Kernel streaming considerations
This article clarifies the requirements and special considerations for kernel streaming related to Bluetooth bypass audio streaming.
The audio driver should fully support the WaveRT port driver, including "pull mode". For more information, see Introducing the WaveRT port driver. Although there is no requirement to implement a hardware audio engine for the synchronous connection oriented (SCO) bypass output, there is no harm in doing so.
The Windows logo requirements for format support include an exception for Bluetooth.
The audio driver should support the formats that are possible through the sideband hardware, typically 8kHz mono audio streaming.
Topology
All Bluetooth Hands-Free devices support both capture and render. The audio driver should expose a kernel streaming (KS) topology for the Hands-Free device, as shown in the following diagram, to support both render and capture.
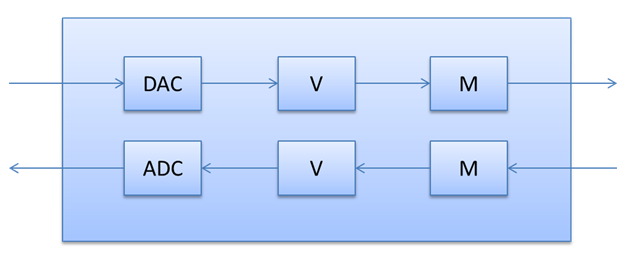
Note: The audio driver developer can choose whether to implement a single filter for both capture and render paths or separate filters. However, the HFP device only allows a single file object on the GUID_DEVINTERFACE_BLUETOOTH_HFP_SCO_HCIBYPASS device interface. Therefore, a design that uses two filters needs to allow both filters to share the single file object.
The DAC and ADC nodes represent the analog/digital conversions but don't support any KS properties.
The volume nodes support KSPROPERTY_AUDIO_VOLUMELEVEL and KSEVENT_CONTROL_CHANGE by sending the SETVOLUME and GETVOLUMESTATUSUPDATE IOCTLs to the HFP driver.
The volume node should be implemented as follows:
- If the Bluetooth headset supports volume control, the audio driver should include a volume node in its KS topology. The audio driver's volume property handlers send the above IOCLTs to the Bluetooth HFP driver to handle the volume.
- If the Bluetooth headset doesn't implement a hardware volume, and the codec (or DSP) has a hardware volume, the audio driver should handle the volume control on the codec (or DSP).
- If neither the Bluetooth headset nor the audio device have hardware volume controls, no volume node should be presented, and Windows will insert a software volume control node.
- The mute node is optional. The audio driver should implement the mute node if and only if the DSP or audio codec provides the capability to mute the bypass PCM signal before passing it to the Bluetooth controller. The mute nodes support KSPROPERTY_AUDIO_MUTE.
Property requests
The audio driver uses the following KS properties to obtain information about any audio jack or jacks in the audio path. The audio driver can also use the appropriate property request to make or break a connection to any Bluetooth audio device in the audio path.
KSPROPERTY_JACK_DESCRIPTION
This property returns a KSJACK_DESCRIPTION structure. The audio driver should set the KSPROPERTY_JACK_DESCRIPTION fields as follows.
- ChannelMapping = KSAUDIO_SPEAKER_MONO
- Color = 0
- ConnectionType = eConnTypeOtherDigital
- GeoLocation = eGeoLocNotApplicable
- GenLocation = eGenLocOther
- PortConnection = ePortConnUnknown
- IsConnected = <BOOL for current connection status>
KSPROPERTY_JACK_DESCRIPTION2
This property returns a KSJACK_DESCRIPTION2 structure. The audio driver should set the KSPROPERTY_JACK_DESCRIPTION2 fields as follows.
- DeviceStateInfo = 0
- JackCapabilities = JACKDESC2_PRESENCE_DETECT_CAPABILITY
KSPROPERTY_ONESHOT_RECONNECT
The audio driver’s filter should support KSPROPERTY_ONESHOT_RECONNECT. To create and initialize this structure, the audio driver sends IOCTL_BTHHFP_DEVICE_REQUEST_CONNECT to the HFP driver. The HFP driver completes this request and then attempts to connect to the Bluetooth audio device asynchronously.
KSPROPERTY_ONESHOT_DISCONNECT
The audio driver’s filter should support KSPROPERTY_ONESHOT_DISCONNECT. To create and initialize this structure, the audio driver sends IOCTL_BTHHFP_DEVICE_REQUEST_DISCONNECT to the HFP driver. The HFP driver completes this request and then attempts to disconnect from the Bluetooth audio device asynchronously.
When an audio driver supports these properties, the Sound dialog box in the Control Panel exposes Connect and Disconnect commands for the HFP endpoint.