Install Python 3
Caution
This article references CentOS, a Linux distribution that is End Of Life (EOL) status. Please consider your use and plan accordingly. For more information, see the CentOS End Of Life guidance.
In the previous exercise, you ran a command to determine whether you had Python 3 installed. If you need to install Python 3, choose your operating system at the top of this page, and then follow the instructions below.
Once you're certain that Python 3 is installed, you can scroll to the bottom of this page and select Continue.
When this module was written, Python 3.11 was the latest version available, so instructions here refer to that version. Install the latest version of Python that is available for your operating system. If you install a different version, the button labels and the filenames may differ slightly from the installation instructions.
Note
These instructions are specifically for Windows 10 and Windows 11. For more information about installation instructions on different versions of Windows, see the official Python downloads page.
Install Python on Windows from the Microsoft Store
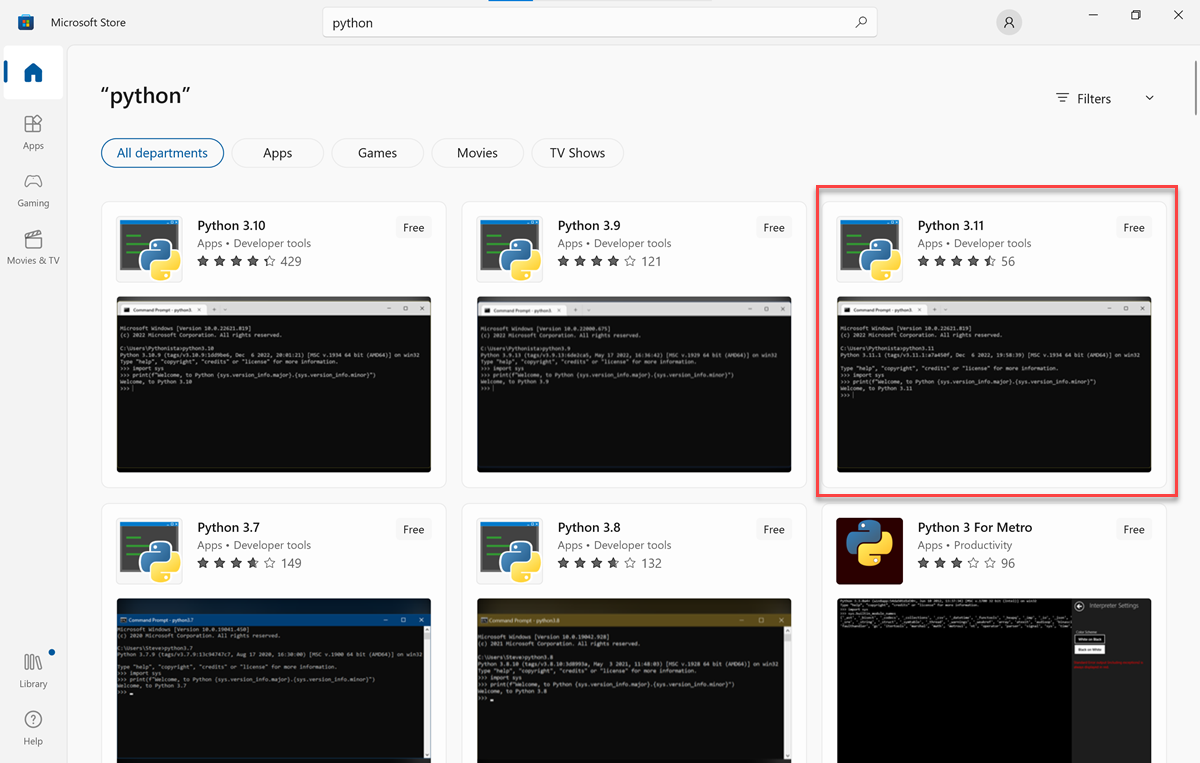
Open the Microsoft Store by selecting Start, and then typing start Microsoft Store.
Once open, search for Python.
You'll find a list of various options.
Select the most recent version of Python.
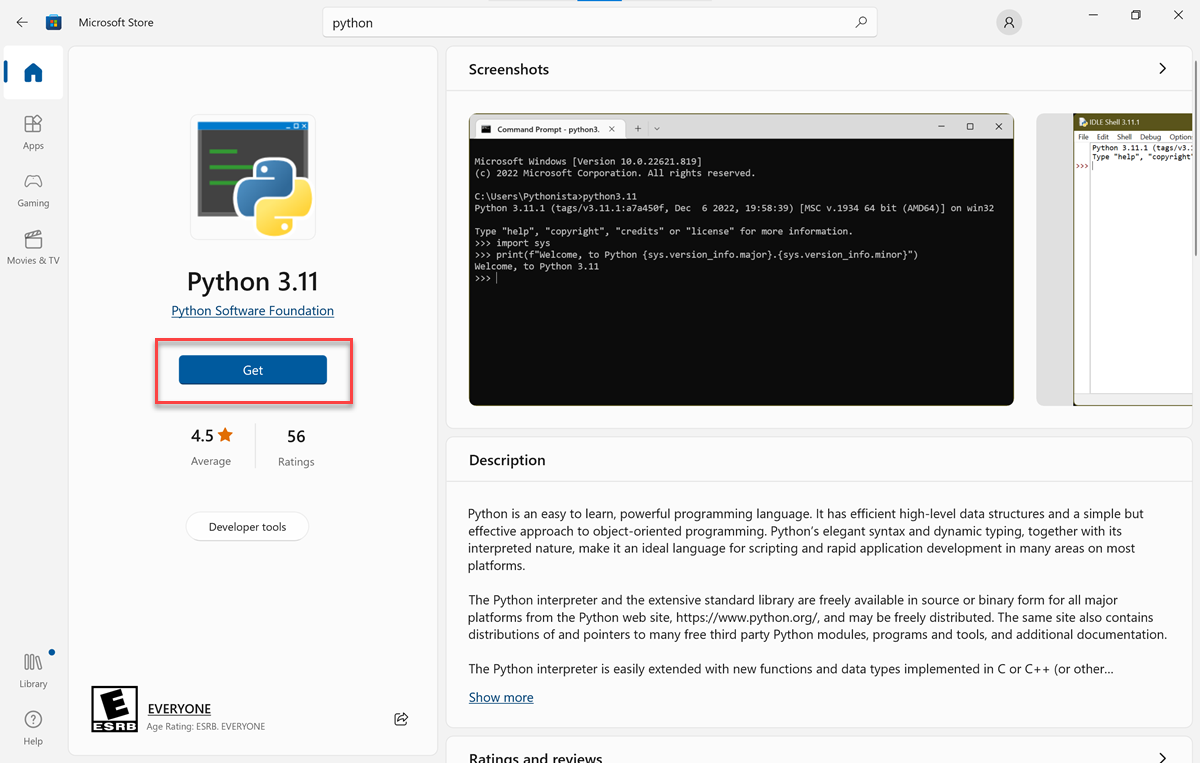
On the Home tab, select Get or Install.
Note
If you're unable to use the installer because you don't have administrator privileges, download the embeddable package (zip file) of Python from the Python website, and then extract the zip file to a local folder, such as C:\Python311.
Python installs in the background. The installation may take a couple of minutes depending on the speed of your system.
After Python installs, return to the command prompt.
Enter the following command
python --versionand then select Enter to see the version of Python:python --version
Install Python on Linux
The package manager you use depends on the version of Linux. Most popular Linux distributions include either APT (an acronym for "Advanced Packaging Tool") or YUM (an acronym for "Yellowdog Updater, Modified").
We provide instructions for APT and YUM in this unit. If your distribution of Linux uses a different package manager, you might need to search for <your Linux distribution> install python 3.
Install by using APT
If you use APT, you can use these instructions to install Python 3.
Open a terminal window.
Enter the following command to update APT package indexes.
sudo apt-get updateThe
apt-get updatecommand updates the list of packages (the package indexes) from the repositories and Personal Package Archives (PPAs) that it's aware of. This update enablesapt-getto find the latest versions of the packages that you want to install and their dependencies.Note
The
sudocommand temporarily elevates your permissions to root, the most powerful level of the system. When you usesudo, you'll usually be asked for your user account's password.apt-get updatedisplays all the items it will update. It might prompt you to approve by enteringyoryes, and then pressing Enter.Run the following command to install Python 3 at a Bash prompt
sudo apt-get install python3.10Note
apt-get installlocates the appropriate packages from the package index, downloads the necessary files, and installs the files into the appropriate folders.Run the
python3command to confirm that Python 3 installed correctly:python3.10 --versionThe output should contain the word
Pythonwith a set of numbers separated by.characters. The following example shows the output you might see.Python 3.10.0As long as the first number is
3, Python 3 installed successfully.If the installation failed, you might see an error message. Enter the exact error message into browser to find possible causes and solutions.
Install by using YUM
The YUM package manager is used mainly by Red Hat systems, like Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Fedora, and by CentOS. If APT isn't installed on your system, you can try YUM instead.
Open a Terminal window
Run
sudo yum update, to update the YUM package indexessudo yum updateyum updatewill make sure all packages and their dependencies are up to date. It's a good idea to update the package list before you install new software.Run the following command
yum installto install Python 3sudo yum install rh-python3.10Run
python3.10 --versionto verify installation:python3.10 --versionThe output includes the word
Pythonwith a set of numbers separated by.characters, for example:Python 3.10.0As long as the first number is
3, Python 3 installed successfully.If the installation failed, you might see an error message; step 5 will help your resolve any error message.
(Optional) Enable the Software Collections feature in Bash
Software Collections enables you to install multiple versions of the same software components on your Red Hat system. When you run the SCL tool, it creates a child process (subshell) of the current shell. Running the command again then creates a subshell of the subshell. When the Software Collections tool is enabled, you need to specify which version of Python you want to run in the shell.
Run the
scl enablecommand at a Bash prompt:scl enable rh-python3.10 bashAgain, verify that everything is OK by running
python3.10 --version.python3.10 --versionThe output of that command should resemble the following format:
Python 3.10.0As long as the first number is
3, Python 3 installed successfully, in the context of a Software Collection.scl enable python36starts a new Bash session, setting Python 3.6 as the default Python version. But Python 3.6 is the default version only for the current shell session. If you exit the session or open a new session from another terminal, Bash will revert to the default Python version.For more information, see Red Hat Software Collections 3.8.
Important
If you needed to use
scl enableto runpython3.10 --version, you might need to run that command every time you want to work in Python. There are workarounds, but this is the intended functionality of Software Collections. See Make a Red Hat Software Collection persist for a possible workaround.
Install Python on macOS
Follow these steps to download the Python installer from the Python website.
Note
You can use Homebrew to install Python and Visual Studio Code. For instructions, see Homebrew documentation.
Download the installer from Python download page.
The website should automatically direct you to a page specifically for macOS. Select the latest release.
You may see a dialog box prompting you to allow downloads from python.org. Select Allow.
After a moment, a file named python-3.10.2-macos11.pkg (or similar) should download to the Downloads stack in your Dock.
To start the installer, double-click the .pkg file that you downloaded. The Python installer prompts you to install, verify, and accept various options and license agreements. Take the time to read through these prompts to understand what the installer will do to your computer.
When the installation process finishes, a Finder window showing the contents of the Python folder and a congratulations screen appear. Select Close to close these windows.
If you're prompted to move the Python installer to the trash, you can do so.
Verify installation by running
python3.10 --versionin a terminal window:python3.10 --versionThe output includes the word
Pythonwith a set of numbers separated by.characters, for example:Python 3.10.0As long as the first number is
3, Python 3 installed successfully.
You have now successfully installed Python on your local system.