Datacenter Firewall on Azure Stack HCI
Azure Stack HCI software-defined networking (SDN) Datacenter Firewall functionality can potentially help enhance your environment's security. Datacenter Firewall can also minimize the sprawl of hardware devices, to support your company's consolidation initiatives. You need to ensure that Datacenter Firewall capabilities extend beyond virtual networking to provide integration with your existing virtual local area network (VLAN) environment.
Like traditional on-premises datacenters that use physical firewall appliances to restrict network connectivity, SDN environments must be able to control connectivity. Distributed Datacenter Firewall provides this functionality and, along with Software Load Balancing and Remote Access Server (RAS) Gateway, serves as a core component of SDN. Network Controller provides a central management and monitoring interface for Datacenter Firewall to help protect virtualized workloads from unauthorized network access.
Benefits of Datacenter Firewall
Traditional firewalls target edge connectivity, filtering traffic between on-premises datacenters and the internet, commonly called North-South communication. This approach offers limited protection in today's world, where the network perimeter has less significance as the protection boundary.
To provide meaningful protection in a zero-trust strategy, firewalls must also help protect resources within a datacenter from internal threats. Using physical firewalls to filter on-premises communication, also called East-West traffic, is challenging because it requires added hardware investment and operational overhead. Routing all protected traffic via a separate physical device also increases latency, which negatively affects internal workloads.
Within Azure Stack HCI, you can define granular software-based filtering of virtualized workloads that's applicable to external and internal traffic. Datacenter Firewall provides this filtering through access control lists (ACLs) in logical and virtual networks.
For Azure Stack HCI administrators, Datacenter Firewall provides the following benefits:
- A highly scalable software-based firewall solution that can be centrally managed.
- The ability to move virtual machines (VMs) across Azure Stack HCI cluster nodes without affecting the firewall configuration.
- Protection of tenant VMs regardless of their guest operating system.
For Azure Stack HCI tenants, Datacenter Firewall provides network level protection in the following scenarios:
- Internet-facing workloads within virtual and logical networks of Azure Stack HCI.
- Communication within and between the virtual and logical network subnets of Azure Stack HCI.
- Communication between datacenter networks and tenant workloads hosted by Azure Stack HCI.
Datacenter Firewall functionality
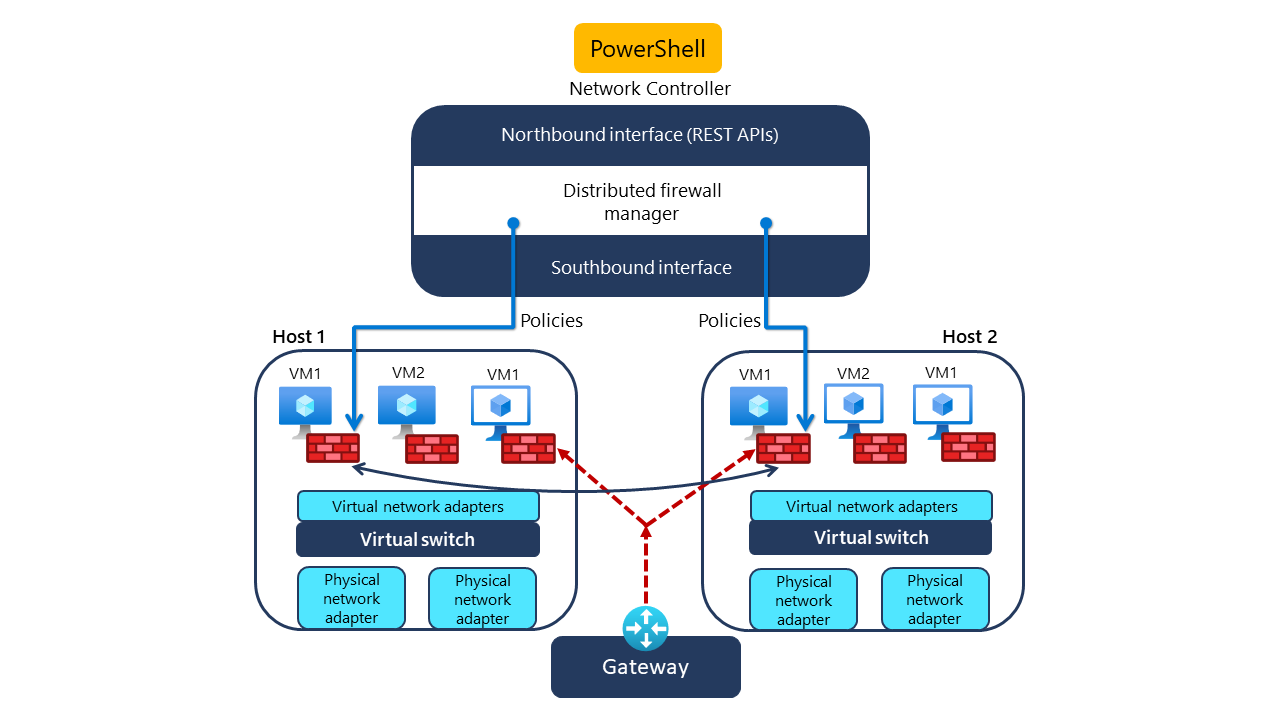
Datacenter Firewall is a network-layer, stateful, multitenant firewall that supports filtering by any combination of five parameters: source and destination port numbers, source and destination IP addresses, and a protocol. Datacenter Firewall is implemented as a distributed firewall, with policies that you can apply at the virtual machine (VM) network interface, logical network subnet, or virtual network subnet level.
You can restrict traffic between virtualized workloads in both external and internal networks. Network Controller applies the firewall policies to the virtual switch ports of Azure Stack HCI cluster nodes that function as Hyper-V hosts. These policies support Azure Stack HCI workloads that are connected to VLAN-based networks.
To implement Datacenter Firewall-based traffic filtering, you define firewall policies by using any management tool that supports communication with the northbound Representational State Transfer (REST) API of Network Controller. These tools include PowerShell, Windows Admin Center, and Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager (VMM).
The rules are automatically updated if you move VMs across cluster nodes. Network Controller also automatically remediates any deviations from the policies you defined due to local configuration changes. This process facilitates portability and helps ensure that firewall-based protection remains consistent.
The following diagram shows how Network Controller works with the distributed firewall. Datacenter Firewall uses policies to administer firewalls that protect the VMs.