Explore Azure Tables
Azure Table Storage is a NoSQL storage solution that makes use of tables containing key/value data items. Each item is represented by a row that contains columns for the data fields that need to be stored.
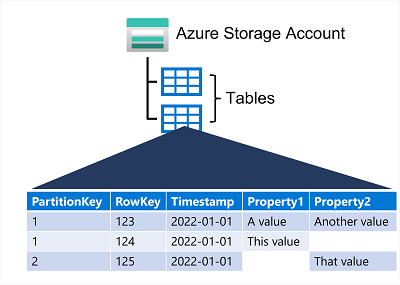
However, don't be misled into thinking that an Azure Table Storage table is like a table in a relational database. An Azure Table enables you to store semi-structured data. All rows in a table must have a unique key (composed of a partition key and a row key), and when you modify data in a table, a timestamp column records the date and time the modification was made; but other than that, the columns in each row can vary. Azure Table Storage tables have no concept of foreign keys, relationships, stored procedures, views, or other objects you might find in a relational database. Data in Azure Table storage is usually denormalized, with each row holding the entire data for a logical entity. For example, a table holding customer information might store the first name, last name, one or more telephone numbers, and one or more addresses for each customer. The number of fields in each row can be different, depending on the number of telephone numbers and addresses for each customer, and the details recorded for each address. In a relational database, this information would be split across multiple rows in several tables.
To help ensure fast access, Azure Table Storage splits a table into partitions. Partitioning is a mechanism for grouping related rows, based on a common property or partition key. Rows that share the same partition key will be stored together. Partitioning not only helps to organize data, it can also improve scalability and performance in the following ways:
Partitions are independent from each other, and can grow or shrink as rows are added to, or removed from, a partition. A table can contain any number of partitions.
When you search for data, you can include the partition key in the search criteria. This helps to narrow down the volume of data to be examined, and improves performance by reducing the amount of I/O (input and output operations, or reads and writes) needed to locate the data.
The key in an Azure Table Storage table comprises two elements; the partition key that identifies the partition containing the row, and a row key that is unique to each row in the same partition. Items in the same partition are stored in row key order. If an application adds a new row to a table, Azure ensures that the row is placed in the correct position in the table. This scheme enables an application to quickly perform point queries that identify a single row, and range queries that fetch a contiguous block of rows in a partition.