What is Azure Service Fabric?
Let's start with a few definitions and a quick tour through Azure Service Fabric. This overview should help you decide whether Service Fabric is a good fit for your distributed computing solution.
What is a container?
A container is an atomic unit of software that wraps an application and all of its dependencies, such as libraries and configuration files, into its own isolated environment that includes everything needed to run the software in that environment. A container runs directly on top of the kernel and has an isolated view of the file system and other resources. The application inside the container has no knowledge of any other applications or processes outside of its container.
Why use containers?
The container model provides the following benefits:
Small: Containers use a single storage space and layer versions and updates to increase efficiency.
Fast: Containers don't have to boot an entire operating system, so they can start faster--typically in seconds.
Portability: A containerized application image can be ported to run in the cloud, on-premises, inside virtual machines, or directly on physical machines.
Resource governance: A container can limit the physical resources that it can consume on its host.
How are containers managed?
Container orchestration is a general term for a piece of software that helps administrators manage environments with containers. An administrator enters a desired state of the environment, such as five copies of a certain service running. Then, the orchestrator attempts to make the environment match the desired state. Once that desired state is reached, the orchestrator attempts to maintain that state. If one of the services fails, the orchestrator tries to deploy a new copy.
Most orchestrators do more than handle initial deployment and failure cases. They can also handle upgrades and address resource consumption and governance.
Container orchestration is fundamentally about achieving and maintaining some desired state of configuration in the environment.
The Cluster Resource Manager is the system component that handles orchestration in Azure Service Fabric.
What is a microservice?
Microservice applications and microservice architecture refer to small, independent, loosely coupled services that work together to achieve a result.
The services can be developed entirely independent of one another, using different technology stacks, libraries, and frameworks. The services can be deployed independently, so a component of the architecture can be updated without having to redeploy the entire application. The services are responsible for persisting their own data. The services communicate using well-defined APIs and remain agnostic of each other's internal implementation.
Why use microservices?
The microservice model provides the following benefits:
Agility: Microservices are deployed independently, which reduces the complexity of releasing features. You can update a service without redeploying the whole application.
Fault isolation: If an individual microservice becomes unavailable, it doesn't disrupt the entire application, provided that upstream microservices are designed to handle faults correctly.
Scalability: Services can be scaled independently, letting you expand subsystems that require more resources without scaling the entire application. You can see how this fits well with the container and container orchestration model.
Data isolation: Schema updates are easier, because only a single microservice is affected.
What are stateless and stateful services?
A stateless service is one where each request and reply can be understood in isolation. You can imagine a simplistic calculator service, where you send a calculation to be performed (2+2, for example) and receive a single answer (4). If you want to perform another calculation on that result (4 x 2, for example), you would manually send a request to compute 4 x 2 and receive 8. However, the service wouldn't be aware you were using the initial calculation's result.
A stateful service is one where each request and reply fit into a history of transactions that the service has knowledge of and can reference. Let's use the calculator service example again, but with a stateful version this time. You request the calculation 2+2 to be performed, and you receive 4. This time, you request the service to take the previous result and multiply by 2 (let's say the syntax looks like Answer x 2). You receive 8 in response, as you did in the first example. However, this time, the calculator service had knowledge that the result of the previous transaction (Answer) was 4.
Why use stateless and stateful services?
Your solution can make use of stateless services, stateful services, or both.
Your choice depends on the needs of your application. If you need a service's state to be persisted between sessions, then you need stateful services. If your services don't need state persisted or can rely on external storage for their state to be persisted, then you can use stateless services.
With microservice architecture, you can mix stateless and stateful services together. Microservices are independent and can make use of entirely different technology stacks, so you can design some of your services to require a persisted state and some do not.
What is Azure Service Fabric?
Azure Service Fabric manages your distributed computing system and makes it simple to deploy and manage containerized applications, implement microservice architecture, and make use of robust stateful services in addition to stateless ones. Service Fabric offers development and operations tooling, support for various programming models, container orchestration, cluster health and monitoring, automatic scaling, and more.
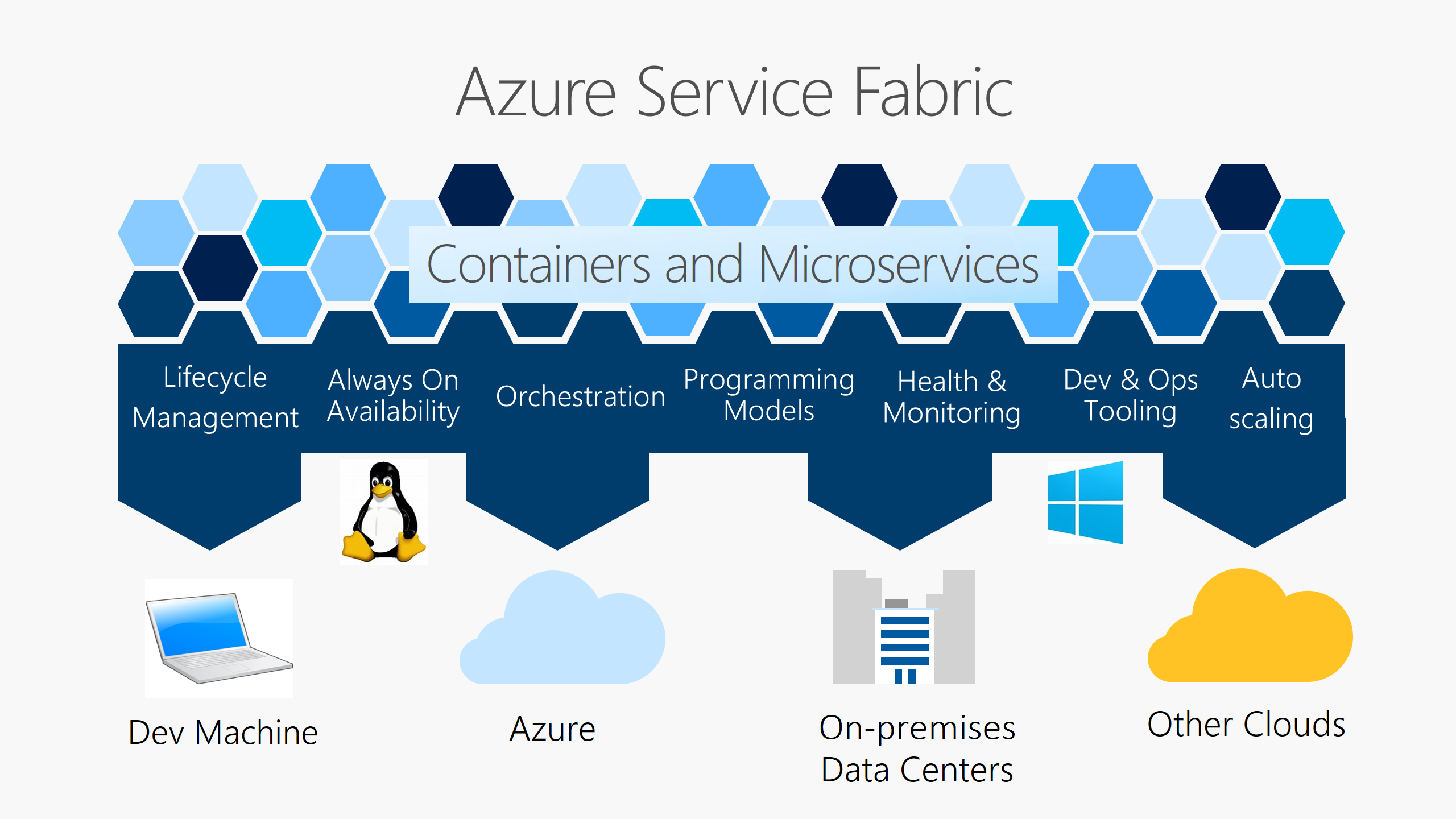
Service Fabric offers two different cluster models, depending on your preference. The standard cluster model requires you to manage all of the underlying resources of your cluster. The managed cluster model abstracts those resources away, and Azure manages them.
You can either create your cluster in the Azure portal or using Azure Resource Manager templates.