Plan and implement a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Web Application Firewall (WAF) provides centralized protection of your web applications from common exploits and vulnerabilities. Web applications are increasingly targeted by malicious attacks that exploit commonly known vulnerabilities. SQL injection and cross-site scripting are among the most common attacks.
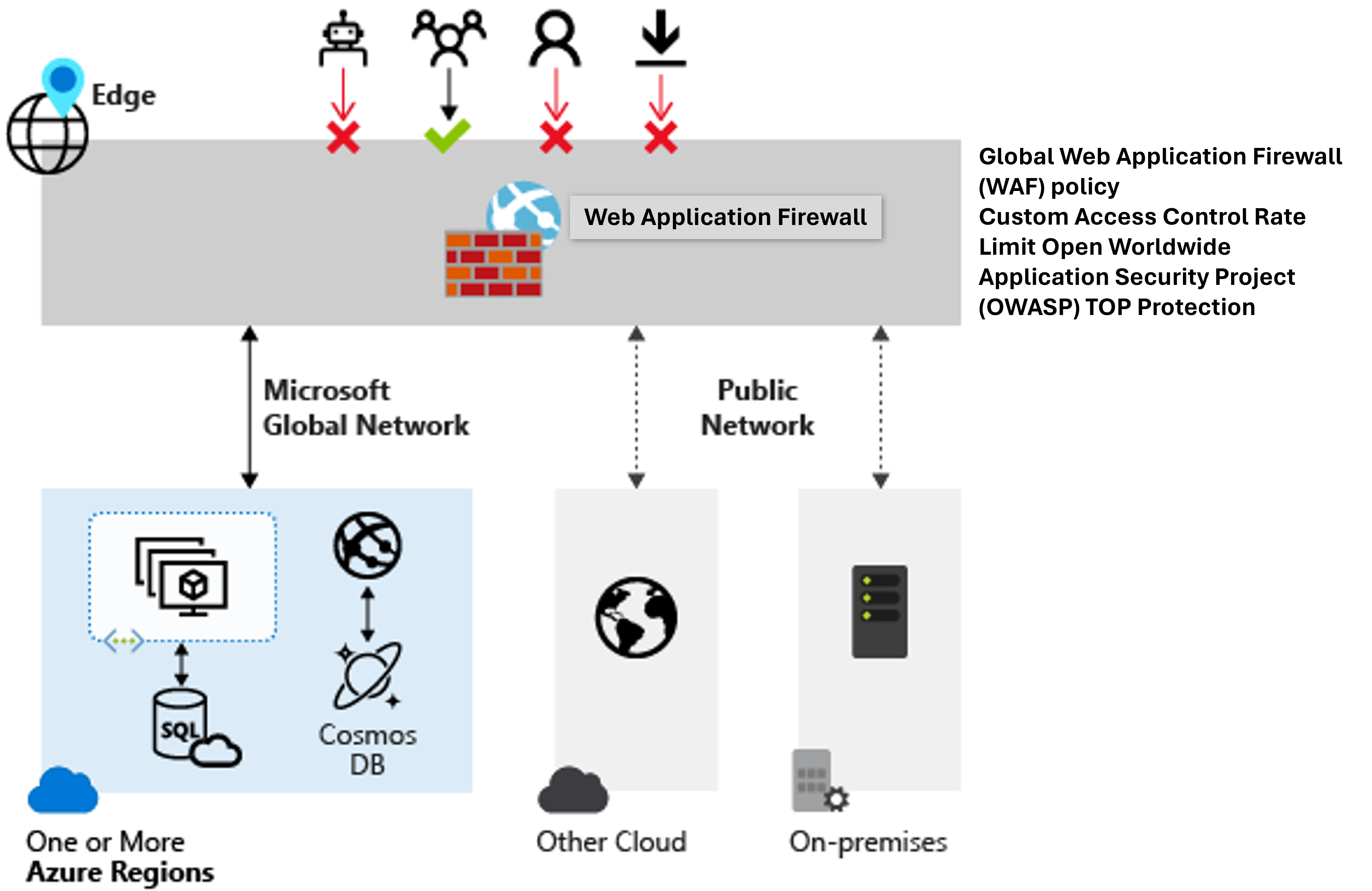
Preventing such attacks in application code is challenging. It can require rigorous maintenance, patching, and monitoring at multiple layers of the application topology. A centralized web application firewall helps make security management much simpler. A WAF also gives application administrators better assurance of protection against threats and intrusions.
A WAF solution can react to a security threat faster by centrally patching a known vulnerability, instead of securing each individual web application.
Supported service
WAF can be deployed with Azure Application Gateway, Azure Front Door, and Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) service from Microsoft. WAF on Azure CDN is currently under public preview. WAF has features that are customized for each specific service. For more information about WAF features for each service, see the overview for each service.
The Azure Web Application Firewall (WAF) on Azure Application Gateway actively safeguards your web applications against common exploits and vulnerabilities. As web applications become more frequent targets for malicious attacks, these attacks often exploit well-known vulnerabilities such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
WAF on Application Gateway is based on the Core Rule Set (CRS) from the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP).
All of the following WAF features exist inside of a WAF policy. You can create multiple policies, and they can be associated with an Application Gateway, to individual listeners, or to path-based routing rules on an Application Gateway. This way, you can have separate policies for each site behind your Application Gateway if needed.
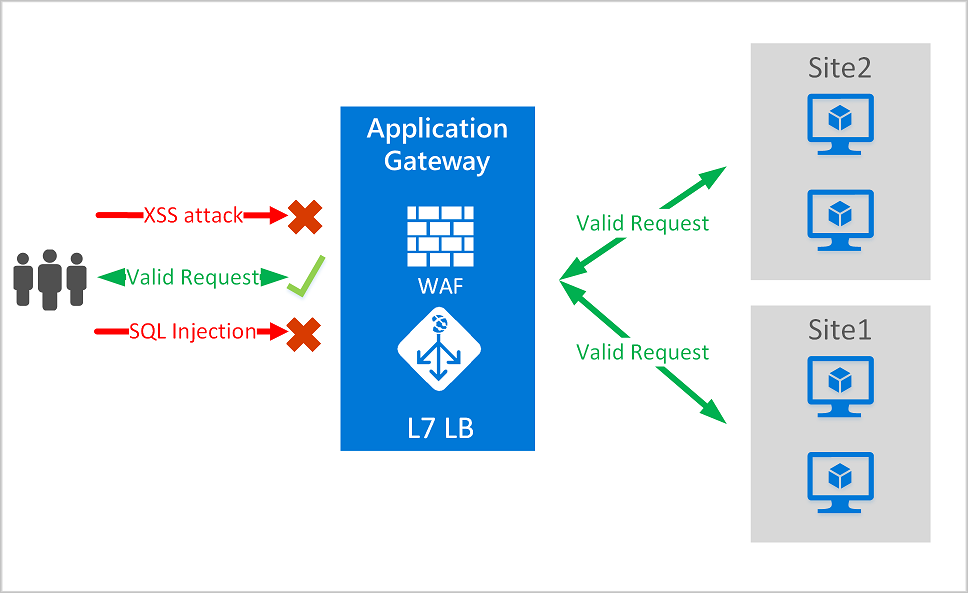
Application Gateway operates as an application delivery controller (ADC). It offers Transport Layer Security (TLS), previously known as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), termination, cookie-based session affinity, round-robin load distribution, content-based routing, ability to host multiple websites, and security enhancements.
Application Gateway enhances security through TLS policy management and end-to-end TLS support. By integrating WAF into Application Gateway, it fortifies application security. This combination actively defends your web applications against common vulnerabilities and offers a centrally manageable, easy-to-configure location.
Protection
- Protect your web applications from web vulnerabilities and attacks without modification to back-end code.
- Protect multiple web applications at the same time. An instance of Application Gateway can host up to 40 websites that are protected by a web application firewall.
- Create custom WAF policies for different sites behind the same WAF.
- Protect your web applications from malicious bots with the IP Reputation ruleset.
- Protect your application against DDoS attacks.
Monitoring
Monitor attacks against your web applications by using a real-time WAF log. The log is integrated with Azure Monitor to track WAF alerts and easily monitor trends.
The Application Gateway WAF is integrated with Microsoft Defender for Cloud. Defender for Cloud provides a central view of the security state of all your Azure, hybrid, and multicloud resources.
Customization
- Customize WAF rules and rule groups to suit your application requirements and eliminate false positives.
- Associate a WAF Policy for each site behind your WAF to allow for site-specific configuration
- Create custom rules to suit the needs of your application
Features
- SQL injection protection.
- Cross-site scripting protection.
- Protection against other common web attacks, such as command injection, HTTP request smuggling, HTTP response splitting, and remote file inclusion.
- Protection against HTTP protocol violations.
- Protection against HTTP protocol anomalies, such as missing host user-agent and accept headers.
- Protection against crawlers and scanners.
- Detection of common application misconfigurations (for example, Apache and Internet Information Services).
- Configurable request size limits with lower and upper bounds.
- Exclusion lists let you omit certain request attributes from a WAF evaluation. A common example is Microsoft Entra ID-inserted tokens that are used for authentication or password fields.
- Create custom rules to suit the specific needs of your applications.
- Geo-filter traffic to allow or block certain countries/regions from gaining access to your applications.
- Protect your applications from bots with the bot mitigation ruleset.
- Inspect JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) and Extensible Markup Language (XML) in the request body
WAF policy and rules
To enable a Web Application Firewall on Application Gateway, you must create a WAF policy. This policy is where all of the managed rules, custom rules, exclusions, and other customizations such as file upload limit exist.
You can configure a WAF policy and associate that policy to one or more application gateways for protection. A WAF policy consists of two types of security rules:
- Custom rules that you create
- Managed rule sets that are a collection of Azure-managed preconfigured set of rules
When both are present, custom rules are processed before processing the rules in a managed rule set. A rule is made of a match condition, a priority, and an action. Action types supported are: ALLOW, BLOCK, and LOG. You can create a fully customized policy that meets your specific application protection requirements by combining managed and custom rules.
Rules within a policy are processed in a priority order. Priority is a unique integer that defines the order of rules to process. Smaller integer value denotes a higher priority and those rules are evaluated before rules with a higher integer value. Once a rule is matched, the corresponding action that was defined in the rule is applied to the request. Once such a match is processed, rules with lower priorities aren't processed further.
A web application delivered by Application Gateway can have a WAF policy associated to it at the global level, at a per-site level, or at a per-URI level.
Core rule sets
Application Gateway supports multiple rule sets, including CRS 3.2, CRS 3.1, and CRS 3.0. These rules protect your web applications from malicious activity.
Custom rules
Application Gateway also supports custom rules. With custom rules, you can create your own rules, which are evaluated for each request that passes through WAF. These rules hold a higher priority than the rest of the rules in the managed rule sets. If a set of conditions is met, an action is taken to allow or block.
Bot protection rule set
You can enable a managed bot protection rule set to take custom actions on requests from all bot categories.
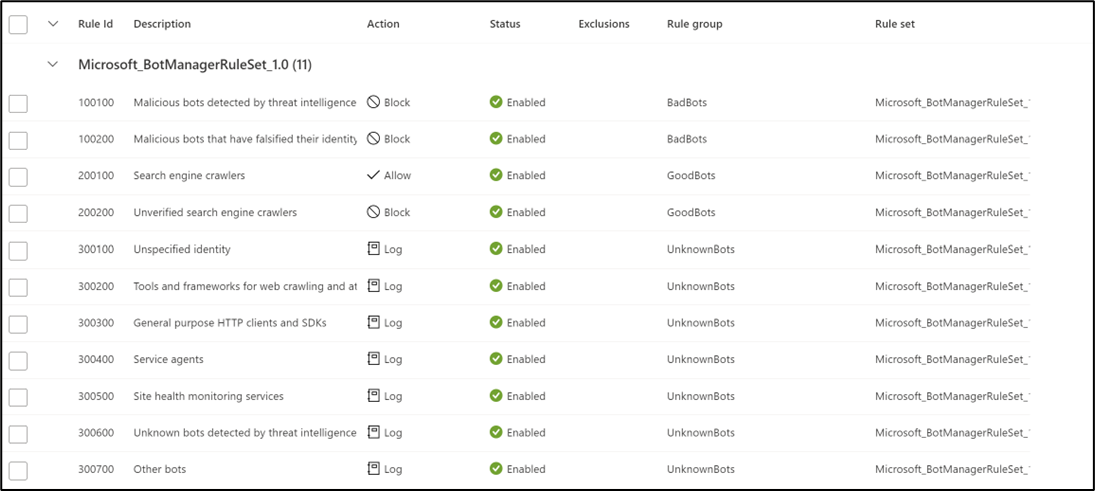
Three bot categories are supported:
- Bad - Bad bots include bots from malicious IP addresses and bots that falsify their identities. Bad bots with malicious IPs are sourced from the Microsoft Threat Intelligence feed’s high confidence IP Indicators of Compromise.
- Good - Good bots include validated search engines such as Googlebot, bingbot, and other trusted user agents.
- Unknown - Unknown bots are classified via published user agents without more validation. For example, market analyzer, feed fetchers, and data collection agents. Unknown bots also include malicious IP addresses that are sourced from Microsoft Threat Intelligence feed’s medium confidence IP Indicators of Compromise.
The WAF platform actively manages and dynamically updates bot signatures.
You can assign Microsoft_BotManagerRuleSet_1.0 by using the Assign option under Managed Rulesets:
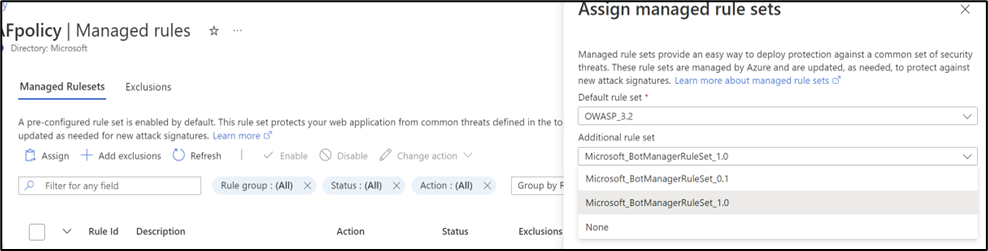
When Bot protection is enabled, it blocks, allows, or logs incoming requests that match bot rules based on the action you've configured. It blocks malicious bots, allows verified search engine crawlers, blocks unknown search engine crawlers, and logs unknown bots by default. You have the option to set custom actions to block, allow, or log different types of bots.
You can access WAF logs from a storage account, event hub, log analytics, or send logs to a partner solution.
WAF modes
The Application Gateway WAF can be configured to run in the following two modes:
- Detection mode: Monitors and logs all threat alerts. You turn on logging diagnostics for Application Gateway in the Diagnostics section. You must also make sure that the WAF log is selected and turned on. Web application firewall doesn't block incoming requests when it's operating in Detection mode.
- Prevention mode: Blocks intrusions and attacks that the rules detect. The attacker receives a "403 unauthorized access" exception, and the connection is closed. Prevention mode records such attacks in the WAF logs.
WAF engines
The Azure web application firewall (WAF) engine is the component that inspects traffic and determines whether a request includes a signature that represents a potential attack. When you use CRS 3.2 or later, your WAF runs the new WAF engine, which gives you higher performance and an improved set of features. When you use earlier versions of the CRS, your WAF runs on an older engine. New features are only available on the new Azure WAF engine.
WAF actions
You can choose which action is run when a request matches a rule condition. The following actions are supported:
- Allow: Request passes through the WAF and is forwarded to back-end. No further lower priority rules can block this request. Allow actions are only applicable to the Bot Manager ruleset, and aren't applicable to the Core Rule Set.
- Block: The request is blocked and WAF sends a response to the client without forwarding the request to the back-end.
- Log: Request is logged in the WAF logs and WAF continues evaluating lower priority rules.
- Anomaly score: This is the default action for CRS ruleset where total anomaly score is incremented when a rule with this action is matched. Anomaly scoring isn't applicable for the Bot Manager ruleset.
Anomaly Scoring mode
Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) has two modes for deciding whether to block traffic: Traditional mode and Anomaly Scoring mode.
In Traditional mode, traffic that matches any rule is considered independently of any other rule matches. This mode is easy to understand. But the lack of information about how many rules match a specific request is a limitation. So, Anomaly Scoring mode was introduced. It's the default for OWASP 3.x.
In Anomaly Scoring mode, traffic that matches any rule isn't immediately blocked when the firewall is in Prevention mode. Rules have a certain severity: Critical, Error, Warning, or Notice. That severity affects a numeric value for the request, which is called the Anomaly Score. For example, one Warning rule match contributes 3 to the score. One Critical rule match contributes 5.
| Severity | Value |
|---|---|
| Critical | 5 |
| Error | 4 |
| Warning | 3 |
| Notice | 2 |
There's a threshold of 5 for the Anomaly Score to block traffic. So, a single Critical rule match is enough for the Application Gateway WAF to block a request, even in Prevention mode. But one Warning rule match only increases the Anomaly Score by 3, which isn't enough by itself to block the traffic.
Configuration
You can configure and deploy all WAF policies using the Azure portal, REST APIs, Azure Resource Manager templates, and Azure PowerShell.
WAF monitoring
It's important to monitor the health of your application gateway. You can support this by integrating your WAF and the applications it protects with Microsoft Defender for Cloud, Azure Monitor, and Azure Monitor logs.
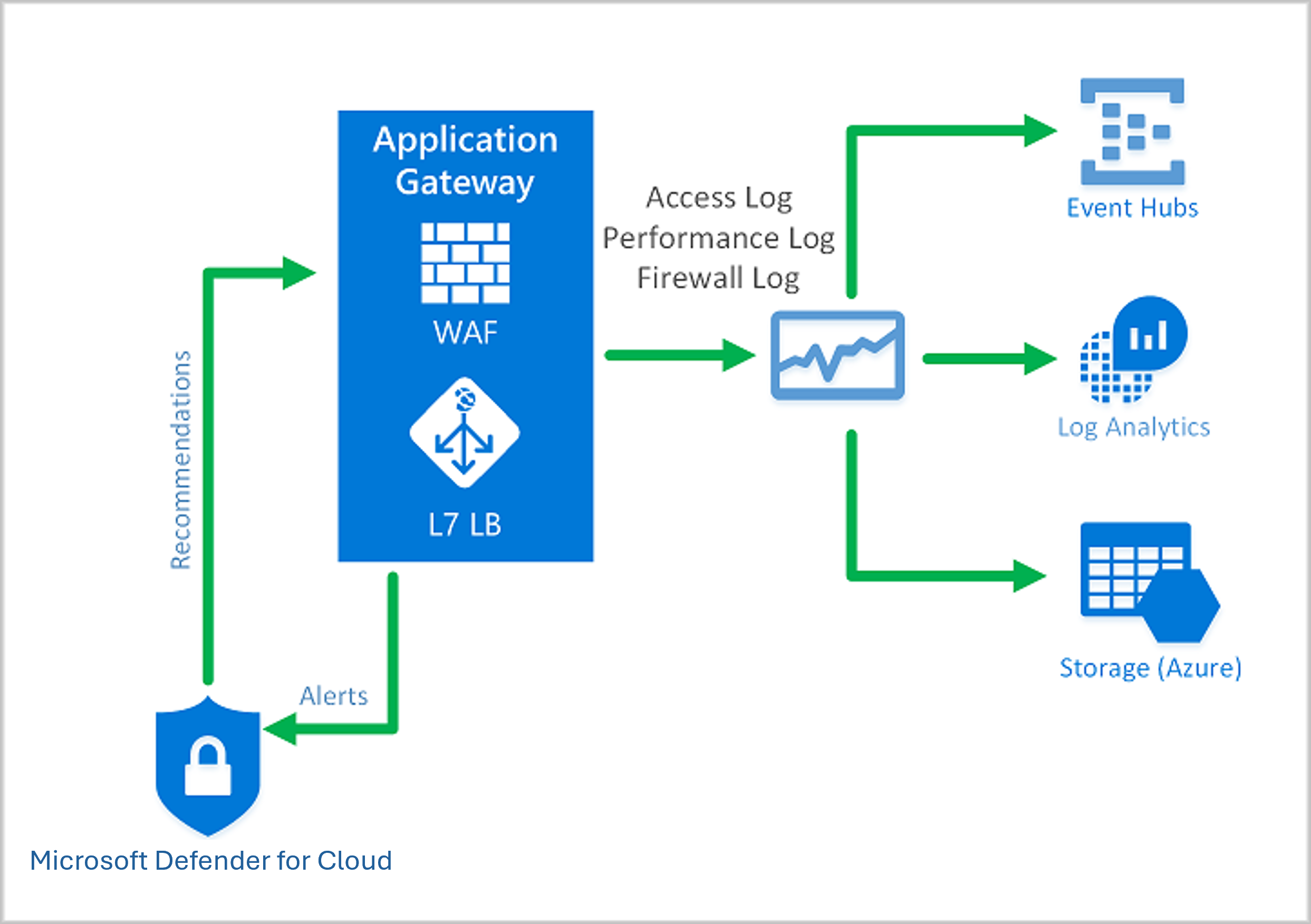
Azure Monitor
Application Gateway logs are integrated with Azure Monitor. This allows you to track diagnostic information, including WAF alerts and logs. You can access this capability on the Diagnostics tab in the Application Gateway resource in the portal or directly through Azure Monitor.