Dynamics 365 leads overview
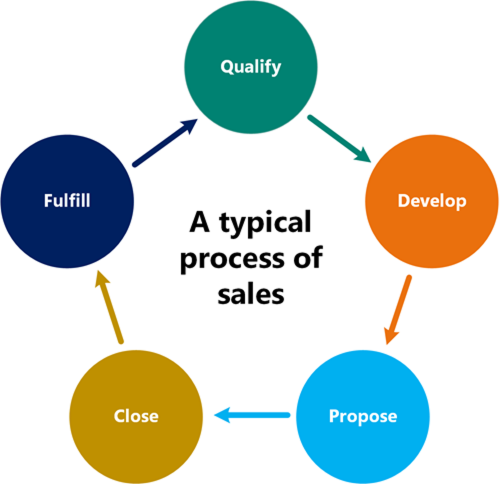
Dynamics 365 Sales enables an organization to manage their sales lifecycle process from start to finish. A typical sales lifecycle would resemble this image:
Most sales processes begin with leads, so let's examine what a lead is in more detail.
A lead is someone with an interest in what you are selling. A lead might be an existing client, or someone that you have never done business with before.
Some common examples of leads may include the following:
Someone who has expressed interest by requesting more information on your website.
Someone who is following a post that you or your organization is making on social media.
Someone who responded to an advertising or email campaign.
Leads are considered temporary records. The goal of a lead is to determine the viability of being a customer. This is referred to as lead qualification. Many organizations implement a lead qualification process. During qualification, leads are contacted, more information is gathered, and finally, a decision is made about the lead's status.
For example, if a salesperson meets someone at a tradeshow and gets a business card, they might not know if this person is a viable customer. It's only after the salesperson researches and engages with the individual, that they can determine if their needs align with what their organization can deliver. Not only are leads used to determine if an organization is good fit for the customer, but they also help determine if the customer is a good fit for the organization. If the lead is considered as a viable customer, they would be qualified and moved to the next stage in the sales process. If they aren't a viable customer, the lead would be disqualified.
Not all organizations use leads. Some organizations deal with opportunities, or only qualified prospective sales. Organizations that depend on mass demand generation processes such as advertisements, road shows, and cold calling prospect lists, will likely use leads. For businesses that have demand generation methods or ones that engage in mass marketing campaigns may benefit from lead management, this process helps businesses sift through the data and helps the sales department focus their efforts in the best direction.
To decide whether to use leads, consider these points:
- Do they invest substantial time and money in generating lists of possible customers like mass mailings or cold calling?
- Do they keep lists of people in the correct demographic, but have limited information on them like little contact information?
- Do they have a process or team dedicated to sifting through these possible customers and contacting them to identify good prospects?
- Do they need to manage lists of potential customers that must not be mixed in with their current customer lists, such accounts and contacts?
If any of these considerations apply, the organization may want to use leads. Even if the organization doesn't have large lead generation initiatives, ask if management wants to track the effort that sales spends tracking and working with prospects. If so, consider using Microsoft Dynamics 365's lead management features.
Leads are a key table in the Dynamics 365 sales process and represent the beginning of many processes. In addition to leads, Dynamics 365 Sales includes several components that are used to not only sell to customers but help in maintaining a long-term healthy relationship with customers.
Here are some of the most commonly used sales components.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Account | An account represents a business or organization. Sometimes it's a customer or a vendor. In some organizations, it might be a different grouping, such as a family. Typically, an account will have related contact records. |
| Activities | An activity is a type of table that offers tracking and scheduling options. By default, the system will have activities such as email, appointment, and phone call already configured. An administrator can add more custom activities to meet other business needs. |
| Business process flow | A business process flow (BPF) is a type of automation in Microsoft Power Platform. The BPF is placed on a table and offers users guidance and a predictable action plan for gathering data. Administrators can add more automation based on triggers from the user's interaction with the BPF. |
| Contact | A contact represents a single individual. A contact will often have many related records such as an account and activities. |
| Customer | A customer can be either an account or a contact. Typically speaking, in a business to business scenario, it's an account. In a business to consumer scenario, it's a contact. |
| Invoice | An order or record of a sales including details about products or services purchased that has been billed to the customer. |
| Opportunity | Like a lead, an opportunity is a potential sales transaction. Typically speaking, an opportunity is a more viable prospect than a lead, and it will contain more information and be tracked for a longer period of time. |
| Order | A confirmed request for delivery of goods and services based on specified terms, or a quote that has been accepted by a customer. |
| Product catalog | A collection of records that interact with opportunities, quotes, orders, and invoices to facilitate management of products, price lists, discounts, and product families for sales transactions. |
| Quote | A formal offer for products or services, proposed at specific prices and related payment terms to a customer. |
The following image shows an example sales process from beginning to end:

In this image, we can see a lead that has contacted our organization about products and services. An account executive reaches out to the lead to gather more information about the lead and determine if we're a good fit for them, and if they're a good fit for us.
If it's determined that it's not a good fit, the lead is disqualified and the sales cycle ends.
If it's determined that they're a good fit, the lead is qualified to an opportunity. A new opportunity is created.
If the lead is an existing customer, the new opportunity is associated with an existing account and/or contact record.
If the lead is a new customer, new account and contact records are created.
Details like the products and services that the lead is interested in, estimated revenue, and timelines are added to the opportunity.
A quote is added to the opportunity that represents the formal proposal to the customer.
When the customer agrees to the quote, an order is generated. The quote and opportunity associated with the order are closed.
After the order is fulfilled, an invoice is generated to bill the customer.