Remote Desktop listener certificate configurations
This article describes the methods to configure listener certificates on a Windows Server 2012-based or Windows Server 2012-based server that is not part of a Remote Desktop Services (RDS) deployment.
Original KB number: 3042780
About Remote Desktop server listener availability
The listener component runs on the Remote Desktop server and is responsible for listening to and accepting new Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) client connections. This lets users establish new remote sessions on the Remote Desktop server. There is a listener for each Remote Desktop Services connection that exists on the Remote Desktop server. Connections can be created and configured by using the Remote Desktop Services Configuration tool.
Methods to configure listener certificate
In Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, or Windows Server 2008 R2, the Remote Desktop Configuration Manager MMC snap-in lets you direct access to the RDP listener. In the snap-in, you can bind a certificate to the listener and in turn, enforce SSL security for the RDP sessions.
In Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2, this MMC snap-in does not exist. Therefore, the system provides no direct access to the RDP listener. To configure the listener certificates in Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2, use the following methods.
Method 1: Use Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) script
The configuration data for the RDS listener is stored in the
Win32_TSGeneralSettingclass in WMI under theRoot\CimV2\TerminalServicesnamespace.The certificate for the RDS listener is referenced through the Thumbprint value of that certificate on a SSLCertificateSHA1Hash property. The thumbprint value is unique to each certificate.
Note
Before you run the wmic commands, the certificate that you want to use must be imported to the Personal certificate store for the computer account. If you do not import the certificate, you will receive an Invalid Parameter error.
To configure a certificate by using WMI, follow these steps:
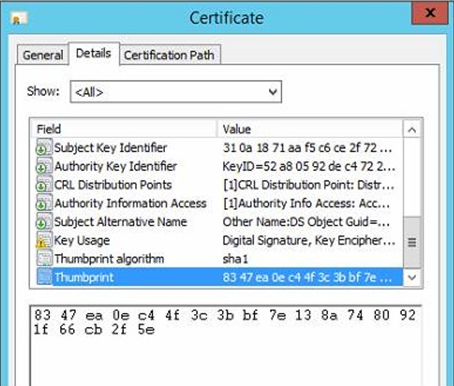
Open the properties dialog for your certificate and select the Details tab.
Scroll down to the Thumbprint field and copy the space delimited hexadecimal string into something like Notepad.
The following screenshot is an example of the certificate thumbprint in the Certificate properties:
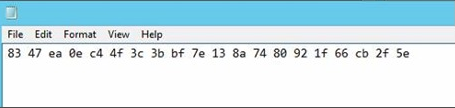
If you copy the string into Notepad, it should resemble the following screenshot:
After you remove the spaces in the string, it still contains the invisible ASCII character that is only visible at the command prompt. The following screenshot is an example:
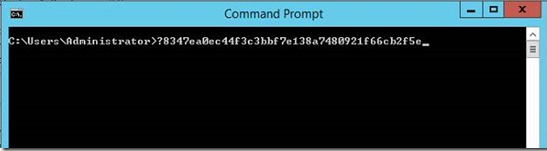
Make sure that this ASCII character is removed before you run the command to import the certificate.
Remove all spaces from the string. There may be an invisible ACSII character that is also copied. This is not visible in Notepad. The only way to validate is to copy directly into the Command Prompt window.
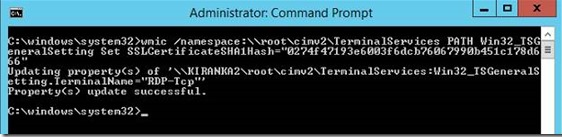
At command prompt, run the following wmic command together with the thumbprint value that you obtain in step 3:
wmic /namespace:\\root\cimv2\TerminalServices PATH Win32_TSGeneralSetting Set SSLCertificateSHA1Hash="THUMBPRINT"The following screenshot is a successful example:
Method 2: Use registry editor
Important
Follow the steps in this section carefully. Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Before you modify it, How to back up and restore the registry in Windows in case problems occur.
To configure a certificate by using registry editor, follow these steps:
Install a server authentication certificate to the Personal certificate store by using a computer account.
Create the following registry value that contains the certificate's SHA1 hash so that you can configure this custom certificate to support TLS instead of using the default self-signed certificate.
- Registry path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp - Value name: SSLCertificateSHA1Hash
- Value type: REG_BINARY
- Value data: certificate thumbprint
The value should be the thumbprint of the certificate and be separated by comma (,) without any empty spaces. For example, if you were to export that registry key, the SSLCertificateSHA1Hash value would be as follows:
SSLCertificateSHA1Hash=hex:42,49,e1,6e,0a,f0,a0,2e,63,c4,5c,93,fd,52,ad,09,27,82,1b,01
- Registry path:
The Remote Desktop Host Services runs under the NETWORK SERVICE account. Therefore, you have to set the system access control list (SACL) of the key file that is used by RDS to include NETWORK SERVICE together with the Read permissions.
To change the permissions, follow these steps on the Certificates snap-in for the local computer:
- Click Start, click Run, type mmc, and then click OK.
- On the File menu, click Add/Remove Snap-in.
- In the Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog box, on the Available snap-ins list, click Certificates, and then click Add.
- In the Certificates snap-in dialog box, click Computer account, and then click Next.
- In the Select Computer dialog box, click Local computer: (the computer this console is running on), and then click Finish.
- In the Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog box, click OK.
- In the Certificates snap-in, on the console tree, expand Certificates (Local Computer), expand Personal, and then select the SSL certificate that you want to use.
- Right-click the certificate, select All Tasks, and then select Manage Private Keys.
- In the Permissions dialog box, click Add, type NETWORK SERVICE, click OK, select Read under the Allow check box, and then click OK.