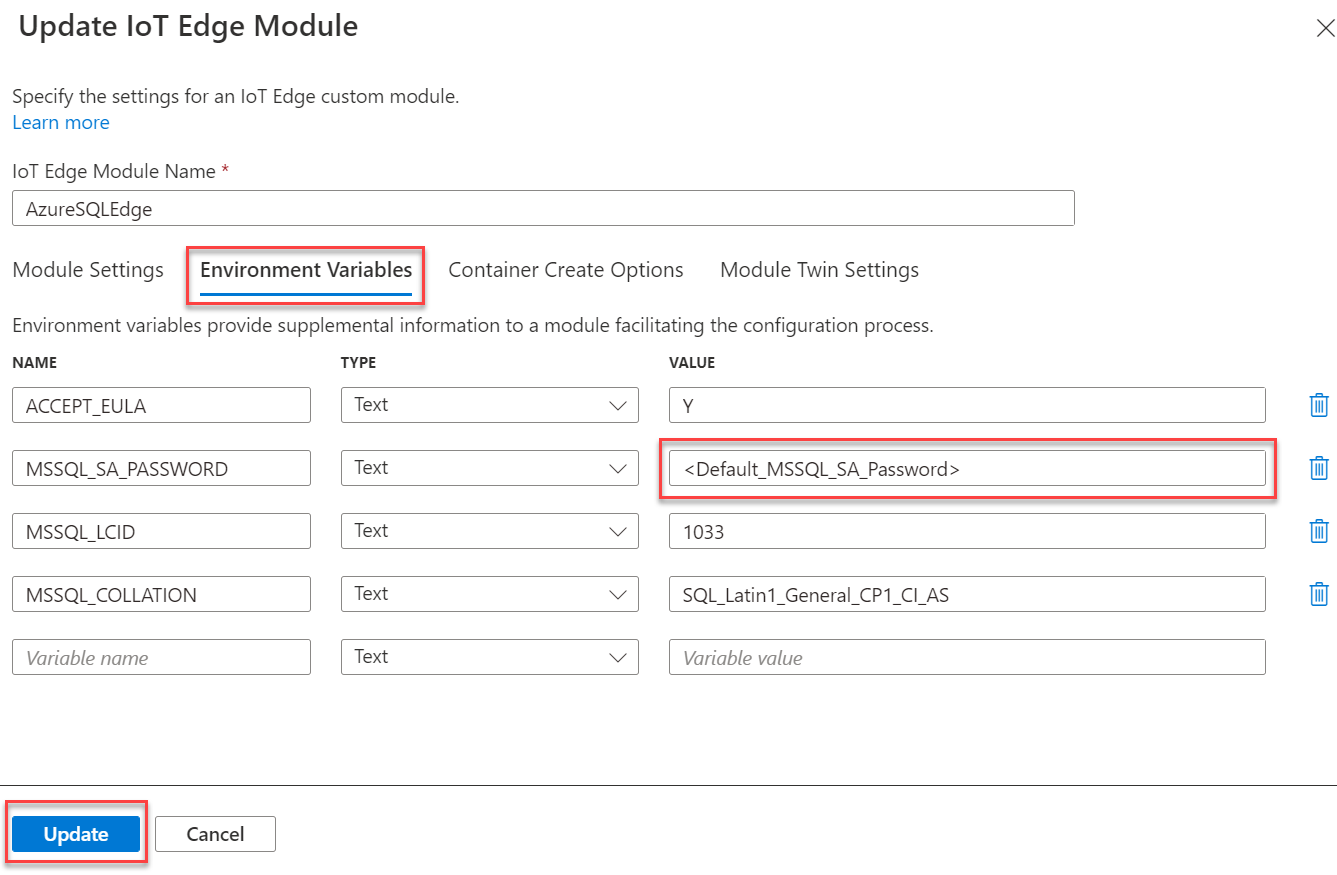
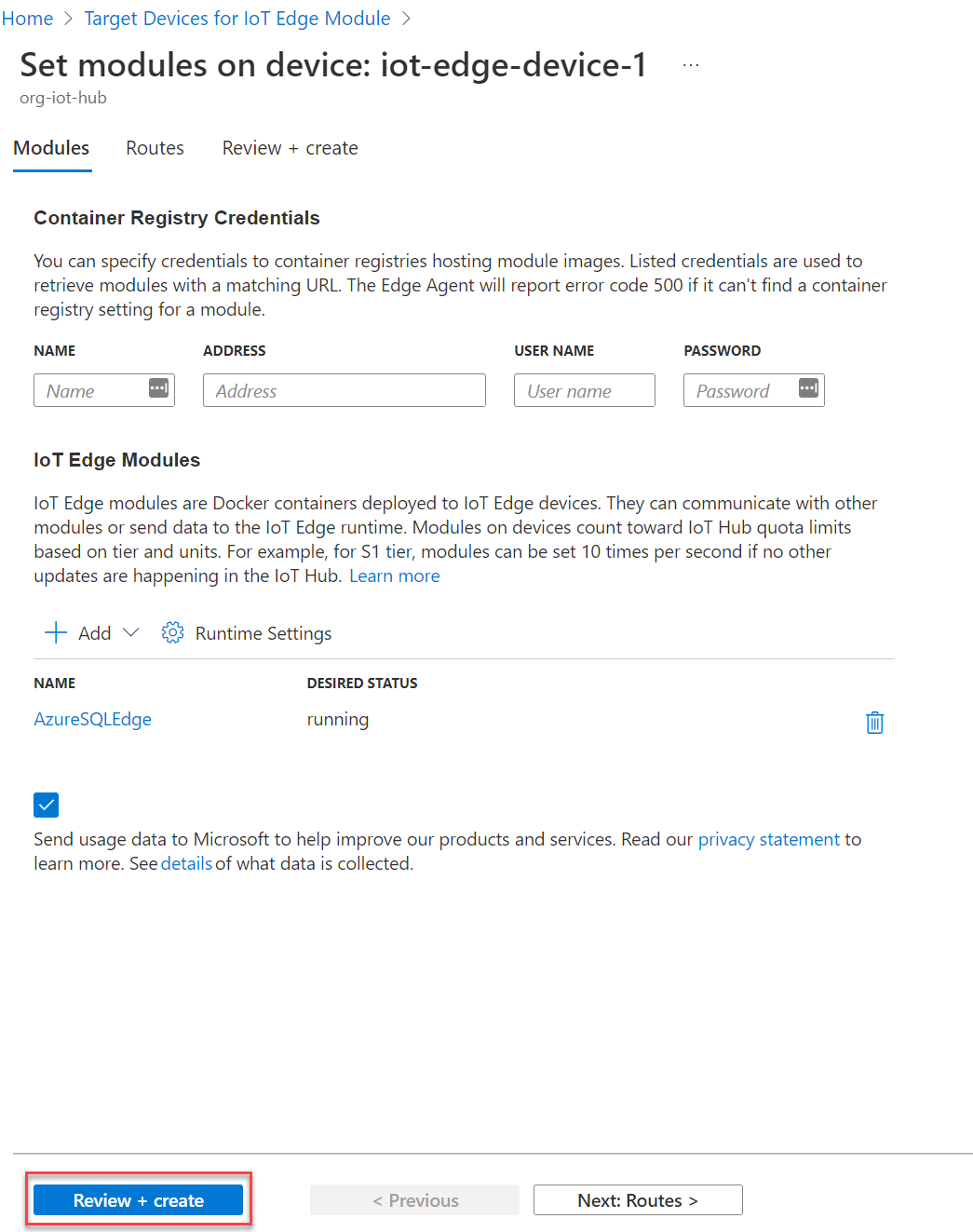
Returning to the Set modules on device blade, optionally configure message routing for the module beneath the Routes tab. Once complete, select Review + create and Create once more on the validation screen.
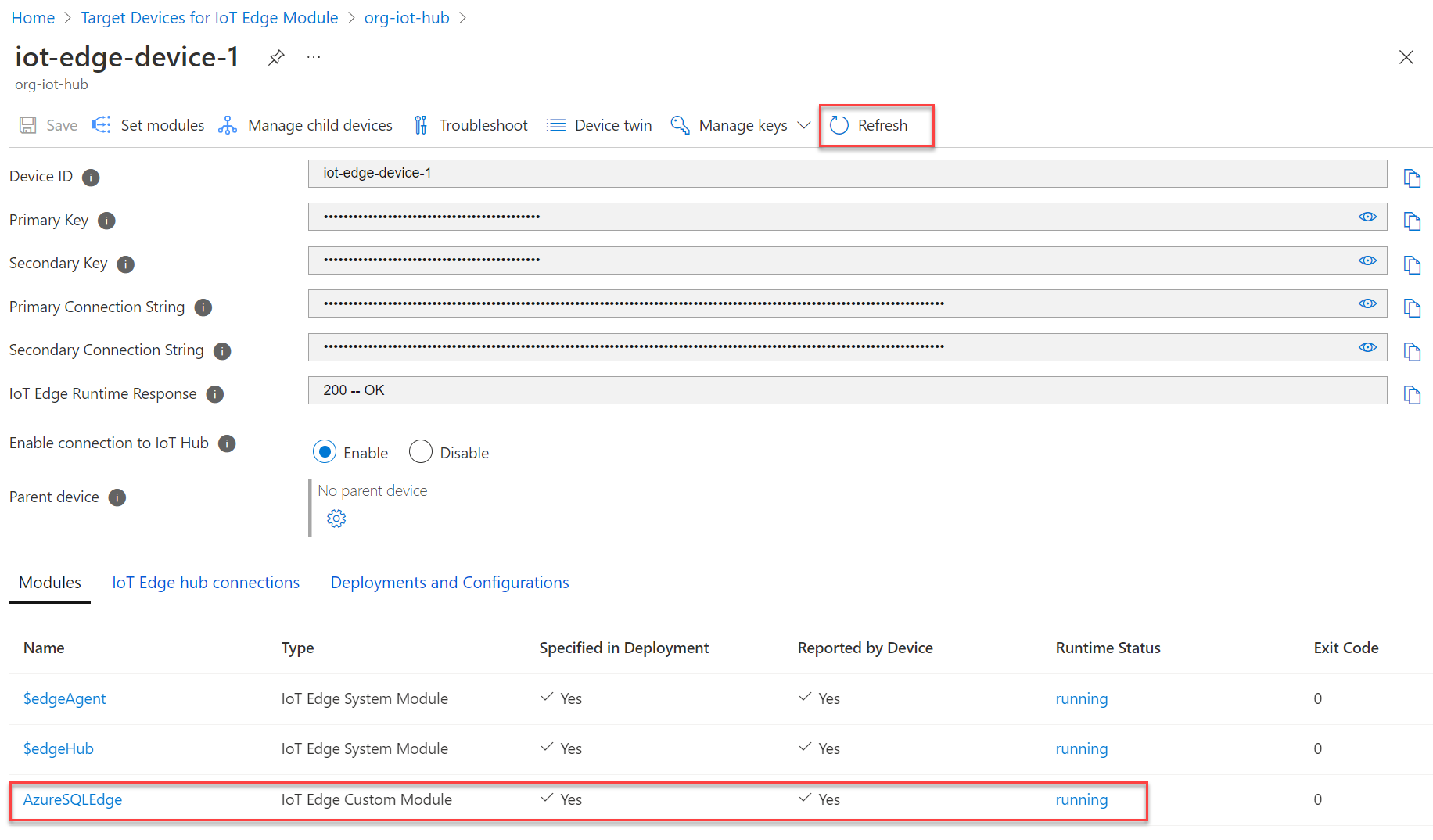
The IoT Edge device screen will display. Wait a few moments, and the device's reported module list now displays AzureSQLEdge in a running state. If the module's startup isn't complete, it will temporarily indicate an error state – wait a few minutes and refresh.
Use your desired connection method and begin using Azure SQL Edge!