Use parameters in a notebook
You can use parameters to pass variable values to a notebook from the pipeline. Parameterization enables greater flexibility than using hard-coded values in the notebook code.
Using parameters in a notebook
To define and use parameters in a notebook, use the dbutils.widgets library in your notebook code.
For example, the following Python code defines a variable named folder and assigns a default value of data:
dbutils.widgets.text("folder", "data")
To retrieve a parameter value, use the get function, like this:
folder = dbutils.widgets.get("folder")
The get function will retrieve the value for the specific parameter that was passed to the notebook. If no such parameter was passed, it will get the default value of the variable you declared previously.
Passing output values
In addition to using parameters that can be passed in to a notebook, you can pass values out to the calling application by using the notebook.exit function, as shown here:
path = "dbfs:/{0}/products.csv".format(folder)
dbutils.notebook.exit(path)
Setting parameter values in a pipeline
To pass parameter values to a Notebook activity, add each parameter to the activity's Base parameters, as shown here:
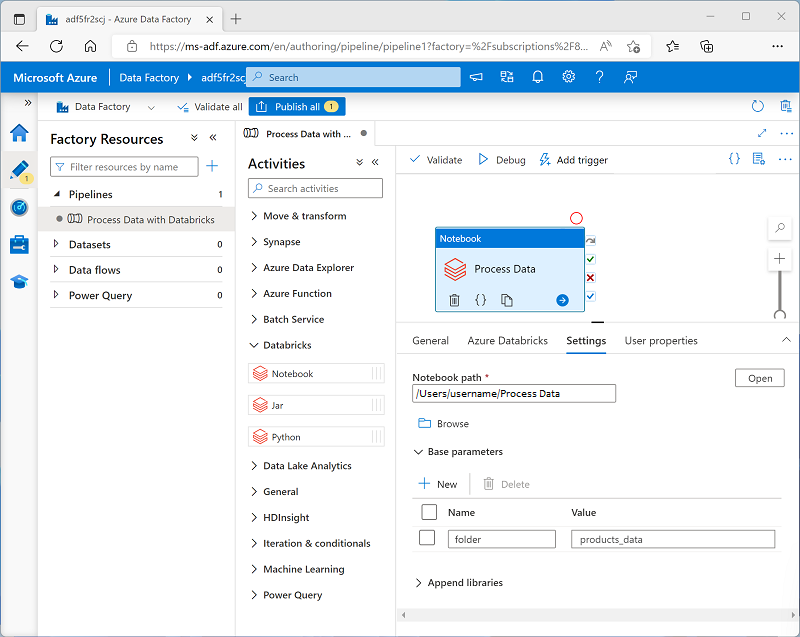
In this example, the parameter value is explicitly specified as a property of the Notebook activity. You could also define a pipeline parameter and assign its value dynamically to the Notebook activity's base parameter; adding a further level of abstraction.
Tip
For more information about using parameters in Azure Data Factory, see How to use parameters, expressions and functions in Azure Data Factory in the Azure Data Factory documentation.